- How to get the summarized sizes of directories and their subdirectories?
- 9 Answers 9
- Размеры папок и дисков в Linux. Команды df и du
- Свободное место на диске (df)
- Опция -h
- Размер конкретного диска
- Размер папок на диске (du)
- Размер конкретной папки:
- Размеры файлов и папок внутри конкретной папки:
- How to Get the Size of a Directory in Linux
- Option 1: Display the Size of a Directory Using the du Command
- Option 2: Get Size of Directory in Linux Using tree Command
- Option 3: Find the Size of a Linux Directory Using ncdu Command
How to get the summarized sizes of directories and their subdirectories?
Let’s say I want to get the size of each directory of a Linux file system. When I use ls -la I don’t really get the summarized size of the folders. If I use df I get the size of each mounted file system but that also doesn’t help me. And with du I get the size of each subdirectory and the summary of the whole file system. But I want to have only the summarized size of each directory within the ROOT folder of the file system. Is there any command to achieve that?
The —total flag was helpful for me. E.g. du -sh —total applications/* . askubuntu.com/a/465436/48214
9 Answers 9
This does what you’re looking for:
- -s to give only the total for each command line argument.
- -h for human-readable suffixes like M for megabytes and G for gigabytes (optional).
- /* simply expands to all directories (and files) in / . Note: dotfiles are not included; run shopt -s dotglob to include those too.
Also useful is sorting by size:
If you have dot-directories in the root directory, you can use shopt -s dotglob to include them in the count.
It’s very usefull, because it’s simple and you can place what path you want instead of /* , e.g. ./ for current directory or ./* for each item in current directory.
@c1phr If your sort doesn’t have -h , you need to leave it off from du as well, otherwise the sorting will mix up kilo/mega/gigabytes. du -s /* | sort -nr .
I often need to find the biggest directories, so to get a sorted list containing the 20 biggest dirs I do this:
du -m /some/path | sort -nr | head -n 20 In this case the sizes will be reported in megabytes.
@Xedecima the problem with using h is the sort doesn’t know how to handle different sizes. For example 268K is sorted higher than 255M, and both are sorted higher than 2.7G
The -h (human readable) argument on the ‘sort’ command should properly read these values. Just like du’s -h flag exports them. Depending on what you’re running I’m guessing.
I like to use Ncdu for that, you can use the cursor to navigate and drill down through the directory structure it works really well.
The existing answers are very helpful, maybe some beginner (like me) will find this helpful as well.
- Very basic loop, but for me this was a good start for some other size related operations:
for each in $(ls) ; do du -hs "$each" ; done The following du invocation should work on BSD systems:
Right portable option combination on BSD/*NIX is du -sk /* . I hate the -k stuff soooo much. Linux’ -h totally rocks.
This isn’t easy. The du command either shows files and folders (default) or just the sizes of all items which you specify on the command line (option -s ).
To get the largest items (files and folders), sorted, with human readable sizes on Linux:
This will bury you in a ton of small files. You can get rid of them with —threshold (1 MB in my example):
The advantage of this command is that it includes hidden dot folders (folders which start with . ).
If you really just want the folders, you need to use find but this can be very, very slow since du will have to scan many folders several times:
find . -type d -print0 | sort -z | xargs --null -I '<>' du -sh '<>' | sort -h @podarok It’s available on OpenSUSE 13.2 Linux. Try to find a more recent version of your distribution or compile a more recent version of the package yourself.
Caching might have been a bad term. I was thinking of something like done in this port superuser.com/a/597173/121352 where we scan the disks contents once into a mapping and then continue using data from that mapping rather than hitting the disk again.
You might also want to check out xdiskusage. Will give you the same information, but shown graphically, plus allows to drill down (very useful). There are other similar utilities for KDE and even Windows.
Be aware, that you can’t compare directories with du on different systems/machines without getting sure, both share the same blocksize of the filesystem. This might count if you rsync some files from a linux machine to a nas and you want to compare the synced directory on your own. You might get different results with du because of different blocksizes.
You could use ls in conjunction with awk :
The output of ls is piped to awk . awk starts processing the data. Standard delimiter is space. The sum variable tot is initialised to zero; the following statement is executed for each row/line outputted by ls . It merely increments tot with the size. $5 stands for fifth column (outputted by ls ). At the end we divide by (1024*1024) to sum in megabytes.
If you would convert this into a script or function (.bashrc) you can also use it to get the size of certain subsets of directories, according to filetypes.
If you want system wide information, kdirstat may came in handy!
Размеры папок и дисков в Linux. Команды df и du
Рассмотрим, как используя команды df и du просматривать свободное место на дисках и размеры папок в Linux.
Свободное место на диске (df)
Для просмотра свободного и занятого места на разделах диска в Linux можно воспользоваться командой df.
Первым делом можно просто ввести команду df без каких-либо аргументов и получить занятое и свободное место на дисках. Но по умолчанию вывод команды не очень наглядный — например, размеры выводятся в КБайтах (1К-блоках).
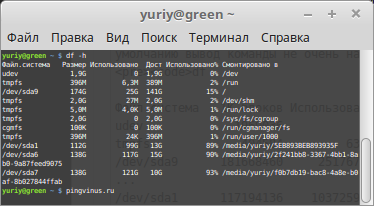
df Файл.система 1K-блоков Использовано Доступно Использовано% Cмонтировано в udev 1969036 0 1969036 0% /dev tmpfs 404584 6372 398212 2% /run /dev/sda9 181668460 25176748 147240368 15% / . /dev/sda1 117194136 103725992 13468144 89% /media/yuriy/5EB893BEB893935F /dev/sda6 144050356 121905172 14804772 90% /media/yuriy/2f24. d9075 Примечание: df не отображает информацию о не смонтированных дисках.
Опция -h
Опция -h (или —human-readable) позволяет сделать вывод более наглядным. Размеры выводятся теперь в ГБайтах.
df -h Файл.система Размер Использовано Дост Использовано% Cмонтировано в udev 1,9G 0 1,9G 0% /dev tmpfs 396M 6,3M 389M 2% /run /dev/sda9 174G 25G 141G 15% / . /dev/sda1 112G 99G 13G 89% /media/yuriy/5EB893BEB893935F /dev/sda6 138G 117G 15G 90% /media/yuriy/2f24. d9075Размер конкретного диска
Команде df можно указать путь до точки монтирования диска, размер которого вы хотите вывести:
df -h /dev/sda9 Файл.система Размер Использовано Дост Использовано% Cмонтировано в /dev/sda9 174G 25G 141G 15% /Размер папок на диске (du)
Для просмотра размеров папок на диске используется команда du.
Если просто ввести команду без каких либо аргументов, то она рекурсивно проскандирует вашу текущую директорию и выведет размеры всех файлов в ней. Обычно для du указывают путь до папки, которую вы хотите проанализировать.
Если нужно просмотреть размеры без рекурсивного обхода всех папок, то используется опция -s (—summarize). Также как и с df, добавим опцию -h (—human-readable).
Размер конкретной папки:
du -sh ./Загрузки 3,4G ./ЗагрузкиРазмеры файлов и папок внутри конкретной папки:
du -sh ./Загрузки/* 140K ./Загрузки/antergos-17.1-x86_64.iso.torrent 79M ./Загрузки/ubuntu-amd64.deb 49M ./Загрузки/data.zip 3,2G ./Загрузки/Parrot-full-3.5_amd64.iso 7,1M ./Загрузки/secret.tgzHow to Get the Size of a Directory in Linux
Many users run Linux from the command line. However, the command line — sometimes known as the terminal — doesn’t have an intuitive interface for checking disk space in Linux.
This guide shows you how to find the size of a specific directory in Linux from the command line.
- A system running Linux
- A command line / terminal window (available by clicking Search, then typing terminal)
- A user account with sudo or root privileges
Note: In Linux, a directory is the equivalent of a folder in Windows. A directory may have directories inside (called subdirectories), or it may only contain files.
Option 1: Display the Size of a Directory Using the du Command
The du command stands for disk usage. This command is included by default in most Linux distributions.
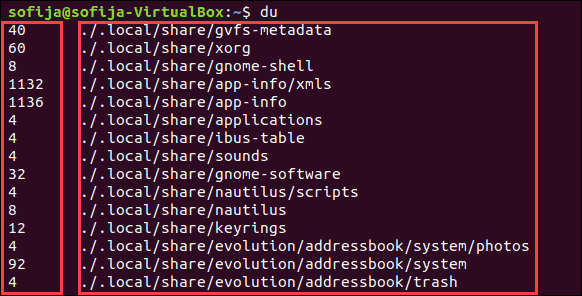
You can display the size of your current directory by typing du in the command line:
The system should display a list of the contents of your home directory, with a number to the left. That number is the size of the object in kilobytes.
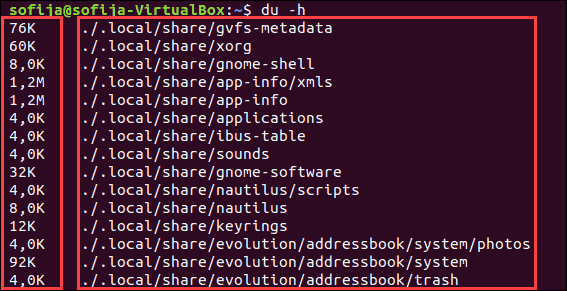
You can add the -h option to make the output more readable:
Each entry will start with a number and a letter. The number is the amount of space used, and the letter (usually K, M, or G) indicates Kilobytes, Megabytes, or Gigabytes. For example:
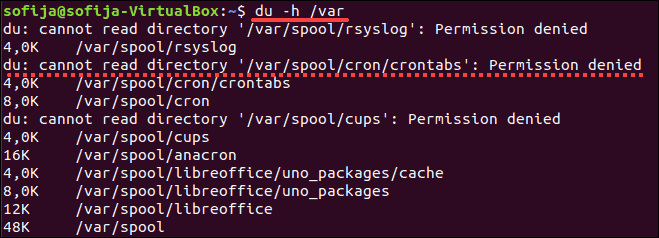
400K – 400 kilobytes 7.3M – 7.3 megabytes 2.2G – 2.2 gigabytesTo find the size of a specific directory different from your current working directory. The du command allows you to specify a directory to examine:
This displays the size of the contents of the /var directory. You may see some entries with an error, as in the image below.
This happens when your user account does not have permission to access a particular directory. Use the sudo or su command to get access privileges:
Note: Some versions of Linux don’t enable sudo by default. You can use the su command to switch to the root user account instead.
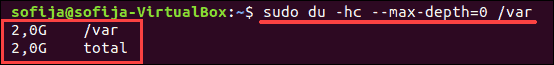
To display total disk usage of a particular directory, use the -c command:
Options can be combined. If you wanted to repeat the previous command in human-readable format, enter the following:
You can limit the scan to a certain level of subdirectory by using the max-depth option. For example, to scan only the size of the top directory, use —max-depth=0 :
If you wanted to list only the top directory and the first layer of subdirectories, change —max-depth=1 :
If you run into trouble or want to explore more options for the du command, enter the following command to display the help file:
Option 2: Get Size of Directory in Linux Using tree Command
By default, the tree command is not included in some versions of Linux. To install it, enter the following:
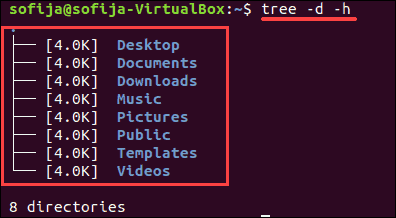
The tree command displays a visual representation of your directories. It uses lines to indicate which subdirectories belong where, and it uses colors to indicate directories and files.
tree can also be used with options. To display a human-readable size of the current directory’s subdirectories, enter the following:
Like the du command, tree can target a specific directory:
This command takes a few moments since the /var directory has many entries.
The tree command also has a help file, which you can access by entering:
Option 3: Find the Size of a Linux Directory Using ncdu Command
The ncdu tool stands for NCurses Disk Usage. Like the tree command, it is not installed by default on some versions of Linux. To install it, enter the following:
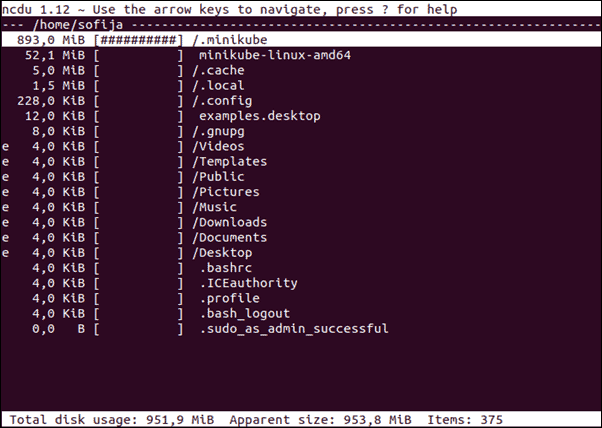
The ncdu utility is an interactive display of your disk usage. For example, enter the following:
In the upper left corner, it displays the current directory being scanned. A column on the left displays the numerical size, a graph of #- signs to indicate the relative size, and the file or directory.
Use the up and down arrows to select different lines. The right arrow will browse into a directory, and the left arrow will take you back.
ncdu can be used to target a specific directory, for example:
For help, press the ? key inside the ncdu interface. To quit, press the letter q .
Note: Learn how to move directories in Linux using the GUI or system commands.
You now have three different options to find the size of a directory in Linux operating systems.
If you want to learn more about directories in Linux, read our article how to rename directories in Linux.