- How to share files/media online
- 1 Answer 1
- Top 10 Free Open Source Cloud File Sharing Platforms
- 1. NextCloud
- 2. Ceph
- 3. Aurora Files
- 4. YouTransfer
- 5. Pydio Cells
- 6. LinShare
- 7. NitroShare
- 8. OnionShare
- 9. FileDrop
- 10. ProjectSend
- How to quickly set up http file sharing on GNU/Linux
- Installing lighttpd
- Edit configuration file
- Connect to the web server
- How to secure?
- Firewall rules
- Netfilter/iptables rules
- nftables rules
- Add authentication
- Add https support
- Обмен файлами
- KTorrent
- rTorrent
- NitroShare
- Vuze (Azureus)
- Tixati
- aMule
- Tribler
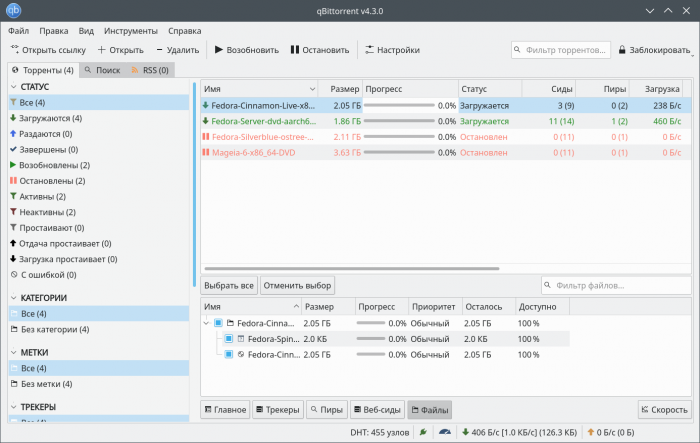
- qBittorrent
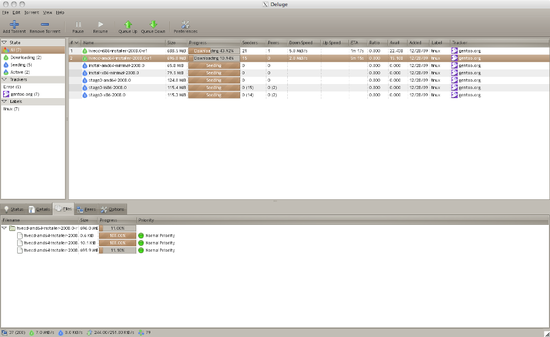
- Deluge
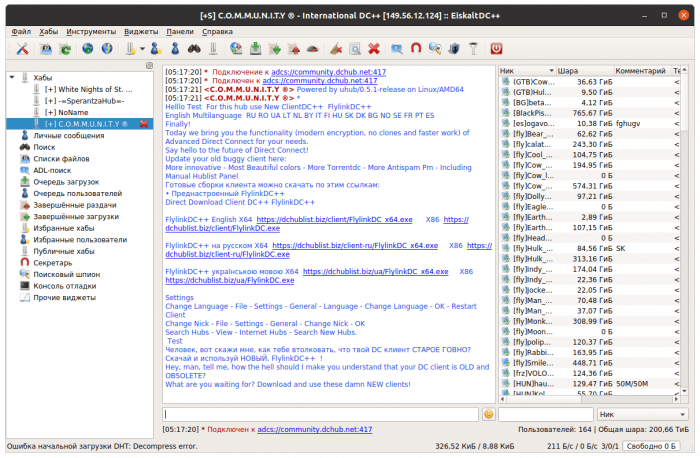
- EiskaltDC++
How to share files/media online
Can someone can direct me to a how to that explains not only how to install an FTP but also how a family member on another coast can access this via online? I have setup an old computer with the intent of sharing movies/music/photos with family members not in my house. I have been searching for over an hour and cannot find a complete guide from installation through user/folder setup to access via a computer not on the same network. Any assistance in this matter would be eternally appreciated.
1 Answer 1
If you want to setup your own server, I’d recommend to install something like «owncloud» which is a web application for uploading and sharing files using the web browser (such as dropbox, iCloud or ubuntu one) (more info http://owncloud.org/)
To install it on your ubuntu computer (that will work as the server)
sudo apt-get install owncloud You can then access the server using any web browser by entering the url http://YOUR-IP/owncloud , it will ask you for the basic config (such login info) the first time you enter.
Keep in mind that if you’r going to access the server from outside your house (or network) you will have to redirect port 80 from your router to your server.
Also, home internet connections are not designed for servers, thus the upload speed is normally low for a server, so expect no-so-fast file transfers when moving files from the outside to your server and the other way around.
I would also consider getting a free account from a cloud provider (ubuntu one, or dropbox, they both offer 5 gig free) and use that to share files, its simpler, faster, you dont have to worry about setting or mantaining the server yourself.
Top 10 Free Open Source Cloud File Sharing Platforms
Cloud file sharing involves a system where users are allocated storage space on a server and are allowed to perform read and write operations on the data they save in their space online.
A popular service is Dropbox and while it offers a free version, it is not open source. There are also many Dropbox alternatives for Linux, but this article focuses on the best free open source cloud file sharing platforms.
1. NextCloud
NextCloud is arguably the most popular open source cloud file sharing service. Apart from sharing files, it allows you to share calendars, contacts, emails and includes professional features like team collaboration and data synchronization and it packs text and video chat apps.
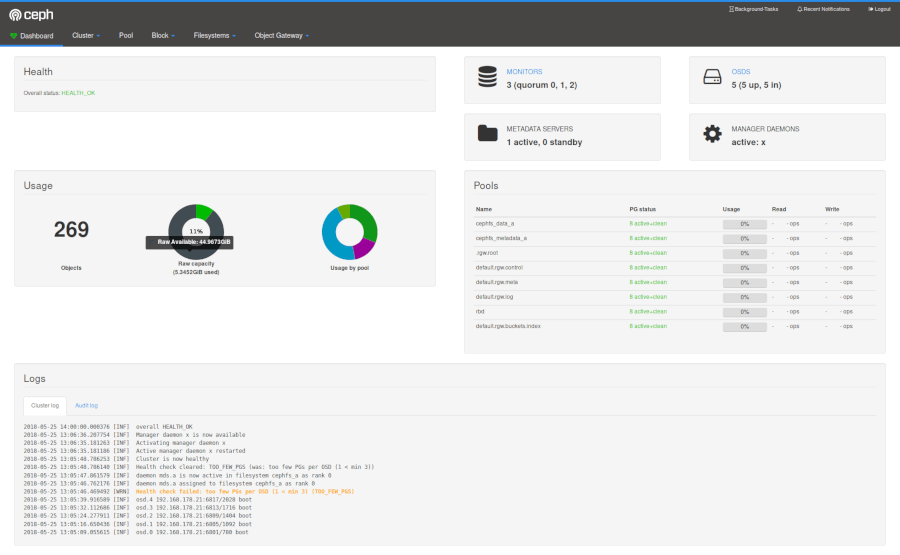
2. Ceph
Ceph is an open source distributed object, block, and file storage platform that uses a POSIX-compliant network file system in order to provide large data storage, high performance, and optimum support for legacy applications.
3. Aurora Files
Aurora Files is a developer friendly, encrypted file-sharing software. It has support for Google Drive and Dropbox as network logins, Zipped file viewer, and MS Office file viewer.
4. YouTransfer
YouTransfer is an open source file transfer cloud service with a few more features than FileDrop given that it has a Docker image for container users.
The file transfer process works via link sharing via email, message, or any other sharing method together with an optional message.
5. Pydio Cells
Pydio Cells is a Golang-based on-premise file management platform that aims to provide reliable file hosting, synchronization, and sharing. It has a strong emphasis on security and can be deployed on any server type of your choosing.
Fun fact, Pydio Cells went by the name of just “Pydio” and was written in PHP and JavaScript before until its entire rewrite in Golang.
6. LinShare
LinShare aims to provide an enterprise-grade cloud file sharing solution for free and it is succeeding. It enables users to share large files, manage activity logs and users, and enjoy healthcare-related features all while enjoying high security.
7. NitroShare
NitroShare is a cross-platform network file transfer app designed to extremely simplify sharing files while maintaining efficient speeds.
8. OnionShare
OnionShare is an open source platform that enables its users to share files of any size across the internet without jeopardizing their security or anonymity.
9. FileDrop
FileDrop is a lightweight web-based UI for sharing files. You can use it as a standalone server in trusted LANs but it is mostly used together with Sandstorm, an open source web-based productivity suite.
10. ProjectSend
ProjectSend is a private clients-oriented web service that provides a file-sharing platform for teams complete with features like uploads auto-expiration, usage logs, user permissions, etc.
There are notable mentions like Syncthing, Seafile, Cozy and Syncany but what is your favourite open source cloud file sharing application? Drop your comments in the section below.
How to quickly set up http file sharing on GNU/Linux
If you have a good internet connexion it could be useful to be able to share files with friends via a home made solution.
We will see here how to set up a web server in order to easily share files via a http protocol on GNU/Linux.
The goal here is to do it quickly with minimal configuration.
We will use lighttpd wich is an open-source web server optimized for speed-critical environments while remaining standards-compliant, secure and flexible.
Small CPU load and low memory footprint, everything I’m looking for.
Installing lighttpd
Edit configuration file
- Edit /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf, and add this line :
- Create upload directory :
- Create example file :
- Reload lighttpd service :
Connect to the web server
- From your web browser connect to your newly web server (http://IP_ADDRESS/upload). From the Index of page you should see your file :
How to secure?
We have a our brand new http server but if we make it accessible from the internet (that’s what we wanted right?), everyone can potentially connect to it.
We will see here, how we can improve security.
Firewall rules
We can use the netfilter/iptables or nftables firewall to restrict access and thus allow only certain ip addresses.
Netfilter/iptables rules
root@host:~# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp —dport 80 -m state -s ALLOWED_IP —state NEW,ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT root@host:~# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp —dport 80 -m state —state NEW,ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j DROP
nftables rules
root@host:~# nft add rule ip filter INPUT tcp dport 80 ip saddr ALLOWED_IP ct state new,established counter accept root@host:~# nft add rule ip filter INPUT tcp dport 80 ct state new,established counter drop
Add authentication
We can also add a user/password prompt window to prevent unwanted users.
- Edit /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf, and add this lines :
server.modules = ( «mod_indexfile», «mod_access», «mod_alias», «mod_redirect», «mod_auth», «mod_authn_file» ) auth.backend = «plain» auth.backend.plain.userfile = «/etc/lighttpd/lighttpd-plain.user» auth.require = ( «/» => ( «method» => «basic», «realm» => «Auth», «require» => «valid-user» ) )
- Add new user login:password :
root@host:~# echo «agent007:secret» > /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd-plain.user
- Restart lighttpd service :
root@host:~# systemctl restart lighttpd.service
- The next time someone tries to log in an authentication request will appear :
Add https support
- Create a self signed certificate :
- Set rights :
- Edit /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf, and add this lines :
- Restart lighttpd service :
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Обмен файлами
Программы для Linux для обмена файлами по интернет и по сети. Клиенты пиринговых сетей, P2P, Bit Torrent клиенты, Direct Connect (DC) и другие.
KTorrent
KTorrent — торрент-клиент, разрабатываемый проектом KDE. Поддерживает все основные возможности по скачиванию торрентов.
rTorrent
rTorrent — консольный torrent-клиент. Использует текстовый интерфейс (ncurses). rTorrent отличает высокая производительность.
NitroShare
NitroShare — кроссплатформенная программа для пересылки файлов и директорий между компьютерами внутри локальной сети.
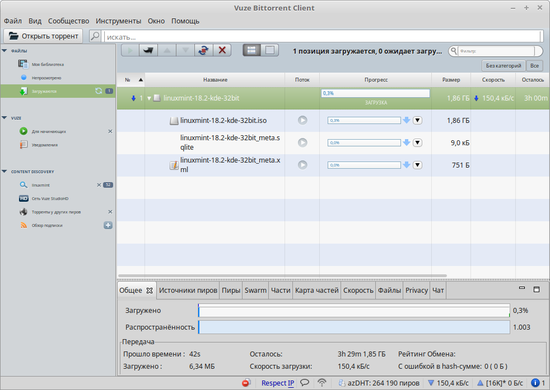
Vuze (Azureus)
Tixati
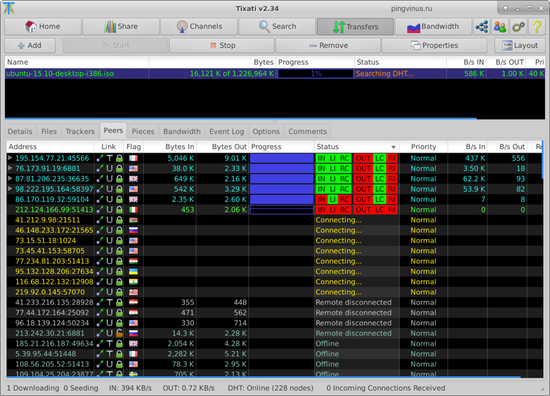
Tixati — бесплатный torrent-клиент для Linux. Разработчики заявляют, что программа использует ультра-быстрые алгоритмы для загрузки торрентов и сверхэффективный выбор пиров.
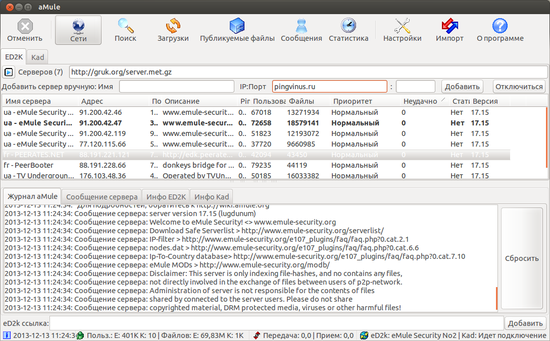
aMule
aMule — бесплатный, кроссплатформенный файлообменный клиент P2P сети eDonkey. Программа была создана на основе популярного клиента eMule и имеет схожий интерфейс.
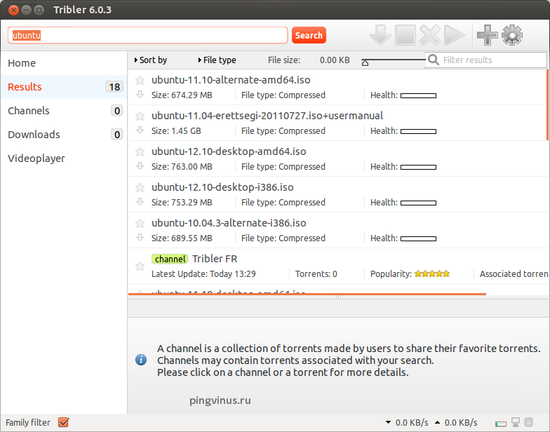
Tribler
Tribler — бесплатный torrent-клиент, который позволяет скачивать торренты без регистрации на сторонних сайтах. Его еще называет децентрализованным. Поиск торрентов можно осуществить по файлам, которые раздают другие пользователи программы Tribler.
qBittorrent
Deluge
Deluge — открытый бесплатный кроссплатформенный торрент-клиент. С помощью программы можно скачивать и раздавать контент в торрент-сетях, создавать свои torrent-файлы. Очень богатый выбор функций и настроек.
EiskaltDC++
EiskaltDC++ — бесплатный DC (Direct Connect) клиент для Linux. Поддерживается многопоточное скачивание файлов, полноценный чат, изменение скорости закачки и отдачи, расширенный поиск и другое.