- How to update software installed via .deb file
- 4 Answers 4
- Debian and Ubuntu based distributions
- How To Update All Packages On Ubuntu
- Method 1:Via Terminal
- Method 2: Update using Package Updater:
- Conclusion:
- How to Update All Packages on Ubuntu 22.04
- How to Update All Packages on Ubuntu?
- Method 1: How to update all the packages on Ubuntu using the terminal
- Method 2: How to update all packages on Ubuntu using the GUI method
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Hammad Zahid
How to update software installed via .deb file
There are so many software which we installed via .deb file because official ubuntu repo has very old version of it. But I was just wondering how to update packages install via .deb file. One particular example is sonic-visualiser The official ubuntu has 3 years old 2.5 version while the official site has 3.0.3 version
4 Answers 4
Disclaimer: I would say that the way distributions encourage users to install software is apt these days, which is a package manager that checks if the dependencies between packages are intact, you can issue an update to all your software that can be fetched from the source repositories list.
While it can be that installing a program with the .deb package doesn’t add the repository to apt for automatic updates, some .deb installations do just that: they add repositories to apt for further updates or make it possible for you to add them manually and then install the software. Example: ‘Visual Studio Code’. https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/setup/linux
I cite from their website:
Debian and Ubuntu based distributions
The easiest way to install Visual Studio Code for Debian/Ubuntu based distributions is to download and install the .deb package (64-bit), either through the graphical software center if it’s available, or through the command line with:
Installing the .deb package will automatically install the apt repository and signing key to enable auto-updating using the system’s package manager. Note that 32-bit and .tar.gz binaries are also available on the VS Code download page.
The repository and key can also be installed manually with the following script:
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | gpg --dearmor > packages.microsoft.gpg sudo install -o root -g root -m 644 packages.microsoft.gpg /usr/share/keyrings/ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/packages.microsoft.gpg] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/vscode stable main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/vscode.list' Then update the package cache and install the package using:
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install code # or code-insiders EDIT: A discussion in the comments to this post started with some people being confused about calling apt with a path to the file being installed. While apt’s great functionality is managing the software packages and updating them from the list of repositories apt gets, it can also be used to install a downloaded package, like in the case above. Perhaps it could also be installed with the dpkg -i with the same effect — I do not know that. What I can say is that the downloaded package from the example above gets the signature, updates the apt list of repositories with the signed source repo. And that the software the Visual Studio recommends for installing it is apt.
How To Update All Packages On Ubuntu
If you are new to Ubuntu, you might be having a difficult time adjusting to the Gnome environment. If you are confused about what a package is, compare it to a real-life example. In real life, a package can be a box containing different items. You can access the items in the box by unpacking the said package. Similarly, a package in Ubuntu is a compressed file archive containing a list of files and scripts required to run a particular application. For Ubuntu to access those files, it needs to unpack or in computer terminology install/update the said package.
Updating packages in Ubuntu is, to be honest, quite a simple task that can be done with just two mouse clicks, or by typing two commands if you are updating via terminal. There are two major ways that you can go about completing this task. You can update your packages via command line, or if you like to perform tasks using GUI, you can update your packages graphically using Package Updater. The choice is yours to make.
Method 1:Via Terminal
On the Ubuntu desktop, go to the terminal by clicking the terminal icon in the shell or simple press Ctrl+Alt+T.
In the terminal type, the following command
After typing the above command, you will be asked for your password. Type the password in the terminal. No characters will be shown on the terminal when you are writing your password. After typing the password, hit enter.
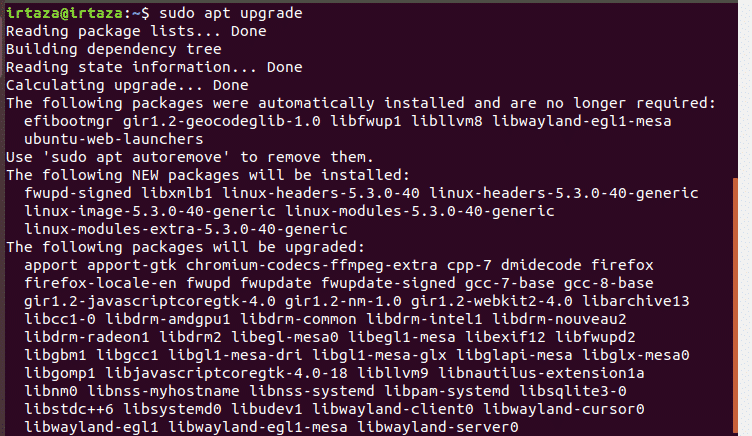
Now contrary to popular belief, this command doesn’t update your system. Instead, it updates your Ubuntu repositories. So your system checks against the repositories. It checks if there are newer versions available of the program installed. It won’t update your existing packages right away; instead, it will update the information about the existing packages and their versions available. This is the reason that when this command finishes execution, Ubuntu shows you the number of packages that can be updated.
In the picture above, you can see that when this command finishes execution, Ubuntu shows you the list of packages that can be updated. In order to view these packages type the following command
You can update a particular package, or you can update all of the updatable packages on your Ubuntu. To update all your packages, just type the following command in the terminal.
After typing the above command again, Ubuntu will ask you for your password. Like before, type in the password and hit enter.
After 2 or 3 seconds Ubuntu will show you the amount needed to update these packages and will further ask for your confirmation. To continue, type y in the terminal and press enter. Once you do this, Ubuntu will start downloading and updating your packages.
This command will download and update all of the packages that need updating. A little pro tip here to make this updating task easy. You can also type the following command instead of typing in these two commands.
As the two commands require to run in succession, we can combine them into a single command. The && between the two commands combines them. So now the first command before the && sign runs. When the first command has completed execution, the rest of the command after the && is executed. The -y at the end will save you one keystroke where Ubuntu asks you whether you want to install the upgrades or not. You should run this command from time to time to keep your system up to date.
Method 2: Update using Package Updater:
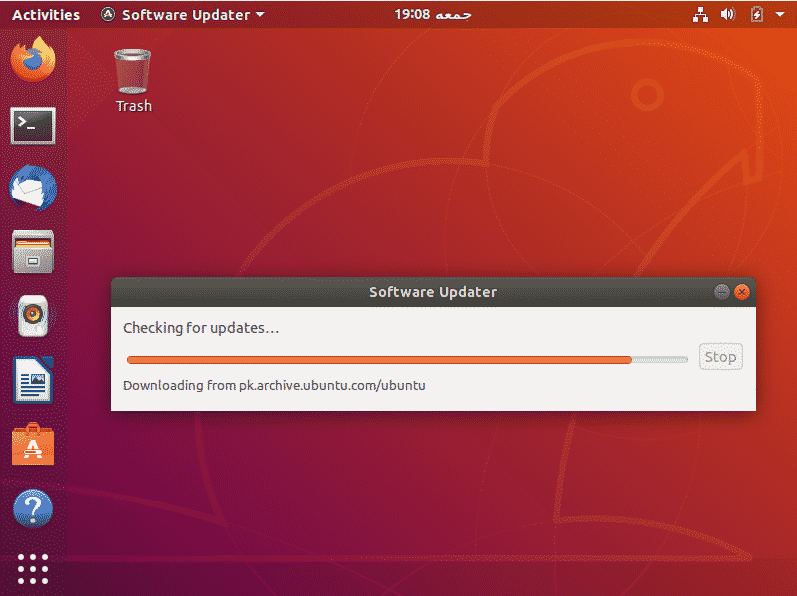
Go to the menu and in the search bar type “Software Updater.”. Now run it.
It will check if there are any packages on your system that can be updated.
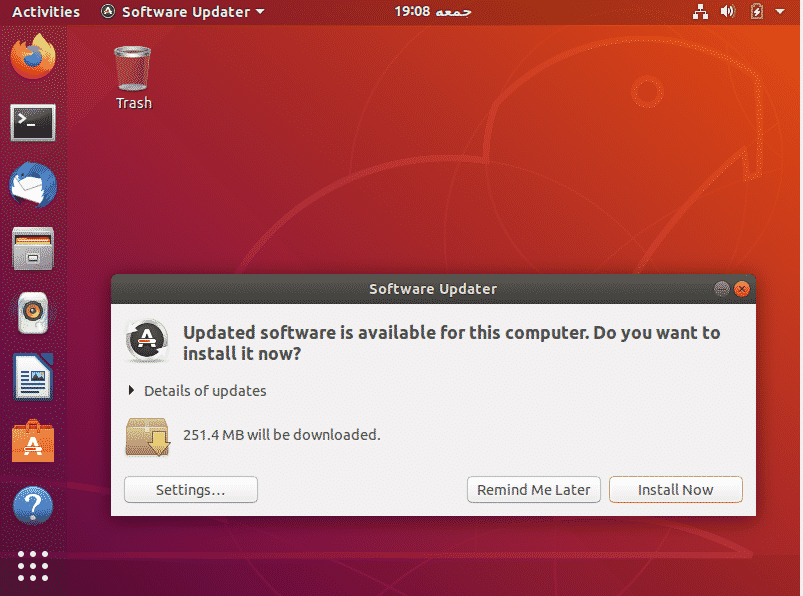
If there are any such packages, it will give you the option to install the updates
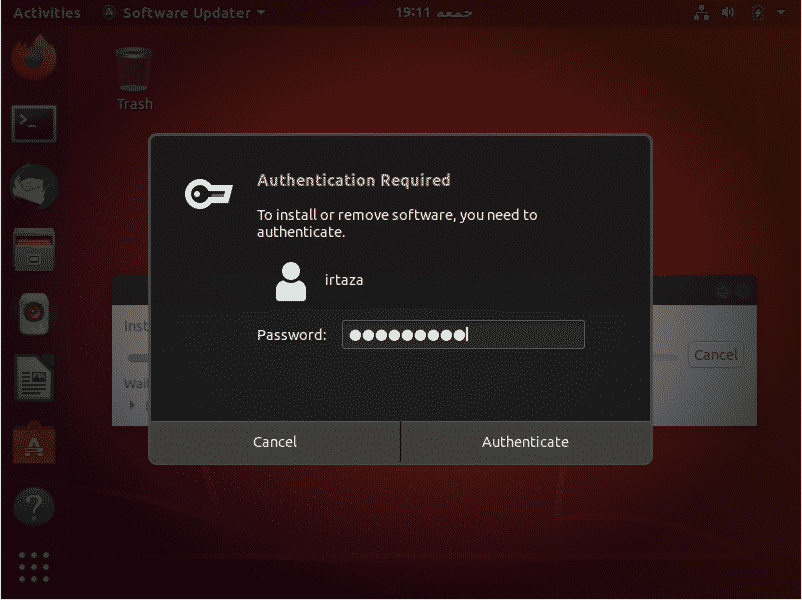
Click on Install Now. It will ask for your password. Type your password and hit Authenticate.
After authenticating, Ubuntu will start downloading and installing the updates.
In some cases, you might be asked to restart your system after the updates. This is so that the installed, updated packages can take full effect and function properly.
In most of the cases after updating, there are some packages the are of no further use to the user. You can delete them, which will free up your system space and keep your system clean and tidy, which is always a good thing. To do so type the following command in the terminal
This tutorial is valid for all the versions of Ubuntu and other Linux distros based on Ubuntu like Linux Lite, Linux Mint, etc.
Conclusion:
I hope this tutorial will be helpful to you. One of the many things you hear about Ubuntu is that it’s a lot safer than Windows. The proof can be seen when updating. Whenever you make any changes to the system, Ubuntu asks you your password for authentication. Updating packages in Ubuntu is quite simple. Bear in mind that this tutorial is for updating packages in Ubuntu. It doesn’t update your Ubuntu version. Also note that this tutorial, including the command line method, is valid for all the versions of Ubuntu and other Linux distros based on Ubuntu like Linux Lite, Linux Mint, etc.
How to Update All Packages on Ubuntu 22.04
Ubuntu is the Linux distribution that comes with different packages used for different daily life applications. The development team of different packages releases updates that include performance updates, security updates, or new version updates.
In this blog, we learn to make sure that we are using the most recent updated versions of the packages by updating and upgrading all the packages with the methods discussed.
How to Update All Packages on Ubuntu?
There are two different methods by which we can update all the packages:
Method 1: How to update all the packages on Ubuntu using the terminal
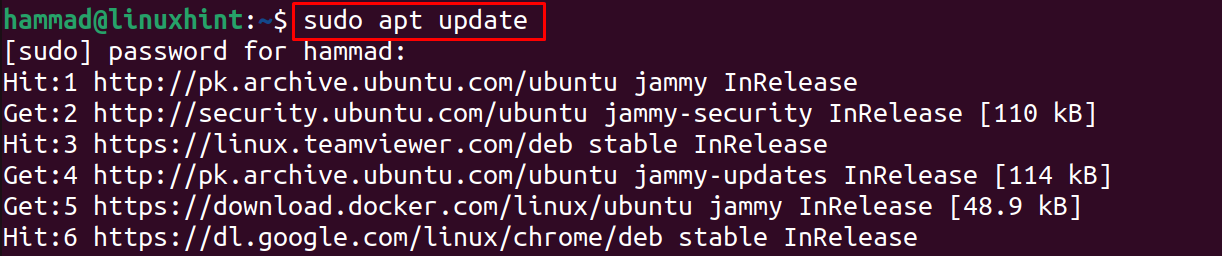
The Ubuntu distribution can be managed by the command-line interface. So, we will first open the terminal using the shortcut key “CTRL+ALT+T” and then use the command given-below to get an update of all the packages:
To view the packages whose updates are available, run the command:
To upgrade all these packages altogether, execute the command:
It will confirm from you to proceed with the process, allow it by typing “Y” and pressing the ENTER key:
When the process is completed, all the packages will be up to date.
Method 2: How to update all packages on Ubuntu using the GUI method
Another method to update all the packages on Ubuntu is by using the GUI (Graphical User Interface) method.
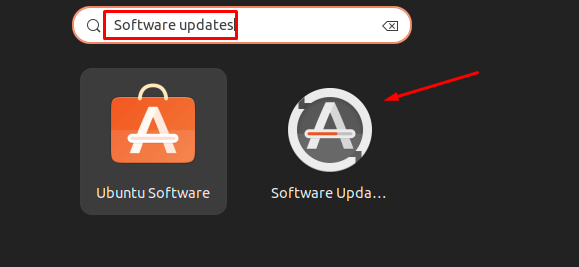
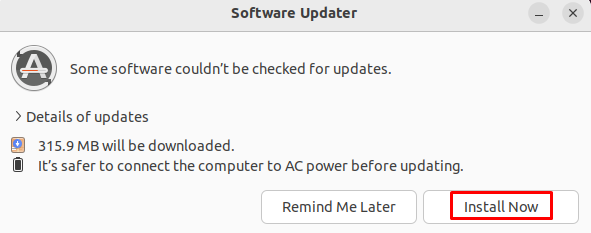
For updating packages through GUI, search for “Software Updates” in the application search bar and open it:
It will show you the packages ready to be upgraded(if any). Click on the “Install Now” button to begin the updating process of all the packages:
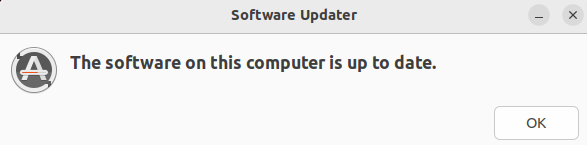
When the upgradation of all the packages is completed, the message will be displayed on the screen.
This way, one can update and upgrade all the packages on Ubuntu 22.04 without any hassle.
Conclusion
Use “sudo apt update” and “sudo apt upgrade -y” commands to update and upgrade all the packages to their newest available versions on Ubuntu 22.04. In this writeup, two different methods are demonstrated by which all the packages of Ubuntu can be updated.
About the author
Hammad Zahid
I’m an Engineering graduate and my passion for IT has brought me to Linux. Now here I’m learning and sharing my knowledge with the world.