- How to find ethernet network card firmware and driver information in Linux
- Linux Base Driver for Intel(R) Ethernet Network Connection¶
- Contents¶
- Identifying Your Adapter¶
- Command Line Parameters¶
- max_vfs¶
- Debug¶
- Additional Features and Configurations¶
- Jumbo Frames¶
- ethtool¶
- Enabling Wake on LAN (WoL)¶
- Multiqueue¶
- MAC and VLAN anti-spoofing feature¶
- Setting MAC Address, VLAN and Rate Limit Using IProute2 Tool¶
- Credit Based Shaper (Qav Mode)¶
- Support¶
- How to find network card driver name and version on Linux
- Method One: dmesg
- Method Two: ethtool
- Method Three: lshw
- Support Xmodulo
How to find ethernet network card firmware and driver information in Linux
Based n the Linux Variant you use the commands and their output may differ. I have worked on Red hat Enterprise Linux and SuSE Enterprise Linux and below commands and method have been really very useful to get the driver and firmware details of the Ethernet Network Card connected to the system
I prefer using the OS provided tools and not some other third party tools because just to get the NIC driver and firmware version I don’t want to go through all browsing, download, getting over my firewall, copying to my blade (as in office environment generally we don’t have internet access to our Linux blades) when we already have bunch of OS provided tools which can be used for this purpose.
Below command can be used on both SuSE and RHEL which has two different sections with separate firmware and driver version details.
# ethtool -i eth0 driver: be2net version: 11.2.1263.16 firmware-version: 11.2.1263.19 expansion-rom-version: bus-info: 0000:06:00.0 supports-statistics: yes supports-test: yes supports-eeprom-access: yes supports-register-dump: no supports-priv-flags: yes
Based on the driver name you get from the above command you can get more details on the module it is using from below command
# modinfo be2net filename: /lib/modules/3.10.0-693.5.2.el7.x86_64/weak-updates/be2net/be2net.ko supported: external license: GPL author: Emulex Corporation description: Emulex OneConnect NIC Driver 11.2.1263.16 version: 11.2.1263.16
Few more examples on a hardware with different Ethernet Network card
# ethtool -i eth0 driver: igb version: 5.2.15-k firmware-version: 2.1.5 bus-info: 0000:01:00.0 supports-statistics: yes supports-test: yes supports-eeprom-access: yes supports-register-dump: yes
# modinfo igb filename: /lib/modules/3.0.101-100-default/kernel/drivers/net/ethernet/intel/igb/igb.ko version: 5.2.15-k license: GPL description: Intel(R) Gigabit Ethernet Network Driver author: Intel Corporation,
Below are some more commands you can use to get the NIC firmware and driver related details and information
On SLES
# hwinfo --network | grep Driver | sort | uniq Driver Modules: "igb" Driver: "igb"
On RHEL 7
Next is ‘lshw’ utility, if this is not available you can get this from the Red Hat repo.
# rpm -qf /usr/sbin/lshw lshw-B.02.18-7.el7.x86_64 # lshw -c network *-network:0 description: Ethernet interface product: OneConnect NIC (Skyhawk) vendor: Emulex Corporation physical id: 0 bus info: pci@0000:06:00.0 logical name: eth0 version: 10 serial: 00:17:a4:77:00:0e size: 1Gbit/s width: 64 bits clock: 33MHz capabilities: pm msix pciexpress vpd bus_master cap_list rom ethernet physical autonegotiation configuration: autonegotiation=on broadcast=yes driver=be2net driverversion=11.2.1263.16 duplex=full firmware=11.2.1263.19 latency=0 link=yes multicast=yes slave=yes speed=1Gbit/s As you see here it also gives us enough detailed information about the available Ethernet Card with the firmware and driver version along with the driver name
Linux Base Driver for Intel(R) Ethernet Network Connection¶
Intel Gigabit Linux driver. Copyright(c) 1999-2018 Intel Corporation.
Contents¶
- Identifying Your Adapter
- Command Line Parameters
- Additional Configurations
- Support
Identifying Your Adapter¶
For information on how to identify your adapter, and for the latest Intel network drivers, refer to the Intel Support website: https://www.intel.com/support
Command Line Parameters¶
If the driver is built as a module, the following optional parameters are used by entering them on the command line with the modprobe command using this syntax:
There needs to be a for each network port in the system supported by this driver. The values will be applied to each instance, in function order. For example:
In this case, there are two network ports supported by igb in the system.
NOTE: A descriptor describes a data buffer and attributes related to the data buffer. This information is accessed by the hardware.
max_vfs¶
This parameter adds support for SR-IOV. It causes the driver to spawn up to max_vfs worth of virtual functions. If the value is greater than 0 it will also force the VMDq parameter to be 1 or more.
The parameters for the driver are referenced by position. Thus, if you have a dual port adapter, or more than one adapter in your system, and want N virtual functions per port, you must specify a number for each port with each parameter separated by a comma. For example:
This will spawn 4 VFs on the first port.
This will spawn 2 VFs on the first port and 4 VFs on the second port.
NOTE: Caution must be used in loading the driver with these parameters. Depending on your system configuration, number of slots, etc., it is impossible to predict in all cases where the positions would be on the command line.
NOTE: Neither the device nor the driver control how VFs are mapped into config space. Bus layout will vary by operating system. On operating systems that support it, you can check sysfs to find the mapping.
NOTE: When either SR-IOV mode or VMDq mode is enabled, hardware VLAN filtering and VLAN tag stripping/insertion will remain enabled. Please remove the old VLAN filter before the new VLAN filter is added. For example:
ip link set eth0 vf 0 vlan 100 // set vlan 100 for VF 0 ip link set eth0 vf 0 vlan 0 // Delete vlan 100 ip link set eth0 vf 0 vlan 200 // set a new vlan 200 for VF 0
Debug¶
This parameter adjusts the level debug messages displayed in the system logs.
Additional Features and Configurations¶
Jumbo Frames¶
Jumbo Frames support is enabled by changing the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) to a value larger than the default value of 1500.
Use the ifconfig command to increase the MTU size. For example, enter the following where is the interface number:
Alternatively, you can use the ip command as follows:
ip link set mtu 9000 dev eth ip link set up dev eth
This setting is not saved across reboots. The setting change can be made permanent by adding ‘MTU=9000’ to the file:
NOTE: The maximum MTU setting for Jumbo Frames is 9216. This value coincides with the maximum Jumbo Frames size of 9234 bytes.
NOTE: Using Jumbo frames at 10 or 100 Mbps is not supported and may result in poor performance or loss of link.
ethtool¶
The driver utilizes the ethtool interface for driver configuration and diagnostics, as well as displaying statistical information. The latest ethtool version is required for this functionality. Download it at:
Enabling Wake on LAN (WoL)¶
WoL is configured through the ethtool utility.
WoL will be enabled on the system during the next shut down or reboot. For this driver version, in order to enable WoL, the igb driver must be loaded prior to shutting down or suspending the system.
NOTE: Wake on LAN is only supported on port A of multi-port devices. Also Wake On LAN is not supported for the following device: — Intel(R) Gigabit VT Quad Port Server Adapter
Multiqueue¶
In this mode, a separate MSI-X vector is allocated for each queue and one for “other” interrupts such as link status change and errors. All interrupts are throttled via interrupt moderation. Interrupt moderation must be used to avoid interrupt storms while the driver is processing one interrupt. The moderation value should be at least as large as the expected time for the driver to process an interrupt. Multiqueue is off by default.
REQUIREMENTS: MSI-X support is required for Multiqueue. If MSI-X is not found, the system will fallback to MSI or to Legacy interrupts. This driver supports receive multiqueue on all kernels that support MSI-X.
NOTE: On some kernels a reboot is required to switch between single queue mode and multiqueue mode or vice-versa.
MAC and VLAN anti-spoofing feature¶
When a malicious driver attempts to send a spoofed packet, it is dropped by the hardware and not transmitted.
An interrupt is sent to the PF driver notifying it of the spoof attempt. When a spoofed packet is detected, the PF driver will send the following message to the system log (displayed by the “dmesg” command): Spoof event(s) detected on VF(n), where n = the VF that attempted to do the spoofing
Setting MAC Address, VLAN and Rate Limit Using IProute2 Tool¶
You can set a MAC address of a Virtual Function (VF), a default VLAN and the rate limit using the IProute2 tool. Download the latest version of the IProute2 tool from Sourceforge if your version does not have all the features you require.
Credit Based Shaper (Qav Mode)¶
When enabling the CBS qdisc in the hardware offload mode, traffic shaping using the CBS (described in the IEEE 802.1Q-2018 Section 8.6.8.2 and discussed in the Annex L) algorithm will run in the i210 controller, so it’s more accurate and uses less CPU.
When using offloaded CBS, and the traffic rate obeys the configured rate (doesn’t go above it), CBS should have little to no effect in the latency.
The offloaded version of the algorithm has some limits, caused by how the idle slope is expressed in the adapter’s registers. It can only represent idle slopes in 16.38431 kbps units, which means that if a idle slope of 2576kbps is requested, the controller will be configured to use a idle slope of ~2589 kbps, because the driver rounds the value up. For more details, see the comments on igb_config_tx_modes() .
NOTE: This feature is exclusive to i210 models.
Support¶
For general information, go to the Intel support website at:
or the Intel Wired Networking project hosted by Sourceforge at:
If an issue is identified with the released source code on a supported kernel with a supported adapter, email the specific information related to the issue to e1000-devel @ lists . sf . net.
© Copyright The kernel development community.
How to find network card driver name and version on Linux
Question: An Ethernet network interface card is attached to my Linux box, and I would like to know which network adapter driver is installed for the NIC hardware. Is there a way to find out the name and version of a network card driver for my network card?
For network interface card (NIC) hardware to operate properly, you need a suitable device driver for the NIC hardware (e.g., ixgbe driver for Intel NICs). A NIC device driver implements a hardware-independent common interface between the Linux kernel and the NIC, so that packets can be moved between the kernel and the NIC. While some drivers may be statically built in the kernel, most drivers for modern NICs are dynamically loaded as kernel modules.
When you are troubleshooting a NIC hardware problem, one thing you can do is to check whether a correct network adapter driver is installed properly. In this case, you need to know which kernel module is your NIC driver.
There are several ways to find the name/version of an Ethernet card driver on Linux.
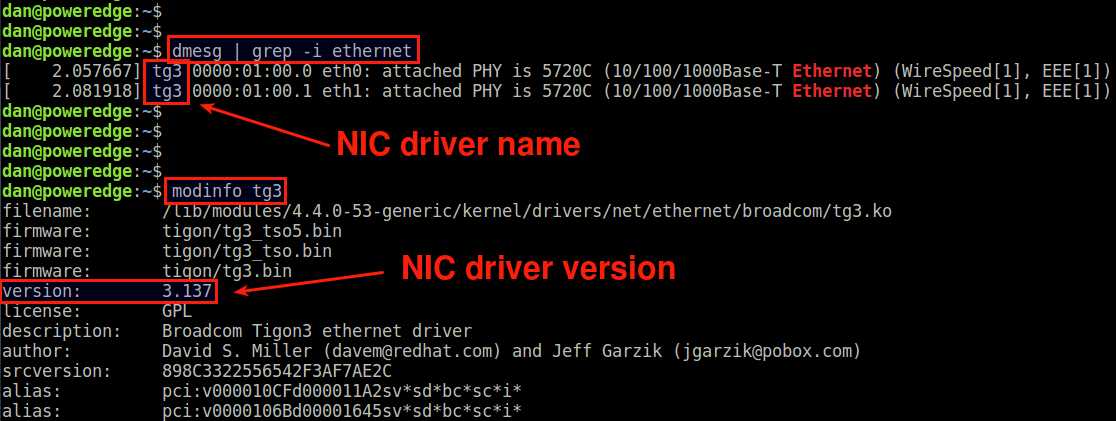
Method One: dmesg
The first method is to to check dmesg messages. Since the kernel loads necessary hardware drivers during boot, dmesg output should tell if an Ethernet card driver is installed.
The above output shows that a driver named tg3 is loaded in the kernel.
If you want to know more detail about this driver (e.g., driver version), you can use modinfo command.
If dmesg does not print any information about Ethernet driver, that means no suitable network device driver is available on your system.
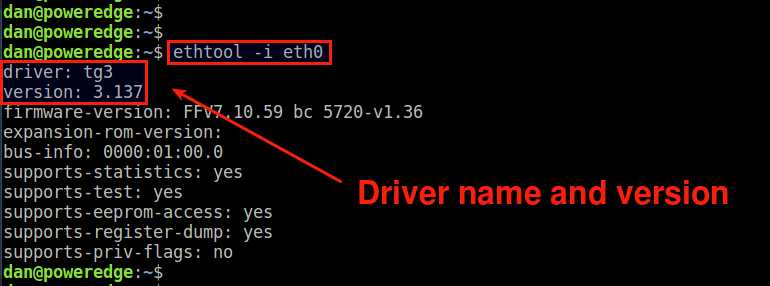
Method Two: ethtool
The second method is to use the ethtool command. To find out the driver name for an interface eth0 , run the following.
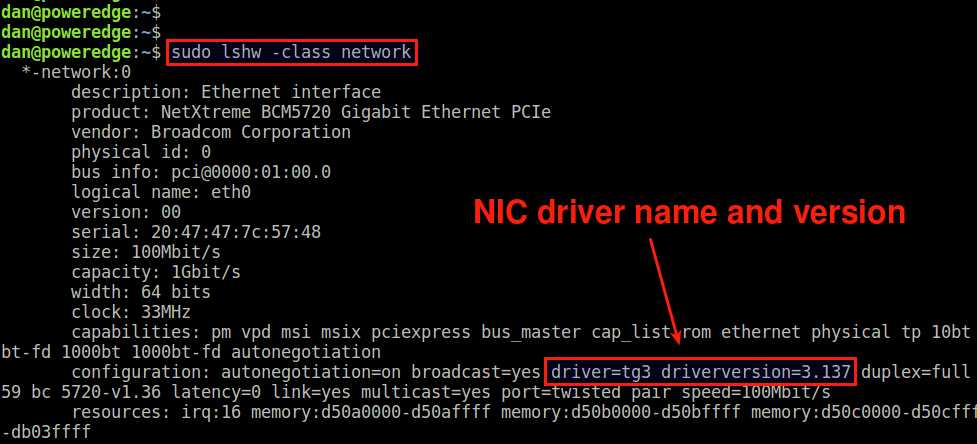
Method Three: lshw
Another useful tool for NIC driver information is lshw . Type the following command to get detailed information about available Ethernet card(s) and their driver.
In the lshw output, look for the capabilities line, and examine driver and driverversion in the line.
If no suitable NIC driver is installed on your system, the driver field will remain empty.
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.