- How to Install and Run a TFTP Server?
- How to Install a TFTP Server?
- How to Run TFTP Server on Linux?
- (Optional): For Dead State
- Transfer a File (Server to Local Machine)
- Transfer a File (Local Machine to Server)
- Conclusion
- How to configure TFTP server on Linux Mint
- How to install TFTP server on Linux Mint
- How to configure TFTP server on Linux Mint
- How to enable the TFTP on Linux Mint
- How to download a file from TFTP server on Linux Mint
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Sharqa Hameed
How to Install and Run a TFTP Server?
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is a simple file transfer protocol that is used to share files between devices over the network. A TFTP server runs the TFTP protocol and allows clients to upload or download files to or from the server. It has various applications, such as updating firmware, transferring configuration files, and synchronizing files between Linux machines.
This guide will present the steps to install and run a TFTP server on Linux.
- How to Install a TFTP Server?
- Update Package Lists
- Install TFTP Server
- Configure TFTP Server
- Create TFTP Server Directory
- Set Permissions on TFTP Server Directory
- Restart TFTP Server
- Check the Services of the TFTP Server
- Enable the TFTP Server
- Test the TFTP Server By Transferring Files
How to Install a TFTP Server?
To install the TFTP server on the linux, follow the below-mentioned steps:
Step 1: Update Package Lists
It is a good practice to update package lists before installing any new software. To update the package lists, use the below commands for some popular Linux distributions:
$ sudo apt update # Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Debian $ sudo yum update # CentOS $ sudo dnf update # Fedora
It ensures that users have the latest package information available.
Step 2: Install TFTP Server
To install the TFTP server, specify the “tftpd-hpa” package with the “install” utility:
$ sudo apt install tftpd-hpa # Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Debian $ sudo yum install tftp-server # CentOS $ sudo dnf install tftp-server tftp # Fedora
This command installs the TFTP server package on the Ubuntu system.
Step 3: Configure TFTP Server
Once the installation is complete, users need to configure the TFTP server. To do this, open the “tftpd-hpa” file via the “nano” editor in the below command:
$ sudo nano /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
It opens the configuration file in the nano text editor. In this file, set the TFTP server directory to “/var/lib/tftpboot” and the TFTP server IP address to 0.0.0.69 to allow connections from any IP address:
TFTP_DIRECTORY="/var/lib/tftpboot" TFTP_ADDRESS="0.0.0.0:69"
Save and close the configuration file.
Note: TFTP servers listen on a designated port (default port number is 69) for incoming client TFTP requests.
Step 4: Create TFTP Server Directory
When setting up a TFTP server, users need to configure the server to point to the directory where the files that clients will request are stored. To create the TFTP server directory, use the “mkdir” command by specifying the path:
$ sudo mkdir /var/lib/tftpboot
It creates a directory named “tftpboot” in the “/var/lib” directory.
Step 5: Set Permissions on TFTP Server Directory
After creating the TFTP server directory, set the 777 permissions on the “tftpboot” directory. It ensures the security and integrity of the system and prevents unauthorized access or modification of files on the server. To do this, execute the below commands:
$ sudo chmod -R 777 /var/lib/tftpboot $ sudo chown -R nobody:nogroup /var/lib/tftpboot
These commands set the permissions on the “tftpboot” directory to allow any user to read, write, and execute files in the directory. They also set the directory ownership to the nobody user and nogroup.
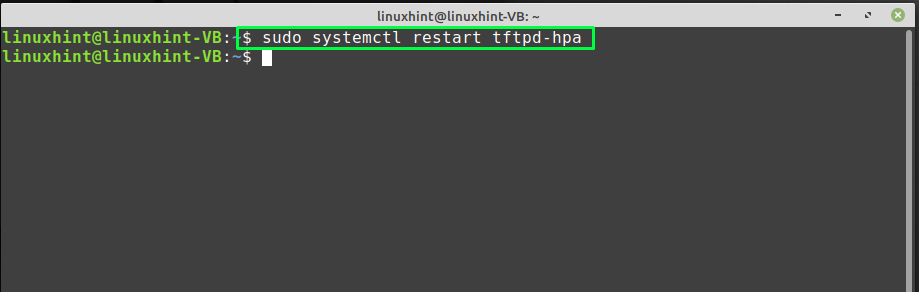
Step 6: Restart TFTP Server
Finally, restart the TFTP server to apply all changes. To do this, run the “systemctl” command with the “restart” option:
$ sudo systemctl restart tftpd-hpa
This command restarts the TFTP server service on your Linux system.
How to Run TFTP Server on Linux?
To run the TFTP server on Linux, follow the step-by-step instructions:
Step 1: Check the Services of the TFTP Server
To verify the services of the TFTP server, utilize the “systemctl” command with the “status” option as below:
$ sudo systemctl status tftpd-hpa
The “active (running)” status represents that the TFTP server has been installed and configured on the Linux system.
(Optional): For Dead State
If the services are in a dead state, users can start them using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl start tftpd-hpa
It starts the TFTP server if services are not in an active state.
Step 2: Enable the TFTP Server
To enable the TFTP server, use the “systemctl” command with the “enable” option to start automatically at boot time using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl enable tftpd-hpa
The output shows that “tftpd-hpa” services have been enabled in the system.
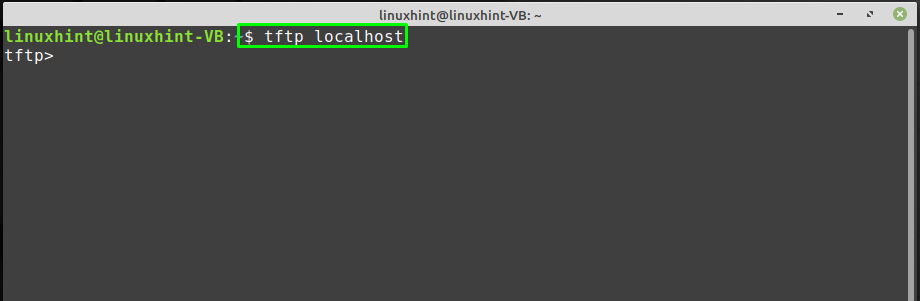
Step 3: Test the TFTP Server
To test that the TFTP server is working properly, use a “tftp” command with the IP address of the machine:
The TFTP server has been successfully connected.
Transfer a File (Server to Local Machine)
To transfer a file from the TFTP server to the local machine, use the “get” command by specifying the filename as “file.txt”:
The output shows that the “file.txt” has been transferred to the local machine from the server.
Transfer a File (Local Machine to Server)
To transfer a file from the local machine to the server, utilize the “put” command by specifying the “file.txt” that is present in the home directory (give the complete path if it is located somewhere else):
The above command confirms that “file.txt” has been transferred from the local machine to the server.
Conclusion
To install the TFTP server on Linux, use the “tftpd-hpa” or “tftp-server” package via the “APT”, “YUM,” or “DNF” package managers. Before running the TFTP, ensure that it is configured properly and perform the necessary modifications in the config file of TFTP. After the configuration, users can transfer files to and from the server via the “tftp” command by specifying the IP address.
This article has illustrated the step-by-step procedure to install and run the TFTP server in Linux.
How to configure TFTP server on Linux Mint
The system administrators and the IT professionals mainly utilize Trivial File Transfer Protocol or TFTP for upgrading codes, booting PCs, transferring files, creating a backup of the router and network configuration files. There are several ways to host a TFTP server on Linux Mint for permitting the users to perform specific tasks. The “tftpd” package is considered the tool for configuring a TFTP server. If you are new to the Linux Mint and want to configure the TFTP server on your Linux Mint server, then you are at the right post! This write-up will explain how to install and configure the TFTP server. Moreover, the method for testing the TFTP server via a file download will also be provided. So, let’s start!
How to install TFTP server on Linux Mint
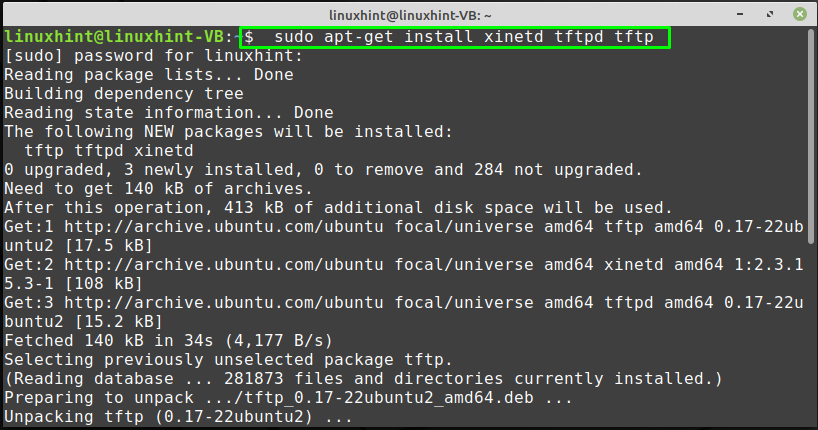
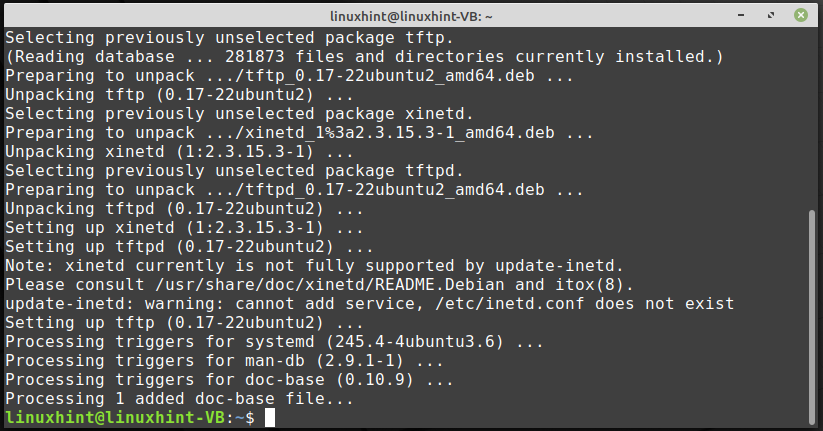
On your Linux Mint system, if you want to install TFTP and its related packages then, open up your terminal by pressing “CTRL+ALT+T” and execute the below-given command:
The error-free output signifies that TFTP has all of the required packages now installed on your system:
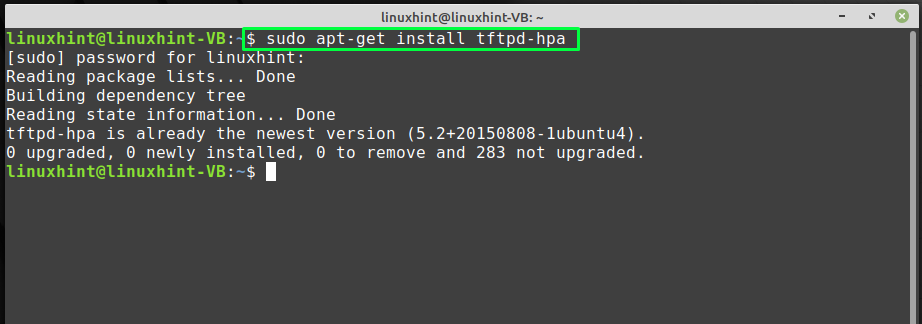
The BSD TFTP client and server have been upgraded with tftp-hpa as it has a lot of bug fixes and improvements. Install “tftpd-hpa” on your Linux Mint system by utilizing the following command:
Now, move towards the configuration of the TFTP server.
How to configure TFTP server on Linux Mint
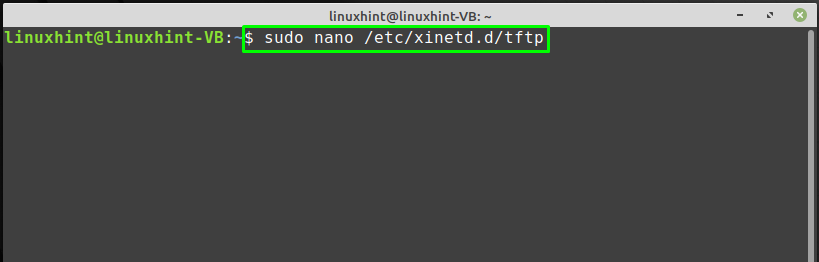
To configure the TFTP server, the first thing you have to do is to create a TFTP configuration file in the “/etc/xinetd.d” directory:
The “nano” editor will create and edit the file in it:
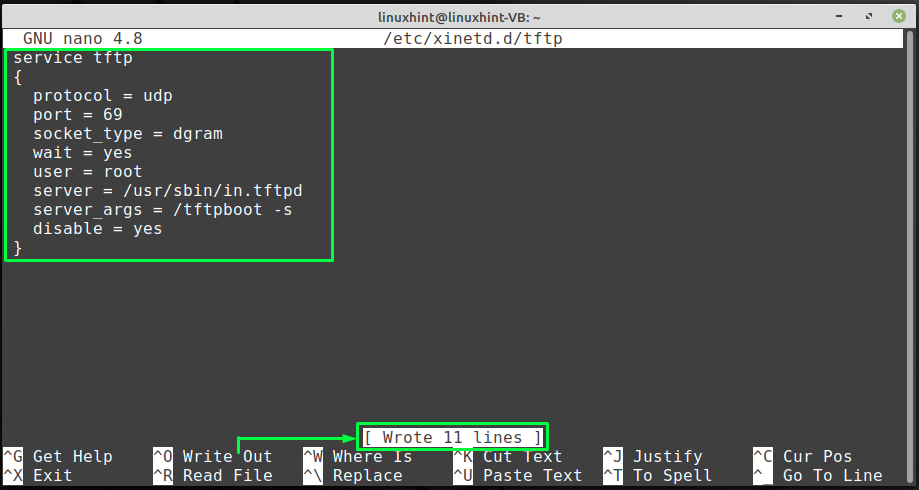
Now, add the following content in the opened “/etc/xinetd.d/tftp” file. Here, we are assigning values to different arguments which are linked with the TFTP configuration, such as the port number, protocol, socket type:
service tftp
{
protocol = udp
port = 69
socket_type = dgram
wait = yes
user = root
server = / usr / sbin / in.tftpd
server_args = / tftpboot -s
disable = yes
}After writing the above-given code in the TFTP configuration file, press “CTRL+O” to save the file content.
Note: Carefully specify the “user” and the “sys_args” arguments, as both of them will be utilized in the whole configuration procedure:
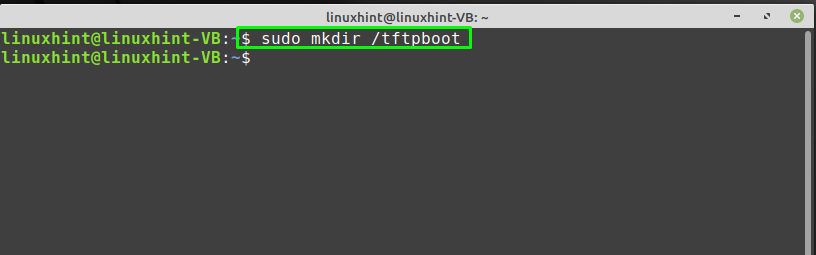
In the next step, we will create a directory “/tftpboot” as specified in the “server_args” of the TFTP configuration file by utilizing the below-given “mkdir” command:
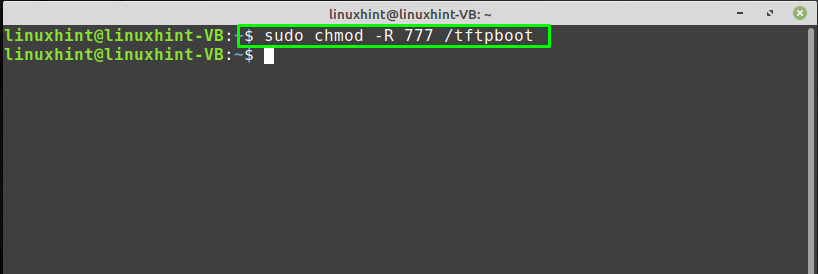
After creating the “/tftpboot” directory, change its permissions with the help of “chmod” command:
The execution of the above-given command will make the “/tftpboot” directory readable, writeable, and executable by all users:
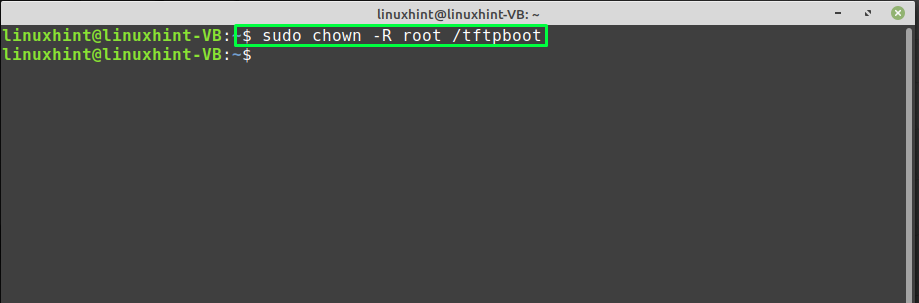
Next, change the owner of the “/tftpboot” directory to one which you have added in the TFTP configuration file “user” argument:
How to enable the TFTP on Linux Mint
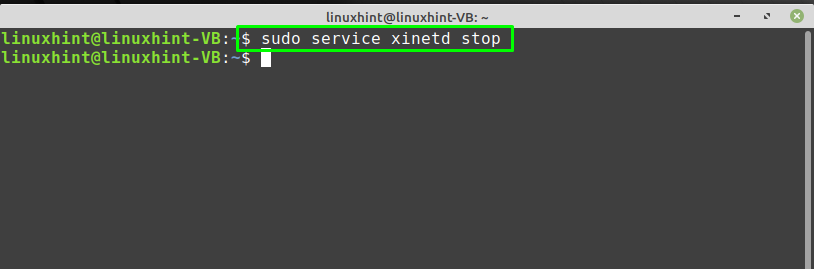
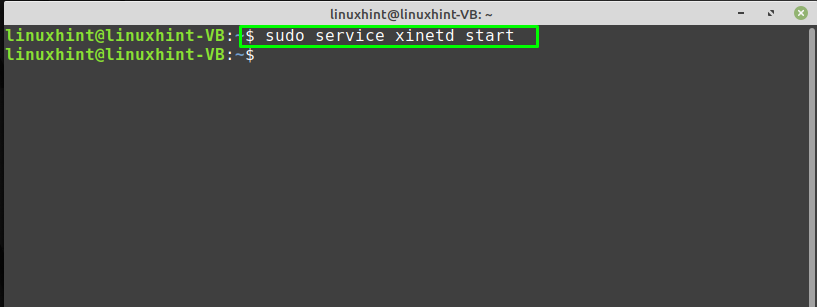
The “xinetd” is an acronym for “Extended Internet Services Daemon“. On Linux-based systems such as Linux Mint, xinetd daemon manages some popular network services, including TFTP. To enable the TFTP service on the Linux Mint, stop the “xinetd” daemon at first and then start it again by typing the following commands:
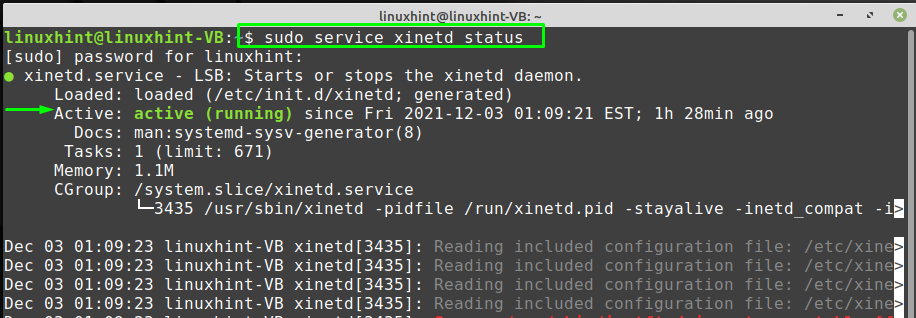
After doing so, check out the status of “xinetd” daemon to verify if it is active or not:
Lastly, enable the “tftpd-hpa” service by executing the following command:
Until now, we have installed and successfully configured the TFTP server on our Linux Mint system. Now, we will test the working of the TFTP server in the next section.
How to download a file from TFTP server on Linux Mint
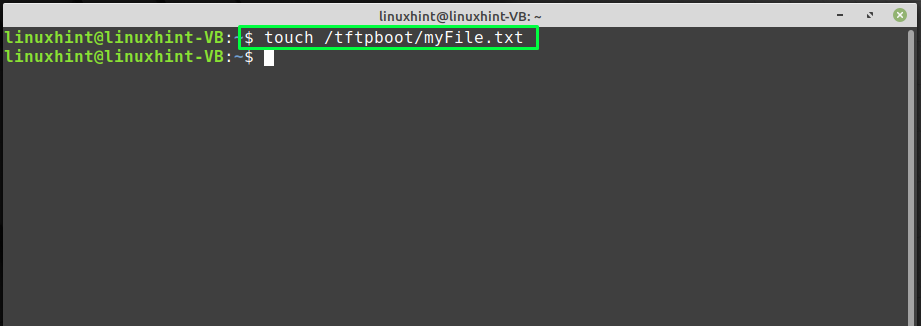
Downloading a file from the TFTP server is a good option for testing the TFTP server. Want to try it out? Firstly, create a new file under the directory you have added in the “sys_args” of the TFTP configuration file. In our case, we will create a sample “myFile.txt” file under the “/tftpboot” directory by writing out the following “touch” command:
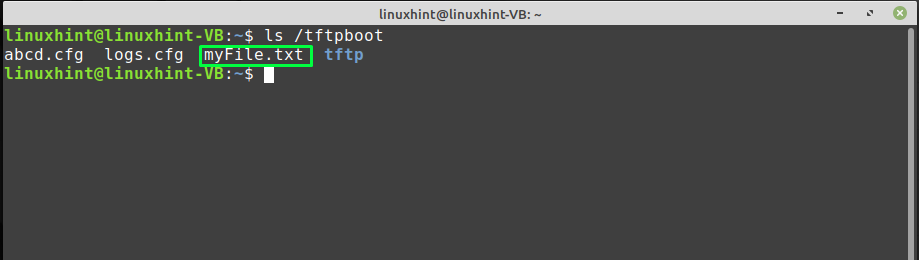
Next, confirm the presence of the created “myFile.txt” file:
Now, we will try to download the created “myFile.txt” from the TFTP server to our home directory by logging in to our TFTP server:
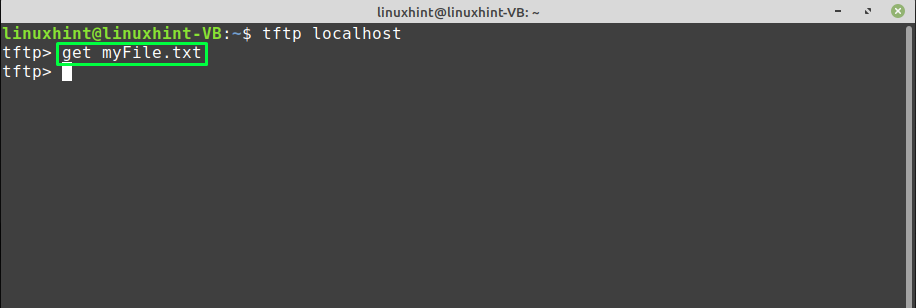
After that, utilize the “get” command with the name of the file, which you want to download from the TFTP server:
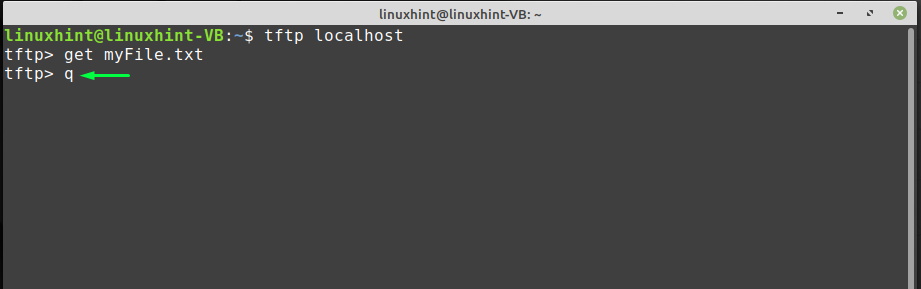
Press “q” to quit and check out the downloaded file in your home directory:
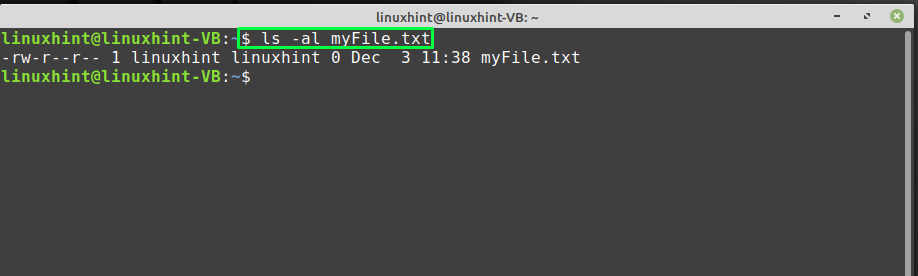
From the output, you can see that the “myFile.txt” file is successfully downloaded from the TFTP server:
Conclusion
IT professionals and network engineers are highly familiar with the TFTP. TFTP provides the backup option, upgrade, and configuration files to its users. It is beneficial to utilize by the users who are continuously monitoring the routers and Cisco switches. On Linux Mint, the configuration of TFTP is not as difficult as it seems. This write-up guided you in installing and configuring the TFTP server on Linux Mint. Moreover, the procedure of downloading a file from a TFTP server is also provided.
About the author
Sharqa Hameed
I am a Linux enthusiast, I love to read Every Linux blog on the internet. I hold masters degree in computer science and am passionate about learning and teaching.