- List all internet connections
- 2 Answers 2
- Using netstat
- Similar to top :
- GUI Interface (just in case):
- Netstat Command Examples in Linux
- 1. Find all the listening ports
- 2. List listening and non-listening ports
- 3. Find TCP listening ports
- 4. Find UDP listening ports
- 5. List all TCP port connections
- 6. List all UDP connections
- 7. Get a statistical summary of each protocol
- 8. Get statistics for a specific connection
- 9. Get raw network statistics
- 10. Find services with PID
- 11. Find a specific listening service on the network
- 12. Show transactions of network interfaces
- 13. Monitor the network continuously using the netstat command
- More on Networking in Linux
- 12 ss Command Examples to Monitor Network Connections
- 1. Listing all Connections
- 2. Listing Listening and Non-listening Ports
- 3. Listing Listening Sockets
- 4. List all TCP Connections
- 5. List all Listening TCP Connections
- 6. List all UDP Connections
- 7. List all Listening UDP Connections
- 8. Display PID (Process IDs) of Sockets
- 9. Display Summary Statistics
- 10. Display IPv4 and IPv6 Socket Connections
- 11. Filter Connections by Port Number
- 12. Check Man Pages for ss Command
List all internet connections
I’d like to know all the connections my system is making to the internet. I tried netstat but that shows a lot of connections — all of which aren’t applicable I think. Can it be displayed like top does for processes ? I’m a little security conscious and would like to know all the incoming and outgoing connections happening on my system.
2 Answers 2
Using netstat
netstat by itself monitors all major protocols including TCP and UDP on every port.
If you want to display TCP and UDP connections:
If you want to display that continously:
Similar to top :
- nethogs — shows a list of the top processes that use bandwidth
- jnettop — shows list of top connections
- iftop — shows list of top connections with bandwidth bars
GUI Interface (just in case):
You may try ss as well, it’s more advanced than netstat .
List all TCP connections (including those with non-established state, e.g. SYN-SENT , LISTEN , and TIME-WAIT ). Read more about TCP states transition in RFC793.
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 4096 127.0.0.1:5672 0.0.0.0:* ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.4:57310 35.157.63.229:443 ESTAB 0 0 127.0.0.1:43764 127.0.0.1:8080 CLOSE-WAIT 1 0 192.168.1.4:34554 142.250.186.33:443 CLOSE-WAIT 1 0 192.168.1.4:34564 142.250.186.33:443 Include information about the owner process of the connections (e.g., process name and PID)
Display all established SSH connections.
List all the TCP sockets in state FIN-WAIT-1 for network 193.233.7/24 and look at their timers with —options , which shows timer information.
Netstat Command Examples in Linux
Netstat is one of the most common networking commands in Linux. Learn some useful examples of netstat in this tutorial.
The netstat is one of the most popular utilities to monitor connections over your network.
It allows you to easily monitor incoming and outgoing connections, listening ports, statistics, and more.
In this tutorial, I will show you some of the most examples of the netstat command on Linux.
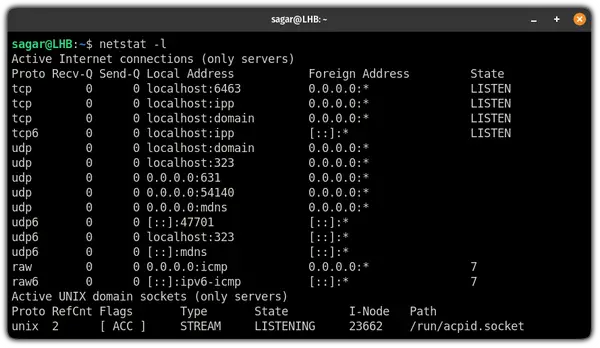
1. Find all the listening ports
To find all the ports (TCP and UDP), you will have to append the -l flag with the netstat command:
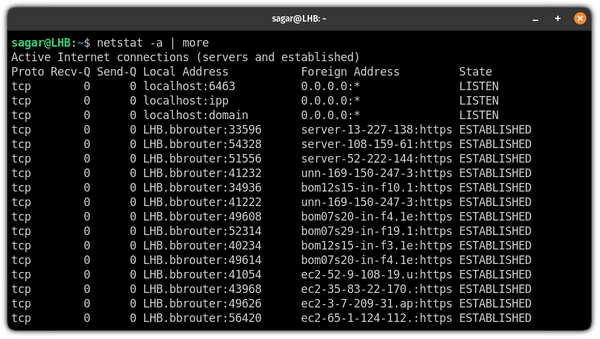
2. List listening and non-listening ports
If you want to get a list of available sockets on your system, you can use the -a flag with the netstat command:
Now, let’s get to more specific ones.
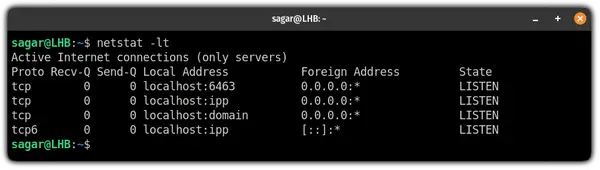
3. Find TCP listening ports
If you want to list ports using TCP protocol and in the listening state, you will have to use -l flag for listening and -t flag for TCP connections:
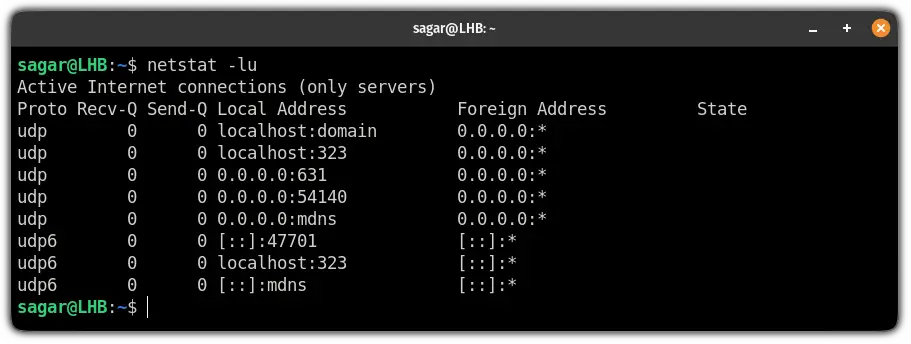
4. Find UDP listening ports
To list every listening UDP port on your system, you will have to append -l and -u flag with the netstat command:
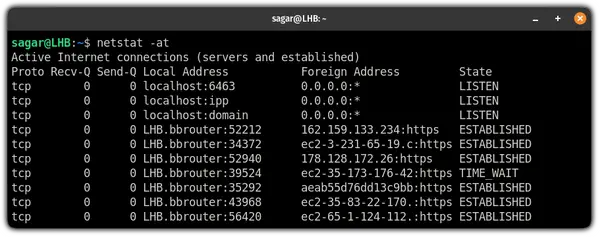
5. List all TCP port connections
If you want to list every socket using a TCP connection including listening and non-listening, use the -at flag with the netstat command:
Want to know the difference between listening and an established state?
- LISTENING means it is listening for incoming connections.
- ESTABLISHED indicates that the socket has an established connection.
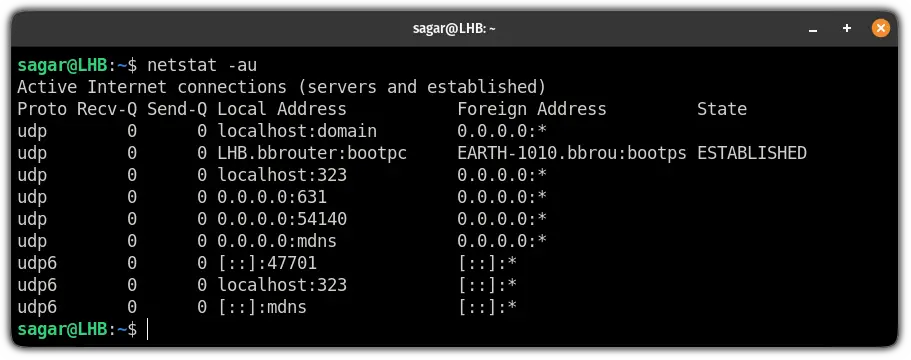
6. List all UDP connections
If you want to list every socket utilizing the UDP, you can use the combination of -a and -u flag:
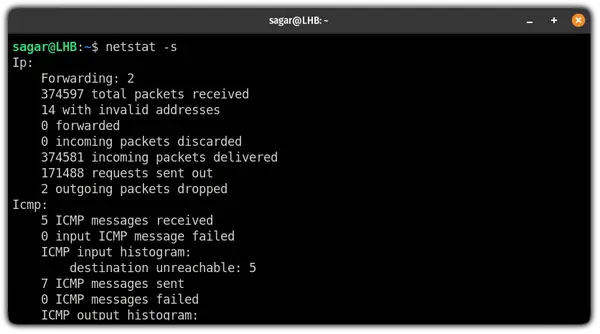
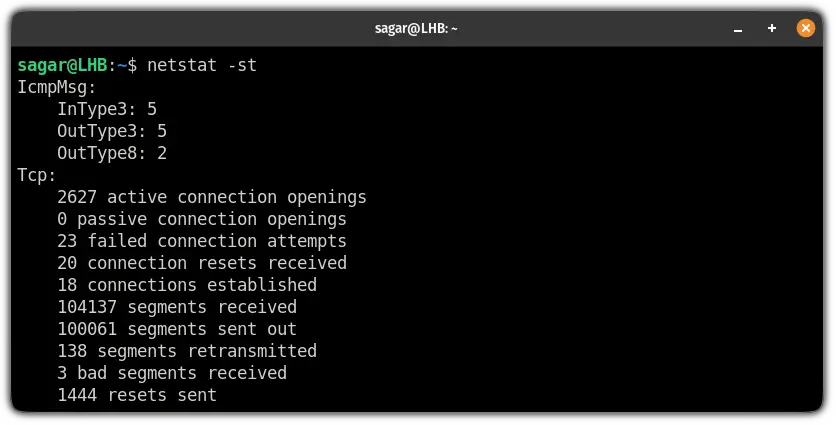
7. Get a statistical summary of each protocol
This is one of the handiest features of netstat which allows you to find the number of connections established, the number of messages sent and received, and a lot more.
To get a summary of each protocol, all you need to do is append the -s flag:
But what if you want statistics on specific protocols? Here’s how you do it.
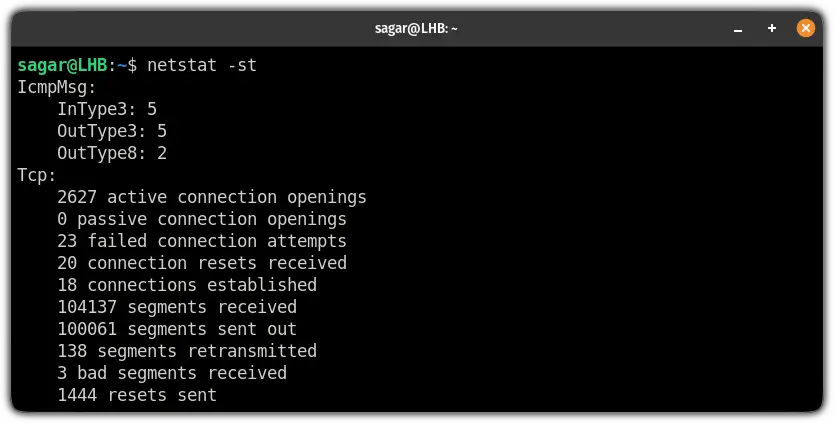
8. Get statistics for a specific connection
To get the statistics of TCP connections, all you need to do is use the -s and -t flag with the netstat command:
Similarly, if you want the same for UDP, you will have to use the -su flag:
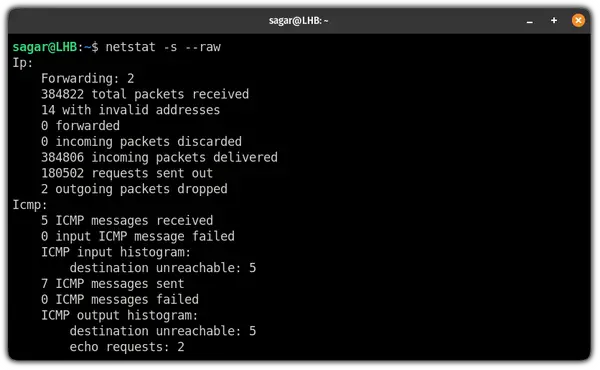
9. Get raw network statistics
If you are looking for raw data rather than filtered one, it can easily be produced using the -s (for statistics) and —raw (for raw):
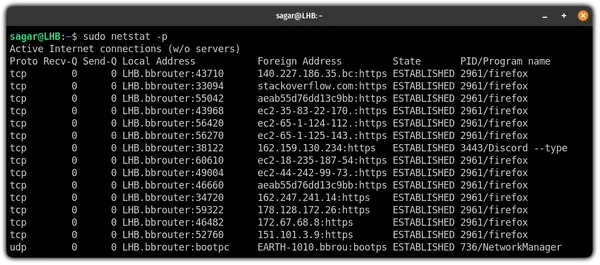
10. Find services with PID
If you are into troubleshooting, getting the PID of the service can be very handy. To get PID, all you need to do is use the -p flag:
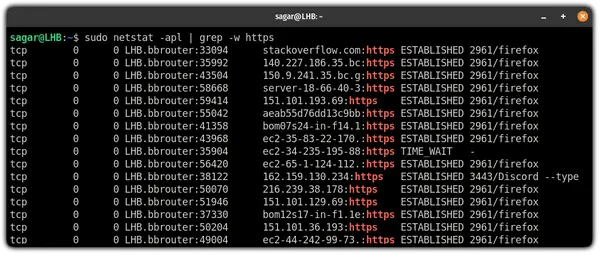
11. Find a specific listening service on the network
To find a specific listening, you can use the grep command which makes a killer combination while troubleshooting.
So let’s suppose, I want to look for an HTTPS service on listening state which can be done through the following command:
sudo netstat -apl | grep -w httpsWant to know how to get more out of grep? you can refer to our detailed guide on that topic:
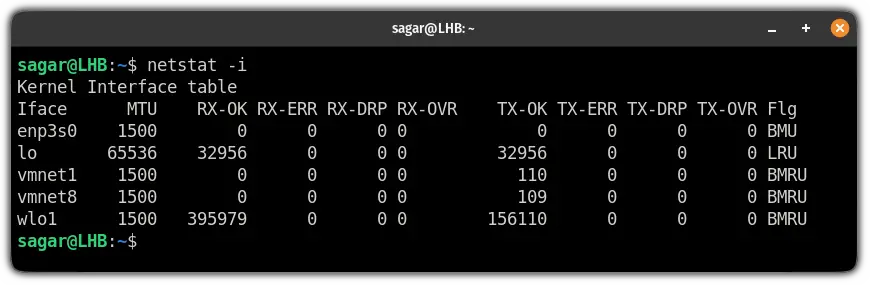
12. Show transactions of network interfaces
The netstat utility can also be used to list available network interfaces and to get transactions of each one.
For that, all you need to do is append the -i flag to the netstat:
13. Monitor the network continuously using the netstat command
If you want to monitor the network continuously, you can do it with -c the option:
You can use appropriate flags such as -lt with -c and it will look for listening TCP connections continuously:
More on Networking in Linux
If you have just started your carries or studies on networking, we have a detailed guide on most basic networking commands:
Want to know more about ports? We got you covered on that too:
That was it from my side. And if you have any doubts or have tips for beginners, you can share your precious knowledge through the comments.
12 ss Command Examples to Monitor Network Connections
ss command is a tool that is used for displaying network socket related information on a Linux system. The tool displays more detailed information that the netstat command which is used for displaying active socket connections.
In this guide, we delve in and see how the ss command can be used to display varied socket connection information in Linux.
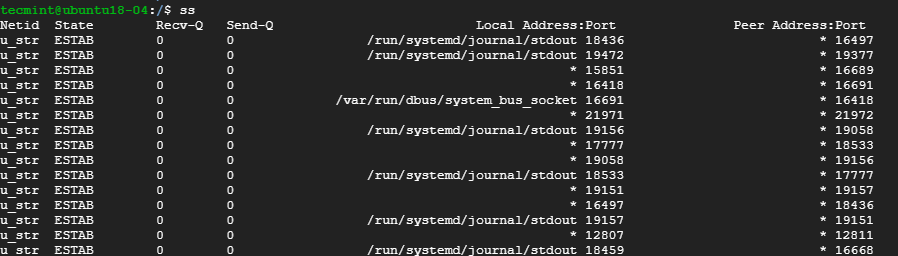
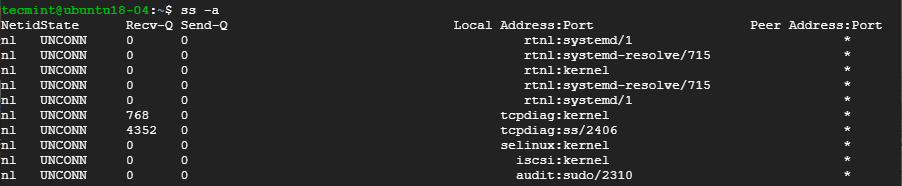
1. Listing all Connections
The basic ss command without any options simply lists all the connections regardless of the state they are in.
2. Listing Listening and Non-listening Ports
You can retrieve a list of both listening and non-listening ports using the -a option as shown below.
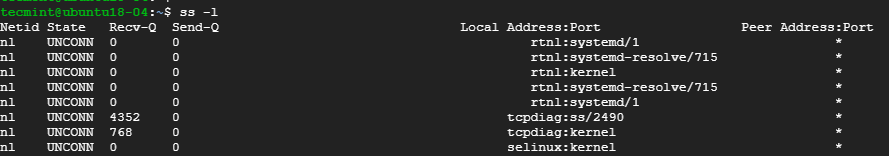
3. Listing Listening Sockets
To display listening sockets only, use the -l flag as shown.
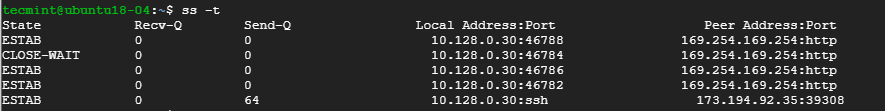
4. List all TCP Connections
To display all TCP connection, use the -t option as shown.
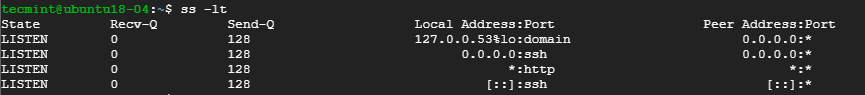
5. List all Listening TCP Connections
To have a view of all the listening TCP socket connection use the -lt combination as shown.
6. List all UDP Connections
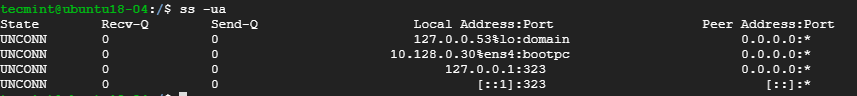
To view all the UDP socket connections use the -ua option as shown.
7. List all Listening UDP Connections
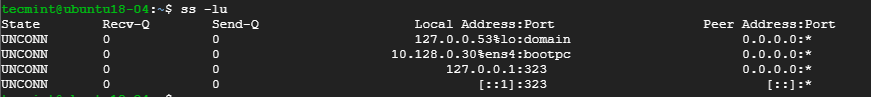
To list listening UDP connections use the -lu option.
8. Display PID (Process IDs) of Sockets
To display the Process IDs related to socket connections, use the -p flag as shown.
9. Display Summary Statistics
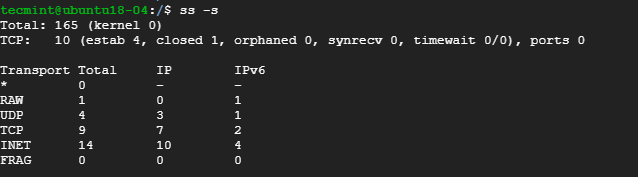
To list the summary statistics, use the -s option.
10. Display IPv4 and IPv6 Socket Connections
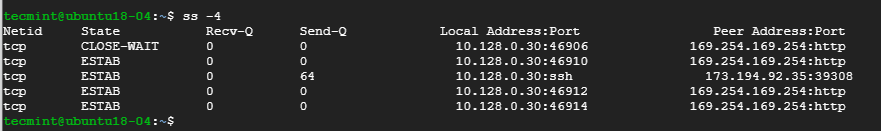
If you are curious about the IPv4 socket connections use the -4 option.
To display IPv6 connections, use the -6 option.
11. Filter Connections by Port Number
ss command also lets you filter socket port number or address number. For example, to display all socket connections with a destination or source port of ssh run the command.
$ ss -at '( dport = :22 or sport = :22 )'
Alternatively, you can run the command.
$ ss -at '( dport = :ssh or sport = :ssh )'
12. Check Man Pages for ss Command
To get more insights into the ss command usage, check the man pages using the command.
Those are some of the commonly used options that are used with ss command. The command is considered more superior to netstat command and provide detailed information about network connections.