- Saved searches
- Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
- License
- parallaxsecond/parsec
- Name already in use
- Sign In Required
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching Xcode
- Launching Visual Studio Code
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- README.md
- About
- Parsec
- Changes in version 3.9.8
- Linux parsec что это
- Play Any PC Game On Your Linux Machine With Cloud Gaming Or Game Streaming
- What We Learned About Hardware Decoding On Linux Machines
- What’s The State Of Linux Gaming?
- A New Era Of Gaming — Play PC Games Anywhere On Any Device
- Architecture¶
- Parsec security model¶
- Separation of actors¶
- Parsec data model¶
- Data sharing model¶
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.
Platform AbstRaction for SECurity service
License
parallaxsecond/parsec
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Name already in use
A tag already exists with the provided branch name. Many Git commands accept both tag and branch names, so creating this branch may cause unexpected behavior. Are you sure you want to create this branch?
Sign In Required
Please sign in to use Codespaces.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Update changelog and crate version
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
PARSEC is the Platform AbstRaction for SECurity, an open-source initiative to provide a common API to hardware security and cryptographic services in a platform-agnostic way. This abstraction layer keeps workloads decoupled from physical platform details, enabling cloud-native delivery flows within the data center and at the edge.

Read the Parsec documentation online.
- A portable interface to your platform’s Root of Trust in order to manage keys and perform cryptographic operations without knowledge of the hardware.
- A simple and portable way to access the best available security of your platform in your preferred programming language.
The value proposition of Parsec is that it provides the following:
- Abstraction – a common API that is truly agnostic and based on modern cryptographic principles
- Mediation – security as a microservice, brokering access to the hardware and providing isolated key stores in a multi-tenant environment
- Ergonomics – a client library ecosystem that brings the API to the fingertips of developers in any programming language: “easy to consume, hard to get wrong”
- Openness – an open-source project inviting contributions to enhance the ecosystem both within the service and among its client libraries
PARSEC is a collaborative project. The current list of the individuals and organizations who maintain this project can be found here.
If you are running on x86 Linux, check out this guide to get started with Parsec quickly!
For examples of how to access PARSEC as a client application, check this Rust client documentation.
Check the user, client developer and service developer guides for more information on building, installing, testing and using Parsec!
Come and ask questions or talk with the Parsec Community in our Slack channel or biweekly meetings. See the Community repository for more information on how to join.
We would be happy for you to contribute to Parsec! Please check the Contribution Guidelines to know more about the contribution process. Check the open issues on the board if you need any ideas 🙂 !
The software is provided under Apache-2.0. Contributions to this project are accepted under the same license.
About
Platform AbstRaction for SECurity service
Parsec
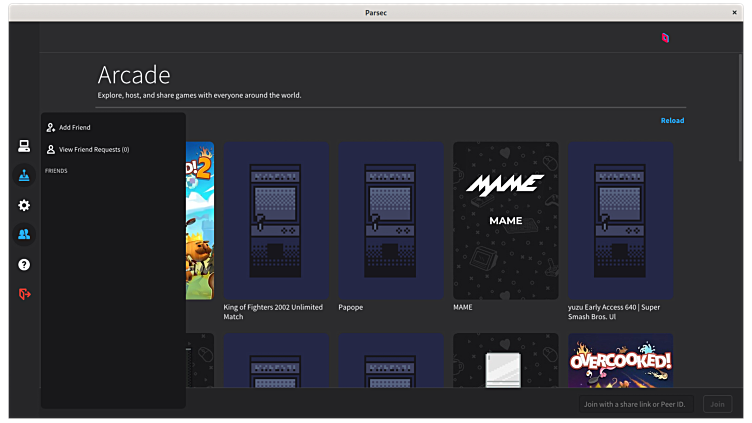
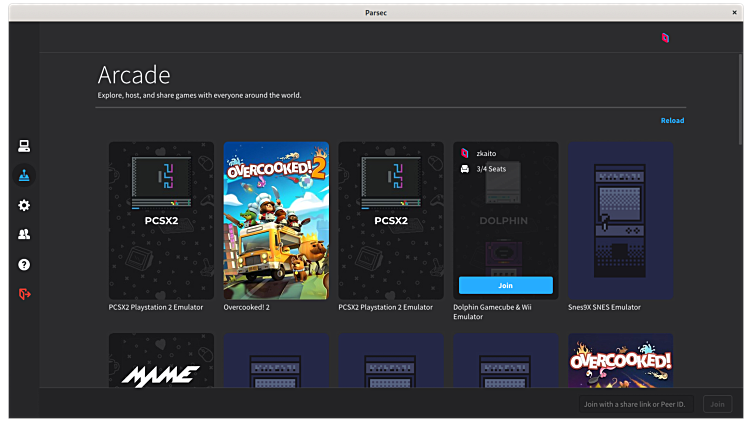
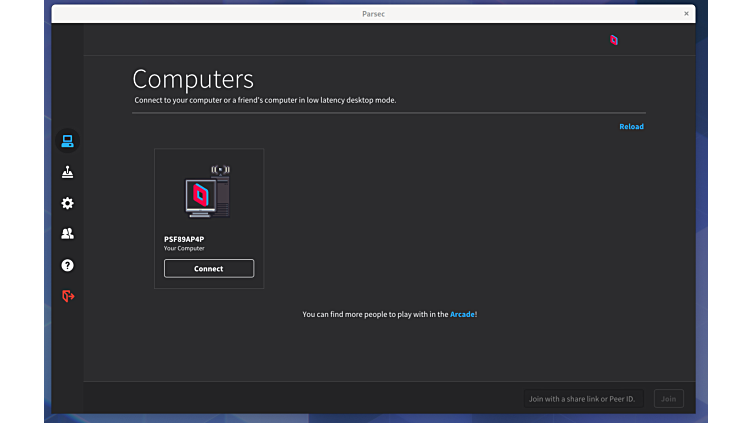
Parsec allows you to access your machine at home, while you are on the go. Share machine access with your friends and family to have a remote couch game evening. Or use the Arcade mode to play with random strangers all sorts of games.
NOTE: A Parsec account is required to use this application.
NOTE: Parsec will not allow you to access your Linux machine remotely. You can only join other host machines.
NOTE: This wrapper is not verified by, affiliated with, or supported by Parsec Cloud, Inc.
Changes in version 3.9.8
Linux parsec что это
Play Any PC Game On Your Linux Machine With Cloud Gaming Or Game Streaming
Tl;dr: As we’ve been working to build our Linux streaming client, we’ve been tripped up by the current state of hardware decoder support in Linux . We wanted to share what we’ve learned so far in case it helps you with your project. Also, we’re looking for some enthusiastic Linux gamers to beta test our our low latency remote gaming streaming tech. Parsec is officially supported on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS Desktop, but some users have figured out how to get it to work on other Linux Distributions.
You don’t need WINE to game on Linux Ubuntu 16.04 anymore 🙂
Initially, we built a Raspberry Pi client to demonstrate the future of low-powered clients accessing computing via the internet and cloud gaming. In addition to showing off our technology, this client attracted a DIY community who regularly come up with new uses of Parsec, build additional functionality, and talk about it on our Discord Server. Because of this, we decided to prioritize another client supporting the doers, engineers, and tinkerers in PC gaming. Supporting the Linux Community is a great way to connect with these technologists and give them access to every game available to their friends on Windows. And there’s a lot of crossover between Linux users and Raspberry Pi owners. In the Linux gaming community, 29% of survey respondents are using a Raspberry Pi at home!
Running a game your computer perhaps cannot handle or from a different operating system (like Windows games for us) is certainly an interesting and useful idea. Sadly, it never usually works well. Enter Parsec, which has genuinely blown me away. — Gaming On Linux
What We Learned About Hardware Decoding On Linux Machines
To achieve the lowest latency possible with our software we’ve been buried in Linux video decoding for awhile. Like much of Linux, the hardware decoding support is fragmented. Two standards dominate the desktop Linux world: VDPAU and VAAPI. VDPAU is developed and maintained by Nvidia for GeForce cards. VAAPI is Intel’s brainchild and works mostly with their own hardware. AMD appears to have one foot in each camp, but in recent years most of their drivers seem to prefer VAAPI. While it isn’t terribly unusual for there to be multiple standards, Linux is compounded by an additional problem in that the drivers are not especially reliable. While in recent years this has improved quite a bit, the drivers which implement these technologies are often proprietary, sometimes competing against open source versions of the same thing. To manage this, there are open source libraries which provide a somewhat stable interface between the drivers and anything that needs to use them. Unfortunately, even on a good day, libva for VAAPI is much less friendly to use than QuickSyncVideo for the same hardware in Windows. To make things even more frustrating, Intel has implemented QSV in Linux, however at the time of this writing it will only reliably work on CentOS with proprietary drivers. Overall, the fragmentation, high learning curve, and sparse manufacturer support in Linux drivers makes using a heavy decoder wrapper like FFMPEG seem almost obligatory, which can be undesirable for performance, compatibility, and licensing reasons. This situation can lead to ports of applications to Linux being heavily delayed, unstable across different distributions, or possibly not attempted at all. At Parsec, however, we weren’t afraid get hip deep in all of it and came out with a nicely performant first shot at Linux support. Expect a wider range of compatibility in the future.
What’s The State Of Linux Gaming?
Statcounter estimates that in April 2017, 0.77% of site visits are from computers running kernel-based Linux. This is a small but mighty crowd. Gaming among this group is just as popular as on other hardware, but they are hampered by the infrequent support from game developers. Unfortunately, if a Linux gamer wants to play all of the games available on Windows, they typically have to employ something like WINE or dual boot to access Windows applications on Linux (if they’re supported). Parsec is a lightweight application that turns your Linux machine into a powerful gaming PC, using the rendering power of a remote Windows gaming PC.
Boiling Steam conducted a survey of the Subreddit for Linux Gamers. The data from this survey of 564 people revealed some insights into the Linux Gaming Community. First, 87.2% of the Linux community is using a desktop PC and 32.4% use a laptop for some gaming. Interestingly, almost 10% are using a dedicated living room PC to power their gaming on a TV.
We thought one of the most surprising data point was that 34.7% of the Linux gaming community was using a Windows machine to game — despite the enormous selection bias toward Linux. This indicates that 35% of Linux gamers have a second computer or they dual boot into Windows, just for gaming.
Parsec has been tested and works on Ubuntu 16.04. 30% of survey respondents were running Ubuntu while 29% are on Arch Linux.
A New Era Of Gaming — Play PC Games Anywhere On Any Device

At Parsec, we believe that a new era of computing is approaching where we shift from owning computers and processing to accessing it. This will eliminate constant upgrade cycles, and low-powered devices with long battery lives will replace expensive hardware. In this vision, software becomes hardware agnostic, and we can choose which operating systems and hardware we want without worrying about access to software. As we set out on this vision, we’re allowing gamers to access PC games from anywhere on any device. Forget $2,500 liquid cooled hardware. Whether you’re hosting your gaming PC in the cloud, connecting to a friend’s PC, or remoting into your hardware to play games, Parsec solves the remote access problem for gaming. With all that being said, we’re excited to announce our newest client — Linux Ubuntu 16.04!
Architecture¶
Parsec is divided between a client (responsible for exposing data to the user and providing an encryption layer) and a server (storing the encrypted data and notifying clients about other users activity such as data modification or new sharing).
Parsec single server, multi organizations showcase
The Parsec server only requires a PostgreSQL DB for metadata (that is encrypted using devices keys for the most part) and an Amazon S3 or OpenStack Swift object storage for data blobs (that are encrypted using Workspaces keys which never leave users’ devices). Redundancy using multiple cloud providers is possible.
Parsec security model¶
Parsec secures sensitive data before they are stored on public clouds, proceeding in 3 steps :
- Splitting of files in blocks before encryption;
- Encryption of each block with a different symmetric key (BLOCK_ENC_KEY);
- Encryption of the metadata (tree structure, composition of files, multiple BLOCK_ENC_KEY, sharing information) with the private key of the user (USER_ENC_S_KEY).
Separation of actors¶
- User: represents a natural person in Parsec. A user owns an asymmetric key (USER_ENC_S_KEY/USER_ENC_P_KEY) enabling the encryption of data intended only for the user, like its User Manifest (see below).
- The Workstation: the physical support – desktop or mobile computer.
- Device: it is through a Device that the user accesses Parsec. A user can have multiple devices (e.g. a desktop and a laptop). Each device has its own asymmetric signature key (DEVICE_SIG_S_KEY/DEVICE_SIG_P_KEY) enabling signing modifications made by itself.
Parsec data model¶
- File Manifest: contains the file name, the list of block composing it and the associated BLOCK_ENC_KEY.
- Folder Manifest: index containing a set of entries, each entry being either a File Manifest or another Folder Manifest.
- Workspace Manifest: index similar to the Folder Manifest, that can also be shared between multiple users.
- User Manifest: root index of each user containing the Workspaces Manifests shared with the user.
Data sharing model¶
- Workspace: a set of users sharing a trust perimeter. Parsec ensures sharing sensitive data by encrypting the Workspace Key (WS_ENC_KEY) using the key of the receiver of that data (USER_ENC_P_KEY) – this step is repeated for each receiver.
- Organization: a set of Workspaces and a set of Users members of the organization. Workspace access can only be granted to members of the organization. A single Workspace cannot be shared between two distincts organizations.
© Copyright 2016-present, Scille SAS Revision 8a98d002 .
Versions latest stable Downloads On Read the Docs Project Home Builds Free document hosting provided by Read the Docs.