- How to Install a Specific Version of a Package in Ubuntu Linux
- Method to Install a Specific Version of the Package
- Install Specific Version of Pacakge from the apt command
- Check the available version of a specific package in the repository
- Install package
- Install a Specific Version of Packages from Synaptic Package Manager
- Wrap up
- How to Install Particular Package Version in CentOS and Ubuntu
- Install Specific Package Version in CentOS/RHEL/Fedora
- Install Specific Package Version in Ubuntu and Debian
- How to install the latest version of a package with apt-get?
- 5 Answers 5
- How to install specific version of some package? [duplicate]
- 2 Answers 2
- How to know the version of installed package?
- Example:
- How to install a specific package version?
- Example:
How to Install a Specific Version of a Package in Ubuntu Linux
When you type sudo apt install package-name , it gives you the most recent version of the package. This may not be what you want if you need to install a specific version of the package for compatibility, features, or other reasons.
Then, in this case, you can ask apt command for the specific version; if they have it, then you can begin with the installation. Otherwise, you can get the binary or source file from the official resource and get it installed.
So let’s start the guide, where I’ll show you how you can use the apt command to ask for a specific version of utilities to install on your system and also show you how you can use Synaptics to get different versions of the same tool.
Method to Install a Specific Version of the Package
There are two methods that I know of that you can use to install particular versions of applications or packages, like using the apt or aptitude command, and if you prefer a GUI, then you can go with the Synaptics package manager.
Install Specific Version of Pacakge from the apt command
The steps are fairly straightforward, so I’d better give you an overview of what we’ll be doing throughout the article. First, I’ll show how you can find the version for which you are looking in the repository and, if it is available, how you can install it on any Ubuntu machine.
Check the available version of a specific package in the repository
One of the foremost steps here is to check whether the version of the package you are looking for is available in the repository. This can be done by running sudo apt policy package-name , sudo apt-cache madison package-name , or sudo apt list -a package-name .
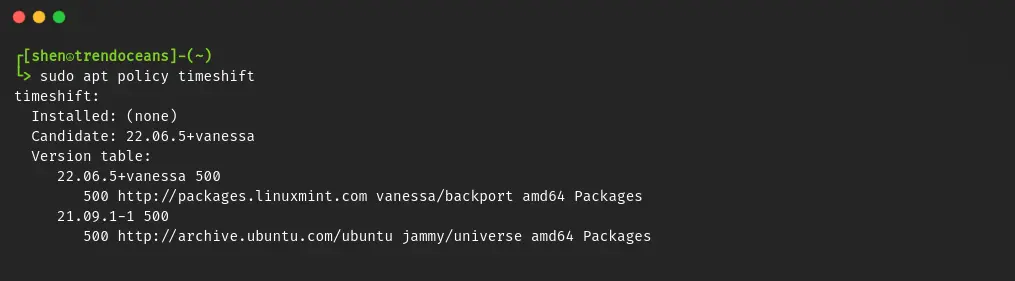
So for demo purposes, let me find the older version of the Timeshift on my Linux Mint by running any of the following commands:
$ sudo apt policy timeshift or $ sudo apt-cache madison timeshift or $ sudo apt list -a timeshiftAs you can see, I have found two different versions of Timeshift: one is 22.06.5+Vanessa and another is 21.09.1-1 from the Ubuntu universe repo.
Tip: If you are not finding applications in your newly installed Ubuntu, then check if you have enabled multiverse or universe in the Software Center.
Install package
Once you find the package available in the repository, you can use the apt command by specifying the package version by following the syntax below:
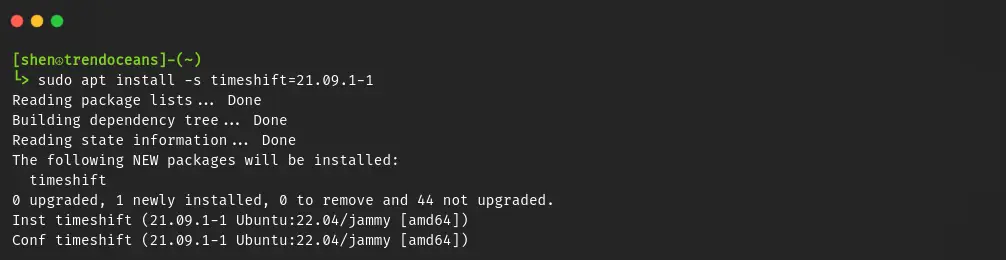
$ sudo apt install package-name=versionBut I suggest you add the -s flag before installing applications, which simulates the installation, so you can be aware of what packages are going to be added to or removed from your system.
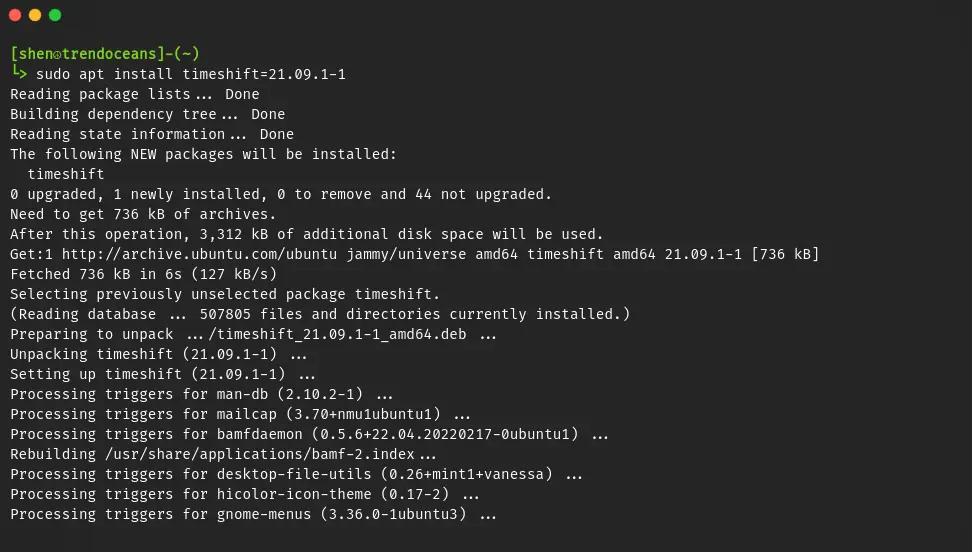
$ sudo apt install -s timeshift=21.09.1-1After reading the output, if you find everything is good to go, then remove the -s flag and run the command as shown below to install the specified version of the package.
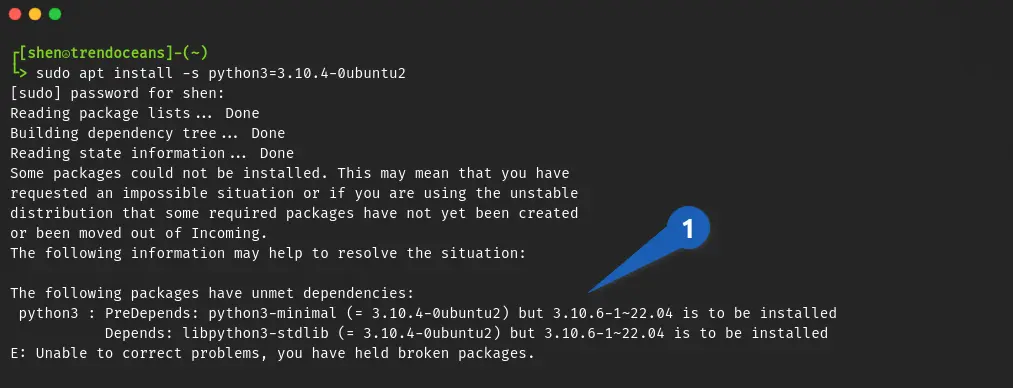
$ sudo apt install timeshift=21.09.1-1When you try to install a certain old version of an application, you may get the error E: Unable to correct problems; you have held broken packages.
To fix that problem, you can look at the error message as shown below and install the dependencies that are needed:
Command to install python3.10.4-0ubuntu2 with missing dependencies.
$ sudo apt install python3=3.10.4-0ubuntu2 python3-minimal=3.10.4-0ubuntu2 libpython3-stdlib=3.10.4-0ubuntu2Or else I would recommend that you use the aptitude command to fulfil all dependencies that are required for the programme by running the following command, which will install the particular version of the application without any difficulty.
$ sudo aptitude install libreoffice=1:7.3.2-0ubuntu2Output may be overwhelming if you’ve never used aptitude , so it’s better to check this article for more information, like how you can install an older version of an application without running into the dependencies issue.
Install a Specific Version of Packages from Synaptic Package Manager
You can also use the Synaptic package manager to install a specific version of a package by choosing the package you want to install, clicking “Package” in the menu bar, and then choosing “Force Version.”
If you don’t have Synaptic installed on your system, then first get it by running the below command:
$ sudo apt install synaptic -yOnce you run Synaptic, you will find the list of applications, buttons, and many other options, but you need to first look at the search option, which you will find on the right of the application interface.
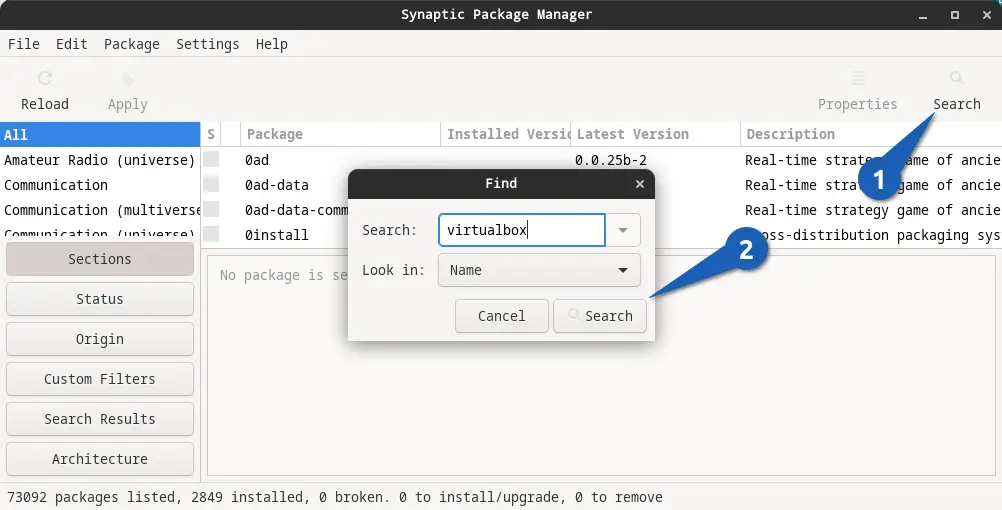
Enter the name of the programme or package you want to install on your system in the “Search” box.
Now select the “virtualbox” or the respective package that you have searched and press Ctrl + E , or you can use the menu option Package -> Force Version.
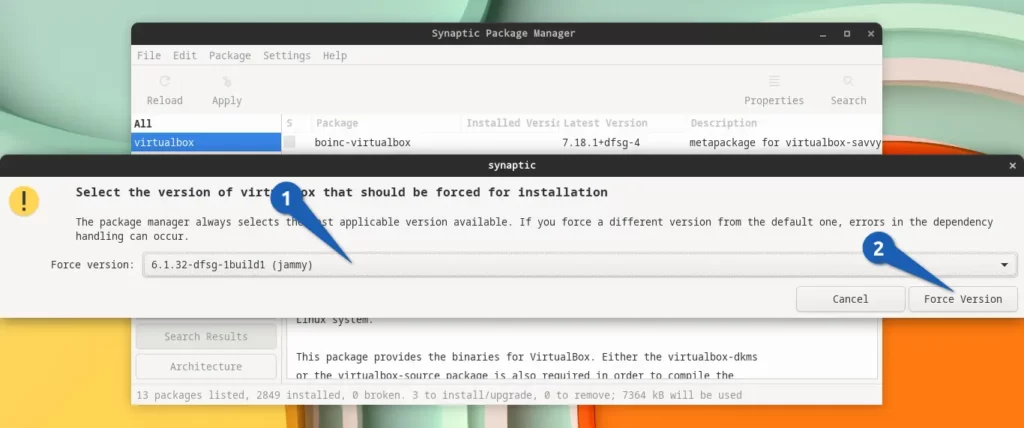
It will open a new prompt where you need to select the version from the drop-down menu that you want to install and click on “Force Version”.
Like I have selected the 6.1.32-dfsg-1build1 (jammy) over the default 6.1.38-dfsg-3~ubuntu.22.04.1 (jammy updates)
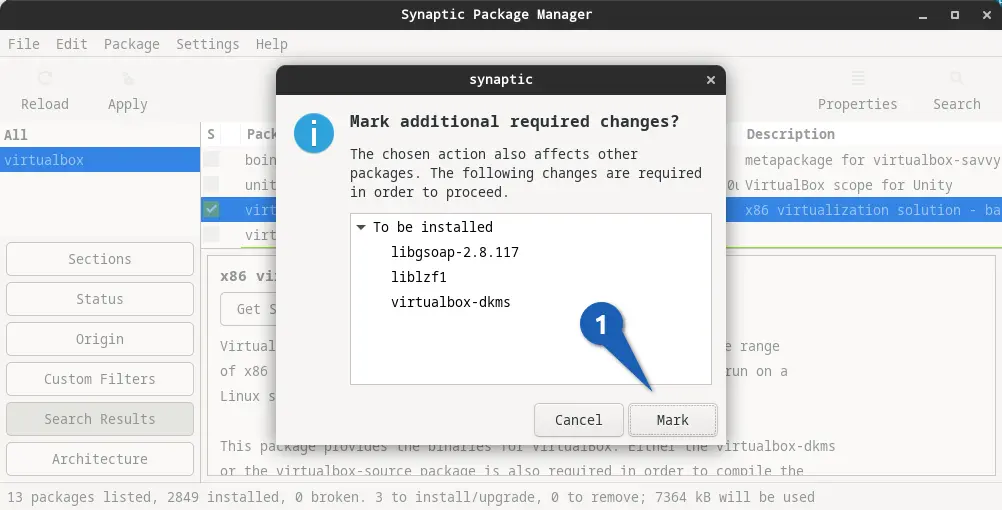
Once you click on “Force version,” it will ask you to mark the following changes:
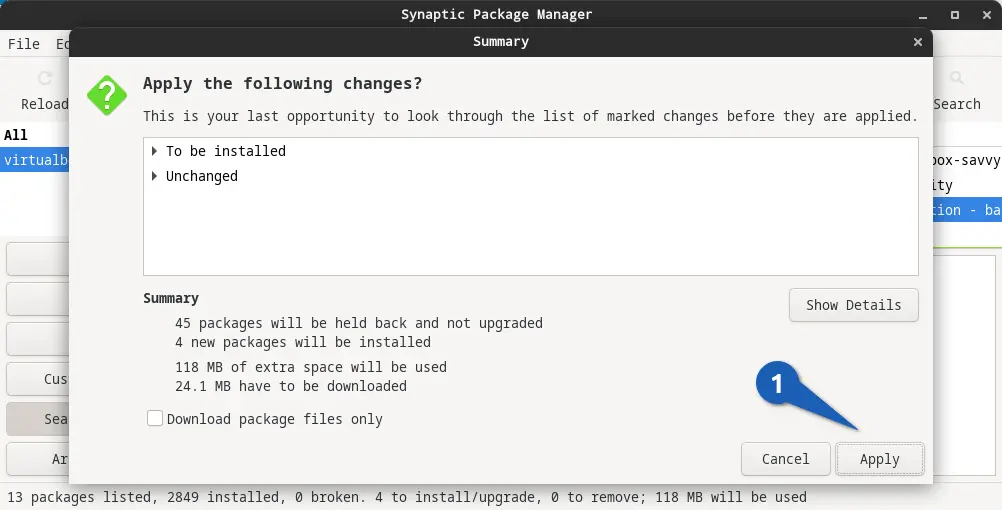
Next, you need to click on the “Apply” button you will find on the application’s main interface, and after that, it will prompt you for the summary, where you need to once again click on “Apply”.
Wait for the installation to complete, and once it’s done, close the window and check the package in the Terminal or Applications menu.
Not every programme can be easily installed using this method because some programmes have this dependency issue. So it’s better to use the aptitude command to install a specific version of the application.
Wrap up
That’s all for this article, where you have learned how to install a specific version of an application in Ubuntu using sudo apt package-name=version , aptitude , and the Synaptic package manager.
If you are not able to install an application due to a dependency issue, then you need to manually fulfil the dependencies, which may be a tiresome process, so it’s better to use the aptitude command for this purpose.
For any reason, if you want to have an older version of the application, then I would suggest you get the AppImage, or if you are using Flatpak, then read this guide to get a specific older version of the application.
If you know any other way to install specific version of command, then let use know in the comment section.
A man with a tech effusive who has explored some of the amazing technology stuff and is exploring more. While moving towards, I had a chance to work on Android development, Linux, AWS, and DevOps with several open-source tools.
How to Install Particular Package Version in CentOS and Ubuntu
Usually, when you install a package in CentOS and Ubuntu, the package management software selects the latest package version from the repository, by default. However, sometimes, for one reason or the other, you may want to install a specific package version on your Linux system.
In this article, we will explain how to install a particular or specific package version in CentOS and Ubuntu using Yum and APT front-end package managers, respectively.
Install Specific Package Version in CentOS/RHEL/Fedora
First, you need to check for all the available versions of a package, whether installed or not. Normally, yum ignores specific versions of a package and will always try to install the latest version available.
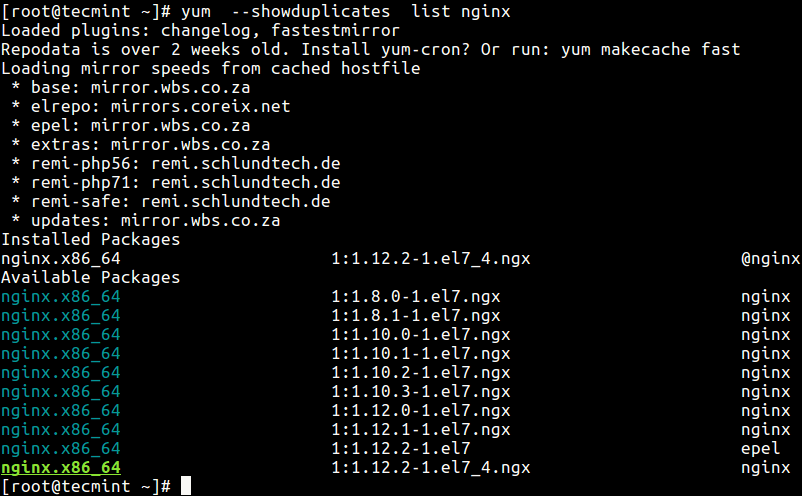
Secondly, when you try to find info about a package, yum only shows the latest version of that package in the output of info, list or search sub-commands; but using the —showduplicates switch, you can display all package versions present in the repository.
# yum --showduplicates list nginx
From the above command output, the naming format for packages are:
package_name.architecture version_number–build_number repository
The build_number represents minor changes made by the package maintainer, not by the program author, such as additional documentation, changes to configuration files, or bug fixes and more.
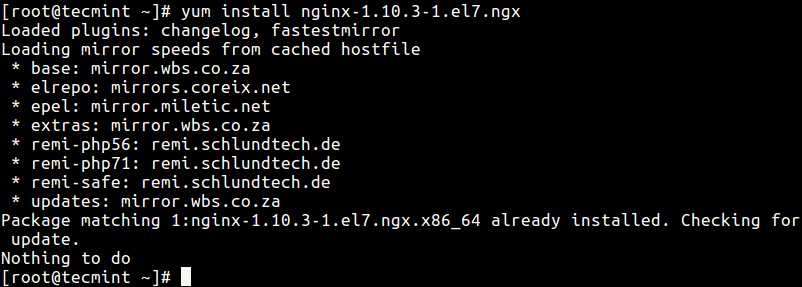
Once you have identified the specific version of a package (for example nginx-1.10.3-1.el7.ngx), install it as follows. Note that the name format will have to change here, to the full RPM desired, package_name-version_number as shown in the following command.
Alternatively, if you want to use a version with certain updates, specify the build_number (package_name-version_number-build_number) as shown.
# yum install nginx-1.10.3-1.el7.ngx
Considering the above situation, a newer version of the packages is already installed on the system. Therefore, you need to remove the installed package version, if you want to install an older version from the available packages as shown.
Once you have removed the installed package, you can then install the specific version you desire as explained above.
Install Specific Package Version in Ubuntu and Debian
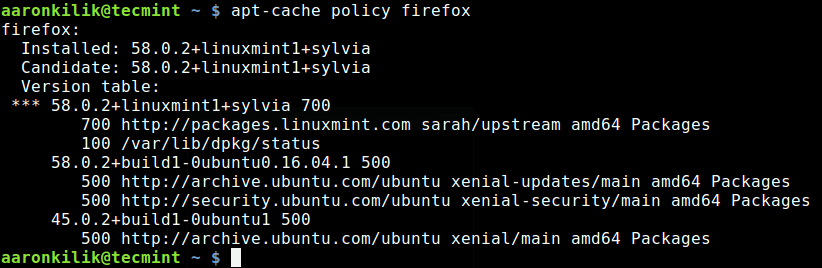
First check the version of the package installed on your system plus all available packages in the repository, using the apt-cache command below.
To install a specific package version, use the following command with syntax below.
$ sudo apt install firefox=45.0.2+build1-0ubuntu1
If a newer version of a package is already installed on your Ubuntu system, you can remove it and then install the version you want.
$ sudo apt remove firefox $ sudo apt install firefox=45.0.2+build1-0ubuntu1
That’s all! For more information, refer to the yum, apt, apt-cache man pages. If you have any queries, use the comment form below to get to us.
How to install the latest version of a package with apt-get?
But is there a shortcut for installing the latest version? For example, say writing a script to automate Jenkins installation. After adding http:/q/pkg.jenkins-ci.org/debian to /etc/apt/sources.list , Jenkins is available from two sources. Now, I’d like to tell apt-get to install the latest version without knowing exactly what the latest version is at the time the script is executed. Is this possible in any simple way?
5 Answers 5
apt-get update apt-get install
And the latest available in all your repositories will be installed.
Thanks, kind of obvious. 🙂 Earlier I’ve run into having an older version installed unintentionally, but maybe that was caused by forgetting to do apt-get update first.
The selected answer works in most cases. However, you might find yourself in a situation where a more recent version is available in a backport repository which will not be installed by apt-get install by default. For example, I recently came across this:
$ apt-cache policy golang golang: Installed: 2:1.3.3-1 Candidate: 2:1.3.3-1 Version table: 2:1.7~5~bpo8+1 0 100 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-backports/main amd64 Packages 2:1.5.1-4~bpo8+1 0 100 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-backports/main amd64 Packages *** 2:1.3.3-1 0 500 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial/main amd64 Packages 100 /var/lib/dpkg/status Selecting a version from the backports can be done by specifying to install from backports: apt-get -t xenial-backports install golang .
How to install specific version of some package? [duplicate]
Please do not vote to delete this post. It is useful as a signpost. Duplicates serve to guide others to the right Q&A.
2 Answers 2
How to know the version of installed package?
The above command will shows installed package version and also all the available versions in the repository according to the version of Ubuntu in which you are running.It doesn’t display the package version which was intended for another version of Ubuntu(not your’s).
Example:
$ apt-cache policy gparted gparted: Installed: 0.16.1-1 Candidate: 0.16.1-1 Version table: *** 0.16.1-1 0 500 http://ubuntu.inode.at/ubuntu/ saucy/main amd64 Packages 100 /var/lib/dpkg/status So the installed gparted version is 0.16.1-1 .
How to install a specific package version?
Example:
$ sudo apt-get install gparted=0.16.1-1 Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done gparted is already the newest version. 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 265 not upgraded. In every case I’ve ever tried this I always get the error The following packages have unmet dependencies: , followed by a list of packages. Any way to make it resolve that automatically?
Please note that it will most likely fail, because there is usually only 1 or 2 versions of the package that are available in the repository. If you want a different version than currently designed for your distribution, you might need to download it and install with sudo dkpg -i