- Как запустить остановить или перезапустить службы в Linux Mint 20
- Предпосылки
- Управление службами с помощью Systemd
- Просмотреть все услуги
- Просмотр запущенных служб
- Запустить службу
- Остановить службу
- Перезапустить службу
- Проверить статус услуги
- Управление службами с помощью сервисной команды
- Просмотреть все службы в вашей системе
- Запустить службу
- Остановить службу
- Перезапустить службу
- Проверить статус услуги
- Управление службами с помощью сценариев инициализации
- Запустить службу
- Остановить службу
- Перезапустить службу
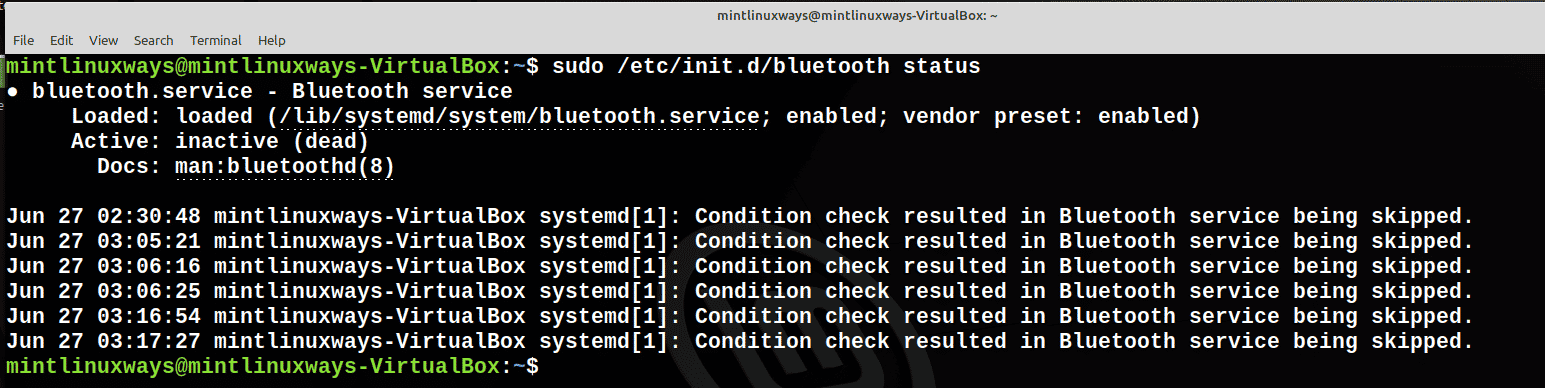
- Проверить статус услуги
- Вывод:
- Рекомендуемый контент
- Privacy Overview
- How to Start, Stop or Restart Services in Linux Mint 20
- Prerequisites
- Managing Services Using Systemd
- View All Services
- View Running Services
- Start a Service
- Stop a Service
- Restart a Service
- Check Status of the Service
- Managing Services Using service Command
- View All Services in Your System
- Start a Service
- Stop a Service
- Restart a Service
- Check Status of the Service
- Managing Services Using init Scripts
- Start a Service
- Stop a Service
- Restart a Service
- Check Status of the Service
- Conclusion:
Как запустить остановить или перезапустить службы в Linux Mint 20

Службы — это приложения, работающие в фоновом режиме операционной системы и ожидающие использования. Linux позволяет вам видеть эти службы и управлять ими, а в целом предлагает больший контроль над ними.
В этой статье вы узнаете о различных способах запуска, остановки и перезапуска любой службы в Linux Mint 20.
Предпосылки
Вам понадобится учетная запись пользователя с привилегиями root/sudo, доступ к терминалу и инструмент systemctl, который поставляется с Linux.
Управление службами с помощью Systemd
Systemd сам по себе является демоном, который относится к библиотекам, пакетам и утилитам вокруг демонов. Это самый продвинутый демон управления системой, который работает быстро и требует гораздо меньше системных ресурсов, чем его аналоги.
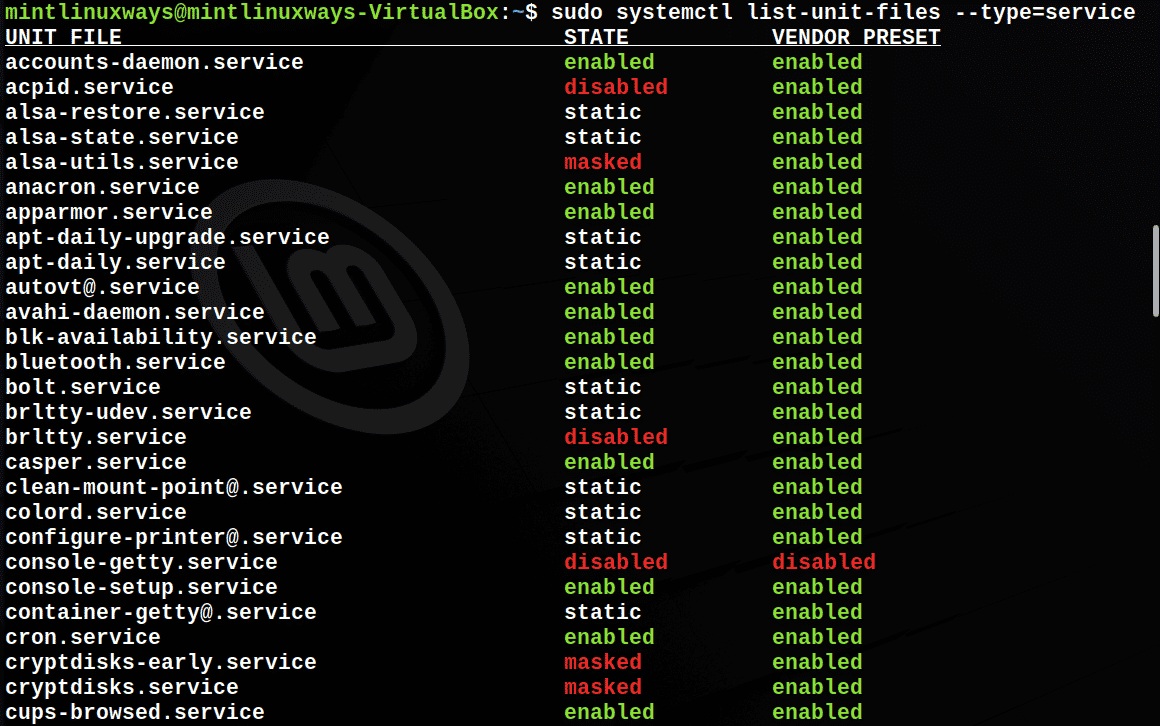
Просмотреть все услуги
sudo systemctl list-unit-files --type=service
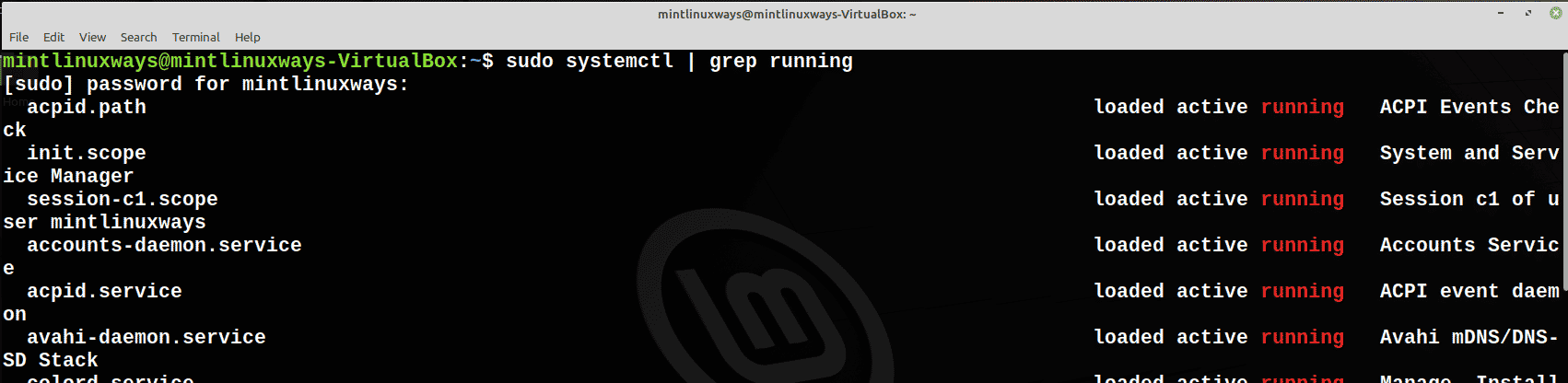
Просмотр запущенных служб
Чтобы увидеть все службы, которые в настоящее время работают в вашей системе, выполните следующую команду.
sudo systemctl | grep running
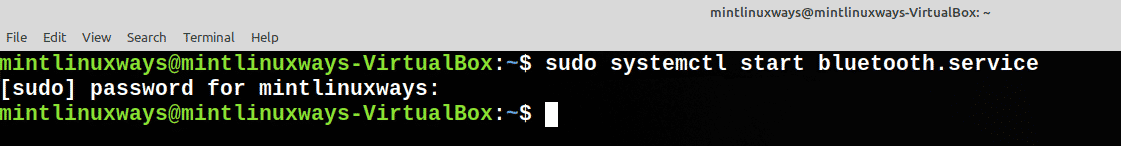
Запустить службу
Используйте следующую команду, чтобы запустить службу.
Примечание. Помните, что — это заполнитель, и вам нужно заменить его именем вашей службы.
Остановить службу
Используйте следующую команду, чтобы остановить службу.
Перезапустить службу
Используйте следующую команду, чтобы перезапустить службу.
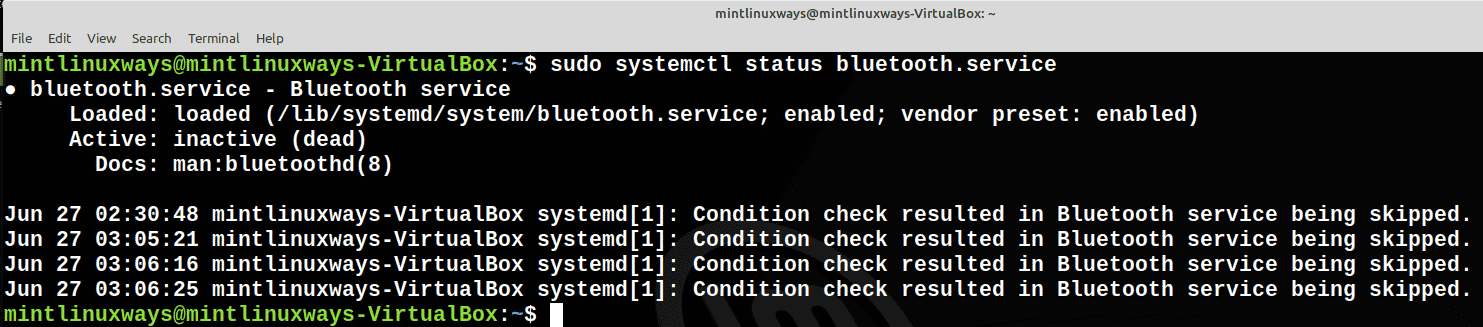
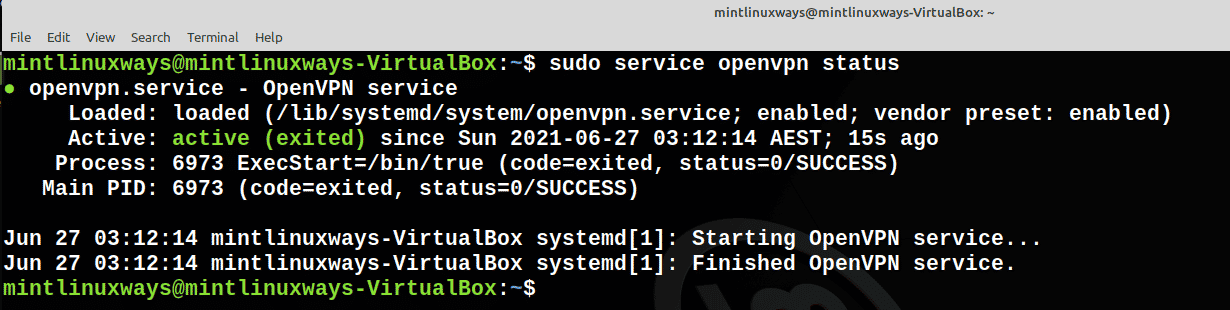
Проверить статус услуги
Используйте следующую команду, чтобы проверить статус вашей службы.
Управление службами с помощью сервисной команды
Service — это расширенная команда, которая является частью init. Но его выполнение сейчас осуществляется путем перенаправления команд в systemctl.
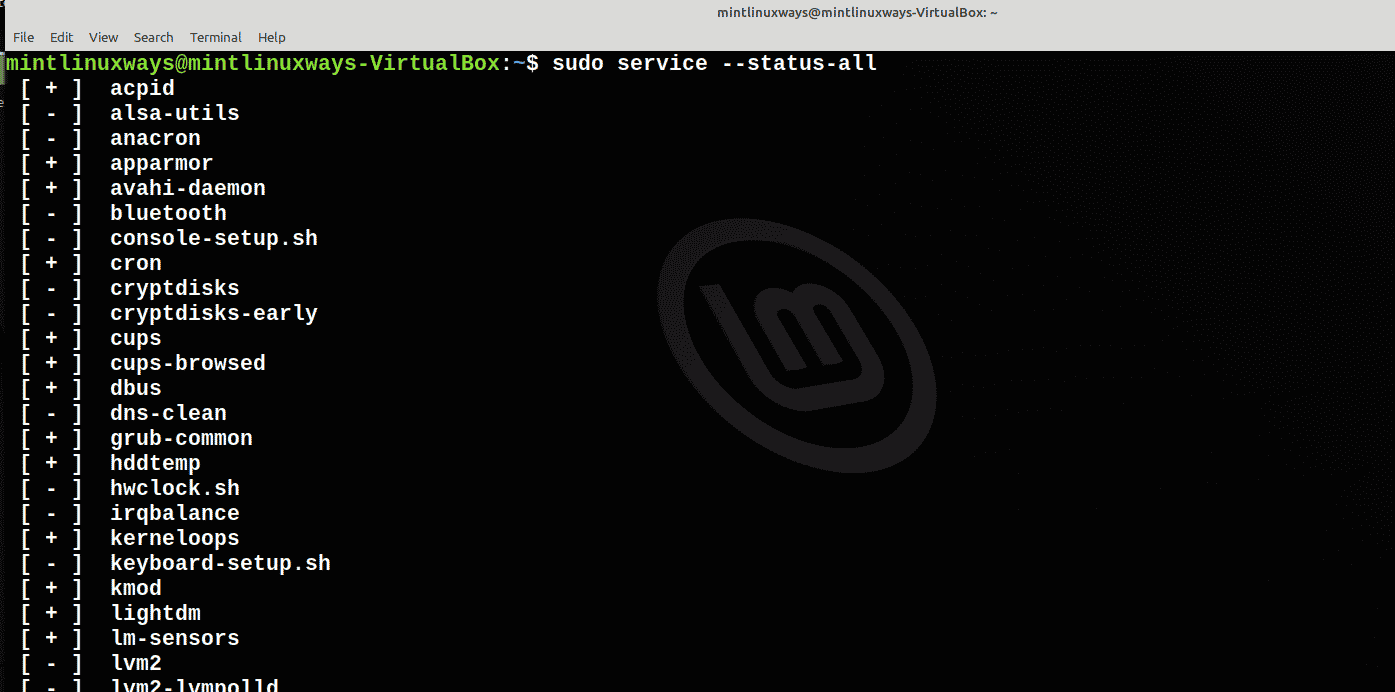
Просмотреть все службы в вашей системе
Чтобы проверить все службы, которые есть в вашей системе, просто запустите команду ниже.
Обратите внимание, что перед всеми включенными службами стоит символ [+] , а перед всеми отключенными службами — символ [-] .
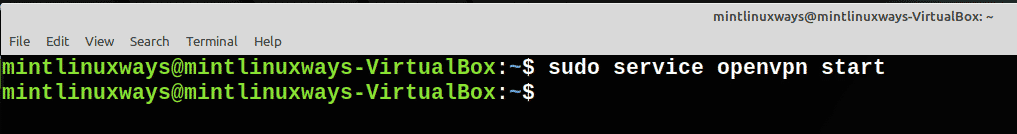
Запустить службу
Вы можете запустить службу, используя следующую команду.
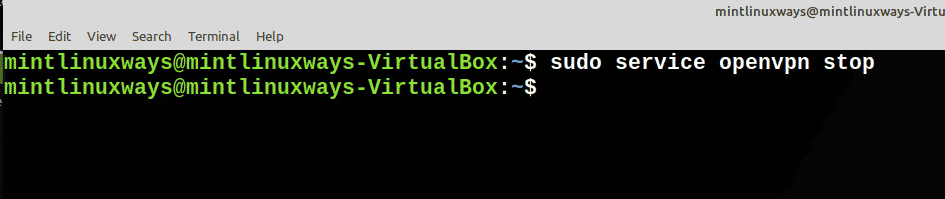
Остановить службу
Чтобы остановить службу, используйте следующую команду.
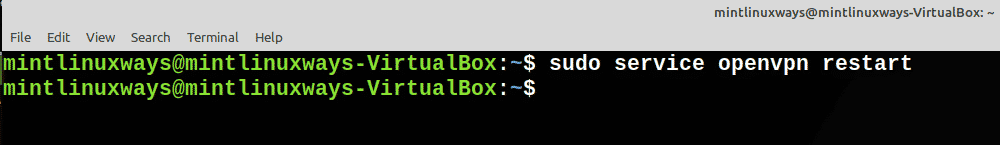
Перезапустить службу
Перезапустите любую службу с помощью следующей команды.
Проверить статус услуги
Вы можете проверить статус любой службы с помощью следующей команды.
Управление службами с помощью сценариев инициализации
Демон инициализации — это система управления демоном, называемая System V init. Он требует много ресурсов, поэтому его заменили на systemd.
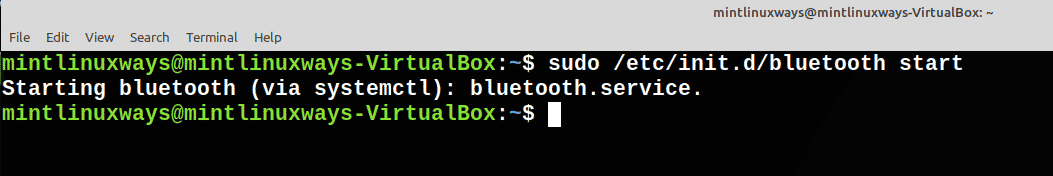
Запустить службу
Запустите службу с помощью следующей команды.
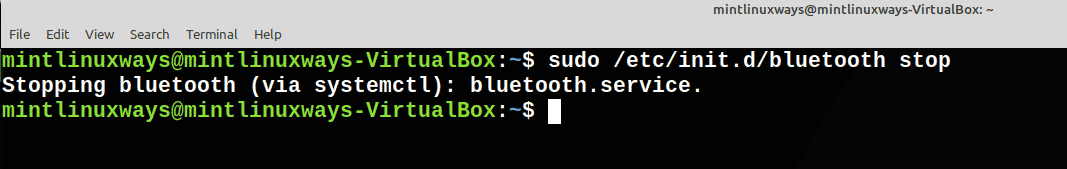
Остановить службу
Чтобы остановить службу, выполните следующую команду.
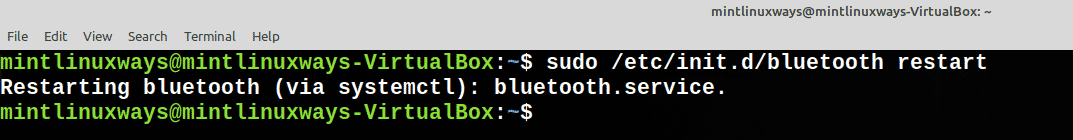
Перезапустить службу
Чтобы перезапустить службу, выполните следующую команду.
Проверить статус услуги
Проверьте состояние службы с помощью следующей команды.
Вывод:
В этой статье рассматриваются все основы управления службами в Linux Mint 20.
Рекомендуемый контент
Мы используем файлы cookie на нашем веб-сайте, чтобы предоставить вам наиболее релевантный опыт, запоминая ваши предпочтения и повторные посещения. Нажимая «Принять все», вы соглашаетесь на использование ВСЕХ файлов cookie. Однако вы можете посетить «Настройки файлов cookie», чтобы предоставить контролируемое согласие.
Privacy Overview
Этот веб-сайт использует файлы cookie, чтобы улучшить вашу работу во время навигации по веб-сайту. Из них файлы cookie, которые классифицируются как необходимые, хранятся в вашем браузере, поскольку они необходимы для работы основных функций веб-сайта. Мы также используем сторонние файлы cookie, которые помогают нам анализировать и понимать, как вы используете этот веб-сайт. Эти файлы cookie будут храниться в вашем браузере только с вашего согласия. У вас также есть возможность отказаться от этих файлов cookie. Но отказ от некоторых из этих файлов cookie может повлиять на ваш опыт просмотра.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category «Analytics». |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category «Functional». |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category «Necessary». |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category «Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category «Performance». |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | Этот файл cookie устанавливается подключаемым модулем GDPR Cookie Consent. Файлы cookie используются для хранения согласия пользователя на файлы cookie в категории «Необходимые». |
Functional cookies help to perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collect feedbacks, and other third-party features.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. These cookies track visitors across websites and collect information to provide customized ads.
Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet.
How to Start, Stop or Restart Services in Linux Mint 20
Services are the applications that run in the operating system’s background waiting to be used. Linux lets you see and manage these services and overall offers more control over them.
In this article, you will learn different ways to start, stop and restart any service in Linux Mint 20.
Prerequisites
You will need a user account with root/sudo privileges, access to the terminal, and the systemctl tool which comes with Linux.
Managing Services Using Systemd
Systemd is itself a daemon which refers to libraries, packages, and utilities around daemons. It is the most advanced system management daemon that is fast and takes much fewer system resources than its counterparts.
View All Services
You can see all the available services in your system with the following command.
sudo systemctl list-unit-files --type=service
View Running Services
To see all the services that are currently running on your system, run the following command.
sudo systemctl | grep running
Start a Service
Use the following command to start your service.
Note: Remember is a placeholder and you need to replace it with the name of your service.
Stop a Service
Use the following command to stop your service.
Restart a Service
Use the following command to restart your service.
Check Status of the Service
Use the following command to check the status of your service.
Managing Services Using service Command
Service is an advanced command that is a part of init. But its execution is done now by redirecting commands to systemctl.
View All Services in Your System
To check all the services you have on your system, simply run the command below.
Note that all the enabled services are preceded by the [+] symbol while all the disabled services have the [-] symbol next to them.
Start a Service
You can start a service using the following command.
Stop a Service
To stop a service, use the following command.
Restart a Service
Restart any service with the following command.
Check Status of the Service
You can check the status of any service with the following command.
Managing Services Using init Scripts
The init daemon is a daemon management system referred to as System V init. It takes a lot of resources so it was replaced by systemd.
Start a Service
Start service with the following command.
Stop a Service
To stop a service, run the following command.
Restart a Service
To restart a service, run the following command.
Check Status of the Service
Check the status of a service using the following command.
Conclusion:
This article covers all the basics of service management in Linux Mint 20.
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications including CCNA RS, SCP, and ACE. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various websites.