- How to Lock and Unlock User After Failed SSH Logins
- What Is pam_faillock module?
- How to Lock User After Failed SSH Logins
- How to Lock Root After Failed SSH Logins
- How to Test SSH User Failed Login Attempts
- How to View Failed SSH Logins
- How to Unlock User After Failed SSH Logins
- Disable User Lock After SSH Failed Logins
- How To Disable Faillock Module
- Lock and Unlock User Account After Failed SSH Logins
- Lock User Account After Failed SSH logins in RHEL like OS
- Unlock User Account After Failed Logins in RHEL Like OS
- Lock User Accounts After Failed Login Attempts in Debian / Ubuntu / Linux Mint
- Unlock User Account using pam_tally2 command
How to Lock and Unlock User After Failed SSH Logins
SSH security is a top priority when setting up your server. The default SSH settings are usually not robust enough to safeguard your server from external attacks.
Therefore, additional tweaks are needed to provide a decent amount of security from brute-force attacks. One of these is implementing fail2ban to keep off unauthorized users after a certain number of incorrect log attempts. Similarly, you can leverage the pam_faillock module to implement an account lockout policy.
This guide will show how to lock a system user’s account after a specifiable number of failed SSH login attempts in RedHat-based distributions. On Debian-based distributions, you need to use the pam_tally2 module to lock failed SSH logins.
Here, the focus is to enforce simple server security by locking a user’s account after a consecutive number of unsuccessful SSH authentications.
What Is pam_faillock module?
The pam_faillock module is a part of the Linux PAM (Pluggable Authentication Modules), a utility made up of shared libraries that separates applications from standard authentication methods.
It accepts authentication checks from programs such as sshd, gdm, login, and many more and authenticates the user to those services or applications in Linux systems. We briefly explained configuring PAM to audit user login shell activity.
The module records failed authentication attempts per user and temporarily locks the user account if the failed authentication attempts exceed a certain limit. Failed login attempts are stored in per-user files in the tally directory which is /var/run/faillock/ by default.
The pam_faillock module replaces the pam_tally and pam_tally2 modules which have been deprecated in RHEL 7 and RHEL 8. It offers more flexibility and options than the two modules.
How to Lock User After Failed SSH Logins
You can configure the above functionality in the /etc/pam.d/system-auth and /etc/pam.d/password-auth files, by adding the entries below to the auth section.
$ sudo vim /etc/pam.d/system-auth $ sudo vim /etc/pam.d/password-auth
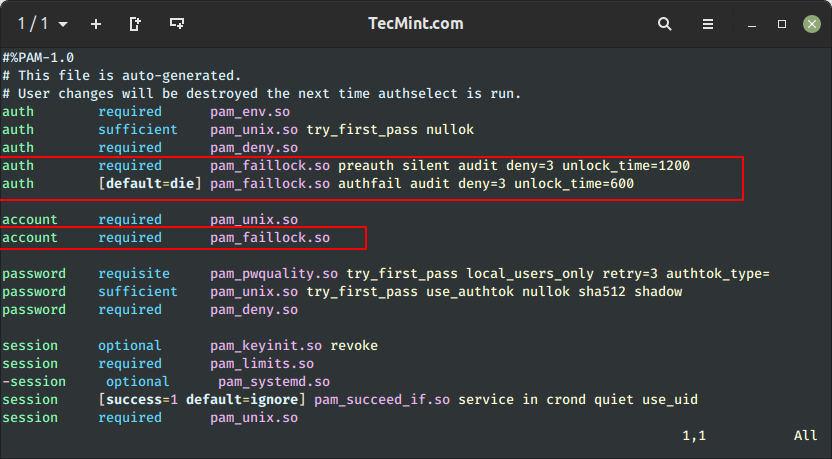
To lock out or deny users access to the system after 3 unsuccessful SSH attempts and unlock the user account after 1200 seconds, add the following lines in the auth section.
auth required pam_faillock.so preauth silent audit deny=3 unlock_time=1200 auth [default=die] pam_faillock.so authfail audit deny=3 unlock_time=600
- audit – enables user auditing.
- deny – used to define the number of attempts (3 in this case), after which the user account should be locked.
- unlock_time – sets the time (600 seconds = 10 minutes) for which the account should remain locked.
Note that the order of these lines is very important, wrong configurations can cause all user accounts to be locked.
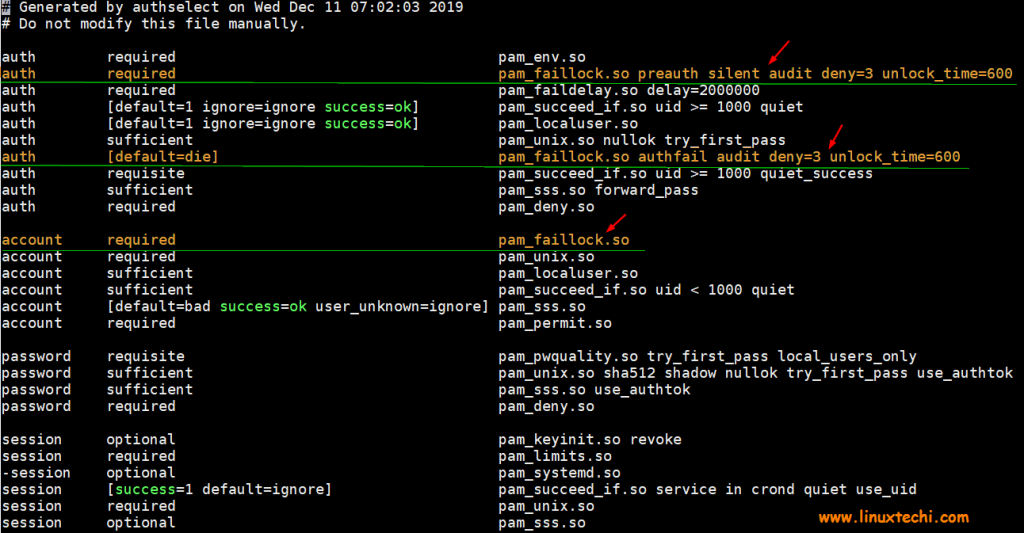
The auth section in both files should have the content below arranged in this order:
#%PAM-1.0 # This file is auto-generated. # User changes will be destroyed the next time authselect is run. auth required pam_env.so auth sufficient pam_unix.so try_first_pass nullok auth required pam_deny.so auth required pam_faillock.so preauth silent audit deny=3 unlock_time=1200 auth [default=die] pam_faillock.so authfail audit deny=3 unlock_time=600
Next, navigate to the account section and add the following line in both of the above files.
account required pam_faillock.so
After adding the above settings, it should appear as follows.
How to Lock Root After Failed SSH Logins
You can add the even_deny_root parameter to auth section to lock out both the user as well as the normal user. In this example, the unlock time for regular users is 1200 seconds (20 minutes) and 3600 seconds (60 min or 1 hr) for the root user after 3 failed SSH login attempts.
auth required pam_faillock.so preauth silent audit deny=3 even_deny_root unlock_time=1200 auth [default=die] pam_faillock.so authfail audit deny=3 even_deny_root unlock_time=3600
Once you have configured everything. You can restart remote access services like sshd, for the above policy to take effect that is if users will employ ssh to connect to the server.
$ sudo systemctl restart sshd
Next, we will run a test and check if the configuration works.
How to Test SSH User Failed Login Attempts
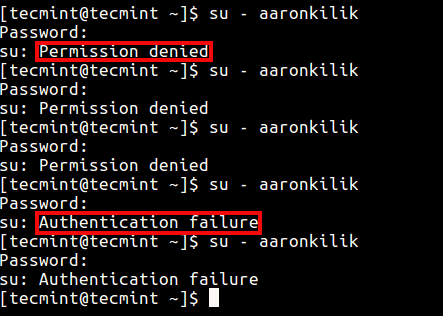
From the above settings, we configured the system to lock a user’s account after 3 failed authentication attempts.
In this scenario, the user tecmint is trying to switch to the user aaronkilik , but after 3 incorrect logins because of a wrong password, indicated by the “Permission denied” message, the user aaronkilik’s account is locked as shown by the “authentication failure” message from the fourth attempt.
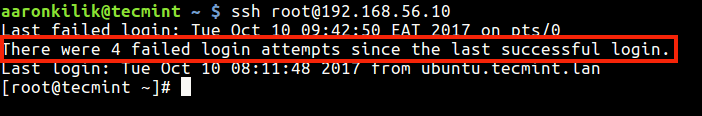
The root user is also notified of the failed login attempts on the system, as shown in the screenshot below.
How to View Failed SSH Logins
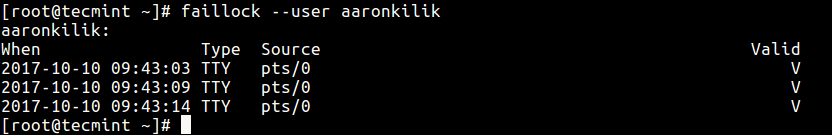
You can see all failed SSH authentication logs using the faillock utility, which is used to display and modify the authentication failure log.
You can view failed login attempts for a particular user like this.
To view all unsuccessful login attempts, run faillock without any argument like so:
How to Unlock User After Failed SSH Logins
To clear a user’s authentication failure logs, run this command.
# faillock --user aaronkilik --reset OR # fail --reset #clears all authentication failure records
Disable User Lock After SSH Failed Logins
Lastly, to tell the system not to lock a user or user’s accounts after several unsuccessful login attempts, add the entry highlighted in bold, just above where pam_faillock is first called under the auth section in both files (/etc/pam.d/system-auth and /etc/pam.d/password-auth) as follows.
#%PAM-1.0 # This file is auto-generated. # User changes will be destroyed the next time authselect is run. auth required pam_env.so auth sufficient pam_unix.so try_first_pass nullok auth required pam_deny.so auth [success=1 default=ignore] pam_succeed_if.so user in tecmint:aaronkilik auth required pam_faillock.so preauth silent audit deny=3 unlock_time=1200 auth [default=die] pam_faillock.so authfail audit deny=3 unlock_time=600
How To Disable Faillock Module
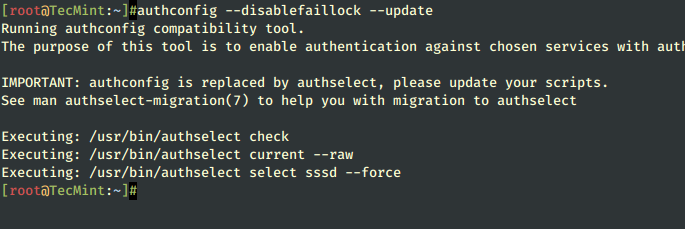
To disable the pam_failock module, execute the following command:
# authconfig --disablefaillock --update
For more information, see the pam_faillock and faillock man pages.
# man pam_faillock # man faillock
You might also like:
That’s all! In this article, we showed how to enforce simple server security by locking a user’s account after x number of incorrect logins or failed authentication attempts.
It’s a handy way of fortifying your SSH security from brute-force attacks. Use the comment form below to share your queries or thoughts with us.
Lock and Unlock User Account After Failed SSH Logins
In today’s interconnected world, the security of our systems is of utmost importance. One crucial aspect of securing a Linux system is protecting it against unauthorized access through SSH. In this blog post, we will explore the steps to lock and unlock user accounts after failed SSH logins, ensuring that your Linux system remains secure.
For production servers. It is recommended that one should enable ssh policy, means user’s account should be locked automatically after n numbers of failed ssh login attempts.
Lock User Account After Failed SSH logins in RHEL like OS
In Linux distribution like RHEL, Rocky Linux, AlmaLinux, CentOS and Fedora, this is achieved by using pam module “pam_faillock” and for Debian like distributions, this can be achieved using “pam_tally2” pam module.
Add the following lines in auth section in these two files using vi editor.
auth required pam_faillock.so preauth silent audit deny=3 unlock_time=600 auth [default=die] pam_faillock.so authfail audit deny=3 unlock_time=600 account required pam_faillock.so
- Audit –> it will enable audit logs for user login attempt in secure log file
- Deny=3 –> it will lock the user after 3 unsuccessful login attempts, you can change this number as per your requirement
- unlock_time=600 –> it means user’s account will remain locked for 10 minutes (600 seconds), if you want user account to be locked forever then set this parameter as “ unlock_time=never “
Note: To lock root account as well after n incorrect logins, add “even_deny_root” parameter in auth section lines, example is shown below
auth required pam_faillock.so preauth silent audit even_deny_root deny=3 unlock_time=600 auth [default=die] pam_faillock.so authfail audit even_deny_root deny=3 unlock_time=600
As we can see above, we have two lines for auth section and one line for account section, order is very important while adding these lines to the files. Example is demonstrated below where these lines needs to be added,
$ sudo vi /etc/pam.d/password-auth
$ sudo vi /etc/pam.d/system-auth
After making changes in both the files, restart the ssh service using below systemctl command,
$ sudo systemctl restart sshd
Let’s do the testing whether user account will be locked after three unsuccessful login attempts or not.
Let’s assume we have a local account with name “ pkumar “, we will try to ssh our Linux system with this account with incorrect passwords,
$ ssh [email protected] [email protected]'s password: [email protected]'s password: [email protected]'s password: Permission denied (publickey,gssapi-keyex,gssapi-with-mic,password).
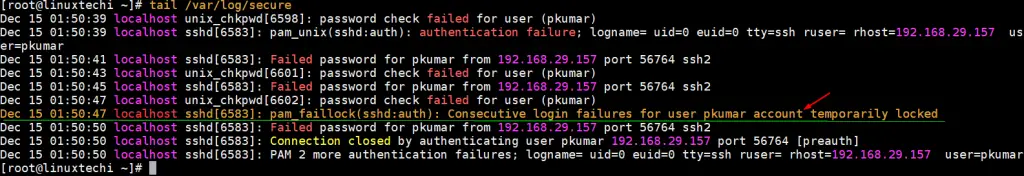
Now view secure logs using tail command,
Above logs confirms that account has been locked after three incorrect login attempts, let’s verify from faillock command as well,
[[email protected] ~]# faillock --user pkumar pkumar: When Type Source Valid 2019-12-15 01:50:39 RHOST 192.168.29.157 V 2019-12-15 01:50:43 RHOST 192.168.29.157 V 2019-12-15 01:50:47 RHOST 192.168.29.157 V [[email protected] ~]#
Unlock User Account After Failed Logins in RHEL Like OS
To flush or clear these unsuccessful login attempts, execute the following faillock command,
$ sudo faillock --user pkumar --reset $ sudo faillock --user pkumar pkumar: When Type Source Valid $
Let’s move to Debian like distribution (Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Debian)
Lock User Accounts After Failed Login Attempts in Debian / Ubuntu / Linux Mint
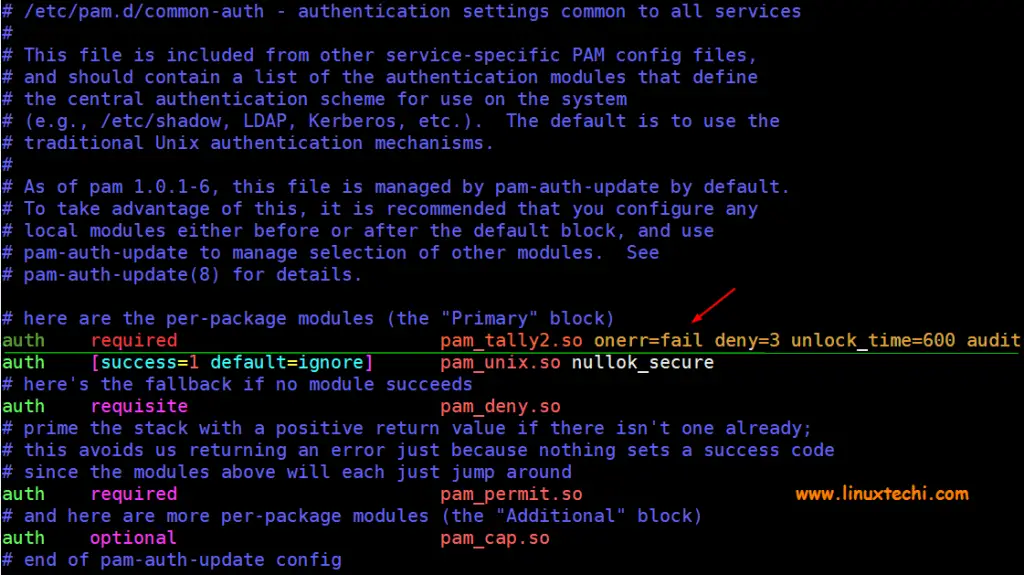
In order to lock user accounts after failed ssh login attempts in Debian, Ubuntu & Linux Mint, add the following line in the file “ /etc/pam.d/common-auth” ,
auth required pam_tally2.so onerr=fail deny=3 unlock_time=600 audit
if you wish to lock root account as well after three incorrect logins then add the following line ,
auth required pam_tally2.so onerr=fail deny=3 unlock_time=600 audit even_deny_root root_unlock_time=600
- Onerr=fail –> In case of error issue a fail
- deny=3 –> After three unsuccessful login attempts account will be locked
- unlock_time=600 –> It means account will remain locked for 10 minutes or 600 seconds
- audit –> It means audit the logs in audit.log file
- even_deny_root –> Lock the root account after three incorrect logins
- root_unlock_time=600 –> Root account will remain locked for 10 minutes or 600 seconds after 3 unsuccessful login attempts
Let’s add above discussed line in file “ /etc/pam.d/common-auth ” using vi editor,
$ sudo vi /etc/pam.d/common-auth
After making the above changes, save and exit the file and restart ssh service using following command,
$ sudo systemctl restart sshd
Let’s test whether accounts are locked after 3 incorrect ssh login attempts.
Assume we have a local user “ devops “, we will try to ssh Ubuntu system with incorrect passwords
$ ssh [email protected] [email protected]'s password: [email protected]'s password: d [email protected]'s password: Permission denied (publickey,password).
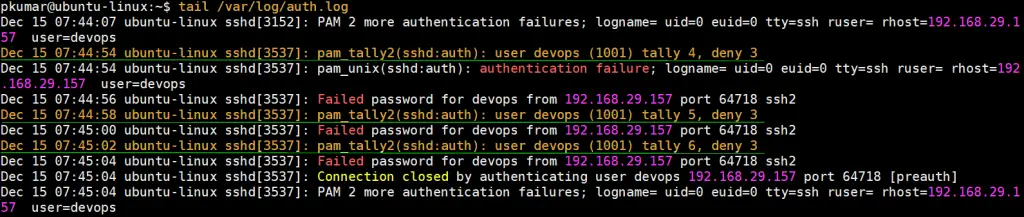
Now view auth log file to see whether incorrect login attempts are captured or not,
Above logs confirms that account has been locked, let’s verify from pam_tally2 command,
$ sudo pam_tally2 -u devops Login Failures Latest failure From devops 6 12/15/19 07:45:02 192.168.29.157 $
Unlock User Account using pam_tally2 command
In Debian like distributions, pam_tally2 command is used to unlock the user account. So, to clear these unsuccessful login attempts for devops user run following pam_tally2 command.
$ sudo pam_tally2 -u devops --reset Login Failures Latest failure From devops 6 12/15/19 07:45:02 192.168.29.157 $ $ sudo pam_tally2 -u devops Login Failures Latest failure From devops 0 $
That’s all from from this post, I hope you have found it informative.Please don’t hesitate to post your queries and feedback in below comments section.