How do I install KDE?
I want to have both KDE and Gnome shells on Ubuntu. Ubuntu only has Gnome installed by default. How do I install KDE?
7 Answers 7
You need to install the kubuntu-desktop package for the full install with the following command.
sudo apt-get install kubuntu-desktop Then the next time you login you can choose what to use from the login screen (under Session).
what about the sudo apt-get install kde-plasma-desktop. i tried it .. but seems to give minimal GUI features.. how do i add to it?
To get just the plasma environment (on 12.04 and newer):
sudo apt-get install plasma-desktop It worked fine for me on 15.10
+1 and this is valid for 12.04 and newer releases. Also, there is kde-plasma-desktop for users who want desktop environment with minimal set of applications.
If you want to log in from KDE run sudo apt-get install kdm , sudu apt-get remove gdm , and dpkg reconfigure kdm .
Just try the following command in a terminal
sudo apt-get install kubuntu-desktop Then just select KDE on the login manager.
On 30/09/2015:
To install KDE on Ubuntu (12.04,14.04,14.10,15.04,15.10) (plasma 5.3)
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade sudo apt-get install kubuntu-desktop To install KDE on Ubuntu (15.04,15.10) (plasma 5.4)
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kubuntu-ci/stable sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade sudo apt-get install kubuntu-desktop Note: To install plasma 5.4,you need to remove backports ppa.
thanks for the super fast response! Pls have a look at this post which i just posted regarding a issue getting plasma 5. askubuntu.com/questions/691331/…
Just open synaptic (If not installed yet, install it by ubuntu software center) and search for desktop environment and install plasma-desktop
I think the most complete answer is here. According to what you want to install (only the GUI or GUI+some packages).
Citing the content of the answer:
plasma-netbook and plasma-desktop differ only by whether they install the netbook or the desktop interface. kde-workspace is identical to plasma-desktop .
kde-plasma-desktop will install a few KDE programs: Dolphin, Konqueror, kde-baseapps, konsole, kwrite, and kde-passwd.
kde-standard installs a bunch of stuff on top of kde-desktop : Akregator, Ark, Dragonplayer, gnupg, Kaddressbook, Kate, KDE wallpapers, Kmail, etc.
kubuntu-desktop installs even more than kde-standard . kubuntu-desktop is the package you would download from the Ubuntu website if you wanted Kubuntu, but if you only want the Plasma interface, not any of the default programs, plasma-desktop might be sufficient.
Choose the package you want and then run sudo apt-get install package-name
How to Install KDE Desktop Environment on Ubuntu
In the world of Linux desktop environments, the ones that dominate are GNOME and KDE. There are several other desktop environments but these two are the leaders.
Ubuntu used to have Unity desktop in its default edition but it switched to GNOME desktop since version 17.10 release.
Ubuntu offers several desktop flavors and the KDE version is called Kubuntu. With Kubuntu you get the KDE desktop baked with Ubuntu, out of the box.
It’s possible that you installed the default Ubuntu with GNOME desktop. If you want to use KDE, you don’t necessarily need to remove the present Ubuntu and install Kubuntu from scratch. You can install KDE desktop in your current Ubuntu system and switch between the available desktop environments.
You may come across two terms: KDE and KDE Plasma. This may confuse you because most of the time, both refers to the same thing: a desktop environment. So, what’s the deal here? Let me explain it to you.
Historically, KDE was the desktop environment when it was created more than twenty years ago. In fact, KDE is the short form for K Desktop Environment. But eventually KDE grow to be more than just a desktop environment. It has a huge list of applications developed under the KDE project like Kdenlive video editor.
Since they were not essentially a desktop environment anymore, a few years ago, they segregated the desktop environment. Plasma is the desktop environment and KDE is the umbrella project responsible for the development of Plasma desktop and a bunch of other applications.
It is still common practice to refer KDE as the desktop environment but now you know that it’s actually Plasma.
Install KDE desktop environment on Ubuntu
Before you start, let me tell you that there are different versions of KDE available, according to the need. We will see what are they and how to install them:
KDE Full
This is the complete KDE pack. It comes with the complete package and core KDE plasma desktop. If you want all of KDE goodness (and its dependencies), this is what you would install. Since it is the complete pack (around 1 GB), it will take some time in downloading and installing. You can install it using the following command:
KDE Standard
The standard KDE includes Plasma desktop with standard set of KDE apps such as Kate (default text editor), Konqueror (default web browser), Kget (Download Manager), KMail (email client), Dolphin (File Manager) etc. The whole package is around 273 MB in size. You can install it using the following command:
sudo apt install kde-standardKDE Plasma Desktop
This is just the minimal package of KDE with just the Plasma desktop and a minimal set of KDE applications such as browse, file manager, text editor etc. No apps are installed by default. You can install them later at any time. Ideal in the case when you just want to give it a try. The download size is around 175 MB.
sudo apt install kde-plasma-desktopKDE Plasma Netbook [Discontinued]
No prizes for guessing that this is for netbooks. This light version was best suited with low end systems and netbooks are just that. It is not available anymore.
sudo apt install kde-plasma-netbookThere is also a package named kubuntu-desktop. It includes all the packages included in Kubuntu. You may install it as well but it may (or may not) lead to conflicts with your existing GNOME desktop.
KDE Plasma desktop installation procedure
Whichever package you chose to install KDE Plasma desktop, the procedure should be similar to the steps mentioned here.
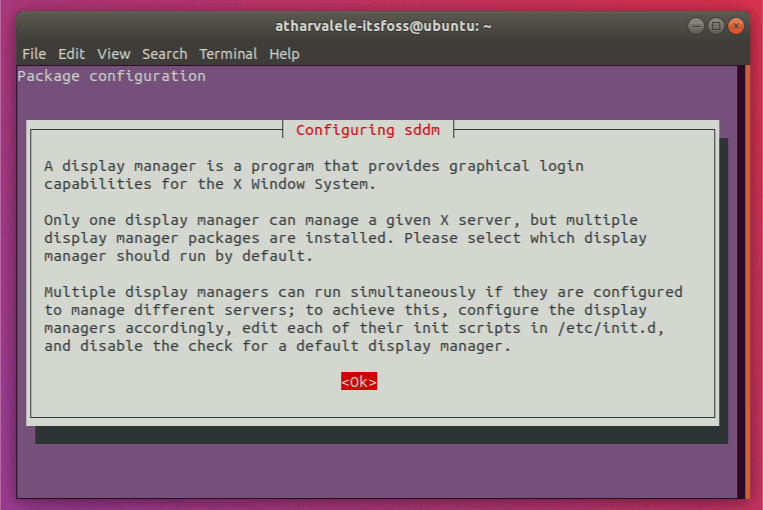
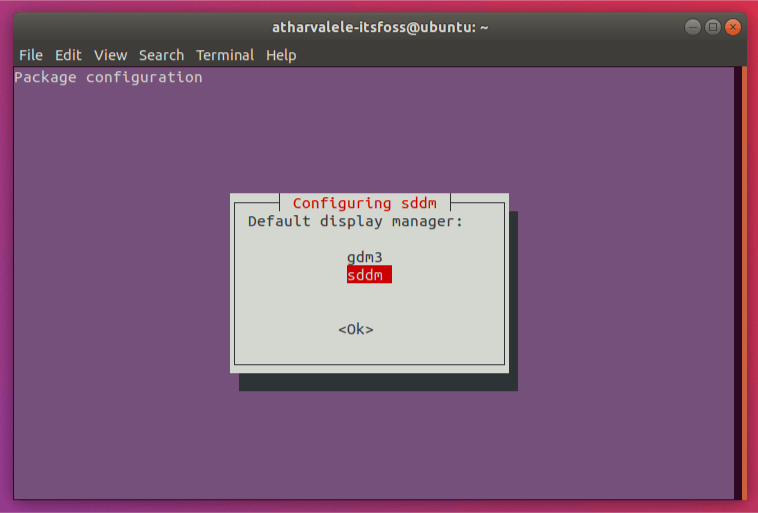
You’ll be prompted to configure SDDM, i.e. Simple Desktop Display Manager, which is the Display Manager used by the KDE Desktop. Select ‘sddm’ from the list and press Enter.
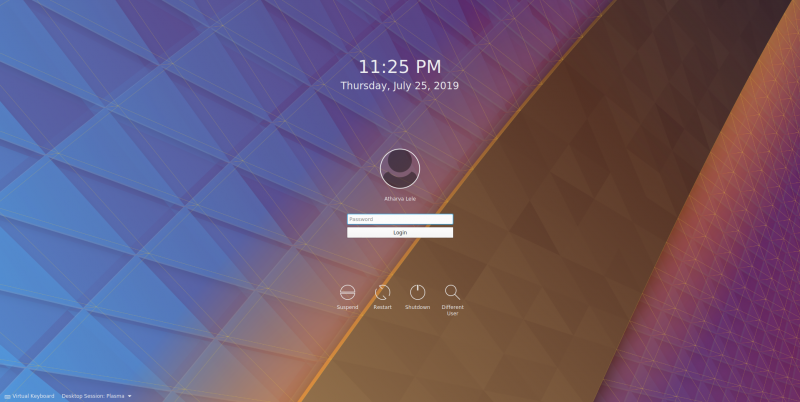
Once this is done, the remaining packages will be configured. After that, you can reboot. After the reboot, you will be greeted by the SDDM Lockscreen.
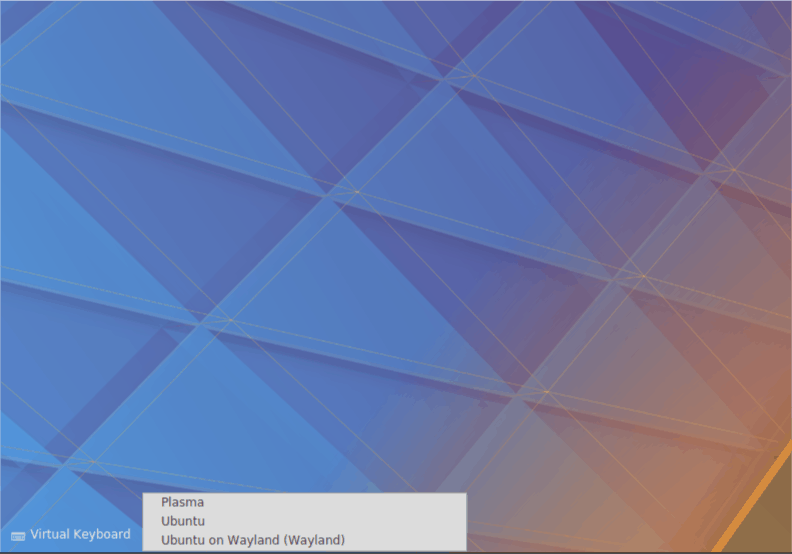
You can also select between KDE and GNOME using the “Desktop Session” option in the lower left corner.
The default GNOME Desktop will be available in the “Ubuntu” session. If you want to use the Wayland Display Server, you can select the appropriate option for that.
After logging in, you will be at the KDE Desktop Home. From here you can start using apps, and customizing it to your liking.
I, for one, love the traditional desktop experience as well as the customization provided by KDE. I hope this guide was helpful to you in installing KDE on Ubuntu.
How do you like your desktop to be? Simple or as customizable as possible? Let us know in the comments below, as well as drop any questions you may have.
Walkthrough
We’ll be using aptitude, because its ability of suggesting multiple solutions to package conflicts can make newbies less likely to break their systems.
(1) Make sure your packages are up to date:
# apt update && apt full-upgrade
2. Select and install KDE packages
- kde-plasma-desktop — Bare-minimum installation. Including basic utilities like a file manager, browser, and terminal emulator.
- kde-standard — Everything in kde-plasma-desktop with a standard suit of system utilities (for example, calculator, email, media player, and advanced text editor)
- kde-full — Everything in kde-standard with extra system utilities, games, and educational applications.
kde-standard is recommended. You can install packages from kde-full afterwards if you want those extra features.
# aptitude install kde-standard
You’ll be asked to choose between gdm3 and sddm. Select sddm. gdm3 is for GNOME and sddm is for KDE.
3. Purge GNOME
Users can switch between «Plasma» (for KDE) and «Ubuntu» (for GNOME) from the login screen. However, errors will begin to pop-up when switching to GNOME this way, probably because configuration files are altered for KDE.
So, whether you’re going to stick to KDE, or you’re gonna switch back to GNOME with no errors popping-up, you’ll want to completely remove GNOME and its configuration files first.
(1) Purge gnome-shell and autoremove associated packages:
# aptitude purge gnome-shell
During the process, aptitude will detect some unmet dependencies caused by this removal, and will propose a few solutions. The first solution is good enough, just type Y for yes.
(2) Purge previously only removed packages:
4. Other packages
Some packages, like Firefox, will also get purged in the process above ’cause they depend on GNOME dependencies. But worry not. Reinstalling them won’t require you to install an entire GNOME Desktop Environment.
Let’s say that you’ve installed kde-standard, and you want all those fancy productivity features from packages of kde-full. Just check out their related packages:
# aptitude install kdeadmin kdegraphics kdemultimedia kdenetwork kdepim kdeutils kdeaccessibility kdesdk kdewebdev
Help
IRC: #kubuntu on freenode
InstallingKDE (последним исправлял пользователь hokma 2021-12-16 14:05:33)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details
You can contribute to this wiki, see Wiki Guide for details