- How to Setup an L2TP/IPsec VPN Client on Linux
- How to Setup L2TP VPN Connection in Linux
- Управление VPN подключениями из консоли Linux
- Как создать L2TP VPN подключение в Linux?
- Создаем PPTP VPN подключение в Linux
- Настройка SSTP VPN подключения в командной строке Linux
- Подключение к OpenVPN серверу из консоли Linux
- Create a VPN connection from Linux Terminal
- Creating an L2TP VPN Connection in Linux
- Adding PPTP VPN Connection in Linux
- How to Set Up SSTP VPN Connection with Command Line on Linux?
- Configure OpenVPN Connection Using Linux Terminal
How to Setup an L2TP/IPsec VPN Client on Linux
L2TP (which stands for Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) is a tunneling protocol designed to support virtual private networks (VPN connections) over the internet. It is implemented in most if not all modern operating systems including Linux and VPN-capable devices.
The L2TP does not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms directly to traffic that passes through it, it is usually implemented with the IPsec authentication suite (L2TP/IPsec) to provide encryption within the L2TP tunnel.
In this article, we will show how to set up an L2TP/IPSec VPN connection in Ubuntu and its derivatives and Fedora Linux.
This guide assumes that the L2TP/IPsec VPN server has been set up and that you have received the following VPN connection details from your organization’s or company’s system administrator.
Gateway IP address or hostname Username and Password Pre-shared Key (Secret)
How to Setup L2TP VPN Connection in Linux
To add an L2TP/IPsec option to the NetworkManager, you need to install the NetworkManager-l2tp VPN plugin which supports NetworkManager 1.8 and later. It provides support for L2TP and L2TP/IPsec.
To install the L2TP module on Ubuntu and Ubuntu-based Linux distributions, use the following PPA.
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nm-l2tp/network-manager-l2tp $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install network-manager-l2tp network-manager-l2tp-gnome
On RHEL/CentOS and Fedora Linux, use the following dnf command to install L2TP module.
# dnf install xl2tpd # dnf install NetworkManager-l2tp # dnf install NetworkManager-l2tp-gnome OR # yum install xl2tpd # yum install NetworkManager-l2tp # yum install NetworkManager-l2tp-gnome
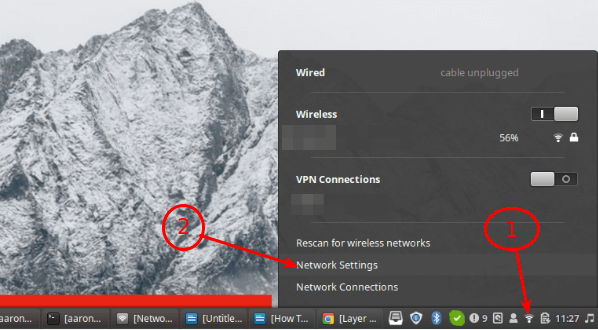
Once the package installation is complete, click on your Network Manager icon, then go to Network Settings.
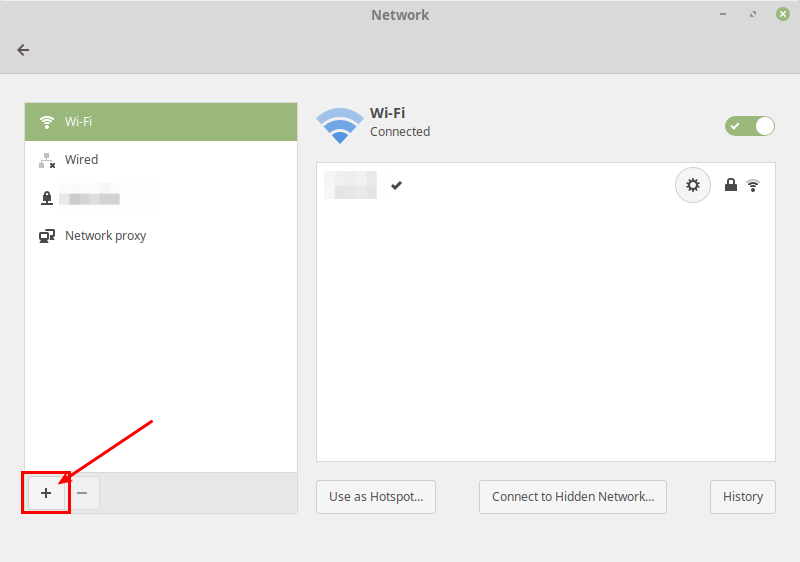
Next, add a new VPN connection by clicking on the (+) sign.
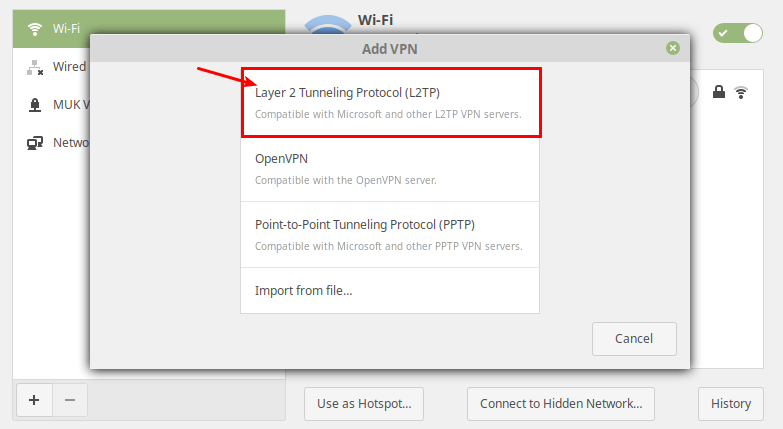
Then select Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) option from the pop-up window.
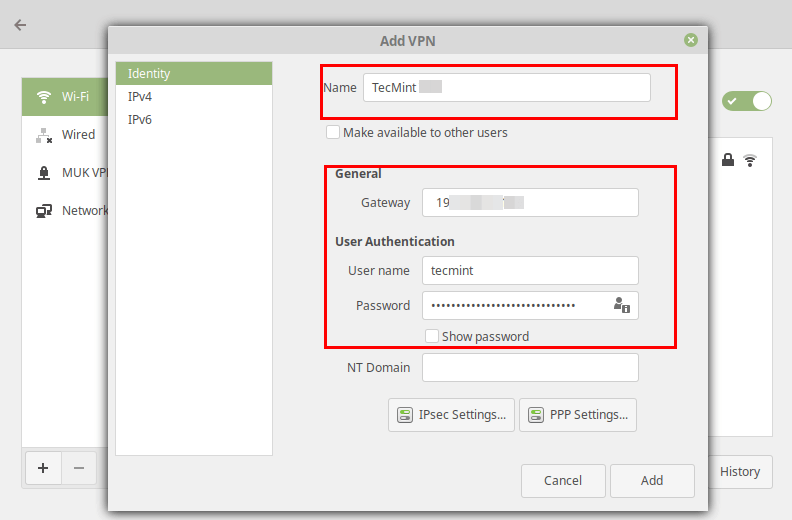
Next, enter the VPN connection details (gateway IP address or hostname, username and password) you received from the system administrator, in the following window.
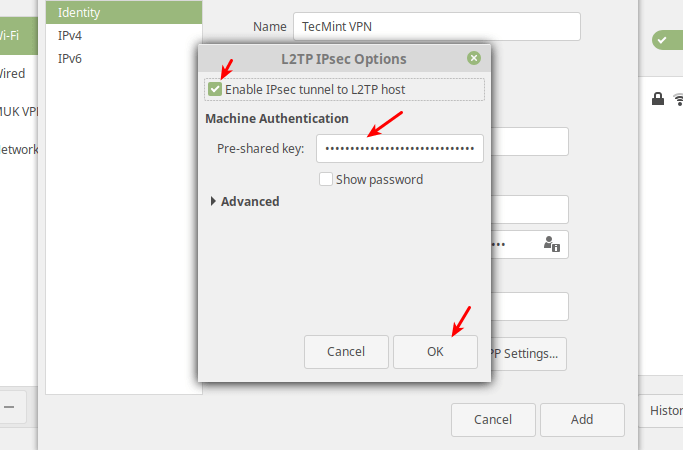
Next, click IPsec Settings to enter the pre-shared key for the connection. Then enable IPsec tunnel to L2TP host, enter (or copy and paste the) the Pre-shared key and click Ok.
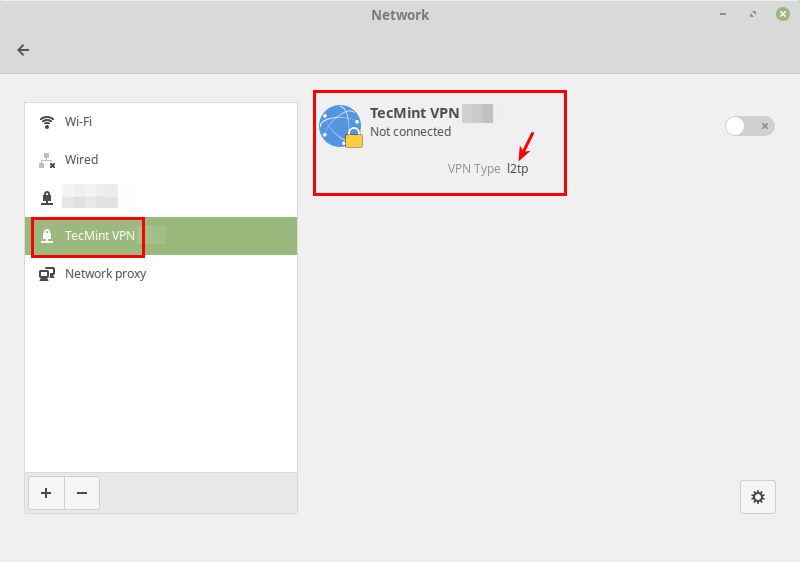
After that, click Add. Now your new VPN connection should be added.
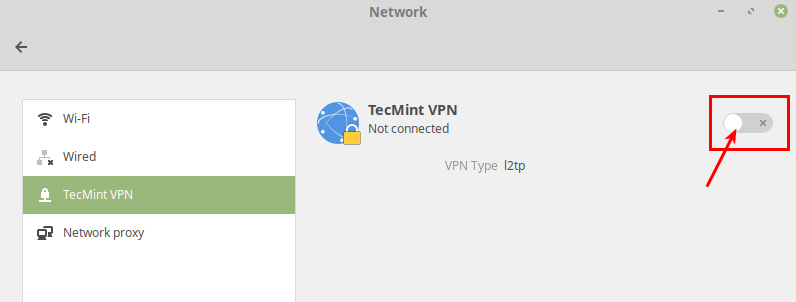
Next, turn on the VPN connection to start using it. If the connection details are correct, the connection should be established successfully.
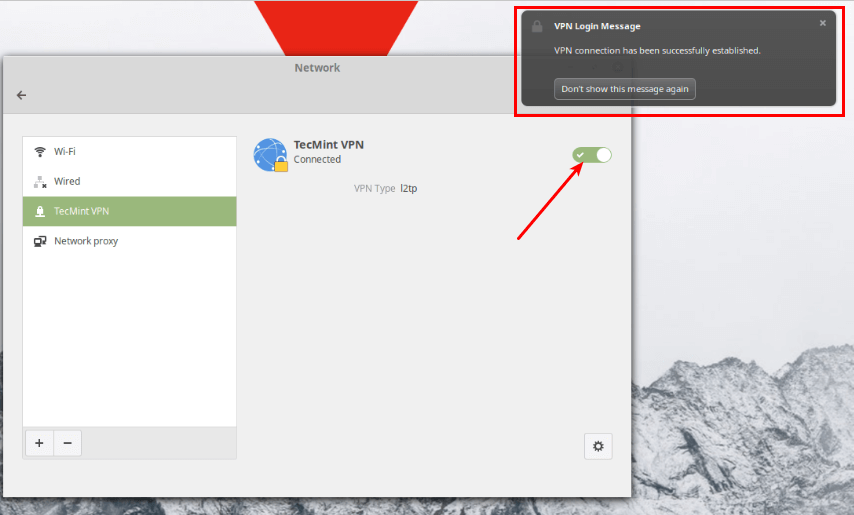
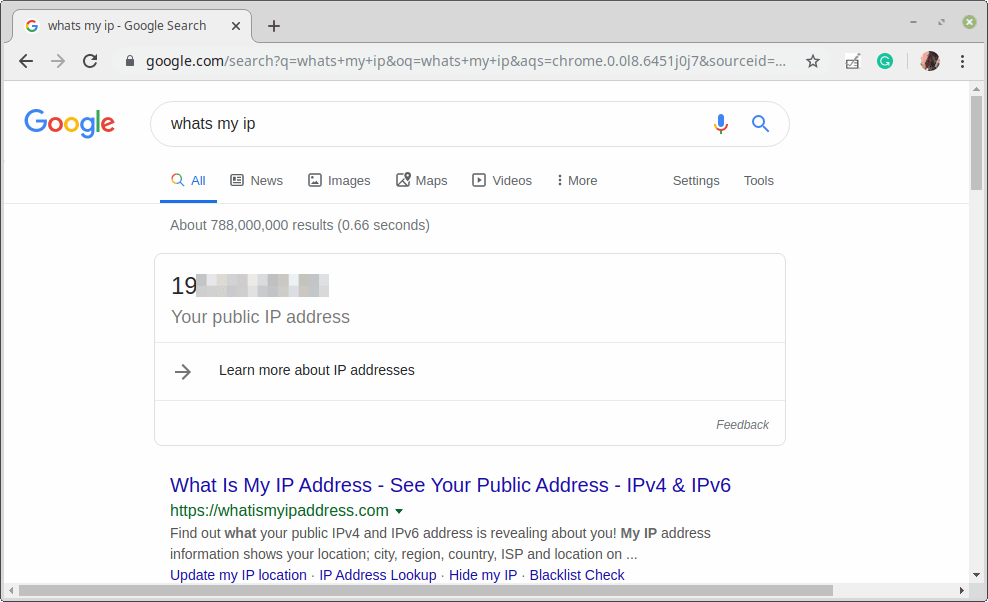
Last but not least, test if the VPN is working fine. You can check your computer’s public IP address to confirm this from a web browser: it should now point to the IP of the gateway.
That’s the end of this article. If you have any queries or thoughts to share, reach us via the feedback form below.
Управление VPN подключениями из консоли Linux
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как создать VPN подключение из консоли Linux и подключиться к удаленному VPN серверу из CLI. Отдельно рассмотрим, как создать L2TP и PPTP VPN подключения.
Как создать L2TP VPN подключение в Linux?
Вы можете использовать NetworkManager для создания VPN подключений L2TP из консоли Linux.
Для установки NetworkManager с поддержкой L2TP выполните команду:
- В CentOS/RHEL/Fedora: # yum -y install NetworkManager-l2tp
- Для установки в Ubuntu/Debian, нужно сначала добавить репозиторий:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nm-l2tp/network-manager-l2tp
$ sudo apt-get install network-manager-l2tp
Для создания нового VPN подключения L2TP используется команда:
$ nmcli connection add connection.id [VPNConnectionName] con-name [VPNConnectionName] type VPN vpn-type l2tp ifname — connection.autoconnect no ipv4.method auto vpn.data «gateway = [ipv4], ipsec-enabled = yes, ipsec-psk = 0s»$(base64
- [VPNConnectionName] — имя VPN соединения
- [ipv4] — ip адрес VPN сервера L2TP/IPSEC
- [PSK] — ключ PSK (Pre Shared Key)
- [user] — имя пользователя VPN
- [user-password] — пароль
Настройки нового VPN подключения сохраняются в файл /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/.
Вывести все подключения в NetworkManager:
Показать информацию о созданном VPN подключении:
$ nmcli c show id [VPNConnectionName]
Для Для подключения к VPN серверу из командной строки:к VPN серверу их командной строки:
$ nmcli c up [VPNConnectionName]
При подключении к удаленному VPN серверу может появится ошибка:
Error: Connection activation failed: Could not find source connection.
- Проверьте логи journactl
- Для физического интерфейса (например, ens33 ) задан шлюз по-умолчанию
- Возможно на сервере используется интерфейс br0 , который не используется. Попробуйте удалить его
Чтобы завершить сессию VPN, выполните:
nmcli c down [VPNConnectionName]
Создаем PPTP VPN подключение в Linux
Для установки PPTP клиента VPN в Ubuntu/Debian, установите утилиту:
$ sudo apt-get install pptp-linux network-manager-pptp
Добавьте следующее содержимое:
pty "pptp YOUR_VPN_SERVER --nolaunchpppd --debug" name VPNUsername password VPNPassword remotename PPTP require-mppe-128 require-mschap-v2 refuse-eap refuse-pap refuse-chap refuse-mschap noauth debug persist maxfail 0 defaultroute replacedefaultroute usepeerdns
Сохраните файл, нажав CTLR+X, Y -> Enter.
$ chmod 600 /etc/ppp/peers/PPTP
Чтобы подключится к PPTP VPN серверу, выполните:
Настройка SSTP VPN подключения в командной строке Linux
Вы можете настроить SSTP подключение к VPN серверу в Linux. В Ubuntu можно использовать пакет sstp для nmcli.
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:eivnaes/network-manager-sstp
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install network-manager-sstp sstp-client
Для подключения к SSTP серверу используется команда:
$ sudo sstpc —cert-warn —save-server-route —user —password usepeerdns require-mschap-v2 noauth noipdefault nobsdcomp nodeflate
Можно сохранить настройки подключения к VPN серверу в текстовый файл:
remotename sstptest linkname sstptest ipparam sstptest pty "sstpc --ipparam sstptest --nolaunchpppd sstpvpn.vmblog.ru" name user1 plugin sstp-pppd-plugin.so sstp-sock /var/run/sstpc/sstpc-sstp-test usepeerdns require-mppe require-mschap-v2 refuse-eap refuse-pap refuse-chap refuse-mschap nobsdcomp nodeflate
Имя пользователя и пароль для аутентификации на VPN сервере нужно задать в файле /etc/ppp/chap-secrets
# Secrets for authentication using CHAP # client server secret IP addresses user1 * xxxxxx *
Теперь для подключения к SSTP серверу с помощью настроенного подключения, выполните:
Чтобы отправить весь трафик через VPN подключение, нужно добавить маршрут:
$ sudo route add default (обычно это устройствл ppp0 )
Или только трафик к определенным подсетям/хостам:
$ sudo route add -net 192.168.2.0/24 dev ppp0
Подключение к OpenVPN серверу из консоли Linux
Для установки пакета OpenVPN в Linux:
- Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Kali Linux:
$ sudo apt-get update && apt-get upgrade
$ sudo apt-get install openvpn - RedHat, Fedora, CentOS, Oracle, Rocky Linux:
# yum install epel-release –y
# yum install openvpn –y
Для подключения к OpenVPN серверу вам понадобится файл конфигурации ovpn. Чтобы подключиться к VPN с помощью ovpn файла:
$ sudo openvpn —config /etc/openvpn/client.ovpn —daemon
Введите имя пользователя и пароль (если настроена AD аутентификация для OpenVPN).
Проверьте что VPN подключение установлено:
Чтобы завершить OpenVPN подключение, нажмите CTRL+C (если клиент запущен без параметра –daemon) или выполните команду:
Чтобы OpenVPN подключение автоматически устанавливалось при старте Linux, нужно создать отдельный юнит systemd:
$ sudo vi /lib/systemd/system/OpenVPNClientCorp.service
[Unit] Description=Hide.me OpenVPN Client Corp After=multi-user.target [Service] Type=idle ExecStart=/usr/sbin/openvpn --config /etc/openvpn/client.ovpn [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Измените разрешения на файл:
$ sudo chmod 644 /lib/systemd/system/OpenVPNClientCorp.service
Добавьте юнит через systemctl
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl enable OpenVPNClientCorp.service
Create a VPN connection from Linux Terminal
In this article, we’ll look at how to create a VPN connection from the Linux terminal console and connect to a remote VPN server from the command line. Consider how to create L2TP, PPTP, OpenVPN, and SSTP VPN connections on Linux.
Creating an L2TP VPN Connection in Linux
You can use NetworkManager to create L2TP VPN connections from the Linux console.
To install NetworkManager with L2TP support, run the command:
# yum -y install NetworkManager-l2tp$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nm-l2tp/network-manager-l2tp $ sudo apt-get install network-manager-l2tpTo create a new L2TP VPN connection, use the command:
$ nmcli connection add connection.id [VPNConnectionName] con-name [VPNConnectionName] type VPN vpn-type l2tp ifname -- connection.autoconnect no ipv4.method auto vpn.data "gateway = [ipv4], ipsec-enabled = yes, ipsec-psk = 0s"$(base64 - [VPNConnectionName]
- [ipv4] — IP address or FQDN of L2TP/IPSEC VPN server
- [PSK] —Pre-Shared Key (PSK)
- [user] — VPN username
- [user-password] — user password
The settings for a new VPN connection are saved to the /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/ file.
List all connections in NetworkManager:
Show information about the created VPN connection:
$ nmcli c show id [VPNConnectionName]
To connect to the L2TP VPN server from the command line:
$ nmcli c up [VPNConnectionName]
Error: Connection activation failed: Could not find source connection.
In this case, check the following:
- journactl logs;
- the default gateway is set for the physical interface (for example, ens33 );
- the br0 interface may be enabled on the server, but is not used. Try to remove it.
To disconnect from a VPN server, run:
$ nmcli c down [VPNConnectionName]
Adding PPTP VPN Connection in Linux
To install a PPTP VPN client on Ubuntu/Debian:
$ sudo apt install pptp-linux
$ sudo nano /etc/ppp/peers/PPTP
Add the following content:
pty "pptp YOUR_VPN_SERVER --nolaunchpppd --debug" name VPNUsername password VPNPassword remotename PPTP require-mppe-128 require-mschap-v2 refuse-eap refuse-pap refuse-chap refuse-mschap noauth debug persist maxfail 0 defaultroute replacedefaultroute usepeerdns
Save the file by pressing CTLR+X, Y -> Enter.
Change file permissions:
$ chmod 600 /etc/ppp/peers/PPTP
To connect to a PPTP VPN server, run the command:
How to Set Up SSTP VPN Connection with Command Line on Linux?
You can set up an SSTP connection to a VPN server on Linux. On Ubuntu, you can use the sstp package for nmcli.
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:eivnaes/network-manager-sstp $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install network-manager-sstp sstp-client
The following command is used to connect to the SSTP VPN server:
$ sudo sstpc --cert-warn --save-server-route --user --password usepeerdns require-mschap-v2 noauth noipdefault nobsdcomp nodeflate
You can save VPN server connection settings to a text file:
$ sudo nano /etc/ppp/peers/sstptest
remotename sstptest linkname sstptest ipparam sstptest pty "sstpc --ipparam sstptest --nolaunchpppd sstpvpn.contoso.com" name user1 plugin sstp-pppd-plugin.so sstp-sock /var/run/sstpc/sstpc-sstp-test usepeerdns require-mppe require-mschap-v2 refuse-eap refuse-pap refuse-chap refuse-mschap nobsdcomp nodeflate
Add the username and password for authentication on the VPN server to /etc/ppp/chap-secrets file:
# Secrets for authentication using CHAP # client server secret IP addresses user1 * xxxxxx *
Now you can connect to the SSTP VPN server using the configured connection:
To send all traffic through the VPN connection, you need to add a route:
(usually, this is ppp0 device)
Or only traffic to specific networks/hosts:
$ sudo route add -net 192.168.2.0/24 dev ppp0
Configure OpenVPN Connection Using Linux Terminal
Install the OpenVPN package on Linux:
Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Kali Linux:
$ sudo apt-get update && apt-get upgrade $ sudo apt-get install openvpn
# yum install epel-release –y. # yum install openvpn –y
You will need the *.ovpn configuration file to connect to an OpenVPN server. In order to connect to VPN using the client.ovpn file:
$ sudo openvpn --config /etc/openvpn/client.ovpn --daemon
Check that the VPN connection is established:
To end the OpenVPN connection, press CTRL+C (if the client is running without the --daemon parameter) or run the command:
In order for an OpenVPN connection to be automatically established when Linux starts, you need to create a separate systemd unit:
$ sudo vi /lib/systemd/system/OpenVPNClientCorp.service
[Unit]
Description=Hide.me OpenVPN Client Corp
After=multi-user.target
[Service]
Type=idle
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/openvpn --config /etc/openvpn/client.ovpn
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Change the file permissions:
$ sudo chmod 644 /lib/systemd/system/OpenVPNClientCorp.service
Add the new unit via systemctl:
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload $ sudo systemctl enable OpenVPNClientCorp.service
I can’t fix the error Error: Connection activation failed: Could not find source connection. can you help me?