How to join a Linux system to an Active Directory domain
Do you need to centrally manage Linux systems and user accounts under an Active Directory domain? Here’s how to do it.
Microsoft’s Active Directory (AD) is the go-to directory service for many organizations. If you and your team are responsible for a mixed Windows and Linux environment, then you probably would like to centralize authentication for both platforms. I’ll cover how to add Linux computers to an Active Directory domain.
Active Directory and the need for centralized access management
Great Linux resources
Microsoft’s Active Directory, more popularly known as AD, has held the lion’s share of the market for enterprise access management for many years now. It is used by institutions and individuals the world over to centrally control access to resources belonging to the organization. It gives you the ability to manage users, passwords, resources such as computers, and dictate who has access to what. For some of you reading this write-up, especially those who work in large institutions, you have interacted with AD before. Usually, the interaction is using one set of login credentials to log in to any workstation in the organization. That is just the tip of a large iceberg.
Imagine a collection of 40 computer systems and 70 users in a firm. Some employees run shifts while others work regular hours. Some have access to printing; others don’t. The traditional way of working is to create local user accounts on each computer a user needs to access. Imagine the workload on the end-user support team. When a user changes his password for any reason, that user has to change the password on all computers he previously had access to, to keep things in sync. In no time, there will be mayhem. Now, imagine two members of the staff resign. I do not need to tell you the monotonous work that has to be repeated any time there’s a change to the staffing or any workstations. For IT teams, this is a nightmare. Time that could be used for innovative tasks is now spent reinventing the wheel. I have not even spoken about managing access to the printers.
This is where a directory service such as Active Directory thrives. It can literally be a lifesaver. With Active Directory, each user is uniquely created as an object in a central database, with a single set of credentials. Each computer system is also created as an object. Automatically, every user can access every workstation with that same set of credentials. Any account changes that need to be made are made once at the central database. Members of staff can access the printers using the same set of credentials. The printers’ authentication mechanism can be coupled with AD to achieve that. Happy users, happy IT team.
Using groups and organizational units, access to various resources can be tailored and maintained. It gets even better. This directory can store staff phone numbers, email addresses, and can be extended to store other information. What if someone resigns? No problem. Just disable the user’s account. That person’s access to all resources is nullified on the spot. The bigger the organization, the greater the need for centralized management. It saves time; it saves emotions.
At its heart, a directory service is just an organized way of itemizing all the resources in an organization while facilitating easy access to those resources. Basically, AD is a kind of distributed database, which is accessed remotely via the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). LDAP is an open protocol for remotely accessing directory services over a connection-oriented medium such as TCP/IP.
AD is not the only directory service based on the x.500 standard, or that can be accessed using LDAP. Other directory services include OpenLDAP and FreeIPA. However, AD is a mature Windows-based service that comes incorporated with Windows Server systems. In other words, it’s going to be the automatic winner when your organization has many Windows systems. This is one of the reasons for its ubiquity. Directory services such as FreeIPA are Linux-based and provide an excellent service for a Linux stable. When the rubber hits the road, the choice boils down to which of the two you can set up quickly, given your current environment and your team’s skill set.
[ Learn how to manage your Linux environment for success by downloading this free eBook. ]
But what happens when you choose AD, and you have a few CentOS servers, and you do not want to maintain a separate set of credentials for your Linux users? That overhead is entirely avoidable. What you need to do is join the Linux servers to the AD domain, like you would a Windows server.
If that is what you need to do, then read on to find out just how to do it. It is possible to join a Windows system to a FreeIPA domain, but that is outside the scope of this article.
Prerequisites
Career advice
This article presupposes that you have at least some introductory-level experience with Active Directory, especially around user and computer account management. Aside from that, the following obvious requirements need to be met:
- An account in AD that has the privileges necessary to join a system to the domain.
- A Linux server (a CentOS 7 server was used for this demonstration).
- A Domain Controller.
- Ensure your Linux server knows how to find the domain controller via DNS.
To make this article easier on everyone, here’s a list of key details. This is how the lab I used for this write up is set up, so you should modify accordingly.
- AD Domain Name: Hope.net
- User account for joining the domain: fkorea (Fullname — Fiifi Korea)
- Linux server hostname: centy2
Packages to install
For this configuration, the essential package to install is realmd . Aside from realmd , there are a host of packages that need to be installed to make this work.
# yum install sssd realmd oddjob oddjob-mkhomedir adcli samba-common samba-common-tools krb5-workstation openldap-clients policycoreutils-pythonRealmd provides a simplified way to discover and interact with Active Directory domains. It employs sssd to do the actual lookups required for remote authentication and other heavy work of interacting with the domain. In the interest of brevity, I won’t dwell on the other packages in the list.
However, for those interested in the details, a quick Google search should be of great help.
Realmd (interacting with the domain)
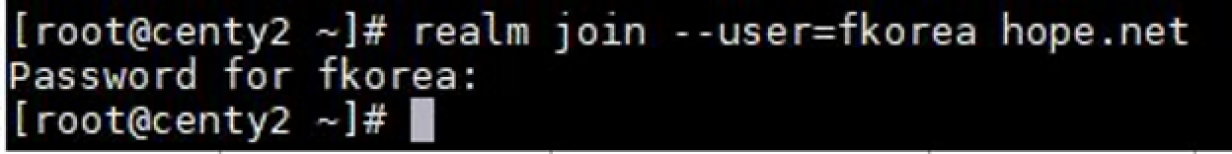
Now that all packages have been installed, the first thing to do is to join the CentOS system to the Active Directory domain. We use the realm application for that. The realm client is installed at the same time as realmd . It is used to join, remove, control access, and accomplish many other tasks. Here is the expected syntax for a simple domain join:
realm join --user=[domain user account] [domain name]The space between the user account and the domain account is not a typo. By inserting the corresponding details, we get the following command:
# realm join --user=fkorea hope.netSupply the password when the prompt appears and wait for the process to end.
Don’t let the short absence of output deceive you. There are a number of operations that go on as part of the process. You can tack on the -v switch for more verbose output. However, the best way to check if the computer is now a member of the domain is by running the realm list command. The command attempts to display the current state of the server with regard to the domain. It is a quick and dirty way to know which groups or users can access the server.
Have a look at its output:
It is also quite trivial to place the newly-created AD computer object in a specific Organizational Unit (OU) from the onset. I’ll leave that for further reading, but, as a tip, you can consult the man page. Using the realm client, you can grant or revoke access to domain users and groups. A deep dive on using realmd in a more fine-grained way is enough to make another article. However, I will not be out of order to pick out a few parameters for your attention, namely client-software and the server-software. By now, you should understand why we had to install so many packages.
To leave the domain altogether, you need two words: realm leave
Further configuration
So now that the Linux server is part of the AD domain, domain users can access the server with their usual credentials. We are done, right? Wrong. «What’s the problem?» I hear you say.
Well, for starters, this is the barebones configuration to get you up and running. But the experience is clunky, to say the least. We need to configure the service further to give it a true AD feel. It should be just like logging on to a domain-joined Windows 10 workstation.
Secondly, there is the big elephant in the room for sysadmins called Dynamic DNS Updates (DynDNS). If it is not set up correctly, we create extra overhead by having to maintain DNS records manually. For an environment that relies heavily on DNS, that could be a problem. For Windows systems, joining a system to the domain means two entries are automatically managed and maintained on the DNS server. When IP addresses change, the change is automatically reflected in DNS. This means you can change the IPs of systems without incurring the cost of manual maintenance. This will only make sense to people who already take advantage of DNS in their environments. Aside from the noticeable productivity gains of automation, it helps to have both Windows and Linux environments working the same way.
The third issue is DNS Scavenging. In an Active Directory domain, DNS is usually provided by the Domain Controllers. Every system joined to the domain has an automatic DNS entry with a corresponding IP address. This is super convenient. Automatically, at a specified interval, stale DNS records are deleted to prevent misdirected packets and also take care of deleted computer objects. This is known as scavenging, and it is not turned on by default in AD. However, if it is turned on, we need to configure it. Typically, the scavenging interval is seven days. If, after that period, there has been no update to the record, it is deleted, unless it is a static record. For Windows systems, the Dynamic Updates feature is automatically set up. However, with Linux servers, a few modifications need to be made. Without doing that, we will have services going down after a while because their records are deleted from DNS, and no one knows how to reach their component parts.
Now that we know some of the potential issues we need to address, let’s take a look at some of the things we can tweak to deliver a more seamless experience to the end-user and the sysadmin.
SSSD (easier logins and dynamic updates)
sssd on a Linux system is responsible for enabling the system to access authentication services from a remote source such as Active Directory. In other words, it is the primary interface between the directory service and the module requesting authentication services, realmd . Its main configuration file is located at /etc/sssd/sssd.conf . As a matter of fact, this is the main configuration file we will modify.
Let’s have a look at its contents before configuration. Once you join the domain, it is immediately modified to contain the minimum information required for a successful logon. My file looked like this: