Where are the OpenVPN connection logs and configuration files?
However, your config files can set the logfile location explicitly, e.g.:
log-append /var/log/openvpn.log This works for both OpenVPN clients and servers. OpenVPN config files are usually located in /etc/openvpn and usually named *.conf . server.conf is canonical; client config filenames are usually like .conf .
Log file location
On servers, OpenVPN is usually run as a system service, i.e., started with the —daemon option. According to the OpenVPN man page, using the —daemon [progname] option has the following effect:
Become a daemon after all initialization functions are completed. This option will cause all message and error output to be sent to the syslog file (such as /var/log/messages ), except for the output of scripts and ifconfig commands, which will go to /dev/null unless otherwise redirected. The syslog redirection occurs immediately at the point that —daemon is parsed on the command line even though the daemonization point occurs later. If one of the —log options is present, it will supercede (sic) syslog redirection.
Use either of the —log file or —log-append file options if you want OpenVPN messages to be logged to a different file. The —log option causes the specified log file to be over-written each time the OpenVPN daemon starts while the —log-append option adds new entries to the log file. These options can also be set in the OpenVPN configuration file, e.g.,
Verbosity
The —verb option can be used to set the log file verbosity from 0 (no output except for fatal errors) to 11 (for maximum debugging information). The man page specifies levels of 1 to 4 as the appropriate range for normal usage. This behaviour can be set in the OpenVPN configuration file, e.g.,
Как просматривать логи OpenVPN в Linux
Интерес к логам появляется в том момент когда что-то перестает работать. Это касается и OpenVPN, например, когда кто-то из пользователей не может подключиться к серверу. Причину по которой это происходить можно найти только в логах. Поэтому всегда настраивайте ведение журналов для всех важных приложений которые вы используете. Так как в большинстве случаев по умолчанию ведение журналов отключено. Сегодня поговорим о том как узнать где хранятся логи OpenVPN в операционных системах Linux.
Где хранятся журналы OpenVPN
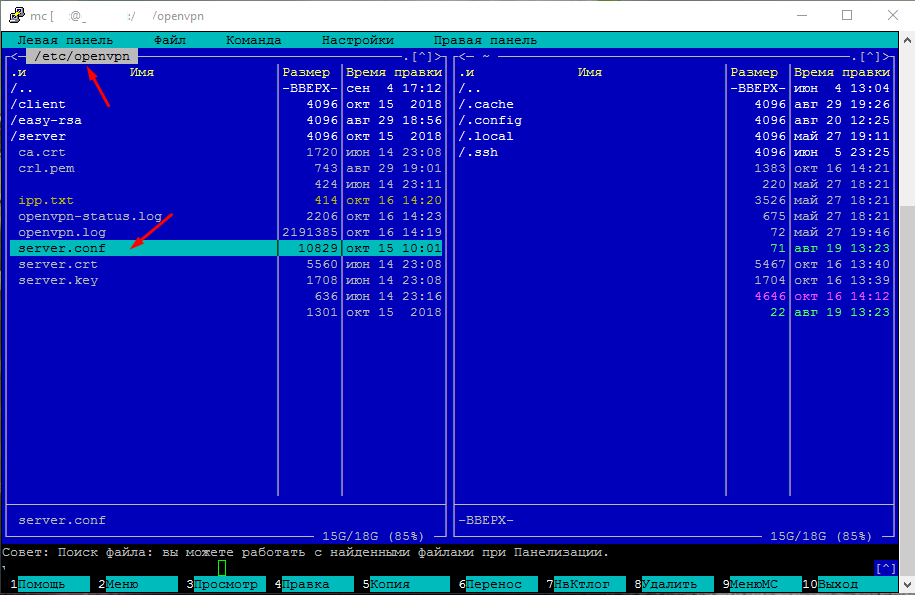
Путь до журналов может быть разный. Посмотреть куда сохраняются логи в OpenVpn можно в файле настроек server.conf. Для этого подключаемся к серверу и запускаем файловый менеджер mc. Лично я рекомендую им пользоваться особенно начинающим пользователям Linux.
Установить mc — apt install mc
После открытия mc переходим в каталог где установлен OpenVpn и открываем файл конфигурации. Для просмотра файла необходимого его выделить и начать F3.
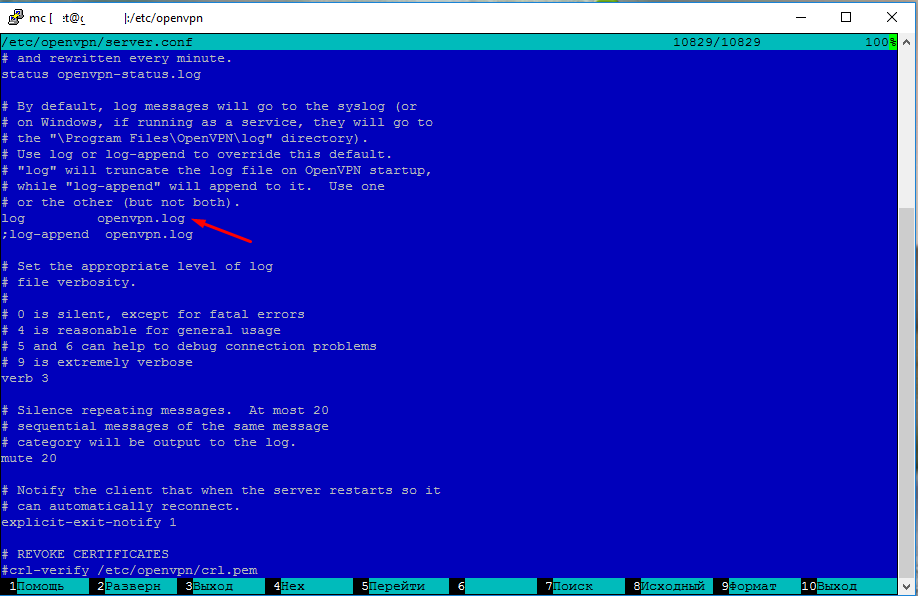
Где хранить логи — log openvpn.log
Если у вас указан такой путь то это значить что лиги хранятся в той же папки что и сам OpenVpn.
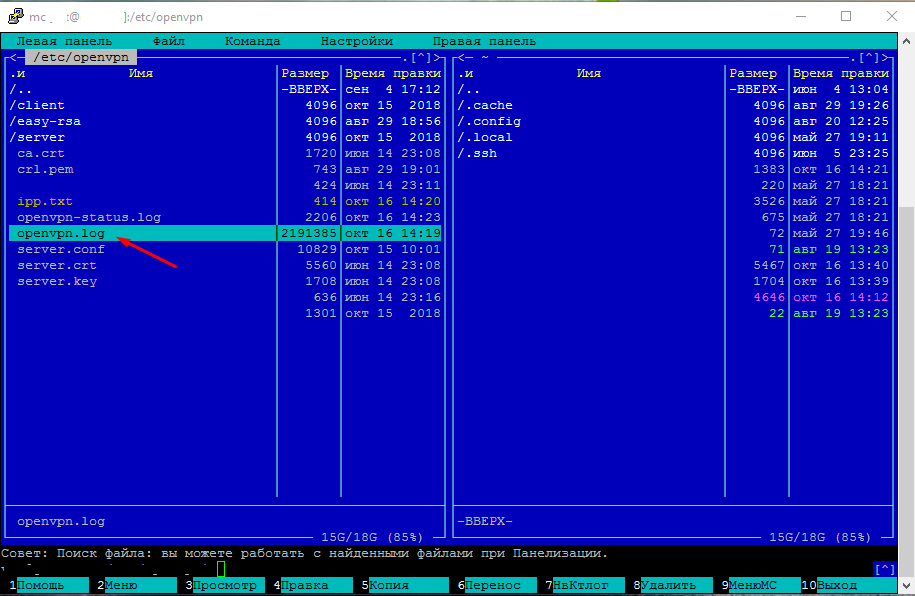
Ищем данный файл по указанному пути. Для просмотра можно также использовать F3.
Если у вас нет mc то можете открыть файл конфигурации введя команду.
Такой же командой можно и просмотреть сам журнал. Как видите нет ни чего сложного.
OpenVpn Log : 1 комментарий
- Иван 17.01.2023 Здравствуйте! при подключении к сервера периодически теряется пинг в каких логах можно это отследить?
How to view OpenVPN connections?
I want to view the open connections between my OpenVPN client and server via the server. Not sure how to do this as tcpdump does not show anything, yet OpenVPN is working and running. Again, when SSHing into my OpenVPN servers, all I can see are my SSH packets being sent over and nothing for OpenVPN. Why? Thanks!
I really don’t know sorry, but have you specified the correct interface? OpenVPN creates a new network interface, maybe you need to specify this.
1 Answer 1
OpenVPN stores open connections in its status logs. You can find the status logs by:
grep ‘^status’ /etc/openvpn/server*.conf
in my case (Ubuntu) produces the following (I have two running OpenVPN instances):
/etc/openvpn/server6.conf:status /var/log/openvpn/openvpn-status6.log /etc/openvpn/server.conf:status /var/log/openvpn/openvpn-status.log OpenVPN CLIENT LIST Updated,Sun Jul 24 22:42:55 2022 Common Name,Real Address,Bytes Received,Bytes Sent,Connected Since wino-surface6,10.9.4.1:20994,76104,10838,Sun Jul 24 22:42:22 2022 ROUTING TABLE Virtual Address,Common Name,Real Address,Last Ref 10.12.0.4,wino-surface6,10.9.4.1:20994,Sun Jul 24 22:42:54 2022 2001:db8::1002,wino-surface6,10.9.4.1:20994,Sun Jul 24 22:42:54 2022 GLOBAL STATS Max bcast/mcast queue length,0 END You can see that there is a single client (wino-surface6) that has 2 ip addresses assigned (an IPv4 and an IPv6) by the first OpenVPN instance.
As to why tcpdump isn’t seeing the OpenVPN packets, you need to make sure you’re looking for the correct protocol and port. You can verify this with:
egrep ‘^(port|proto)’ /etc/openvpn/server*.conf