- How to save rules of the iptables? [duplicate]
- 2 Answers 2
- Ubuntu 16.04 Server
- Permanently saving Iptables Rules in Linux Using the Iptables-Save Command
- Working with Iptables Rules
- 1. Viewing Available Rules
- 2. Adding Iptables Rules
- 3. Saving Iptables Rules
- 4. Restoring Iptables Rules
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Denis Kariuki
How to save rules of the iptables? [duplicate]
I create the rules to iptables. But, when I restart the computer, the rules don’t work! How to save the rules on Ubuntu ? The was problem solved! do: After of the write the commands iptables, do:
1. sudo su 2. iptables-save > /etc/iptables.rules 3. In /etc/network/if-pre-up.d/iptables,put: #!/bin/sh iptables-restore < /etc/iptables.rules exit 0 4. After, in /etc/network/if-post-down.d/iptables,put: #!/bin/sh iptables-save -c >/etc/iptables.rules if [ -f /etc/iptables.rules ]; then iptables-restore < /etc/iptables.rules fi exit 0 5. After, give permission to the scripts: sudo chmod +x /etc/network/if-post-down.d/iptables sudo chmod +x /etc/network/if-pre-up.d/iptables It would be helpful if you updated the ticket with specifics on what you have tried, on what results you have encountered. It would also be good to know whatever it is a desktop install or a server install; whatever it uses NetworkManager or not.
Since you found a solution, you should accept the answer that led you to that result or you should put your answer content in the "answer" box and then accept your own answer. This allows this question to be marked as "answered" in the system, which will help other users if they have a similar problem. Have a good day!
Message during installation of iptables-persistent is as follows: Current iptables rules can be saved to the configuration file /etc/iptables/rules.v4. These rules will then be loaded automatically during system startup. Rules are only saved automatically during package installation. See the manual page of iptables-save(8) for instructions on keeping the rules file up-to-date.
2 Answers 2
The easy way is to use iptables-persistent .
sudo apt-get install iptables-persistent After it's installed, you can save/reload iptables rules anytime:
sudo /etc/init.d/iptables-persistent save sudo /etc/init.d/iptables-persistent reload Ubuntu 16.04 Server
The installation as described above works without a problem, but the two commands for saving and reloading above do not seem to work with a 16.04 server. The following commands work with that version:
sudo netfilter-persistent save sudo netfilter-persistent reload netfilter-persistent is run as a service offering hooks at shutdown time and at at boot time. After installing iptables-persistent as a plugin for netfilter-persistent, the iptables-persistent plugin should be called by netfilter-persistent service to do the saving and loading. But in some configurations seem to intentionally skip writing. The reason for that is and how to control it is opaque.
Message during installation of iptables-persistent is as follows: Current iptables rules can be saved to the configuration file /etc/iptables/rules.v4. These rules will then be loaded automatically during system startup. Rules are only saved automatically during package installation. See the manual page of iptables-save(8) for instructions on keeping the rules file up-to-date.
The generic method of saving iptables rules is to use the command iptables-save, which writes to stdout.
iptables-save > /etc/network/iptables.rules The output created by iptables-save can then by read on stdin by iptables-restore. If on a server, without NetworkManager, a common approach is then to use a pre-up command in /etc/network/interfaces.
iface eth0 inet static . pre-up iptables-restore < /etc/network/iptables.rules If you are using NetworkManager it should be possible to run the same command from a script created under /etc/NetworkManager/dispatcher.d/. In the Community Documentation - iptables howto, see Configuration on Startup for NetworkManager for more information.
Do note that the commands iptables, iptables-save and iptables-restore are IPv4 only. For IPv6 traffic the equivalent commands are ip6tables, ip6tables-save and ip6tables-restore.
Permanently saving Iptables Rules in Linux Using the Iptables-Save Command
Defining the net-filter rules is mandatory when working with a server to ensure the security of your system. For the Linux system administrators, you often need to add, restore, or update the network firewall rules defined in the iptables. The good news is that the process is simple, but it can get annoying when you’ve defined your rules and they get lost after a reboot.
Normally, the defined rules are set to sustain until the next reboot. If working with complex and multiple rules, you may need to save them. If you have no idea how to go about this, the Linux iptables-save command does the job. This guide covers a practical usage of the command.
Working with Iptables Rules
To filter the network traffic, one must clearly define the iptables rules. The defined rules get stored in the system memory. Therefore, the rules are not persistent. And when the system reboots, you must define your rules again. Working with few rules is practical. But how about when you have multiple common rules? The solution is to save them, and there is a way you can do it.
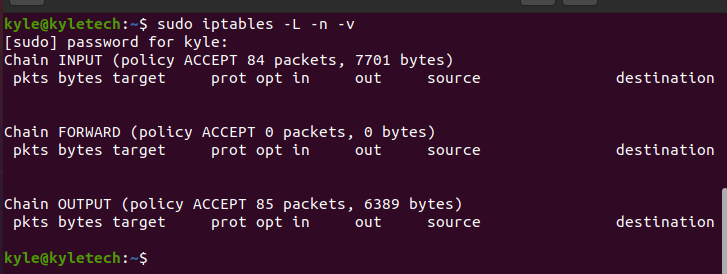
1. Viewing Available Rules
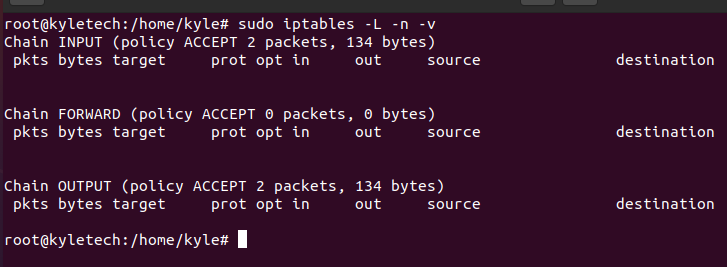
If you are unsure of the rules that you already set, you can always list them. The iptables command offers a few options for listing the rules. Use the following command to list the rules in line numbers:
We currently have no firewall rule set for this example, but we will add them later. Your output should display the set rules.
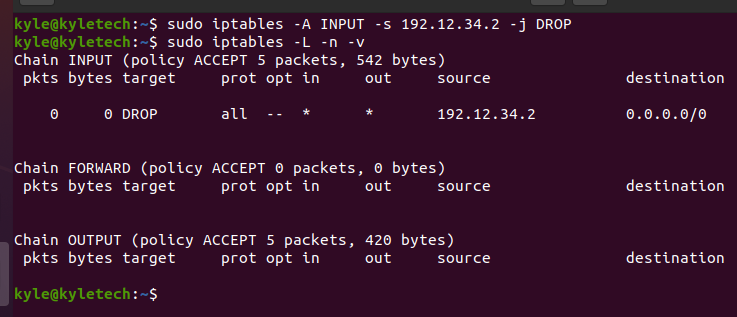
2. Adding Iptables Rules
The iptables allow the defining of the firewall rules for your network. For our example, we will create a rule to block all the connections from a specific IP address. Our target IP is 192.12.34.2, and we will block its connections using the following rule:
Go ahead and list the available rules. In this case, we will see our new rule added.
However, the rule will be lost if we reboot the system and check the same iptables rules. To avoid clearing the rules each time the system reboots, we should save the files after adding them.
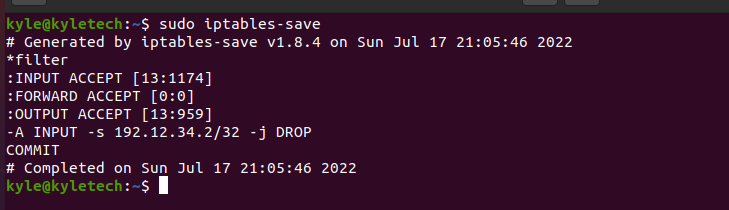
3. Saving Iptables Rules
The command to save the firewall rules is iptables-save. By using it, you can specify the file to save and access it later.
To save the rules without specifying a file, run the command shown in the following image:
The bad side with this method is that you can’t restore the rules from a file.
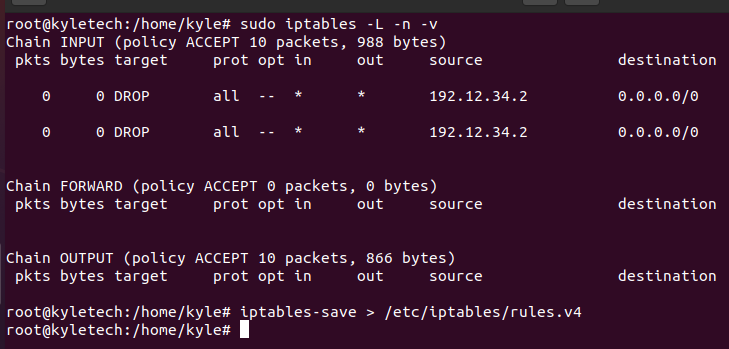
To save the file on a file, for instance, in a file named rules.v4, the command will be:
Remember, you must be the root before you execute the command.
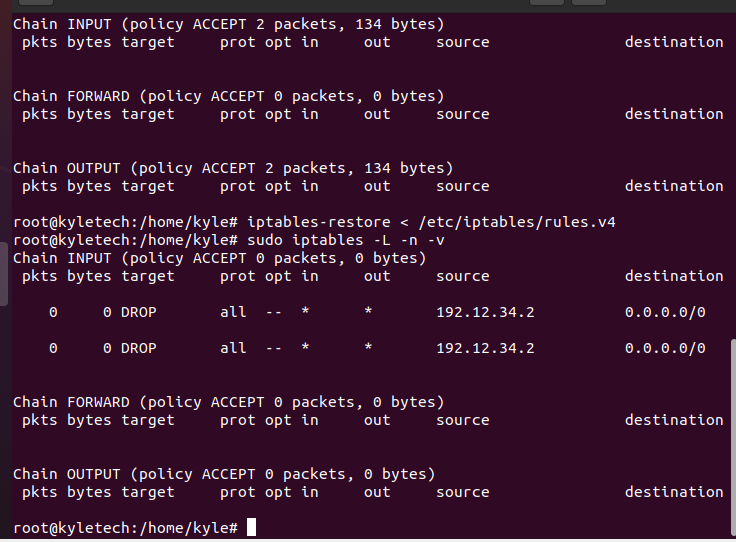
Now, let’s reboot the system and open our iptables to confirm if there are any rules defined.
From the output, no rules are currently set. However, unlike where we had to create the rules again, we can now restore the saved rules from the file.
4. Restoring Iptables Rules
The process of restoring the rules is easy. You only need to specify the path to the file like in the following command:
Once restored, you can open the iptables to see the available rules.
That’s it! We have our previously created rules restored to use for the session. All you need to use the same rules in the future is to restore them from the file. Besides, you can also update them depending on your need.
Conclusion
You no longer need to get frustrated in losing your firewall rules after a reboot. We’ve covered how you can use the iptables-save Linux command which lets you save your rules and restore them from the file whenever necessary.
About the author
Denis Kariuki
Denis is a Computer Scientist with a passion for Networking and Cyber Security. I love the terminal, and using Linux is a hobby. I am passionate about sharing tips and ideas about Linux and computing.