- Command not found when using sudo
- 11 Answers 11
- How to resolve this error for ‘help’ command not found in Kali Linux? [closed]
- 1 Answer 1
- Troubleshooting «Bash: Command Not Found» Error in Linux
- Fixing “bash: command not found” error
- Method 1: Double check the command name (no, seriously)
- Method 2: Ensure that the command is installed on your system
- Method 3: Make sure that the command is real, not an alias
- Method 4: Check if it is an executable script with correct path
- Adding it to the PATH
- Did it help you?
Command not found when using sudo
I have a script called foo.sh in my home folder. When I navigate to this folder, and enter ./foo.sh , I get -bash: ./foo.sh: Permission denied . When I use sudo ./foo.sh , I get sudo: foo.sh: command not found . Why does this happen and how I can fix it?
11 Answers 11
Permission denied
In order to run a script the file must have an executable permission bit set.
In order to fully understand Linux file permissions you can study the documentation for the chmod command. chmod, an abbreviation of change mode, is the command that is used to change the permission settings of a file.
To read the chmod documentation for your local system , run man chmod or info chmod from the command line. Once read and understood you should be able to understand the output of running .
. which will list the READ, WRITE and EXECUTE permissions for the file owner, the group owner and everyone else who is not the file owner or a member of the group to which the file belongs (that last permission group is sometimes referred to as «world» or «other»)
Here’s a summary of how to troubleshoot the Permission Denied error in your case.
$ ls -l foo.sh # Check file permissions of foo -rw-r--r-- 1 rkielty users 0 2012-10-21 14:47 foo.sh ^^^ ^^^ | ^^^ ^^^^^^^ ^^^^^ | | | | | Owner| World | | | | Name of Group | Group Name of Owner Owner has read and write access rw but the — indicates that the executable permission is missing
The chmod command fixes that. (Group and other only have read permission set on the file, they cannot write to it or execute it)
$ chmod +x foo.sh # The owner can set the executable permission on foo.sh $ ls -l foo.sh # Now we see an x after the rw -rwxr-xr-x 1 rkielty users 0 2012-10-21 14:47 foo.sh ^ ^ ^ foo.sh is now executable as far as Linux is concerned.
Using sudo results in Command not found
When you run a command using sudo you are effectively running it as the superuser or root.
The reason that the root user is not finding your command is likely that the PATH environment variable for root does not include the directory where foo.sh is located. Hence the command is not found.
The PATH environment variable contains a list of directories which are searched for commands. Each user sets their own PATH variable according to their needs. To see what it is set to run
Here’s some sample output of running the above env command first as an ordinary user and then as the root user using sudo
rkielty@rkielty-laptop:~$ env | grep ^PATH PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games rkielty@rkielty-laptop:~$ sudo env | grep ^PATH [sudo] password for rkielty: PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/X11R6/bin Note that, although similar, in this case the directories contained in the PATH the non-privileged user (rkielty) and the super user are not the same.
The directory where foo.sh resides is not present in the PATH variable of the root user, hence the command not found error.
How to resolve this error for ‘help’ command not found in Kali Linux? [closed]
I know that help is a shell built-in internal command used to find about built in commands such as cd . But it is not working in my Kali Linux terminal in VirtualBox. It is showing the following error:
Command 'help' not found, did you mean: command 'dhelp' from deb dhelp command 'yelp' from deb yelp Try: sudo apt install
1 Answer 1
help is a builtin command in bash , not all shells. You seem to be using something that isn’t bash. Most likely zsh since that is the default shell in recent versions of Kali. If you want to use bash , either run it manually with bash or use chsh to set it as the default for your account:
And then follow the prompts and give it /bin/bash . If your username isn’t rs90 , use whatever your user name is.
A final note: Kali is not a regular operating system. It is a highly specialized tool for professionals. If you are new to Linux, as your question suggests, Kali is a very bad choice to learn the system. Although it has been popularized by some movies and TV shows, there’s nothing a «hacker» can do on Kali than cannot be done with regular Linux flavors, you just need to install some Kali packages. I would urge you to start with a regular distribution and not use Kali since using Kali will just make your life harder. Also see: Why is Kali Linux so hard to set up? Why won’t people help me?
Troubleshooting «Bash: Command Not Found» Error in Linux
This beginner tutorial shows how to go about fixing the Bash: command not found error on Debian, Ubuntu and other Linux distributions.
When you use commands in Linux, you expect to see an output. But sometimes, you’ll encounter issues where the terminal shows ‘command not found’ error. There is no straightforward, single solution to this error. You have to do a little bit of troubleshooting on your own. It’s not too difficult, honestly. The error gives some hint already when it says “bash: command not found”. Your shell (or Linux system) cannot find the command you entered. There could be three possible reasons why it cannot find the command:
- It’s a typo and the command name is misspelled
- The command is not even installed
- The command is basically an executable script and its location is not known
Let’s go in detail on each possible root cause.
Fixing “bash: command not found” error
Method 1: Double check the command name (no, seriously)
It is human to make mistakes, specially while typing. It is possible that the command you entered has a typo (spelling mistake).
You should specially pay attention to:
- The correct command name
- The spaces between the command and its options
- The use of 1 (numeral one), I (capital i) and l (lowercase L)
- Use of uppercase and lowercase characters
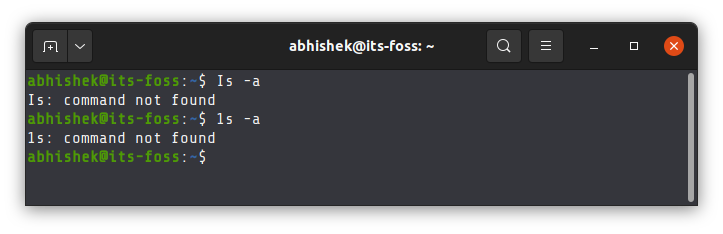
Take a look at the example below, where I have misspelled the common ls command.
So, make double sure what you are typing.
Method 2: Ensure that the command is installed on your system
This is another common reason behind the command not found error. You cannot run a command if it is not installed already.
While your Linux distribution comes with a huge number of commands installed by default, it is not possible to pre-install all the command line tools in a system. If the command you are trying to run is not a popular, common command, you’ll have to install it first.
You can use your distribution’s package manager to install it.
In some cases, popular commands may get discontinued and you may not even install it anymore. You’ll have to find an alternative command to achieve the result.
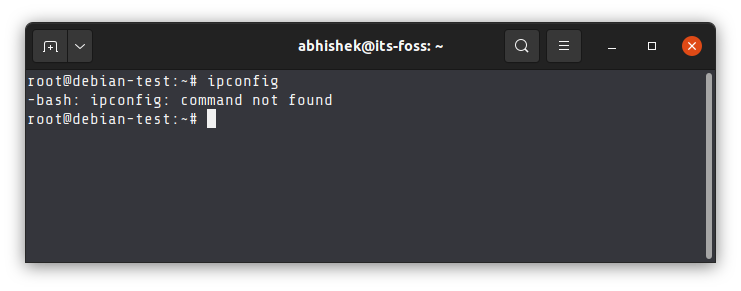
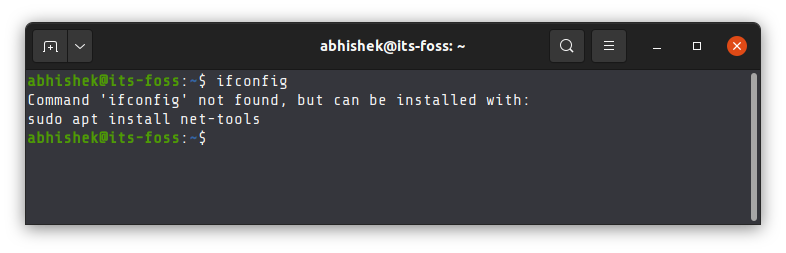
Take the example of ifconfig command. This deprecated command was used for getting Ip address and other network interface information. Older tutorials on the web still mention using this command but you cannot use it anymore in newer Linux versions. It has been replaced by the ip tool.
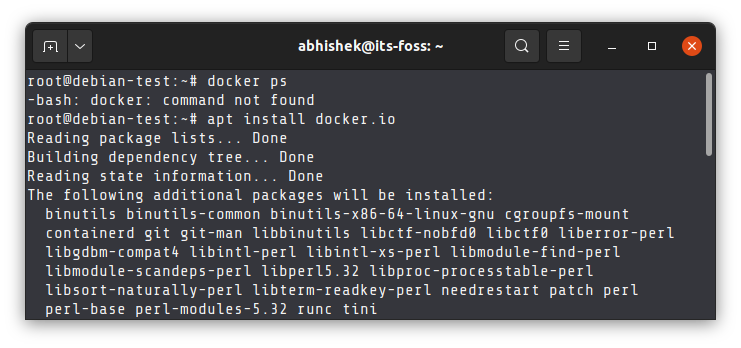
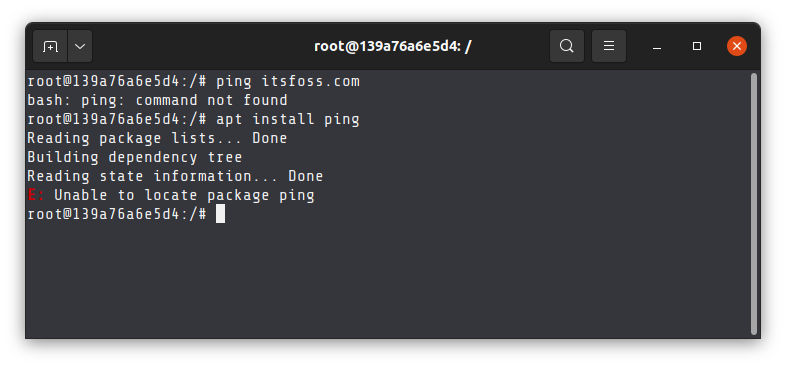
Occasionally, your system won’t find even the extremely common commands. This is often the case when you are running a Linux distribution in Docker containers. To cut down on the size of the operating system image, the containers often do not include even the most common Linux commands.
This is why Docker user stumble across things like ping command not found error etc.
So, the solution is to either install the missing command or find a tool that could do the same thing you were trying to do with the missing command.
Method 3: Make sure that the command is real, not an alias
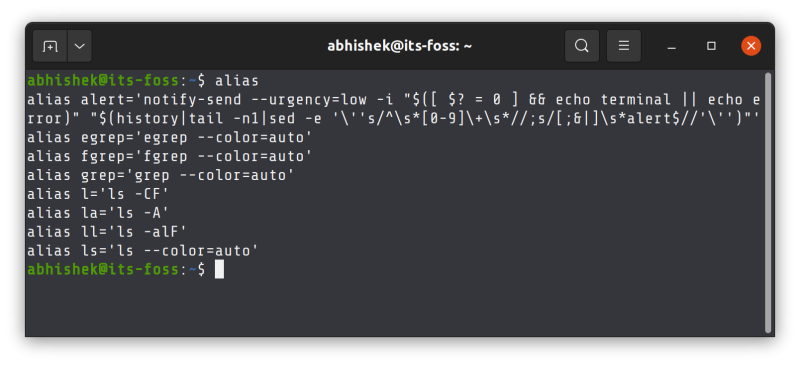
I hope you are aware of the alias concept in Linux. You can configure your own shorter commands to replace the typing of a longer command.
Some distributions like Ubuntu automatically provide commands like ll (which is aliased to ls -l), la (aliased to ls -a) and so on.
Imagine that you are used to of typing ll and la on your personal system and you log on to another Linux system and find that ll command does not exist. You cannot even install the ll command because it is not a real command.
So, if you cannot find a command and it cannot even be installed, you should try searching on the internet if that command even exists. If it does not, probably it was an alias on some other system.
Method 4: Check if it is an executable script with correct path
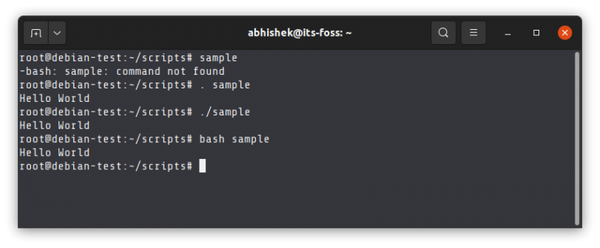
This is a common mistake Linux rookies make while running a shell script.
Even if you are in the same directory and try to run an executable script just by its name, it will show an error.
[email protected]:~/scripts# sample -bash: sample: command not foundYou need to either specify the shell interpreter explicitly or its absolute path.
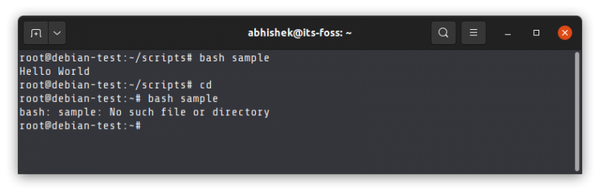
If you are in some other directory and try to execute the shell script without giving the correct path to the file, it will complain about not finding the file.
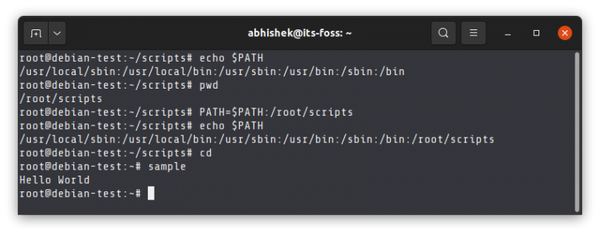
Adding it to the PATH
In some cases, you download the entire software in a tar file, extract it and find an executable file along with other program files. To run the program, you need to run the executable file.
But for that, you need to be in the same directory or specify the entire path to the executable file. This is tiresome.
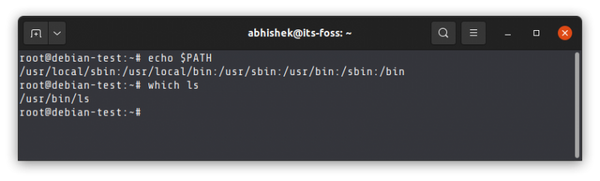
Here, you can use the PATH variable. This variable has a collection of directories and these directories have the binary (executable) files of various Linux commands. When you run a command, your Linux system checks the mentioned directories in the PATH variable to look for the executable file of that command.
You can check the location of the binary of a command by using the which command:
If you want to run an executable file or script from anywhere on the system, you need to add the location of the file to this PATH variable.
The PATH variable then needs to be added to the rc file of the shell so that the changes made to PATH variable are permanent.
You get the gist here. It is important that your Linux system has knowledge about the location of the executable script. Either you give the path while running it or you add its location to the PATH variable.
Did it help you?
I understand that when you are new to Linux, things could be overwhelming. But when you understand the root cause of the problem, it gradually improved your knowledge.
Here, there is no straightforward solution possible for the ‘command not found error’. I gave you some hints and pointers and that should help you in troubleshooting.
Similarly, you may encounter ‘unable to locate package’ error in Ubuntu. Here’s what you need to know about it.
If you still have doubts or need help, please let me know in the comment section.