- 2 ways to list hidden files in Linux
- what are hidden files in Linux
- Why would I want to list hidden files in Linux?
- List hidden files with ls command in Linux
- Procedure to list hidden files in Linux
- List hidden files with find command in Linux
- Hide Folders and Show Hidden Files in Ubuntu Linux
- Show hidden files in Linux terminal
- Display hidden files in the file manager (for desktop users)
- Hide files and folders in Ubuntu
- Bonus Tip: Hiding multiple files and folders without renaming them (valid for GUI only)
- Hide it or lock it?
- How to recursively list all hidden files and directories?
- 4 Answers 4
2 ways to list hidden files in Linux
In Linux, there are two types of files: regular files and hidden files. Hidden files are those that start with a dot (“.”). By default, Linux does not show hidden files when you list the contents of a directory. In this blog post, we will discuss three ways to list hidden files in Linux.
what are hidden files in Linux
Hidden files are files that are not normally displayed. They are hidden from view for a variety of reasons, such as to protect the privacy of the user or to keep the contents of the file from being accidentally modified. The name of the hidden files usually starts with a period(.).
An example of a hidden file in Linux is the .bash_history file. This is a file that contains a list of all the commands that have been entered in the Bash shell. It’s hidden because it’s a system file and you don’t need to see it unless you’re troubleshooting a problem.
Why would I want to list hidden files in Linux?
There are a few reasons why you might want to list hidden files in Linux. For example, you may want to view or edit a configuration file that is normally hidden. Or, you may be trying to troubleshoot an issue on your system and need to view log files that are hidden.
Another reason you might want to list hidden files in Linux is to protect the privacy of the user. Some hidden files may contain sensitive information that the user doesn’t want others to see.
For example, the .bash_history file mentioned earlier contains a list of all the commands that have been entered in the Bash shell. If someone else got access to this file, they would be able to see all of your command history.
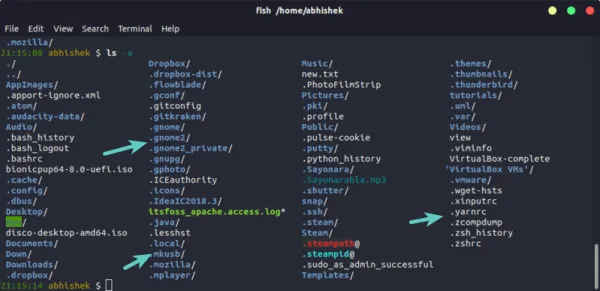
List hidden files with ls command in Linux
The easiest way to list hidden files in Linux is to use the ls command with the -a option. This will show all files, including hidden ones.
The output of this command will show all files in the current directory, including hidden ones.
If you want to list the contents of a specific directory, you can specify the path to that directory. For example, to list the contents of the /etc/ directory, you would use the following command:
The output of this command will show all files in the /etc/ directory, including hidden ones.
If you want to see more information about the files, such as file size and when they were last modified, you can use the -l option. For example:
This command will show a long listing of all files in the /etc/ directory, including hidden ones.
Procedure to list hidden files in Linux
- Open the terminal.
- Type ls -a and press Enter. This will show you all of the files in the current directory, including hidden files.
- To view hidden files in a different directory, type ls -a /path/to/directory and press Enter.
- To view only hidden files, type ls -ld .* and press Enter.
List hidden files with find command in Linux
Another way to list hidden files in Linux is to use the find command with -name and -type option. The find command can be used to search for files in a directory hierarchy. To list hidden files, use the -name option with a dot (“.*”) as the argument.
- The -type option tells find which type of files you want to find. The most common type of file is a regular file, which is denoted by f . But there are other types of files, such as directories ( d ), symbolic links ( l ), and so on.
- The -name option tells find to search through the directories for files that have the specific word in their name. In this case, we are using a dot (“.*”) as the pattern, which will match all files that start with a dot.
The output of this command will show all hidden files in the current directory and its subdirectories.
If you want to list the contents of a specific directory, you can specify the path to that directory. For example, to show all hidden files in the /etc/ directory and its subdirectories, you would use the following command:
These are two effective ways to list hidden files in Linux. Try them out and see which one works best for you. Thanks for reading!
David is a Cloud & DevOps Enthusiast. He has years of experience as a Linux engineer. He had working experience in AMD, EMC. He likes Linux, Python, bash, and more. He is a technical blogger and a Software Engineer. He enjoys sharing his learning and contributing to open-source.
howtouselinux.com is dedicated to providing comprehensive information on using Linux.
We hope you find our site helpful and informative.
Hide Folders and Show Hidden Files in Ubuntu Linux
Wondering how to see or hide files in Ubuntu Linux? Its damn easy to do so. Here’s how to show hidden files in Ubuntu and other Linux distributions.
You are probably familiar with the concept of “hiding” a folder or file in Windows. Hiding a folder or file just “removes” the folder from the normal view, and then you can choose to display “hidden files” to see it. So how do you see the hidden files in Linux, then? Let me show you that.
Show hidden files in Linux terminal
If you are in a terminal, you can use the ls command to display all the files, including the hidden ones:
You can recognize the hidden files and folders with the dot (.) before their names.
You can also use the -A option of the ls command to show hidden files but without the . and .. files.
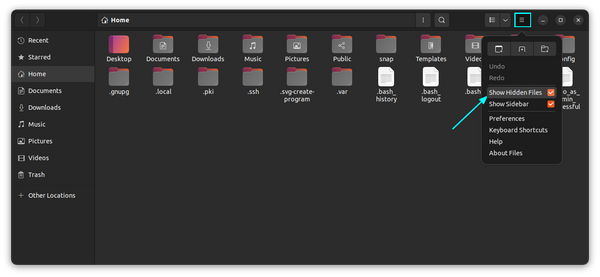
Display hidden files in the file manager (for desktop users)
If you are in the file manager, you can use the Ctrl+H keyboard shortcut in Ubuntu and I presume other distributions also display all the files, including the hidden ones. Pressing Ctrl+H again will hide the files. If you are not a fan of keyboard shortcuts, you can use the file manager GUI to display the hidden folders and files. To see a hidden file or hidden folder in Ubuntu, go to the file manager (Ubuntu’s counterpart of Windows Explorer and the default is Nautilus). Now go to the top-right hamburger menu → Show hidden files:
Hide files and folders in Ubuntu
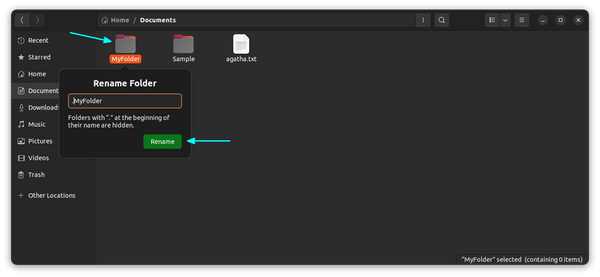
Now that you have learned to see hidden files in Ubuntu, let’s now see how you can hide files and folders in Linux. In Linux, if a file name starts with . (dot), it is considered a hidden file. Now if you want to hide a file or folder, let’s say MyFolder, just rename it to .MyFolder and it will be taken as a hidden file or folder. I hope you know how to rename files in Linux command line using mv command.
If you are using a Linux desktop, right-click and choose the rename option and add the dot before the name. Unfortunately/interestingly, there is no similar way as in Windows to hide a folder. In Windows, you right-click on a file and choose the option of making it hidden. But this option is not available in Ubuntu.
Bonus Tip: Hiding multiple files and folders without renaming them (valid for GUI only)
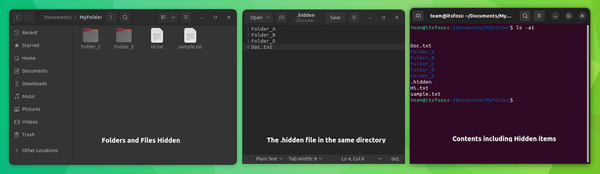
This is a neat little trick that will let you hide several files and folders from the normal view in your desktop Linux’s file manager. Traditionally, if you create a new file named .hidden and add the name of the folders in this file; those folders will be hidden from normal view when you close your file manager and open it again. Keep in mind that this trick works with only the current directory you are in. It won’t work for nested directories. You can create the .hidden file in any directory to hide files and folders in it.
Hide it or lock it?
This .hidden file is one of the many lesser-known tweaks of the Nautilus file manager. Here are a few more. This was about hiding files in Linux. There are separate methods for locking a folder in Linux. I hope you like this little bit of Linux knowledge.
How to recursively list all hidden files and directories?
I want to list all hidden files and directories and then save result to file. Is there any command for this?
4 Answers 4
If using GNU find, you can do
find /path -path '*/.*' -ls | tee output-file To avoid to show non-hidden items contained in hidden directories
find /path -name '.*' >output-file (as noted, tee could be avoided if you do not need to see the output, and -ls option should be used only if required).
This also lists the contents of hidden directories, which isn’t what the question asks for (probably — it is a little ambiguous).
Note that the first one is not GNU-specific. -path is POSIX since 2008. -ls is not standard but quite common.
To list the hidden files and directories in the current directory, including . and .. :
To list the hidden files and directories in the current directory and its subdirectories recursively:
If you want to save the results to a file, use a redirection:
find . -name '.*' >output-file.txt To include non-hidden files in hidden directories:
setopt extendedglob print -rl ./**/*~^*/.*(D) You can actually put the same argument multiple times in the same command line:
find /storage/. -. / -iname ‘.*’ -iname «*» | tee -a file-list-micSD-20190801163729.fli
The tee -a command is able to display the command’s output (or stdout) simultaneously whie writing it to a file. The -a options prevents clobbering and does append the information to the target output file instead.
/storage/. -. / is an example path. It is the path to the MicroSD card of newer Android Mobile phones (there is also a terminal application for Android, with fewer commands but still many and significantly increased since Android 6.0). The MicroSD card was formerly /storage/extSdCard . Now, it is the volume serial number.