- Find the files that have been changed in last 24 hours
- 7 Answers 7
- Find Files That Have Been Modified Recently in Linux
- 1. Introduction
- 2. The find Command
- 2.1. -mtime and -mmin
- 2.2. -newermt
- 3. The ls Command
- 4. Conclusion
- How to Find Last Modified Files in Linux?
- Finding last day modified files in Linux:
- Find Last Modified Specific File Type in Linux:
- Finding Last Hour Modified Files in Linux:
- Finding Files Modified on a Specific Date in Linux:
- Find Last Modified Files Recursively:
- Search File by Date Omitting Files or Directories:
- Find Files by Access Date:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- David Adams
Find the files that have been changed in last 24 hours
E.g., a MySQL server is running on my Ubuntu machine. Some data has been changed during the last 24 hours. What (Linux) scripts can find the files that have been changed during the last 24 hours? Please list the file names, file sizes, and modified time.
7 Answers 7
To find all files modified in the last 24 hours (last full day) in a particular specific directory and its sub-directories:
find /directory_path -mtime -1 -ls The — before 1 is important — it means anything changed one day or less ago. A + before 1 would instead mean anything changed at least one day ago, while having nothing before the 1 would have meant it was changed exacted one day ago, no more, no less.
The argument to -mtime is interpreted as the number of whole days in the age of the file. -mtime +n means strictly greater than, -mtime -n means strictly less than.
Another, more humanist way, is to use -newermt option which understands human-readable time units (see man find and search for -newerXY ).
Unlike -mtime option which requires the user to read find documentation to figure our what time units -mtime expects and then having the user to convert its time units into those, which is error-prone and plain user-unfriendly. -mtime was barely acceptable in 1980s, but in the 21st century -mtime has the convenience and safety of stone age tools.
Example uses of -newermt option with the same duration expressed in different human-friendly units:
find / -newermt "-24 hours" -ls find / -newermt "1 day ago" -ls find / -newermt "yesterday" -ls Find Files That Have Been Modified Recently in Linux
The Kubernetes ecosystem is huge and quite complex, so it’s easy to forget about costs when trying out all of the exciting tools.
To avoid overspending on your Kubernetes cluster, definitely have a look at the free K8s cost monitoring tool from the automation platform CAST AI. You can view your costs in real time, allocate them, calculate burn rates for projects, spot anomalies or spikes, and get insightful reports you can share with your team.
Connect your cluster and start monitoring your K8s costs right away:
1. Introduction
There are various occasions when we want to search for files that have been changed recently.
For example, as a system admin, we’re responsible to maintain and configure computer systems. Sometimes, because we’re dealing with a lot of configuration files, we probably want to know what are the files recently modified.
In this tutorial, we’re going to find the files that have been changed recently in Linux using bash commands.
2. The find Command
First, we’ll explore the find utility which is the most common way to achieve the intended purpose. This command is used to find files and directories recursively and to execute further operations on them.
2.1. -mtime and -mmin
-mtime is handy, for example, if we want to find all the files from the current directory that have changed in the last 24 hours:
Note that the . is used to refer to the current directory. -mtime n is an expression that finds the files and directories that have been modified exactly n days ago.
In addition, the expression can be used in two other ways:
- -mtime +n = finds the files and directories modified more than n days ago
- -mtime -n = finds the files and directories modified less than n days ago
In the same way, we can use the -mmin n expression to rely on minutes instead of days:
So, this command recursively finds all the files and directories from the /home/sports directory modified at least 120 minutes ago.
Next, if we want to limit the searching only to files, excluding directories, we need to add the -type f expression:
find /home/sports -type f -mmin +120Furthermore, we can even compose expressions. So, let’s find the files that have been changed less than 120 minutes ago and more than 60 minutes ago:
find . -type f -mmin -120 -mmin +602.2. -newermt
There are times when we want to find the files that were modified based on a particular date. In order to fulfill this requirement, we have to explore another parameter, which has the following syntax:
By using this expression, we can get the files that have been changed earlier than the specified date.
So, let’s build a command to better understand the new parameter:
find . -type f -newermt 2019-07-24Moreover, we could get the files modified on a specific date by using a composed expression.
So, we’re going to get the files modified on ‘2019-07-24’:
find . -type f -newermt 2019-07-24 ! -newermt 2019-07-25Finally, there’s another version of the -newermt parameter similar to -mmin and -mtime.
The first command finds the files modified in the last 24 hours. The rest of them are similar:
find . -type f -newermt "-24 hours" find . -type f -newermt "-10 minutes" find . -type f -newermt "1 day ago" find . -type f -newermt "yesterday"3. The ls Command
We know that the ls command lists information about the files in a specific directory. One of its usages is to show the long format of the files and to sort the output by modification time:
Which would result in something like:
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4233 Jul 27 18:44 b.txt -rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 2946 Jul 27 18:12 linux-commands.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5233 Jul 20 17:02 a.txtWe may not be able to list the files recently modified exactly as the find command does. But, we can filter the above output based on a specific date or time by applying the grep command on the result of the ls command:
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4233 Jul 27 18:44 b.txt -rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 2946 Jul 27 18:12 linux-commands.txt-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5233 Jul 20 17:02 a.txtNote that the find command is recursive by default. In order to enable the recursive capability on the ls command, we also need to add the R(uppercase) parameter:
4. Conclusion
In this quick tutorial, we’ve described a few ways that help us find the files that have been changed recently on a Linux operating system.
First, we’ve explored the find command and created several examples with different parameters like -mtime, -mmin and -newermt.
Then, we’ve shown how we can achieve similar results using a combination of two better known Linux utilities like the ls and grep commands.
How to Find Last Modified Files in Linux?
This tutorial explains how to find last modified files in Linux using different commands and according to custom needs.
After reading this tutorial you’ll know how to execute the following tasks:
- How to find files modified in a specific day range
- How to find last modified specific file type (e.g mp4, png)
- Finding files modified before / after X minutes
- How to find files modified in a specific date
- Finding modified files recursively
- Search omitting files or directories
- Find files by access date
Finding last day modified files in Linux:
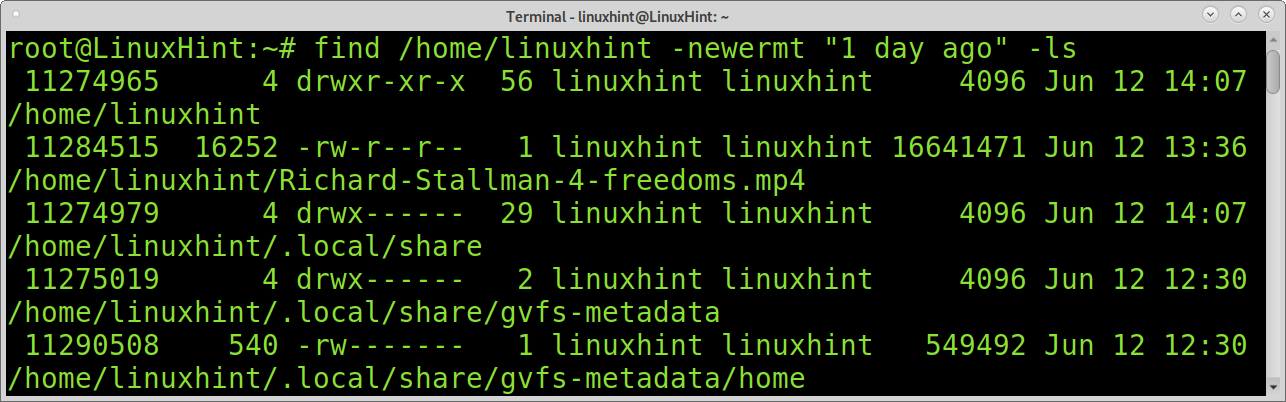
To start, let’s search files modified less than a day ago. To find files modified a day ago you can use the commands find and newermt used in the following example.
The find command is used to search files. The newermt command compares files timestamp with the argument passed, in this case “1 day ago”. Then, the ls command is passed to list the files.
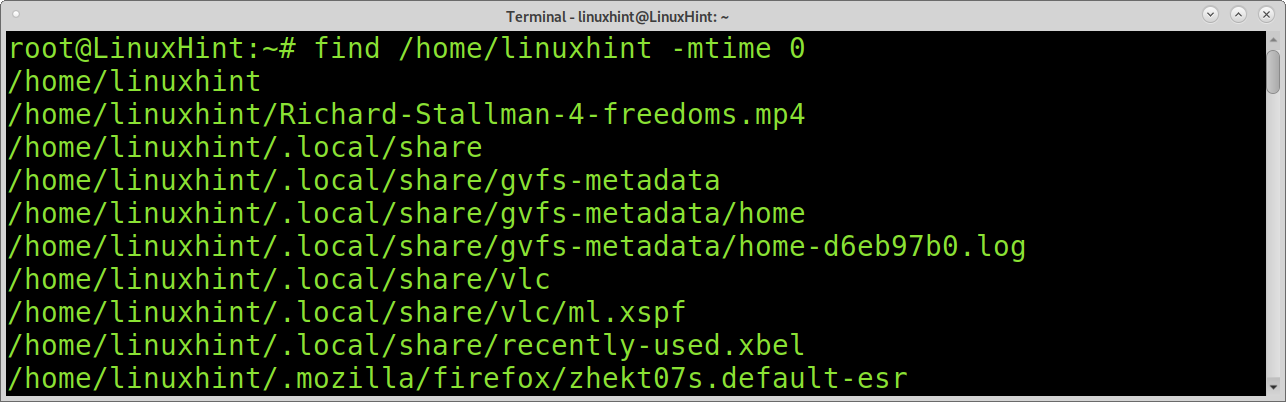
To find last day modified files, you can also use the mtime command together with find. By specifying the option 0 as in the example below, mtime will return all files modified in the last 24 hours.
Find Last Modified Specific File Type in Linux:
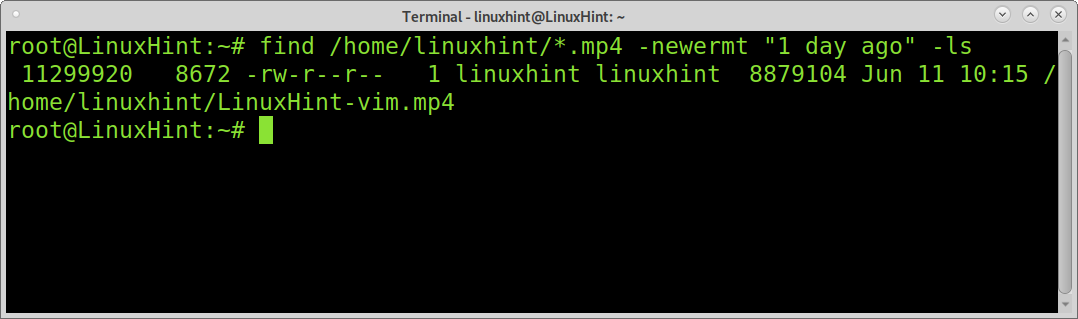
You can use a wildcard to limit your search to a specific file type. In the following example, find and newermt are instructed to list all mp4 files modified a day ago.
cc lang=”bash” width=”100%” height=”100%” escaped=”true” theme=”blackboard”]$ find /home/linuxhint/*.mp4 -newermt “1 day ago” -ls[/cc
In the following example, find and newermt are used to find all .png images less than 15 days old.
Finding Last Hour Modified Files in Linux:
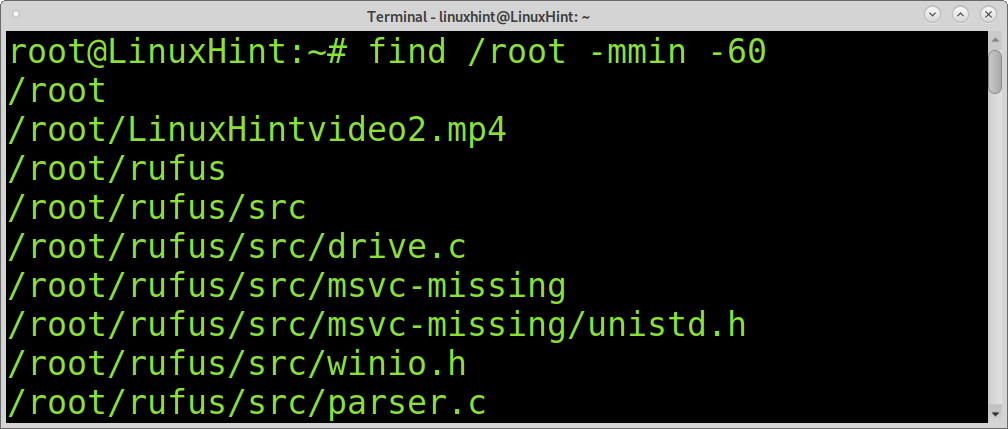
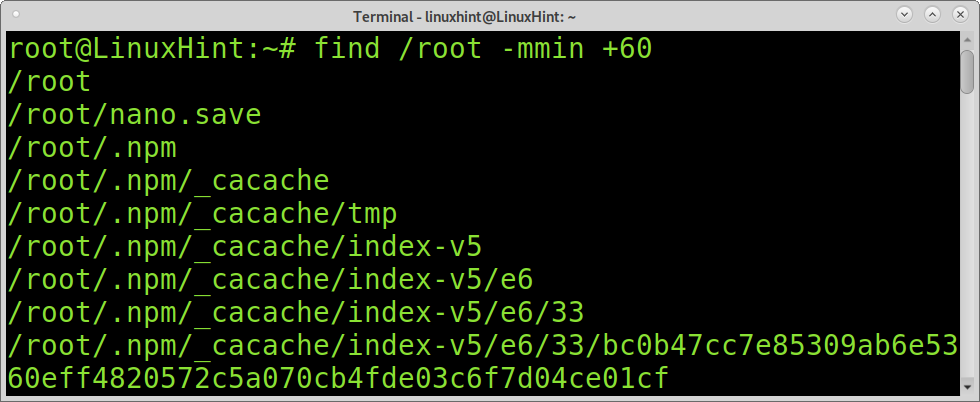
The following example combines the find command with the mmin command. We can use the mmin command to specify minutes. In the example below, the find and mmin commands will print all files under the /root directory, whose modifications are less than 60 minutes old.
Contrary to the previous example in which files modified in the past 60 minutes were found. You can also use +mmin to search files modified after X minutes. For example, the following command will show files modified 60 minutes ago or more.
Finding Files Modified on a Specific Date in Linux:
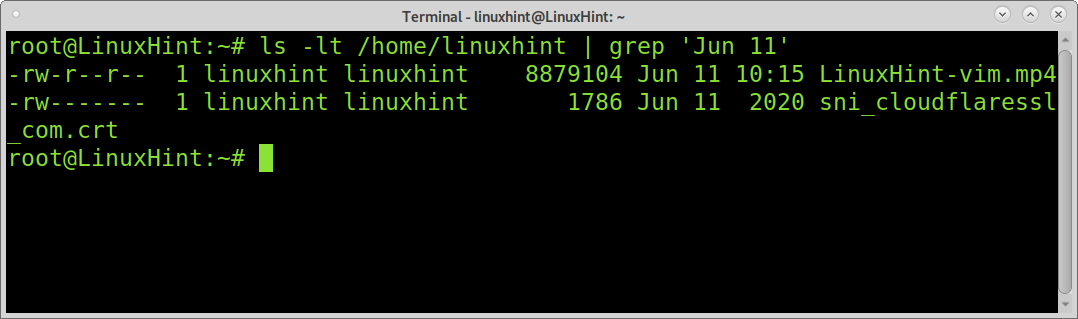
You can use the ls command to list files including their modification date by adding the -lt flag as shown in the example below. The flag -l is used to format the output as a log. The flag -t is used to list last modified files, newer first.
Then you can combine ls -lt with grep to print all files which were modified on a specific date.
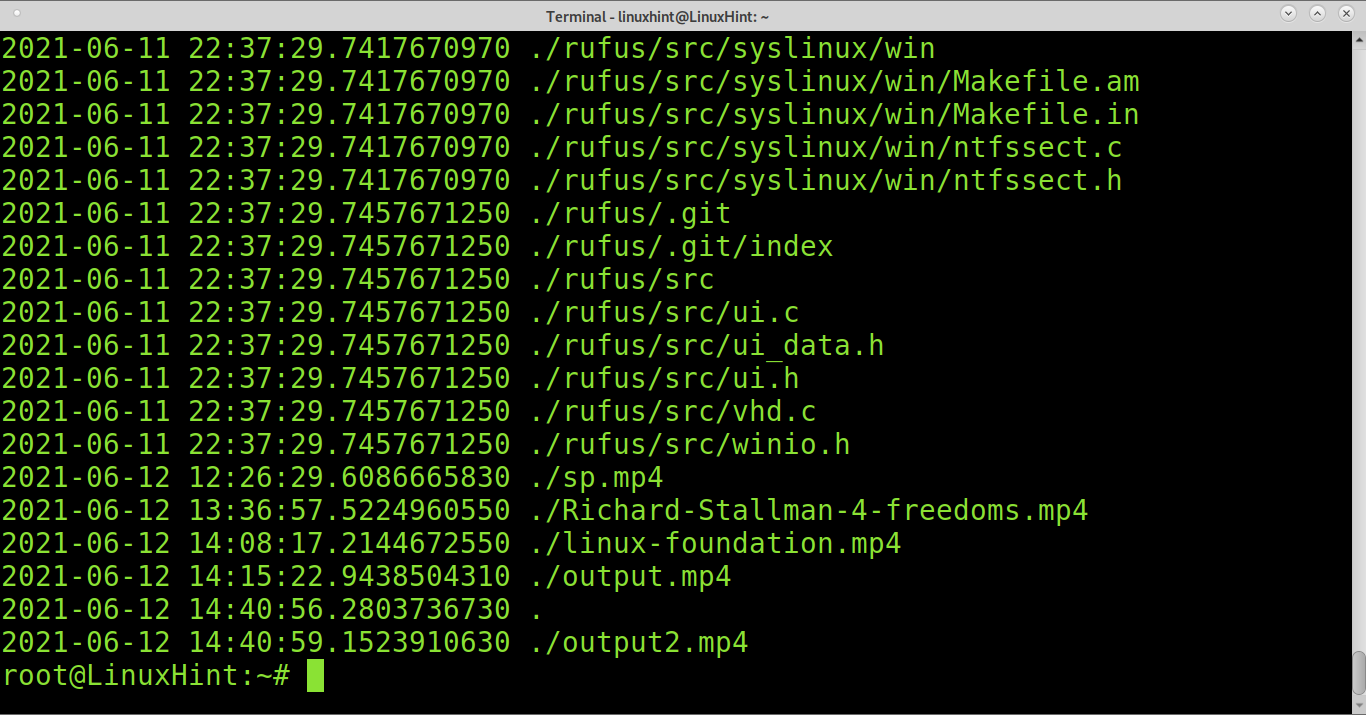
Find Last Modified Files Recursively:
Previous examples are useful to find last modified files
The command below can be used to print last modified files recursively.
Search File by Date Omitting Files or Directories:
Contrary to the previous example, you can search files omitting directories. For this purpose, you need to implement the -type flag with the option f (file) as shown in the following example. As a result, you’ll see only final files and no directories.
You can also search directories only and the output will omit files. For this, just replace the f with a d after the -type flag.
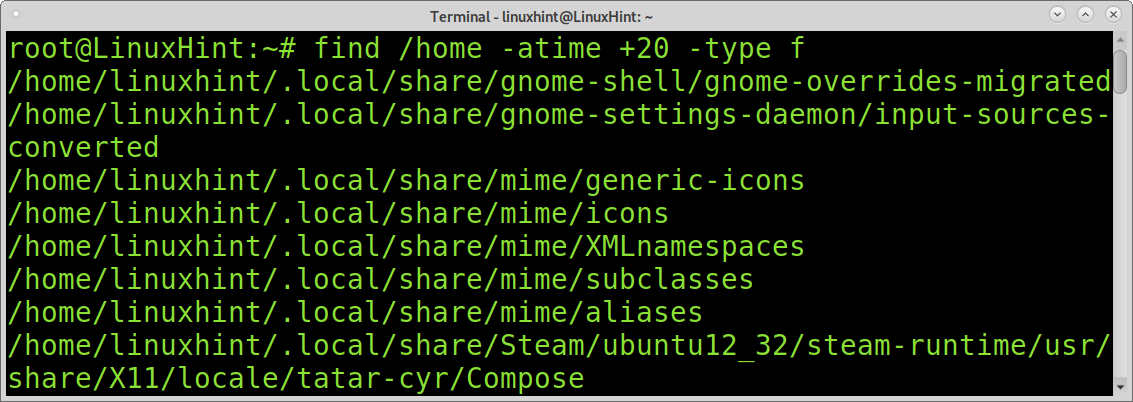
Find Files by Access Date:
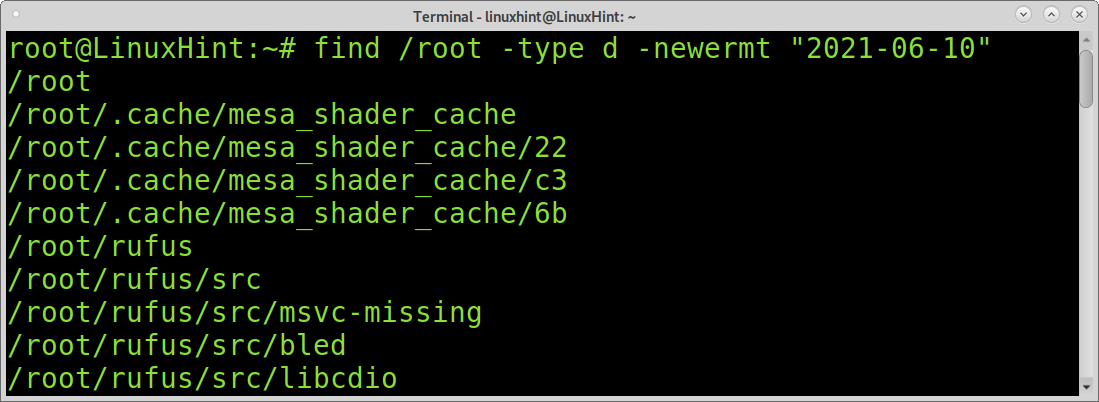
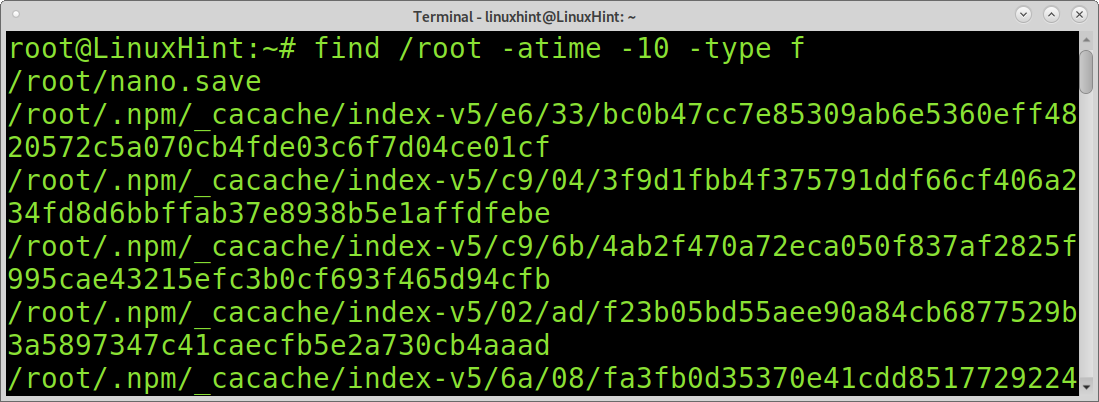
You also may want to find unmodified files by access date. For this purpose, you can use the atime command. It is similar to the mtime command explained before, but instead of identifying files by modification, it can display files by access. With this command you can learn the last accessed files and directories in the system.
The following command shows all files accessed in the past 10 days.
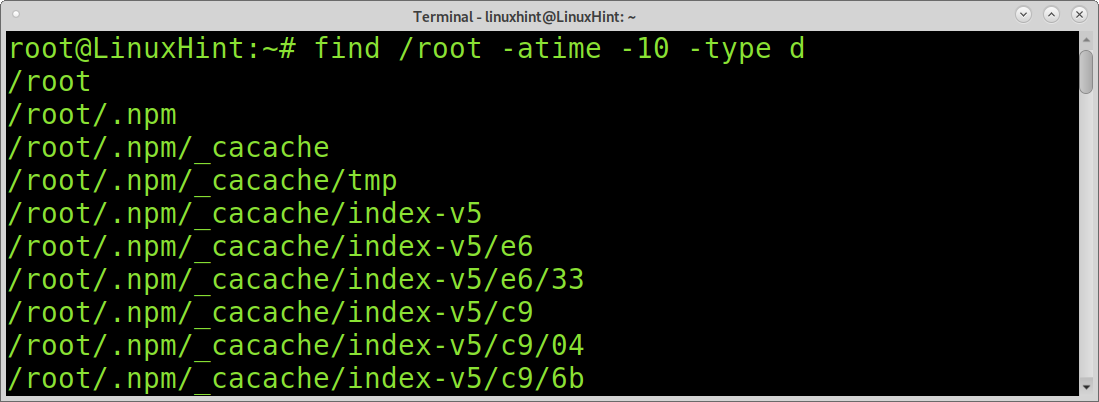
Like the previous command, you can also use the d option to show only directories:
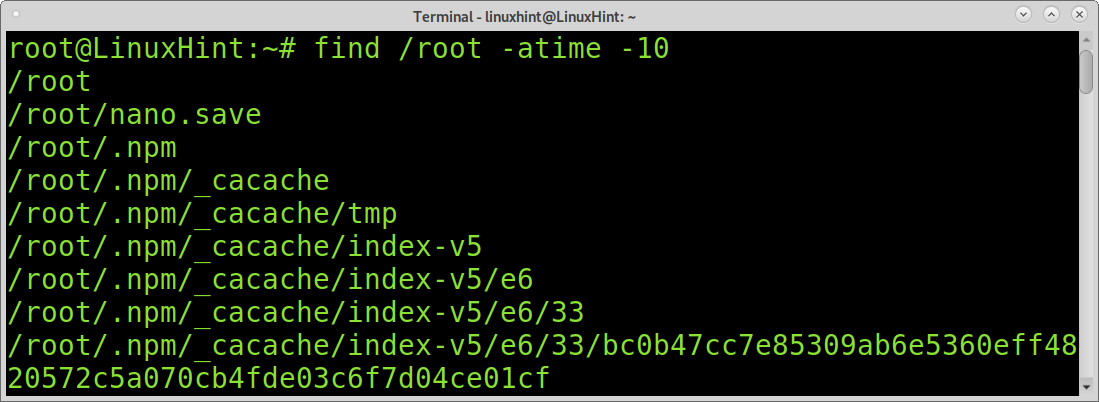
If you don’t specify a type, atime will show all files and directories:
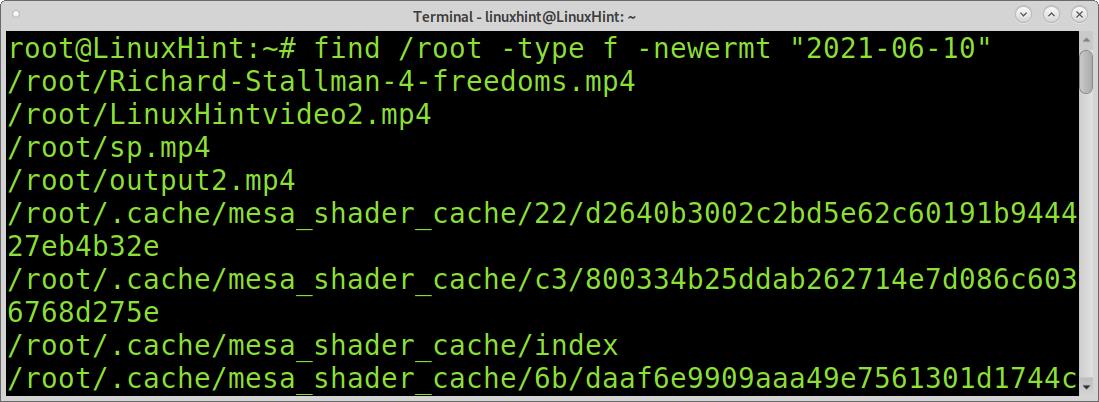
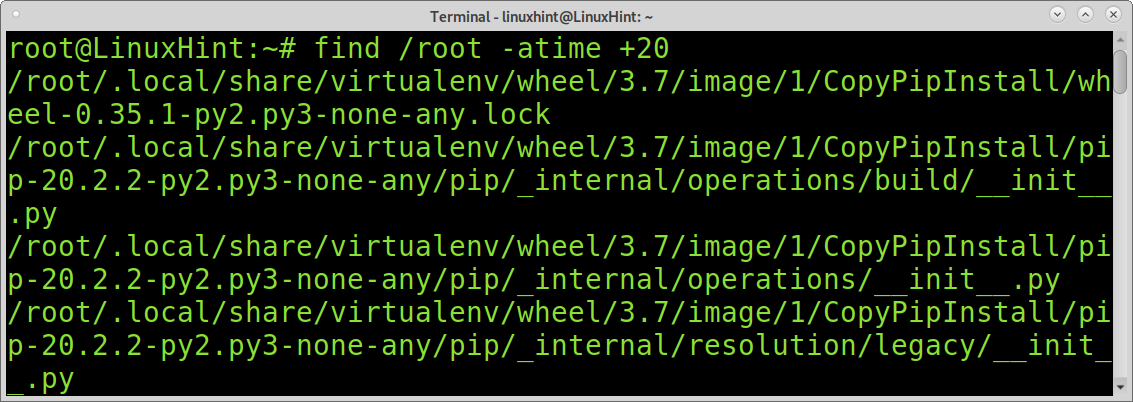
In the following example, find and atime are used to find files and directories with modification older than 20 days.
As with previous examples, you can also limit the listing to files or directories with the -type flag.
Conclusion:
As you can see, Linux offers different methods to find files according to modification time. Any Linux user level can easily learn those methods to search files with a single command. Finding files by modification or access within a system is part of the basic knowledge a Linux user needs.
I hope this tutorial was useful. Keep following Linux Hint for more Linux tips and tutorials.
About the author
David Adams
David Adams is a System Admin and writer that is focused on open source technologies, security software, and computer systems.