- Linux mint нет sshd
- Как включить SSH в Linux Mint
- Возможно вам будет интересно:
- Как работает SSH
- Как установить сервер Openssh в Linux Mint
- Как разрешить ssh соединение в брандмауэре Linux Mint
- Заключение
- How To Enable SSH on Ubuntu 20.04/18.04, Linux Mint 20/19 & Debian 10/9
- Prerequisites
- Enable SSH on Ubuntu / Linux Mint / Debian
- Allow SSH in Firewall
- Access Ubuntu / Linux Mint / Debian Machine via SSH
- Windows
- Linux
- Enable SSH Root Access on Ubuntu / Linux Mint / Debian
- Disable SSH on Ubuntu / Linux Mint / Debian
- Conclusion
Linux mint нет sshd
How To Enable SSH in Linux Mint
By default OpenSSH server is not installed in Linux Mint. This quick guide will show you how to install and enable SSH in Linux Mint, allowing you to remotely access the operating system over the network through SSH.
1. Open Terminal
We’ll be doing this through command line, so begin by first opening up a terminal. You can find the terminal icon in the task bar in a default GUI installation, as shown below.
2. Install OpenSSH Server
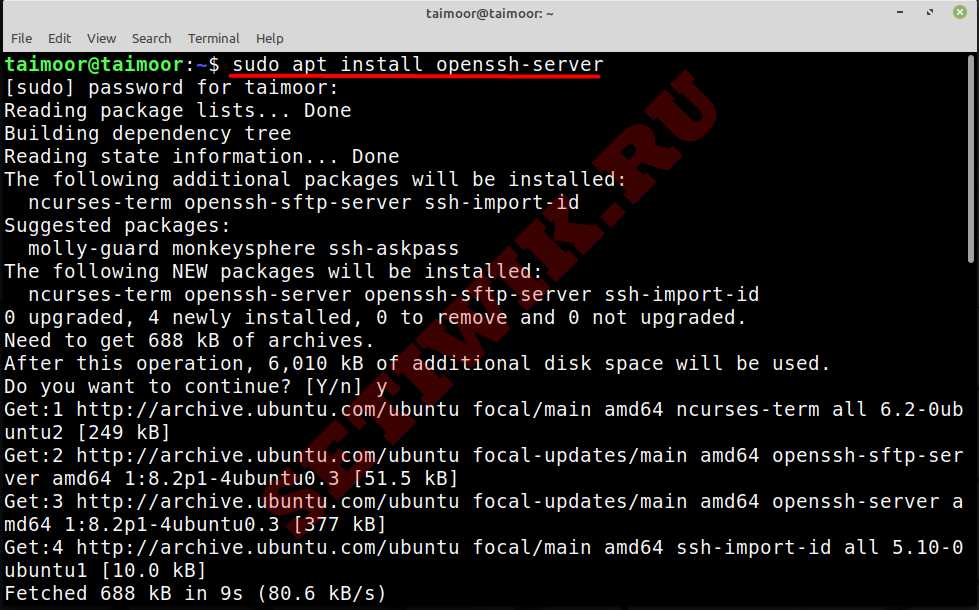
Within the terminal, run the following command as root to install the OpenSSH server package.
apt-get install openssh-server -y
Note: You must do this with root privileges, otherwise you will receive the following error message:
E: Could not open lock file /var/lib/dpkg/lock — open (13: Permission denied)
E: Unable to lock the administration directory (/var/lib/dpkg/), are you root?
You can become root by running ‘sudo su’, followed by your password. By default the first account that you create when you install Linux Mint should be able to become root.
3. Check OpenSSH Status
Once installed SSH should be automatically configured to start on system boot, and be already running. We’ll of course check this though rather than just assuming!
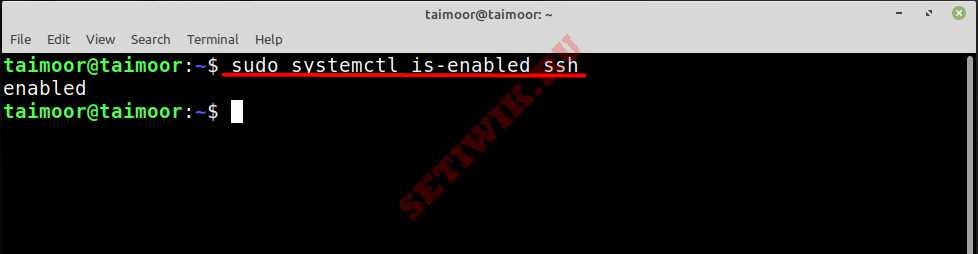
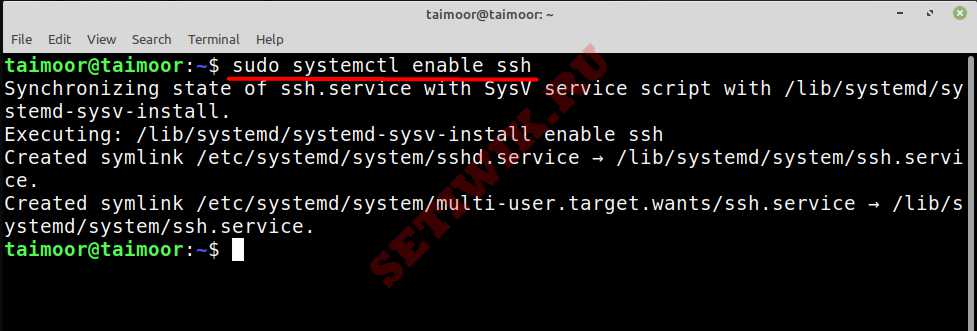
We can use ‘systemctl is-enabled’ as shown below to check that ssh is enabled to start automatically on system boot. If it comes back with ‘enabled’ then SSH should automatically start up on boot. If it’s disabled, you can run ‘systemctl enable ssh’ to enable to to start up on system boot.
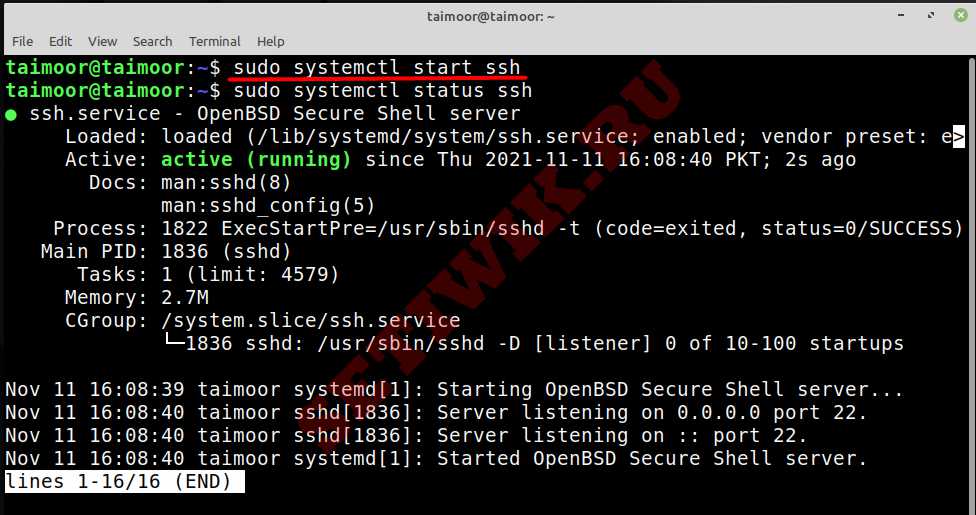
We can then use ‘systemctl is-active’ as shown below to check that ssh is currently active and running. If it comes back with ‘active’ then SSH is currently running. If it’s not running, you can run ‘systemctl start ssh’ to start it up.
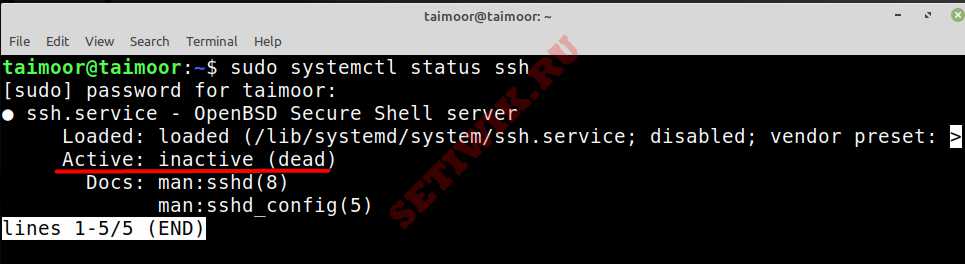
We can also use ‘systemctl status’ to get a quick overview of all information, in the example below we can see that it’s actively running as well as various useful information about the service.
4. Testing SSH Access
In this example we have confirmed that SSH is configured to start up on system boot automatically and is currently running, so let’s try and SSH to it from an external Windows system! We’ll do this using PuTTY.
You can display the IP address of the Linux Mint machine by running ‘ip a’ from the terminal.
rootusers@rootusers-virtual-machine ~ $ ip a
2: ens33: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:d3:f5:b0 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.20/24brd 192.168.1.255 scope global dynamic ens33
valid_lft 83316sec preferred_lft 83316sec
inet6 fe80::3286:aa53:7220:5fa7/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
We can see here that the IP address of our Linux Mint system is 192.168.1.20, so we’ll SSH to this using PuTTY from Windows. All you need to do is specify your username and password.
Note that by default the user ‘root’ will not have SSH access. This behaviour can be modified by editing the PermitRootLogin value in the ‘/etc/ssh/sshd_config’ file and then restarting SSH.
That’s all there is too it! We have now successfully established an SSH connection from Windows to Linux Mint, allowing us to remotely administer the Linux system over the network by running various commands via SSH.
Request a Login
Paul Allen maintains several publicly accessible historic computer systems, including an XKL TOAD-2 running TOPS-20. Request a login from Living Computers: Museum + Labs and try running TOPS-20 on a hardware emulated PDP-10.
Как включить SSH в Linux Mint
Включение SSH в Linux Mint— это одно из первых действий, которые вы должны сделать после установки операционной системы. Так как SSH предоставляет зашифрованный сетевой протокол для защиты удаленных учетных записей сервера и клиентов. Это позволяет вам удаленно получать доступ к вашей машине и безопасно выполнять операции сервером. SSH шифрует весь трафик между клиентом и сервером, чтобы предотвратить подслушивание, перехват соединений и другие типы атак.
Протокол Secure Shell (SSH) используется для управления или передачи данных между компьютерами через Интернет. Старые методы выполнения этих действий, такие как telnet, не обладают этими возможностями. Они небезопасны, так как передают пароль пользователя в виде открытого текста. А SSH предлагает безопасный маршрут по незащищенной сети, соединяющий клиентскую программу SSH с сервером SSH. В архитектуре клиент-сервер. Протокол Secure Shell в основном используется для связи с Unix-подобными операционными системами, хотя он также может использоваться в Windows.
Возможно вам будет интересно:
Как работает SSH
Клиент SSH по умолчанию позволяет подключаться к рабочим станциям Linux по защищенному каналу, и по умолчанию используется TCP-порт 22. SSH кодирует пакеты, делая невозможным для кого — либо наблюдение за вашей деятельностью. В отличие от telnet который не шифрует пакеты, так же telnet оставляет открытой возможность того, что кто-то прочитает, что вы делаете по SSH. В этой статье мы покажем вам, как включить безопасную оболочку (ssh) в Linux Mint.
Как установить сервер Openssh в Linux Mint
Вы можете установить сервер OpenSSH, открыв терминал и введя там следующую команду.
SSH должен автоматически запускаться при запуске системы и запускаться после установки. Однако вместо того, чтобы просто предполагать, мы перепроверим.
Чтобы проверить, включен ли SSH, и автоматически запуститься при запуске системы, выполните приведенную ниже команду.
Если терминал возвращает «включено» (enabled), SSH должен запускаться сразу после загрузки компьютера. Если он отключен или если статус неактивен, как показано на следующем рисунке:
Исправьте это используя следующую команду:
Теперь вы можете запустить службу SSH, набрав:
Мы также можем использовать «‘systemctl status» для получения краткой сводки всей информации. На приведенном выше изображении мы видим, что служба запущена и работает, а так же другие полезные сведения.
Как разрешить ssh соединение в брандмауэре Linux Mint
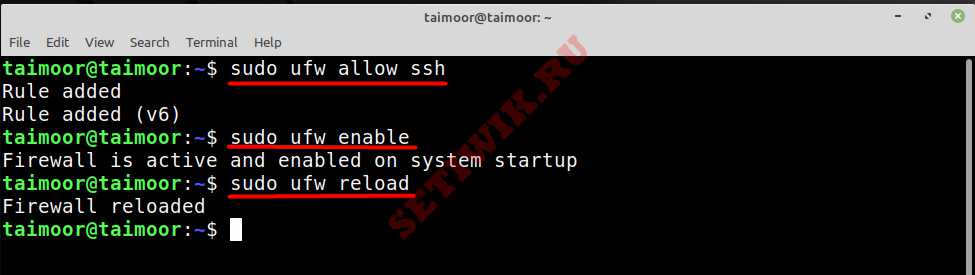
Иногда брандмауэр запрещает вам использовать соединение между клиентом и сервером. Итак, чтобы разрешить соединение, вам требуется ввести.
Это добавит правило в ваш брандмауэр, разрешающее подключение по ssh. Так же вы можете включить брандмауэр, если он в настоящее время отключен, введя.
Вам необходимо обновить вновь созданные настройки, чтобы реализовать их.Сделать это просто введите команду.
В приведенной выше команде UFW — это «простой брандмауэр» (uncomplicated firewall), который используется для управления брандмауэром Linux:
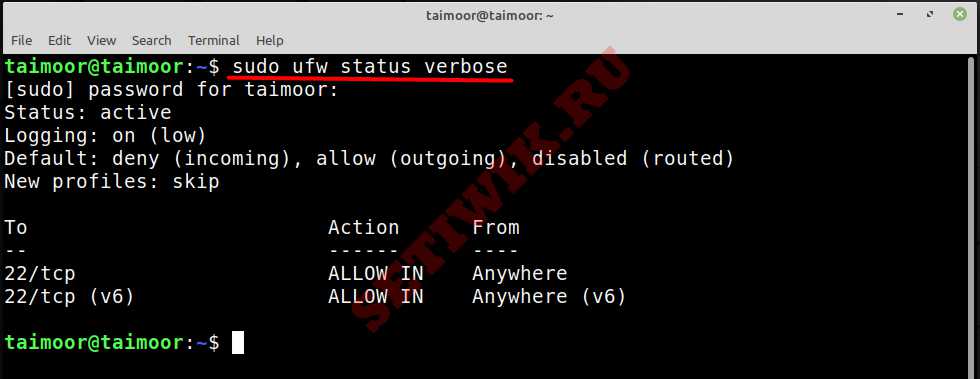
Вы также можете проверить состояние и полные сведения о брандмауэре ufw, введя команду.
Заключение
OpenSSH не установлен по умолчанию в Linux Mint, но его легко установить или включить. Это приложение устанавливает безопасное и зашифрованное соединение между сервером и клиентом. Мы продемонстрировали, как быстро настроить и использовать SSH в Linux Mint. После выполнения вышеупомянутого метода SSH будет активен автоматически при загрузке системы.
How To Enable SSH on Ubuntu 20.04/18.04, Linux Mint 20/19 & Debian 10/9
SSH (Secure Shell) is a cryptographic network protocol used for securing the remote login between server and client. SSH is a replacement for Telnet and other shell protocols such as rlogin, rsh, and rexec protocols.
Enabling SSH on Ubuntu is one of the tasks to do after the fresh installation of OS and helps you to connect your system remotely and perform tasks securely.
This post will show you how to enable SSH on Ubuntu 20.04/18.04, Linux Mint 20/19 & Debian 10/9. The steps mentioned in this article should also work on previous versions of Ubuntu / Linux Mint & Debian.
Prerequisites
To be able to enable SSH service, you need to be logged in as a root user or a user with sudo privileges.
Enable SSH on Ubuntu / Linux Mint / Debian
The reason you are not able to use SSH is that SSH server package is not installed on Ubuntu or Linux Mint or Debian by default. The SSH server package is available in the OS base repository, and it can be easily installed with apt command.
Open up a terminal with Ctrl + Alt + T .
Install SSH Server package using apt command.
sudo apt update sudo apt install -y openssh-server
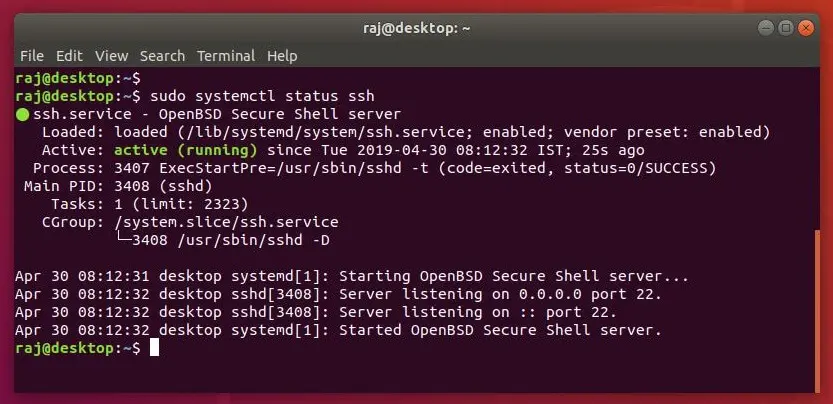
The SSH service will start automatically upon the completion of package installation. You can verify the SSH server package installation by running the following command.
sudo systemctl status ssh
The above screenshot confirms that the SSH service is up and running.
Allow SSH in Firewall
You may need to allow SSH incoming connections in firewall (Thanks to @arocee). So, use the below command to create a rule in UFW to allow SSH connections from external machines.
sudo ufw allow ssh sudo ufw enable sudo ufw reload
Access Ubuntu / Linux Mint / Debian Machine via SSH
You can connect to your system via SSH using putty from Windows or built-in SSH clients from Linux or macOS.
Windows
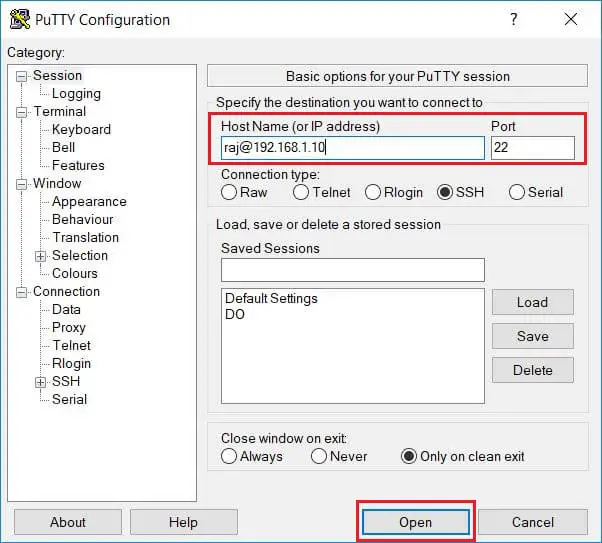
Enter the machine’s ip in the session window and click Open.
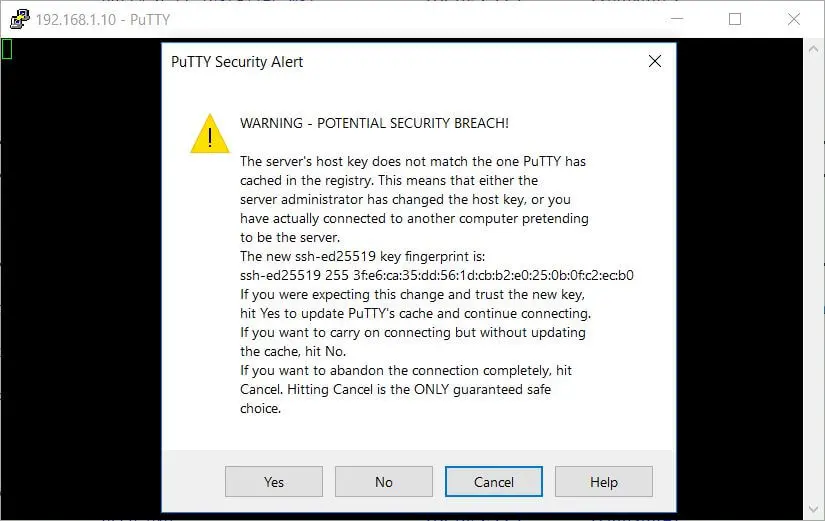
When you connect to the Ubuntu system for the first time, You may get a pop-up window to accept fingerprint. Click Yes to connect.
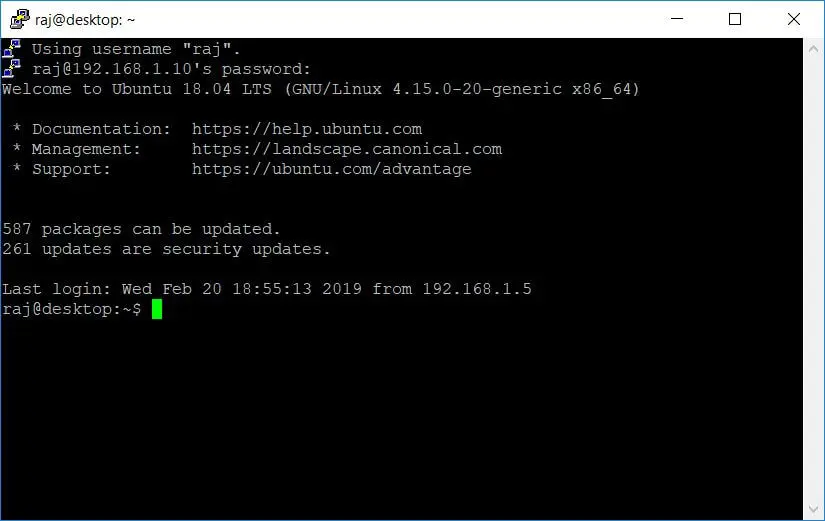
Enter the user’s password to login to the system. Upon successful login, you will get the shell prompt.
Linux
When you connect to the Ubuntu system for the first time, you will get a below message. Type Yes to continue connecting to your system.
The authenticity of host '192.168.1.10 (192.168.1.10)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:sueTz6FURcKDbeyGkpE7lUHOaosW/rkkvlG18v98T7Y. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? Yes Enter your system password.
On successful login, you will see a message similar to this.
You are now in into your system, and you can start performing administration tasks.
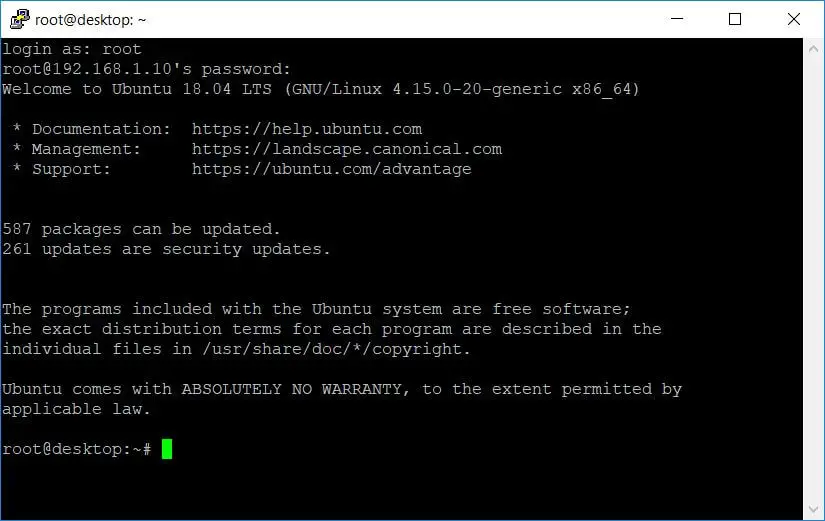
Enable SSH Root Access on Ubuntu / Linux Mint / Debian
By default, root login over SSH is not allowed on Ubuntu / Linux Mint / Debian. But, you can enable root login by editing the SSH configuration file.
Edit the sshd_config file.
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Set the PermitRootLogin to Yes
sudo systemctl restart ssh
Now you should be able to login directly as the root via ssh.
Disable SSH on Ubuntu / Linux Mint / Debian
For any reason you want to disable SSH on your system, you can just stop the SSH service by running the below command.
Also, you need to disable the SSH service so that it doesn’t start on system reboot.
sudo systemctl disable ssh
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned how to enable SSH on Ubuntu 20.04/18.04, Linux Mint 20/19 & Debian 10/9 system. You are now able to perform administration activities over a remote location through terminal.
Additionally, you can set up SSH Key-based authentication to connect to your Linux system without entering a password.
You can visit the official SSH manual page for more information on configuring SSH service.