- How to clear the ARP cache on Linux?
- results matching » «
- No results matching » «
- How to Check and Clear the ARP Cache in Windows, Linux and Mac?
- What is ARP cache?
- When to clear the ARP cache ?
- How to clear the ARP cache?
- Windows
- Linux
- Mac
- Conclusion
- Как очистить arp кэш в Linux
- Как посмотреть таблицу MAC адресов
- Как добавить запись в таблицу MAC адресов и очистить arp кэш на Linux сервере (ip neigh delete)
How to clear the ARP cache on Linux?
In some cases you might need to clear your ARP cache. There are two common ways on Linux, using the arp or ip utility.
Clearing cache with arp The arp utility does not accept an option to clear the full cache. Instead, it allows to flush out entries found with the -d option.
After deleting, have a look with the arp utility again to see the new list:
[email protected]:~# arp -n Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface 192.168.1.1 (incomplete) eth0 192.168.1.2 ether 00:02:9b:a2:d3:f3 C eth0 192.168.1.3 ether 00:02:9b:d9:d1:a2 C eth0 Clearing cache with ip Newer Linux distributions have the ip utility, which has a more advanced way to clear out the full ARP cache
[email protected]:~# ip -s -s neigh flush all 192.168.1.1 dev eth0 lladdr 00:a1:04:c6:10:14 used 757/757/28 probes 6 STALE 192.168.1.2 dev eth0 lladdr 00:02:9b:a2:d3:f3 used 2555/719/659 probes 6 STALE 192.168.1.3 dev eth0 lladdr 00:02:9b:d9:d1:a2 ref 1 used 0/0/0 probes 6 DELAY Round 1, deleting 3 entries Flush is complete after 1 round The first -s will provide a more verbose output. The second one defines the neighbor table, which equals the ARP and NDISC cache.
Conclusion Depending on your distribution, the ip utility is quicker if you want to flush out the full ARP cache. For individual entries the arp tool will do the job as quickly.
results matching » «
No results matching » «
How to Check and Clear the ARP Cache in Windows, Linux and Mac?
Invicti Web Application Security Scanner – the only solution that delivers automatic verification of vulnerabilities with Proof-Based Scanning™.
Misconfigured or expired ARP cache entries in the system might be one of the reasons for network connectivity problems.
Are you aware that clearing the ARP cache in your system may fix loading problems and connectivity errors?
This article will look at how to check and clear the ARP cache in the different operating systems.
What is ARP cache?
ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol, which is responsible for discovering MAC addresses and mapping them to IP addresses in order to communicate successfully with other systems on the local network. This protocol works between the data link layer and network layer.
Instead of asking the router every time where the particular device is located and what its mac address is, our system would just connect using the previously resolved IP address.
When our systems find the MAC addresses for the particular IP address using ARP protocol, they will be stored in a table for future use. This table is called ARP cache. It contains a list of known IP addresses and their MAC addresses.
ARP request is a broadcast, and ARP reply is unicast.
When to clear the ARP cache ?
If the IP addresses of the network-linked devices change, ARP entries can get corrupted or expired, and new entries may not always overrule the database’s expired entries.
As a result, it may impact network performance and may cause loading or connectivity problems. In this case, you can simply clear the ARP cache to resolve the issue because clearing the ARP cache will cause all of your requests to go through the entire ARP process again. During this process, the new entries will be saved in the ARP table.
Some errors may occur during the rebuilding of the ARP cache table, so deleting the ARP cache all the time is not recommended. Instead, you can also reboot your router or system to resolve the connectivity problems.
How to clear the ARP cache?
We can easily clear the ARP cache in any operating system by using the command line. Let’s get started.
Windows
Step 1: Open a command prompt and run it as an administrator.
Step 2: To view the ARP cache table, just type the following command.
This command displays the IP addresses, and it’s associated mac addresses.
Step 3: Next, to delete the cache table, you can use netsh utility.
netsh interface IP delete arpcacheStep 4: If you want to delete any specific entry in the cache, not the whole table.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>arp -a Interface: 192.168.29.64 --- 0xd Internet Address Physical Address Type 192.168.29.1 a8-da-0c-e8-0e-e6 dynamic 224.0.0.22 01-00-5e-00-00-16 static 224.0.0.251 01-00-5e-00-00-fb static 224.0.0.252 01-00-5e-00-00-fc static Interface: 192.168.56.1 --- 0x14 Internet Address Physical Address Type 224.0.0.22 01-00-5e-00-00-16 static 224.0.0.251 01-00-5e-00-00-fb static 239.255.255.250 01-00-5e-7f-ff-fa static C:\WINDOWS\system32>netsh interface IP delete arpcache Ok. You will get ‘OK’ as a response if you use the netsh utility to clear the cache table.
Linux
Step 1: Open a terminal and use the following IP utility command to clear the whole ARP table.
Step 2: If you want to delete the ARP record for a particular address, use arp utility.
Step 3: After deleting the entries, you can simply use the following command to view the ARP table in Linux.
This command displays the whole arp table.
┌──(root💀kali)-[/home/geekflare] └─# arp -d 10.0.2.1 ┌──(root💀kali)-[/home/geekflare] └─# arp -n Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Interface 10.0.2.1 (incomplete) 10.0.2.2 ether 01:00:5e:00:00:fc C eth0 10.0.2.3 ether a8:da:0c:e8:0e:e6 C eth0Here, you can observe the cache entry for the specific address is cleared.
Mac
Step 2: To view the existing ARP entries.
Step 3: To delete the cache for a particular interface
sudo arp -d 192.168.29.1 ifscope en0 Step 4: To clear the whole cache table
$ sudo arp -a ? (192.168.29.1) at 01:00:5e:00:00:fc on en0 ifscope [ethernet] ? (192.168.2.13) at a8:da:0c:e8:0e:e6 on en0 ifscope [ethernet] ? (192.168.1.21) at 01:00:5e:00:0e:16 on en0 ifscope permanent [ethernet] $ sudo arp -a -d 192.168.29.1 (192.168.29.1) deleted 192.168.2.13 (192.168.2.13) deleted 192.168.1.21 (192.168.1.21) deletedConclusion
If you can’t ping a particular IP address in the same network even though they’re working correctly, it’s a sign that something is wrong. Your ARP cache table may need to be reconstructed again.
I hope you found this article helpful in learning how to clear the ARP cache in different operating systems.
Как очистить arp кэш в Linux
Рассмотрим как очистить arp кэш в Linux системах. Это может быть нужно когда у устройства в локальной сети сменился ip адрес или MAC.
Как посмотреть таблицу MAC адресов
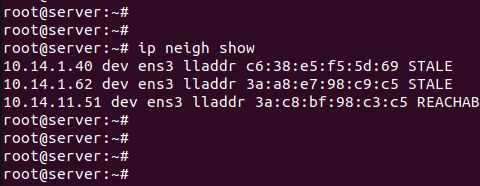
Команда ip neigh show позволяет увидеть все устройства в локальной сети, адреса которых отдаются из кэша. Для этих устройств есть ответ в кэше arp и разрешать MAC в ip при запросе не нужно.
192.168.88.1 dev wlp7s0 lladdr b8:69:f4:0d:92:78 REACHABLE
В кэш на некоторое время ответы попадают автоматически, достаточно одного запроса.
Пример записей в кэше на Linux сервере на скриншоте:
Как добавить запись в таблицу MAC адресов и очистить arp кэш на Linux сервере (ip neigh delete)
Добавить ответ в кэш можно просто пропинговав узел.
192.168.88.1 dev wlp7s0 lladdr b8:69:f4:0d:92:78 REACHABLE
192.168.4.5 dev уер0 lladdr b8:69:67:рА:92:78 REACHABLE
Если взаимодействие с адресом будет регулярно — адрес будет оставаться в кэше, в противном случае — удалится по таймауту.
Также запись можно удалить из arp cache:
Поскольку протокол ARP относится ко второму уровню модели OSI — на нём работают коммутаторы.
Всё взаимодействие сервера с другими хостами идёт через них. Это означает, что в кэше ARP могут быть только хосты, которых можно достичь через коммутатор. Это всегда хосты, которые расположены в том же сегменте сети.
Читайте про публичные и приватные диапазоны ip адресов и про первый — физический уровень модели OSI.