- How To Configure NTP Server to Synchronize Time in Linux
- Synchronizing Time with NTP Server in Ubuntu / Linux Mint / Xubuntu / Debian
- To Install
- How to configure NTP on Linux Mint
- How to install NTP on Linux Mint
- How to allow NTP through firewall
- How to check NTP stats in Linux Mint
- How to configure NTP server on Linux Mint
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Taimoor Mohsin
- How To Setup NTP Server on Ubuntu & LinuxMint
- Pre-requisites:
- Step 1: Update Your System
- Step 2: Install NTP
- Step 3: Configure NTP Server
- Step 4: Allow NTP Through the Firewall
- Step 5: Restart NTP Service
- Step 6: Verify NTP is Working
- Conclusion
How To Configure NTP Server to Synchronize Time in Linux
Synchronizing Time with NTP Server in Ubuntu / Linux Mint / Xubuntu / Debian
Time synchronization is very important in order to determine when events happen in our system. You would like to have your system time to be accurate. The Network Time Protocol (NTP) helps you to keep your system clock updated and contacts its servers around the world depending upon the configuration and you may also configure it manually. To do so you need to edit default configuration file in /etc/ntp.conf file and then it will fetch the local time. The Network Time Protocol uses UDP port 123.
To Install
First open terminal and enter the following command to install NTP.
In case any error update your packages list or check your sources.list file at /etc/apt/ path.
[email protected]:~# apt-get install ntp Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required: libavahi-client-dev libavahi-common-dev libavahi-compat-libdnssd1 libdbus-1-dev libntdb1 libruby2.1 libyaml-0-2 python-ntdb ruby2.1 rubygems-integration Use ' apt-get autoremove' to remove them. The following extra packages will be installed: libopts25 Suggested packages: ntp-doc The following NEW packages will be installed: libopts25 ntp . . . Processing triggers for systemd (225-1ubuntu9) . Check NTP service status by running the following command.
[email protected]:~# service ntp status ? ntp.service - LSB: Start NTP daemon Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/ntp) Active: active (running) since Sat 2016-05-07 09:45:58 IST 36s ago Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8) CGroup: /system.slice/ntp.service ??9078 /usr/sbin/ntpd -p /var/run/ntpd.pid -g -u 121:129 May 07 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: proto: precision = 0.164 usec May 07 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: ntp_io: estimated max descriptors: 10. 16 May 07 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listen and drop on 0 v4wildcard 0.0.0. 23 May 07 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listen and drop on 1 v6wildcard :: UDP 123 May 07 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listen normally on 2 lo 127.0.0.1 UDP 123 May 07 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listen normally on 3 eno16777736 192. 23 May 07 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listen normally on 4 lo ::1 UDP 123 May 07 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listen normally on 5 eno16777736 fe80. 23 May 07 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: peers refreshed May 07 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listening on routing socket on fd #22. es Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full. NTPQ command utility is used to monitor NTP daemon and it’ s performance can be displayed using the command. [email protected]:~# ntpq -p remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter ============================================================================== 125.62.193.121 204.152.184.72 2 u 65 64 3 46.121 25.726 0.125 123.108.200.124 83.137.225.123 3 u 63 64 3 75.791 -9.424 17.527 juniperberry.ca 193.79.237.14 2 u 61 64 3 151.195 -4.491 16.551
You can also check the synchronization of ntp logs using the command.
[email protected]:~# tail -f /var/log/syslog May 7 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listen and drop on 1 v6wildcard :: UDP 123 May 7 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listen normally on 2 lo 127.0.0.1 UDP 123 May 7 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listen normally on 3 eno16777736 192.168.5.147 UDP 123 May 7 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listen normally on 4 lo ::1 UDP 123 May 7 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listen normally on 5 eno16777736 fe80::20c:29ff:fe28:2907 UDP 123 May 7 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: peers refreshed May 7 09:45:58 linuxhelp ntpd[9078]: Listening on routing socket on fd #22 for interface updates How to configure NTP on Linux Mint
NTP, also known as Network Time Protocol, is one of the most reliable methods for synchronizing internal clock timings on systems in a network, as its name implies. After that, you don’t need to manually check and set your time if your system supports NTP. The operating system is in charge of time zone management, whereas NTP is in charge of synchronizing the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
A fraction of a time difference might trigger various problems for your system. When it comes to tracking security-related concerns, having perfectly synched time is critical; troubleshooting can be tough if the timestamps in log files are inaccurate and even in financial services, reliable timekeeping is essential. Troubleshooting issues, performance monitoring, network acceleration, and network management systems all rely on the accuracy of timestamps. So you can save yourself from such problems if you have properly configured NTP on your operating system.
How to install NTP on Linux Mint
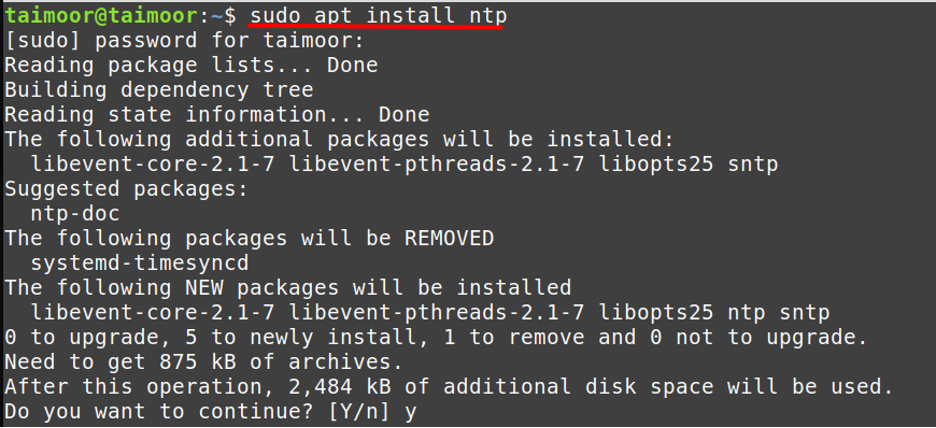
So the first step is to install the Network Time Protocol to utilize its functionality by typing:
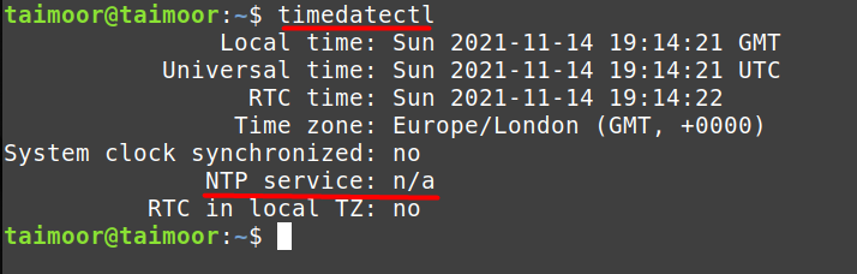
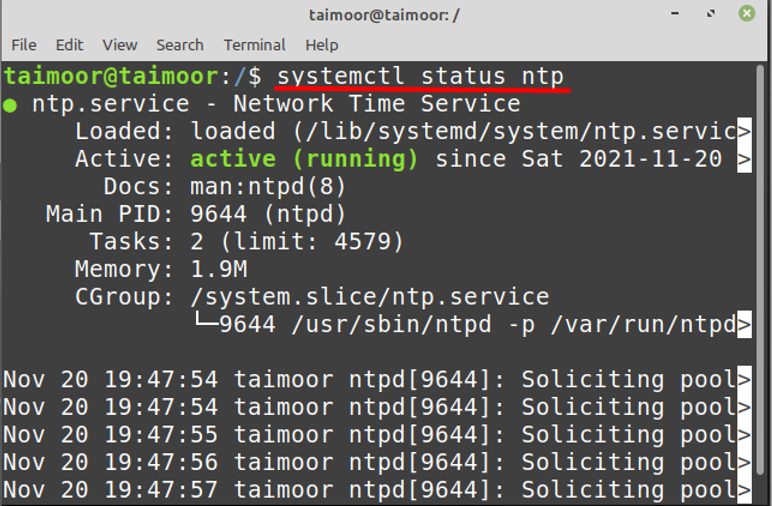
After that you need to verify if the NTP services are now active or not by typing:
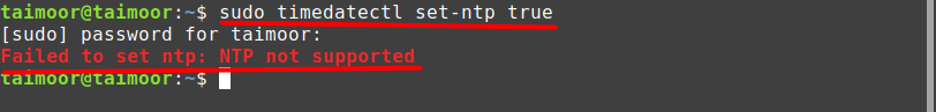
As you can see currently, the NTP service is not available although you have already installed it. So there are multiple ways to activate this service and for that, you can type.
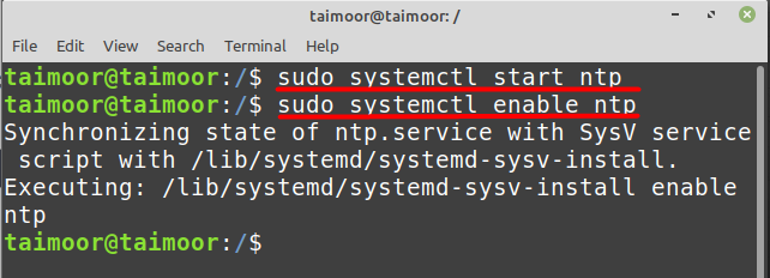
It can be seen that after running the command it is still showing an error that “NTP not supported”. Now what you can do in such a situation is to run start and enable commands that can solve this issue and activate the NTP services:
After enabling the NTP services the next step is to restart the services so that these new settings can be worked:
There is a high chance that you are able to solve this problem after using this command, you can verify it by typing.
How to allow NTP through firewall
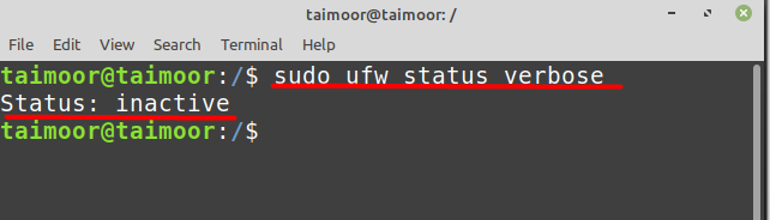
After installing and activating the NTP services, the next step is to allow it through the firewall so that it can synchronize the network on all the servers. But, before that you need to make sure that the firewall is currently active in your OS or not by typing:
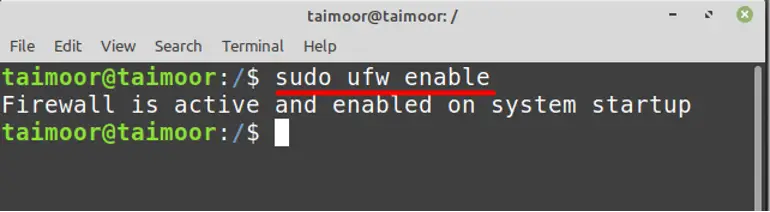
The firewall is currently inactive, so you can activate it by typing:
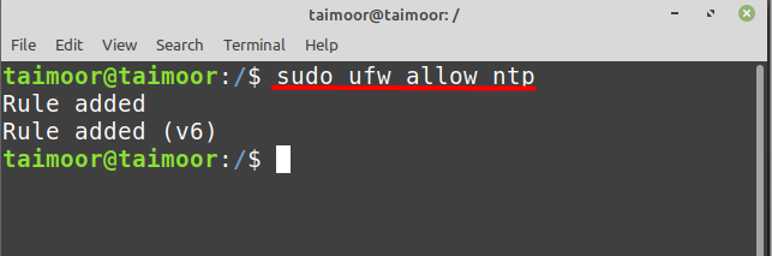
Now you need to allow the NTP services on the firewall so that the communication can be established between the client and server by typing.
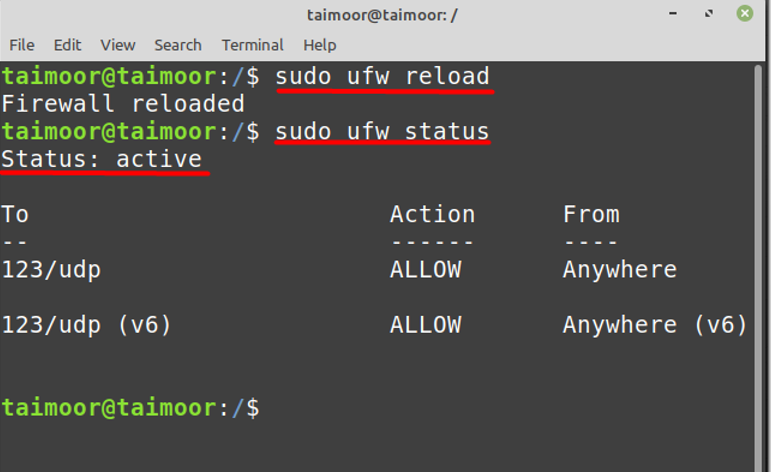
To implement the newly made changes, you need to restart the firewall settings:
Later you can check the status of the firewall and the NTP by typing:
How to check NTP stats in Linux Mint
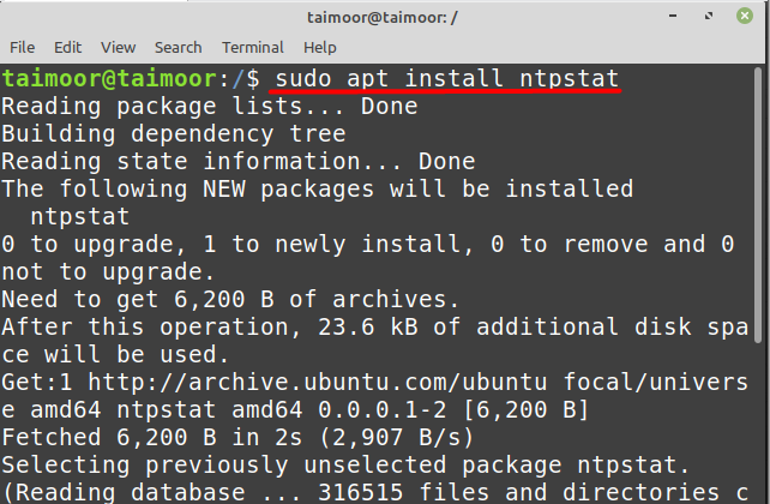
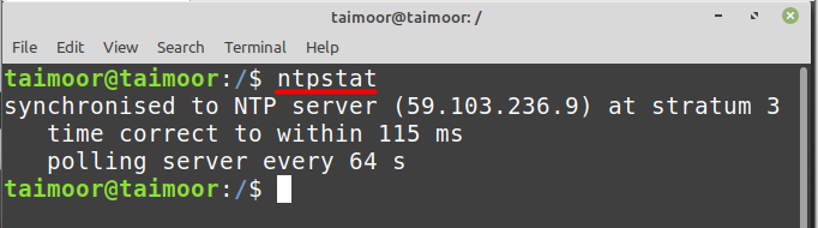
Now to check if your NTP services are synchronized with the server or not and you can do that by installing the NTP stat utility:
After its installation, you can verify the NTP synchronization by typing:
How to configure NTP server on Linux Mint
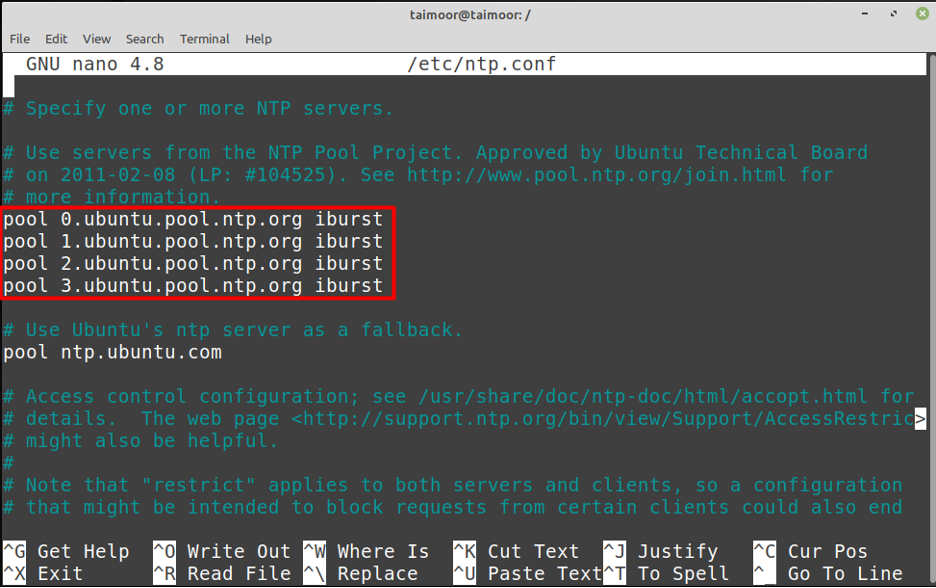
To set up an NTP server you need to make some changes to the NTP configuration which is available on “/etc/ntp.conf ” file and you can do that by using any editor:
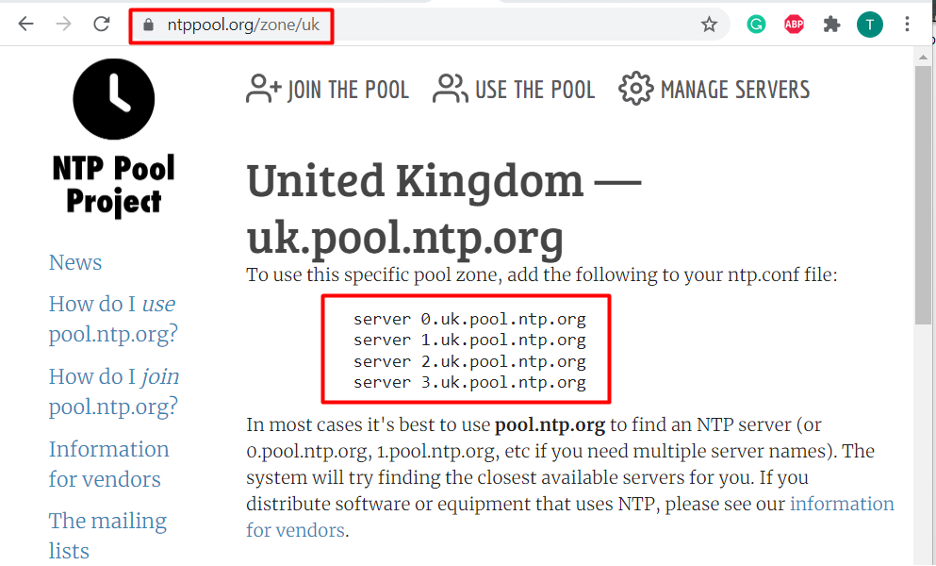
Now, the next step is to choose the pool server that you want to synchronize with your NTP server by visiting their official website. After that, you need to select a server pool from which you need to synchronize your time, as in our case we have selected the pool from the United Kingdom.
After that you need to copy the UK pool zone and then paste those in the ntp.conf file that you have already opened:
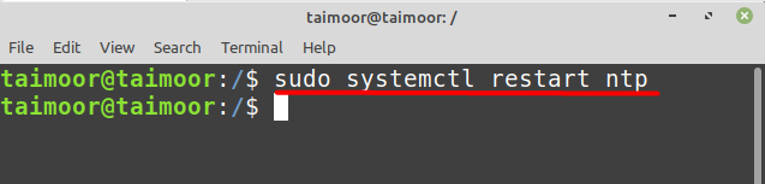
Now you need to restart the NTP to implement the newly made settings by typing again:
After that you need to check the status of NTP if everything is working fine or not by typing:
Conclusion
Network time protocol is a very essential utility if you want to synchronize your clock with the outside world. Monitoring security-related concerns necessitate exact time alignment; similarly, troubleshooting might be difficult if log file timestamps are inaccurate. In this article, we have discussed what problems you can face while configuring the NTP, and how you can solve those problems in Linux Mint distribution.
About the author
Taimoor Mohsin
Hi there! I’m an avid writer who loves to help others in finding solutions by writing high-quality content about technology and gaming. In my spare time, I enjoy reading books and watching movies.
How To Setup NTP Server on Ubuntu & LinuxMint
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a protocol used to synchronize computer clock times in a network of computers. NTP uses Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) to synchronize computer clock times to a millisecond, and sometimes to a fraction of a millisecond. Setting up an NTP Server on Ubuntu & Linux Mint involves a series of steps which are detailed below.
Pre-requisites:
Before we begin, please ensure you have the following:
- A machine running Ubuntu or Linux Mint.
- Sudo or root access to run privileged commands.
- A stable internet connection.
Step 1: Update Your System
First, update your system to the latest package versions. This helps to ensure that you have the latest security patches and system updates. Open Terminal and execute the following commands:
sudo apt-get updatesudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2: Install NTP
The next step is to install the NTP package which is available in the default Ubuntu & Linux Mint repositories. Run the following command to install NTP:
Step 3: Configure NTP Server
Once installed, you need to configure the NTP server. The configuration file for NTP is located at /etc/ntp.conf. Use your favorite text editor to edit this file. For example, to use nano, type:
In this configuration file, you can specify the NTP servers to which your machine will synchronize. These servers are specified in lines that begin with “server”. For example:
The iburst option allows the system to send a burst of packets if the server is unreachable.
Save your changes and close the editor.
Step 4: Allow NTP Through the Firewall
If you have a firewall enabled, you need to allow NTP through it. NTP uses UDP port 123, so you will need to allow this port through the firewall. If you’re using ufw firewall, you can do this with the following command:
Step 5: Restart NTP Service
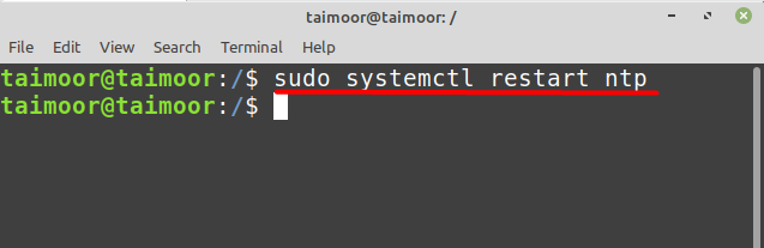
After making the changes, restart the NTP service for the changes to take effect. Use the following command to restart the NTP service:
sudo systemctl restart ntp Step 6: Verify NTP is Working
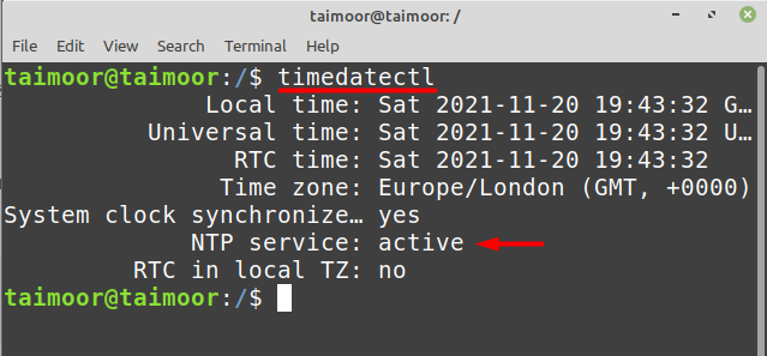
Finally, you should verify that NTP is working correctly. You can do this by querying the NTP service status and peers.
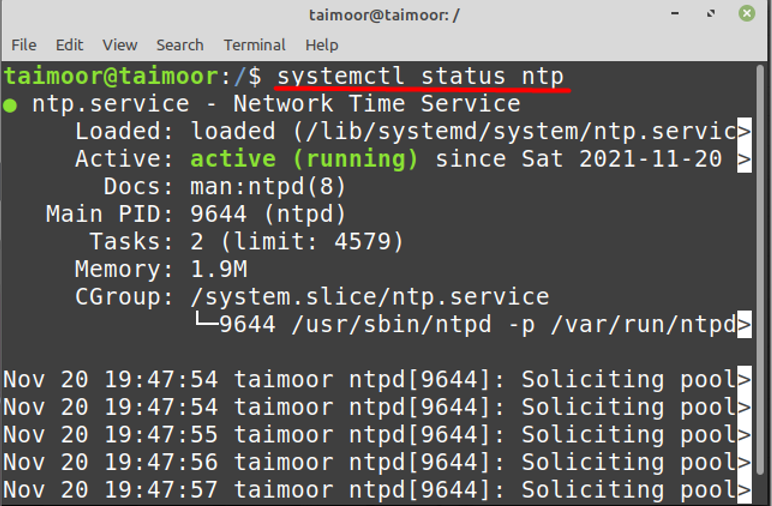
To check the status of the NTP service, use:
sudo systemctl status ntp To check the synchronization status, use:
This will display a list of configured NTP peers, along with information about the synchronization with each. Look for a * symbol next to one of the peers. This indicates that your NTP server is synchronizing with that peer.
Congratulations, you’ve set up an NTP server on your Ubuntu or Linux Mint machine!
Conclusion
Setting up an NTP server is a crucial task for maintaining correct time across all machines in a network. By following this guide, you now have a better understanding of how to install, configure, and verify the NTP server in Ubuntu & Linux Mint.
Bear in mind, managing an NTP server involves regular monitoring to ensure accurate synchronization of time. You should also keep your system and NTP software updated for best security and performance.