- Ошибка 500 internal server error Nginx
- Как исправить 500 internal server error Nginx
- 1. Ошибка в скрипте PHP
- 2. Превышено время выполнения или лимит памяти
- 3. Неверные права на файлы
- Выводы
- Internal Error 500 Apache, but nothing in the logs?
- 11 Answers 11
- This is an Ancient answer from 2013, back when PHP was new and security wasn’t an issue:
Ошибка 500 internal server error Nginx
При разработке веб-сайтов и веб-приложений можно столкнуться с ошибкой 500 internal server error. Сначала она может испугать и ввести в заблуждение, поскольку обычно веб-сервер выдает более конкретные ошибки, в которых указана точная причина проблемы, например, превышено время ожидания, неверный запрос или файл не найден, а тут просто сказано что, обнаружена внутренняя ошибка.
Но не все так страшно и в большинстве случаев проблема вполне решаема и очень быстро. В этой статье мы разберем как исправить ошибку Internal server error в Nginx.
Как исправить 500 internal server error Nginx
Дословно Internal server error означает внутренняя ошибка сервера. И вызвать её могут несколько проблем. Вот основные из них:
- Ошибки в скрипте на PHP — одна из самых частых причин;
- Превышено время выполнения PHP скрипта или лимит памяти;
- Неправильные права на файлы сайта;
- Неверная конфигурация Nginx.
А теперь рассмотрим каждую из причин более подробно и разберем варианты решения.
1. Ошибка в скрипте PHP
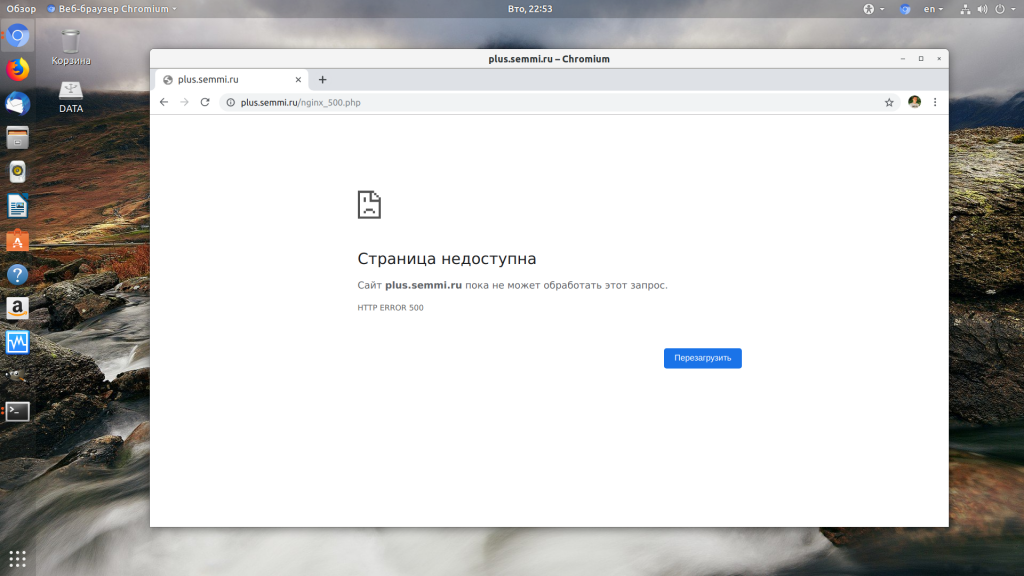
Мы привыкли к тому, что если в PHP скрипте есть ошибки, то сразу же видим их в браузере. Однако на производственных серверах отображение сообщений об ошибках в PHP отключено, чтобы предотвратить распространение информации о конфигурации сервера для посторонних. Nginx не может отобразить реальную причину ошибки, потому что не знает что за ошибка произошла, а поэтому выдает универсальное сообщение 500 internal server error.
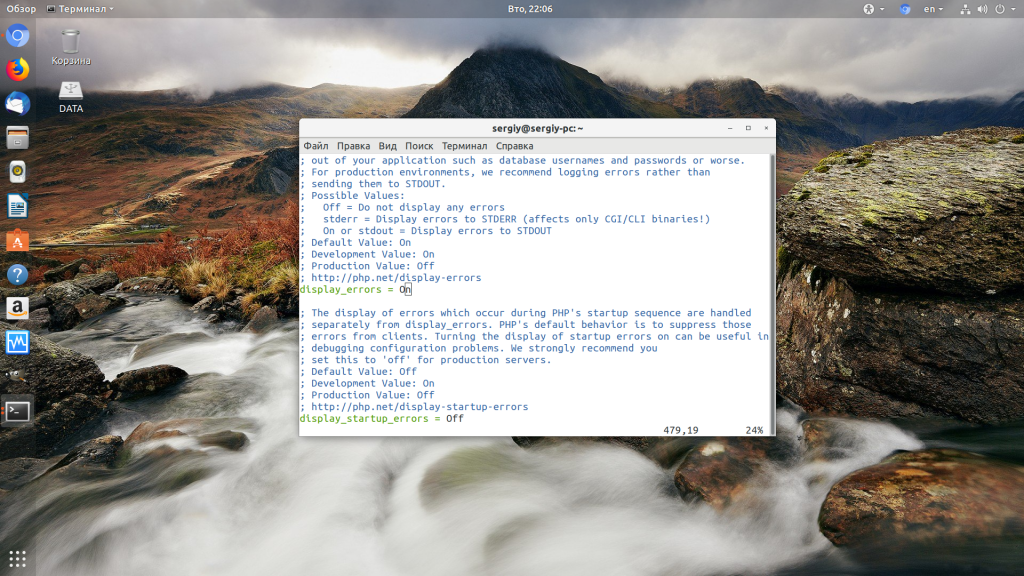
Чтобы исправить эту ошибку, нужно сначала понять где именно проблема. Вы можете включить отображение ошибок в конфигурационном файле php изменив значение строки display_errors с off на on. Рассмотрим на примере Ubuntu и PHP 7.2:
sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
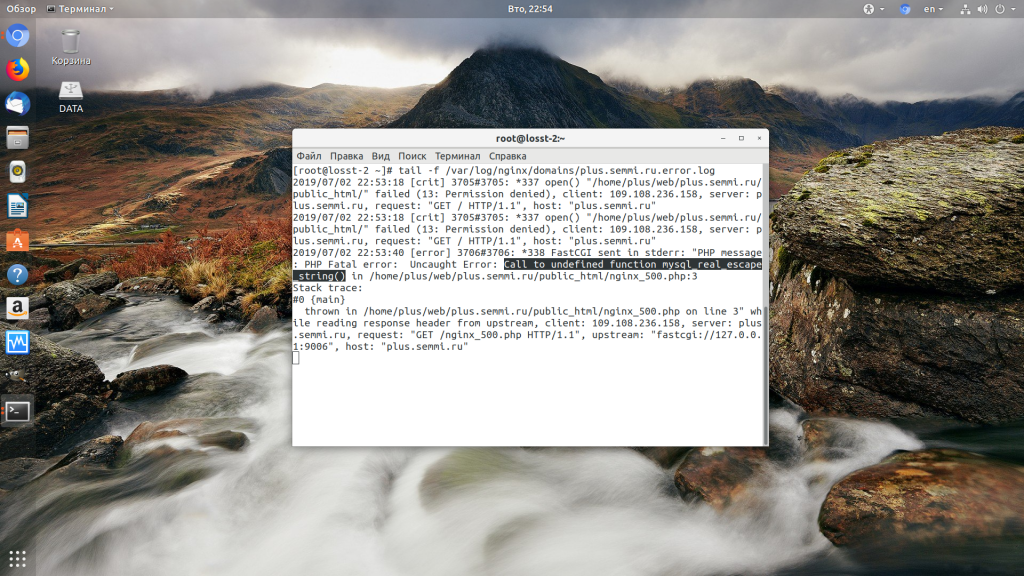
Затем обновите страницу и вы увидите сообщение об ошибке, из-за которого возникла проблема. Далее его можно исправить и отключить отображение ошибок, тогда все будет работать. Ещё можно посмотреть сообщения об ошибках PHP в логе ошибок Nginx. Обычно он находится по пути /var/log/nginx/error.log, но для виртуальных доменов может настраиваться отдельно. Например, смотрим последние 100 строк в логе:
tail -n 100 -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
Теперь аналогично, исправьте ошибку и страница будет загружаться нормально, без ошибки 500.
2. Превышено время выполнения или лимит памяти
Это продолжение предыдущего пункта, так тоже относится к ошибкам PHP, но так, как проблема встречается довольно часто я решил вынести её в отдельный пункт. В файле php.ini установлены ограничения на время выполнения скрипта и количество оперативной памяти, которую он может потребить. Если скрипт потребляет больше, интерпретатор PHP его убивает и возвращает сообщение об ошибке.
Также подобная ошибка может возникать, если на сервере закончилась свободная оперативная память.
Если же отображение ошибок отключено, мы получаем error 500. Обратите внимание, что если время ожидания было ограничено в конфигурационном файле Nginx, то вы получите ошибку 504, а не HTTP ERROR 500, так что проблема именно в php.ini.
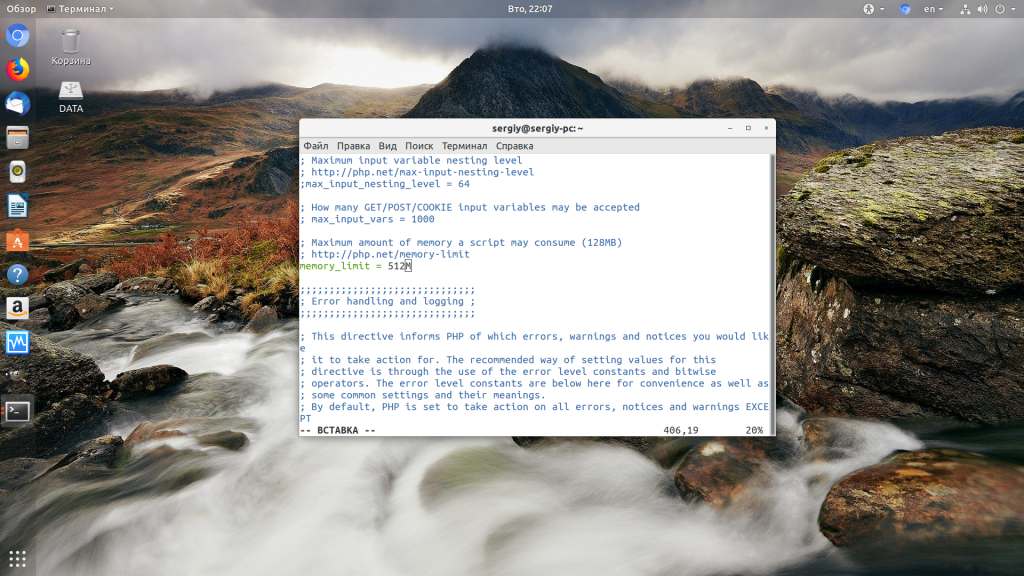
Чтобы решить проблему увеличьте значения параметров max_execution_time и memory_limit в php.ini:
max_execution_time 300
memory_limit 512M
Также проблема может быть вызвана превышением других лимитов установленных для скрипта php. Смотрите ошибки php, как описано в первом пункте. После внесения изменений в файл перезапустите php-fpm:
sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
3. Неверные права на файлы
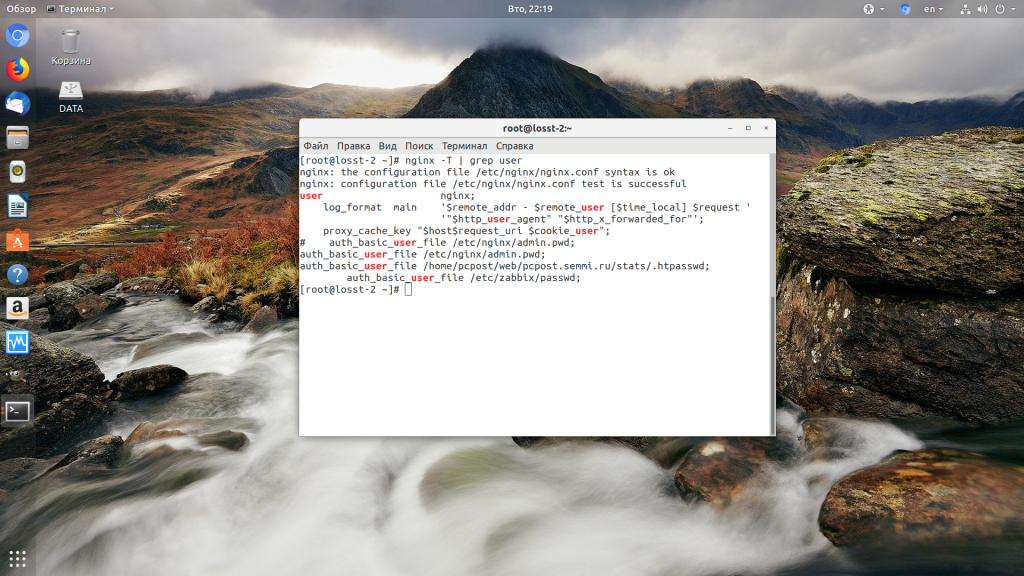
Такая ошибка может возникать, если права на файлы, к которым обращается Nginx установлены на правильно. Сервисы Nginx и php-fpm должны быть запущены от имени одного и того же пользователя, а все файлы сайтов должны принадлежать этому же пользователю. Посмотреть от имени какого пользователя запущен Nginx можно командой:
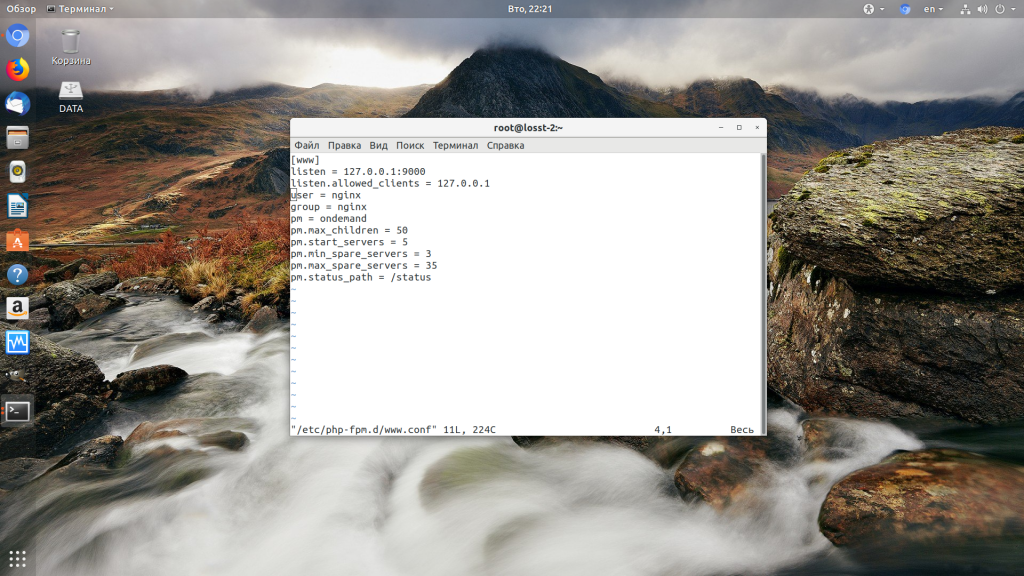
Чтобы узнать от какого пользователя запущен php-fpm посмотрите содержимое конфигурационного файла используемого пула, например www.conf:
sudo vi /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
В моем случае это пользователь nginx. Теперь надо убедится, что файлы сайта, к которым вы пытаетесь обратиться принадлежат именно этому пользователю. Для этого используйте команду namei:
Файлы сайта должны принадлежать пользователю, от имени которого запущены сервисы, а по пути к каталогу с файлами должен быть доступ на чтение для всех пользователей. Если файлы принадлежат не тому пользователю, то вы можете все очень просто исправить:
sudo chown nginx:nginx -R /var/www/site
Этой командой мы меняем владельца и группу всех файлов в папке на nginx:nginx. Добавить права на чтение для всех пользователей для каталога можно командой chmod. Например:
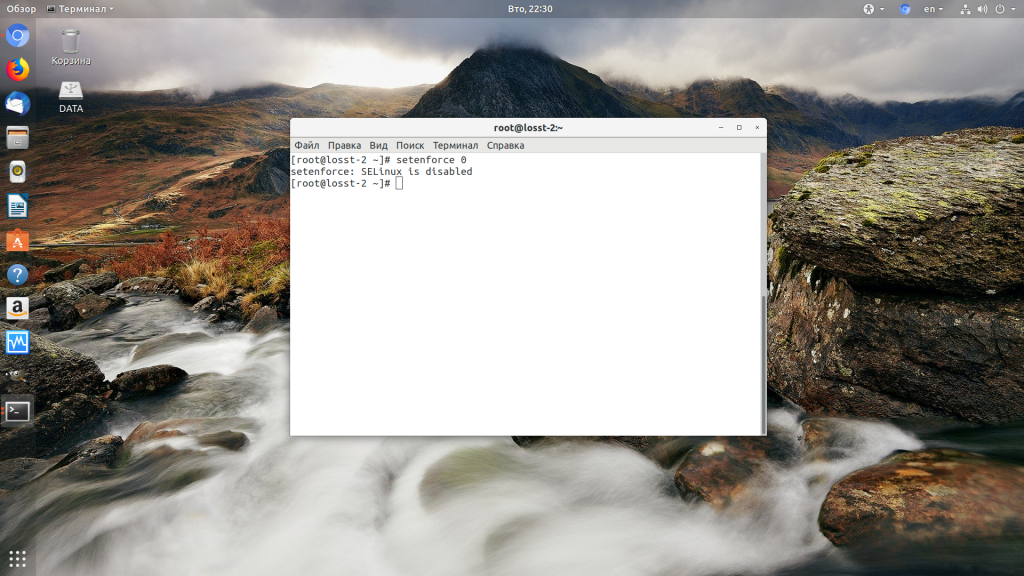
Далее все должно работать. Также, проблемы с правами может вызывать SELinux. Настройте его правильно или отключите:
Выводы
В этой статье мы разобрали что делать если на вашем сайте встретилась ошибка 500 internal server error nginx. Как видите проблема вполне решаема и в большинстве случаев вам помогут действия описанные в статье. А если не помогут, напишите свое решение в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Internal Error 500 Apache, but nothing in the logs?
I’m getting 500 Internal Server errors when I try to make an HTTP POST to a specific address in my app. I’ve looked into the server logs in the custom log directory specified in the virtual hosts file, but the error doesn’t show up there so debugging this has been a pain in the ass. How do I cause Apache to log Internal 500 errors into the error log?
I had same issue using PHP with virtual hosts. no errors (Apache2, Ubuntu). Ended up being missing PHP modules (mysql, json, etc.)
On ours, it was sending them to the access log (presumably because from Apache’s point of view, it was working correctly and merely passing them along, from a deeper layer — in our case, Passenger/Rails). Just putting this note here in case somebody is scratching their head.
11 Answers 11
This is an Ancient answer from 2013, back when PHP was new and security wasn’t an issue:
Here in the future it’s a security risk to dump errors to screen like this. You better not be doing this in any production setting.
Why are the 500 Internal Server Errors not being logged into your apache error logs?
The errors that cause your 500 Internal Server Error are coming from a PHP module. By default, PHP does NOT log these errors. Reason being you want web requests go as fast as physically possible and it’s a security hazard to log errors to screen where attackers can observe them.
These instructions to enable Internal Server Error Logging are for Ubuntu 12.10 with PHP 5.3.10 and Apache/2.2.22 .
Make sure PHP logging is turned on:
el@apollo:~$ locate php.ini /etc/php5/apache2/php.ini sudo vi /etc/php5/apache2/php.ini ;display_startup_errors ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off ;error_reporting ; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE ; Development Value: E_ALL | E_STRICT ; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED display_startup_errors = On ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off error_reporting = E_ALL ; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE ; Development Value: E_ALL | E_STRICT ; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED tail -f /var/log/apache2/error.log [Wed Dec 11 01:00:40 2013] [error] [client 192.168.11.11] PHP Fatal error: Call to undefined function Foobar\\byob\\penguin\\alert() in /yourproject/ your_src/symfony/Controller/MessedUpController.php on line 249 @WanLiqun It’s a pretty good piece of info but it only applies to PHP, which is not even mentioned in the question.
«The errors that cause your 500 Internal Server Error are coming from a PHP module. By default, PHP does NOT log these errors.» Who mentioned PHP? Server 500 Logging being disabled in PHP is an assumption and most often a wrong assumption. Apache will log server 500 errors from a faulting module (in this case php) but most often it will go to /var/log/apache2/error.log (assuming debian or similar)
I just ran into this and it was due to a mod_authnz_ldap misconfiguration in my .htaccess file. Absolutely nothing was being logged, but I kept getting a 500 error.
If you run into this particular issue, you can change the log level of mod_authnz_ldap like so:
LogLevel warn authnz_ldap_module:debug That will use a log level of debug for mod_authnz_ldap but warn for everything else (https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/en/mod/core.html#loglevel).
The question was, «How do I cause Apache to log Internal 500 errors into the error log?» This should probably be a comment.
This is very useful, thank you. In my case, it was mod_proxy so LogLevel warn proxy:debug helped me track down the issue.
Check your php error log which might be a separate file from your apache error log.
Find it by going to phpinfo() and check for error_log attribute. If it is not set. Set it: https://stackoverflow.com/a/12835262/445131
Maybe your post_max_size is too small for what you’re trying to post, or one of the other max memory settings is too low.
The question was, «How do I cause Apache to log Internal 500 errors into the error log?» This should probably be a comment.
If your Internal Server Error information doesn’t show up in log files, you probably need to restart the Apache service.
I’ve found that Apache 2.4 (at least on Windows platform) tends to stubbornly refuse to flush log files—instead, logged data remains in memory for quite a while. It’s a good idea from the performance point of view but it can be confusing when developing.
This was the correct answer for me on Linux. Even after deleting the original error.log (which was a character device file) and replacing it with a touch 777 error.log, Apache wouldn’t write to it until being restarted.
(╯°□°)╯︵ ┻━┻ And by restart, that means cold restart, not graceful or reload. This applies to more than php . I just fought this with a rails/passenger server.
Please Note: The original poster was not specifically asking about PHP. All the php centric answers make large assumptions not relevant to the actual question.
The default error log as opposed to the scripts error logs usually has the (more) specific error. often it will be permissions denied or even an interpreter that can’t be found.
This means the fault almost always lies with your script. e.g you uploaded a perl script but didnt give it execute permissions? or perhaps it was corrupted in a linux environment if you write the script in windows and then upload it to the server without the line endings being converted you will get this error.
print "content-type: text/html\r\n\r\n"; There are many reasons for it. so please first check your error log and then provide some more information.
The default error log is often in /var/log/httpd/error_log or /var/log/apache2/error.log .
The reason you look at the default error logs (as indicated above) is because errors don’t always get posted into the custom error log as defined in the virtual host.
Assumes linux and not necessarily perl