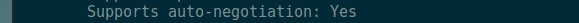- How to find network card driver name and version on Linux
- Method One: dmesg
- Method Two: ethtool
- Method Three: lshw
- Support Xmodulo
- How to find ethernet network card firmware and driver information in Linux
- ethtool Commands and Examples
- Checking ethtool Availability:
- Installing ethtool on Ubuntu and Debian:
- Installing ethtool on CentOS 7 and RHEL 7:
- Displaying Network Interface Card Information with ethtool:
- Checking Which Driver your NIC is Using:
- Display Network Usage Statistics with ethtool:
- Making your NIC Blink Using ethtool:
- Setting Speed and Modes on NICs Manually:
- Getting Help on ethtool:
- About the author
- Shahriar Shovon
How to find network card driver name and version on Linux
Question: An Ethernet network interface card is attached to my Linux box, and I would like to know which network adapter driver is installed for the NIC hardware. Is there a way to find out the name and version of a network card driver for my network card?
For network interface card (NIC) hardware to operate properly, you need a suitable device driver for the NIC hardware (e.g., ixgbe driver for Intel NICs). A NIC device driver implements a hardware-independent common interface between the Linux kernel and the NIC, so that packets can be moved between the kernel and the NIC. While some drivers may be statically built in the kernel, most drivers for modern NICs are dynamically loaded as kernel modules.
When you are troubleshooting a NIC hardware problem, one thing you can do is to check whether a correct network adapter driver is installed properly. In this case, you need to know which kernel module is your NIC driver.
There are several ways to find the name/version of an Ethernet card driver on Linux.
Method One: dmesg
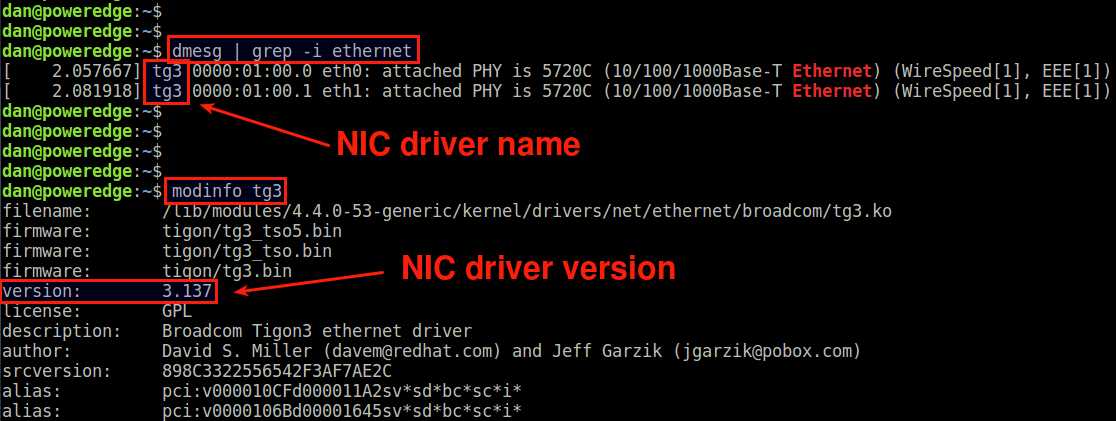
The first method is to to check dmesg messages. Since the kernel loads necessary hardware drivers during boot, dmesg output should tell if an Ethernet card driver is installed.
The above output shows that a driver named tg3 is loaded in the kernel.
If you want to know more detail about this driver (e.g., driver version), you can use modinfo command.
If dmesg does not print any information about Ethernet driver, that means no suitable network device driver is available on your system.
Method Two: ethtool
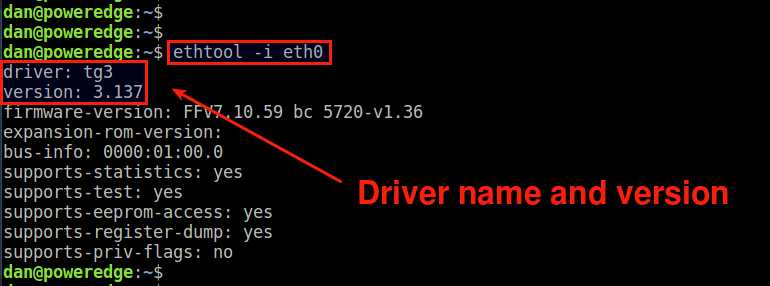
The second method is to use the ethtool command. To find out the driver name for an interface eth0 , run the following.
Method Three: lshw
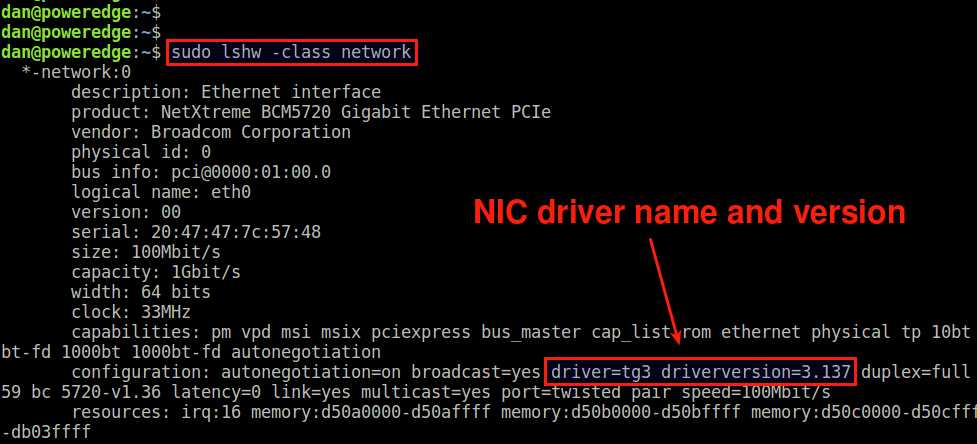
Another useful tool for NIC driver information is lshw . Type the following command to get detailed information about available Ethernet card(s) and their driver.
In the lshw output, look for the capabilities line, and examine driver and driverversion in the line.
If no suitable NIC driver is installed on your system, the driver field will remain empty.
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.
How to find ethernet network card firmware and driver information in Linux
Based n the Linux Variant you use the commands and their output may differ. I have worked on Red hat Enterprise Linux and SuSE Enterprise Linux and below commands and method have been really very useful to get the driver and firmware details of the Ethernet Network Card connected to the system
I prefer using the OS provided tools and not some other third party tools because just to get the NIC driver and firmware version I don’t want to go through all browsing, download, getting over my firewall, copying to my blade (as in office environment generally we don’t have internet access to our Linux blades) when we already have bunch of OS provided tools which can be used for this purpose.
Below command can be used on both SuSE and RHEL which has two different sections with separate firmware and driver version details.
# ethtool -i eth0 driver: be2net version: 11.2.1263.16 firmware-version: 11.2.1263.19 expansion-rom-version: bus-info: 0000:06:00.0 supports-statistics: yes supports-test: yes supports-eeprom-access: yes supports-register-dump: no supports-priv-flags: yes
Based on the driver name you get from the above command you can get more details on the module it is using from below command
# modinfo be2net filename: /lib/modules/3.10.0-693.5.2.el7.x86_64/weak-updates/be2net/be2net.ko supported: external license: GPL author: Emulex Corporation description: Emulex OneConnect NIC Driver 11.2.1263.16 version: 11.2.1263.16
Few more examples on a hardware with different Ethernet Network card
# ethtool -i eth0 driver: igb version: 5.2.15-k firmware-version: 2.1.5 bus-info: 0000:01:00.0 supports-statistics: yes supports-test: yes supports-eeprom-access: yes supports-register-dump: yes
# modinfo igb filename: /lib/modules/3.0.101-100-default/kernel/drivers/net/ethernet/intel/igb/igb.ko version: 5.2.15-k license: GPL description: Intel(R) Gigabit Ethernet Network Driver author: Intel Corporation,
Below are some more commands you can use to get the NIC firmware and driver related details and information
On SLES
# hwinfo --network | grep Driver | sort | uniq Driver Modules: "igb" Driver: "igb"
On RHEL 7
Next is ‘lshw’ utility, if this is not available you can get this from the Red Hat repo.
# rpm -qf /usr/sbin/lshw lshw-B.02.18-7.el7.x86_64 # lshw -c network *-network:0 description: Ethernet interface product: OneConnect NIC (Skyhawk) vendor: Emulex Corporation physical id: 0 bus info: pci@0000:06:00.0 logical name: eth0 version: 10 serial: 00:17:a4:77:00:0e size: 1Gbit/s width: 64 bits clock: 33MHz capabilities: pm msix pciexpress vpd bus_master cap_list rom ethernet physical autonegotiation configuration: autonegotiation=on broadcast=yes driver=be2net driverversion=11.2.1263.16 duplex=full firmware=11.2.1263.19 latency=0 link=yes multicast=yes slave=yes speed=1Gbit/s As you see here it also gives us enough detailed information about the available Ethernet Card with the firmware and driver version along with the driver name
ethtool Commands and Examples
ethtool is a networking utility on Linux. It is used to configure Ethernet devices on Linux. ethtool can also be used to find a lot of information about connected Ethernet devices on your Linux computer.
In this article, I will show you how to use ethtool command on Linux. I will be using Debian 9 Stretch for the demonstration. But any modern Linux distribution should work. Let’s get started.
Checking ethtool Availability:
In most cases, ethtool should already be installed on your favorite Linux distribution. You can check whether ethtool is installed already with the following command:
As you can see, ethtool 4.8 is installed on my Debian 9 Stretch machine.
If you see an error, then ethtool may not be installed on your computer. You can install ethtool very easily in your favorite Linux distribution. I will show you how to install ethtool on Ubuntu, Debian, RHEL 7 and CentOS 7 in the next sections of this article below.
Installing ethtool on Ubuntu and Debian:
ethtool is available in the official package repository of Ubuntu and Debian. So it is really easy to install.
First, update the APT package repository cache with the following command:
Now, install ethtool with the following command:
Installing ethtool on CentOS 7 and RHEL 7:
ethtool is available in the official package repository of CentOS 7 and RHEL 7. You can install it very easily.
First, update the YUM cache with the following command:
Finally, install ethtool with the following command:
Displaying Network Interface Card Information with ethtool:
You can display information about the network interface cards (NICs) connected to your computer with ethtool utility. To do that, you need the network interface name of your network interface card (NIC).
On Linux, every network interface card (NIC) is assigned unique names such as eth0, ens32 etc.
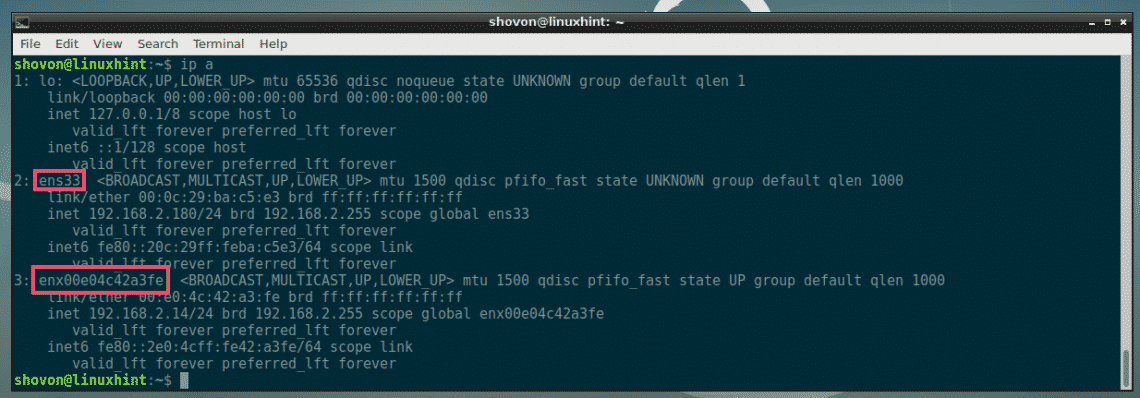
First, find the assigned names of all the available network interfaces of your computer, with the following command:
As you can see, I have only two network interface cards (NICs) connected to my computer. If you have more, it should show up here. The assigned names of my network interfaces are ens33 and enx00e04c42a3fe respectively. Yours should be different. But take a note of these as you will need it from now on.
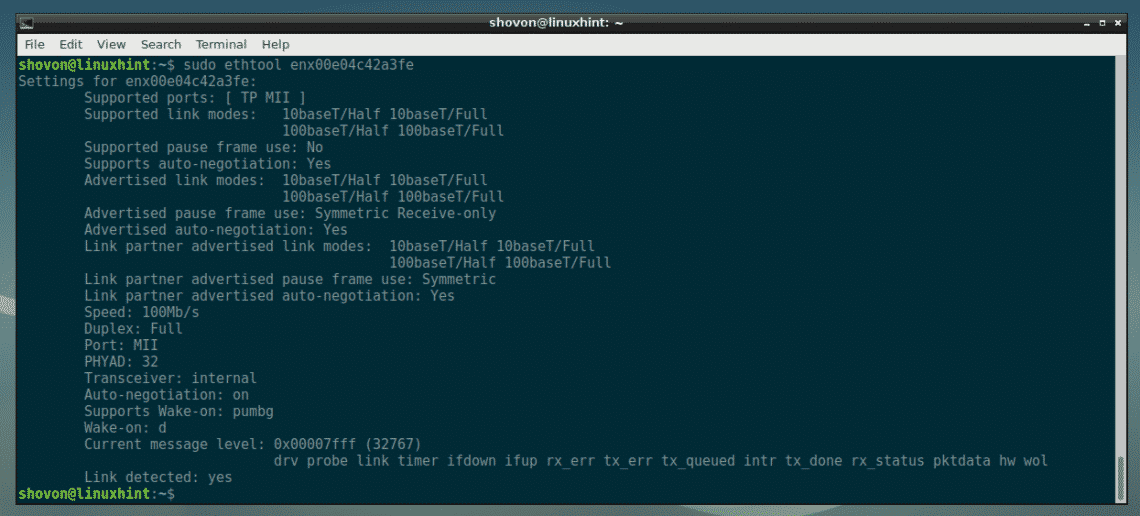
Now, to display more information about a network interface card (let’s say enx00e04c42a3fe) with ethtool, run the following command:
As you can see, a lot of information about the network interface card enx00e04c42a3fe is listed here.
For example, the supported link modes of your NIC is displayed here.
The currently used duplex mode and speed is displayed here as well. As you can see, it is connected in full duplex mode at 100 Mbps speed.
You can also find out whether your NIC supports auto negotiation from here. If auto negotiation is enabled, your NIC picks a random link mode from one of its supported link modes depending on the Router or switch port it’s connected to.
Checking Which Driver your NIC is Using:
You can also check which driver your NIC is using with ethtool command.
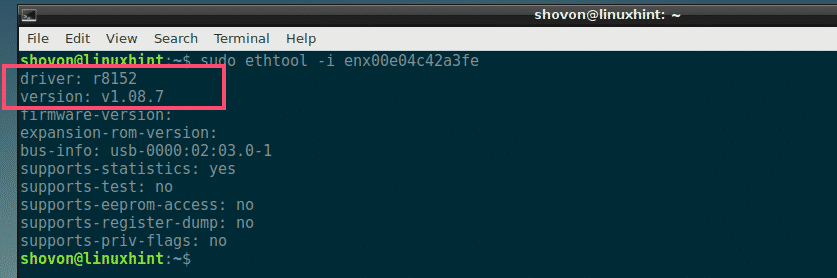
For example, to check for the driver used by one of your NIC (let’s say enx00e04c42a3fe), run ethtool command as follows:
As you can see, my enx00e04c42a3fe NIC is using Realtek r8152 driver version 1.08.7. Yours may be different.
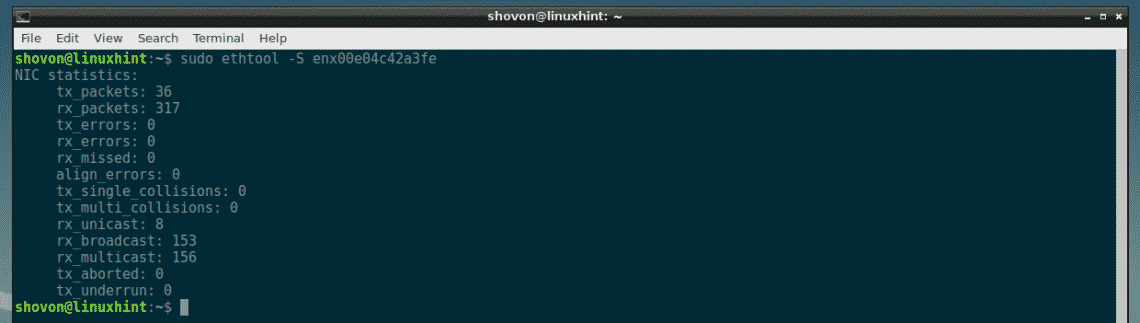
Display Network Usage Statistics with ethtool:
You can find out how many packets the NIC sent (Tx or transmitted) and received (Rx or received) using ethtool. You can also find out how many of these packets collided, transmission (Tx) errors and receiver errors (Rx) and many more.
To display your NIC (let’s say enx00e04c42a3fe) statistics, run ethtool as follows:
As you can see, a lot of statistics data on your NIC is displayed.
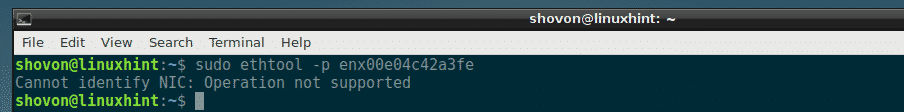
Making your NIC Blink Using ethtool:
Making your NIC blink may sound useless. But imagine a case where your computer has lots of network interfaces. How would you know which port is assigned what network interface name? Well, just blink each network interface and find out for yourself using ethtool. Simple!
To blink a network interface (let’s say enx00e04c42a3fe) with ethtool, run ethtool as follows:
This feature may not be available on your NIC card. Check the manual of your NIC card for more information on this.
My NIC card do not have this feature, so all I get is an error.
Setting Speed and Modes on NICs Manually:
At times, auto negotiation may fail and your NIC may use the wrong speed and mode. You can easily fix that with ethtool.
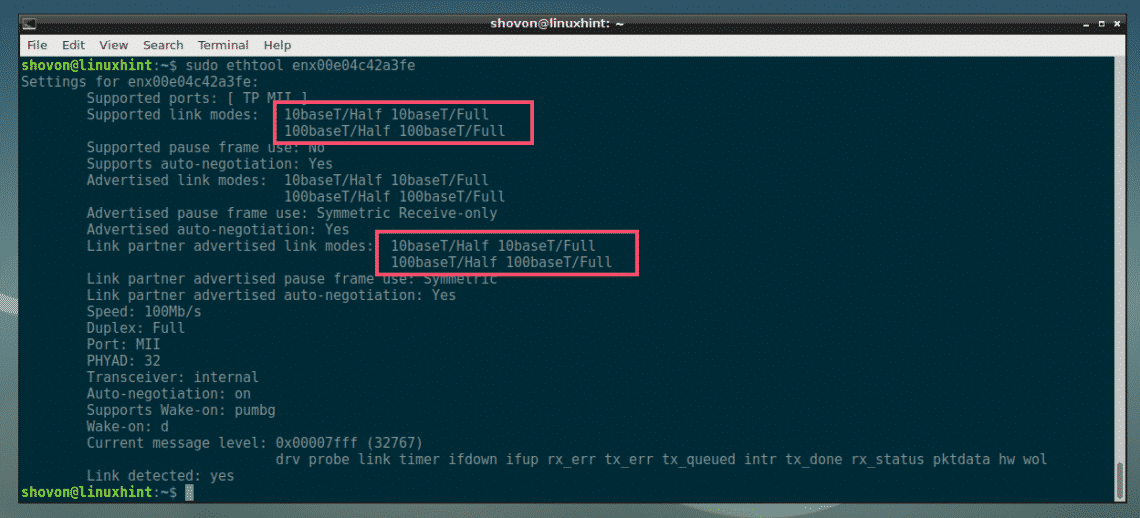
First, check what speeds and modes are supported on your NIC (Let’s say enx00e04c42a3fe) with the following command:
You can find the supported link modes of your NIC in the Supported link modes section and your Routers or Switches advertised link modes on Link partner advertised link modes section as you can see in the marked section of the screenshot below. My NIC and Router supports, 10baseT and 100baseT in Half and Full duplex mode.
Currently, my NIC enx00e04c42a3fe is working in Full duplex mode at 100 Mbps speed.
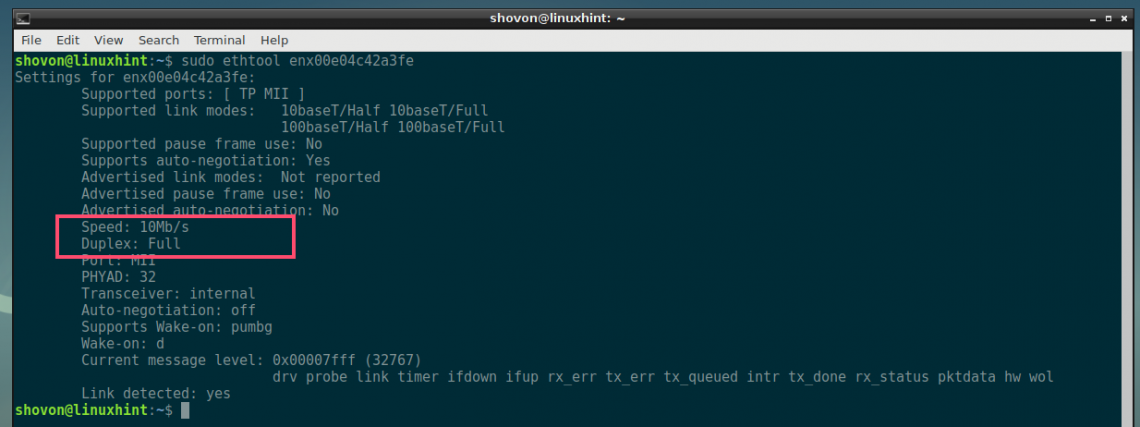
To change it, let’s say in Full duplex mode at 10 Mbps speed, run ethtool as follows:
As you can see, the speed is changed to 10Mbps and the duplex mode is full. Also, auto negotiation is turned off.
Getting Help on ethtool:
The ethtool command has lots of options. It’s not possible to show how every option work in this article due to the scope and hardware limitation of my computer.
But you should be able to find what you need on the manpage of ethtool, which you can access with the following command:
So, that’s how you use ethtool on Linux. Thanks for reading this article.
About the author
Shahriar Shovon
Freelancer & Linux System Administrator. Also loves Web API development with Node.js and JavaScript. I was born in Bangladesh. I am currently studying Electronics and Communication Engineering at Khulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET), one of the demanding public engineering universities of Bangladesh.