- How do I determine the total size of a directory (folder) from the command line?
- Размеры папок и дисков в Linux. Команды df и du
- Свободное место на диске (df)
- Опция -h
- Размер конкретного диска
- Размер папок на диске (du)
- Размер конкретной папки:
- Размеры файлов и папок внутри конкретной папки:
- How to Get the Size of a Directory in Linux
- Option 1: Display the Size of a Directory Using the du Command
- Option 2: Get Size of Directory in Linux Using tree Command
- Option 3: Find the Size of a Linux Directory Using ncdu Command
- Команда du в Linux
- Синтаксис и опции команды du
- Примеры использования du
- Выводы
How do I determine the total size of a directory (folder) from the command line?
The -h flag on sort will consider «Human Readable» size values.
If want to avoid recursively listing all files and directories, you can supply the —max-depth parameter to limit how many items are displayed. Most commonly, —max-depth=1
du -h --max-depth=1 /path/to/directory I use du -sh or DOOSH as a way to remember it (NOTE: the command is the same, just the organization of commandline flags for memory purposes)
There is a useful option to du called the —apparent-size. It can be used to find the actual size of a file or directory (as opposed to its footprint on the disk) eg, a text file with just 4 characters will occupy about 6 bytes, but will still show up as taking up ~4K in a regular du -sh output. However, if you pass the —apparent-size option, the output will be 6. man du says: —apparent-size print apparent sizes, rather than disk usage; although the apparent size is usually smaller, it may be larger due to holes in (‘sparse’) files, internal fragmentation, indirect blocks
This works for OS X too! Thanks, I was really looking for a way to clear up files, both on my local machine, and my server, but automated methods seemed not to work. So, I ran du -hs * and went into the largest directory and found out which files were so large. This is such a good method, and the best part is you don’t have to install anything! Definitely deserved my upvote
@BandaMuhammadAlHelal I think there are two reasons: rounding ( du has somewhat peculiar rounding, showing no decimals if the value has more than one digit in the chosen unit), and the classical 1024 vs. 1000 prefix issue. du has an option -B (or —block-size ) to change the units in which it displays values, or you could use -b instead of -h to get the «raw» value in bytes.
Размеры папок и дисков в Linux. Команды df и du
Рассмотрим, как используя команды df и du просматривать свободное место на дисках и размеры папок в Linux.
Свободное место на диске (df)
Для просмотра свободного и занятого места на разделах диска в Linux можно воспользоваться командой df.
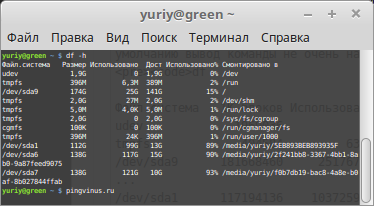
Первым делом можно просто ввести команду df без каких-либо аргументов и получить занятое и свободное место на дисках. Но по умолчанию вывод команды не очень наглядный — например, размеры выводятся в КБайтах (1К-блоках).
df Файл.система 1K-блоков Использовано Доступно Использовано% Cмонтировано в udev 1969036 0 1969036 0% /dev tmpfs 404584 6372 398212 2% /run /dev/sda9 181668460 25176748 147240368 15% / . /dev/sda1 117194136 103725992 13468144 89% /media/yuriy/5EB893BEB893935F /dev/sda6 144050356 121905172 14804772 90% /media/yuriy/2f24. d9075 Примечание: df не отображает информацию о не смонтированных дисках.
Опция -h
Опция -h (или —human-readable) позволяет сделать вывод более наглядным. Размеры выводятся теперь в ГБайтах.
df -h Файл.система Размер Использовано Дост Использовано% Cмонтировано в udev 1,9G 0 1,9G 0% /dev tmpfs 396M 6,3M 389M 2% /run /dev/sda9 174G 25G 141G 15% / . /dev/sda1 112G 99G 13G 89% /media/yuriy/5EB893BEB893935F /dev/sda6 138G 117G 15G 90% /media/yuriy/2f24. d9075Размер конкретного диска
Команде df можно указать путь до точки монтирования диска, размер которого вы хотите вывести:
df -h /dev/sda9 Файл.система Размер Использовано Дост Использовано% Cмонтировано в /dev/sda9 174G 25G 141G 15% /Размер папок на диске (du)
Для просмотра размеров папок на диске используется команда du.
Если просто ввести команду без каких либо аргументов, то она рекурсивно проскандирует вашу текущую директорию и выведет размеры всех файлов в ней. Обычно для du указывают путь до папки, которую вы хотите проанализировать.
Если нужно просмотреть размеры без рекурсивного обхода всех папок, то используется опция -s (—summarize). Также как и с df, добавим опцию -h (—human-readable).
Размер конкретной папки:
du -sh ./Загрузки 3,4G ./ЗагрузкиРазмеры файлов и папок внутри конкретной папки:
du -sh ./Загрузки/* 140K ./Загрузки/antergos-17.1-x86_64.iso.torrent 79M ./Загрузки/ubuntu-amd64.deb 49M ./Загрузки/data.zip 3,2G ./Загрузки/Parrot-full-3.5_amd64.iso 7,1M ./Загрузки/secret.tgzHow to Get the Size of a Directory in Linux
Many users run Linux from the command line. However, the command line — sometimes known as the terminal — doesn’t have an intuitive interface for checking disk space in Linux.
This guide shows you how to find the size of a specific directory in Linux from the command line.
- A system running Linux
- A command line / terminal window (available by clicking Search, then typing terminal)
- A user account with sudo or root privileges
Note: In Linux, a directory is the equivalent of a folder in Windows. A directory may have directories inside (called subdirectories), or it may only contain files.
Option 1: Display the Size of a Directory Using the du Command
The du command stands for disk usage. This command is included by default in most Linux distributions.
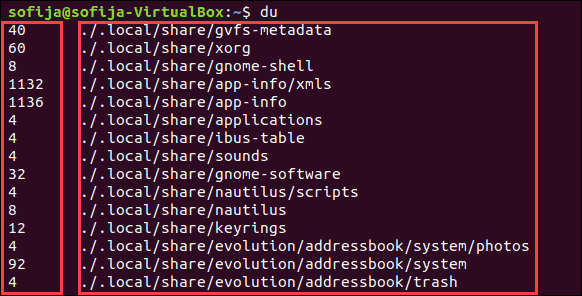
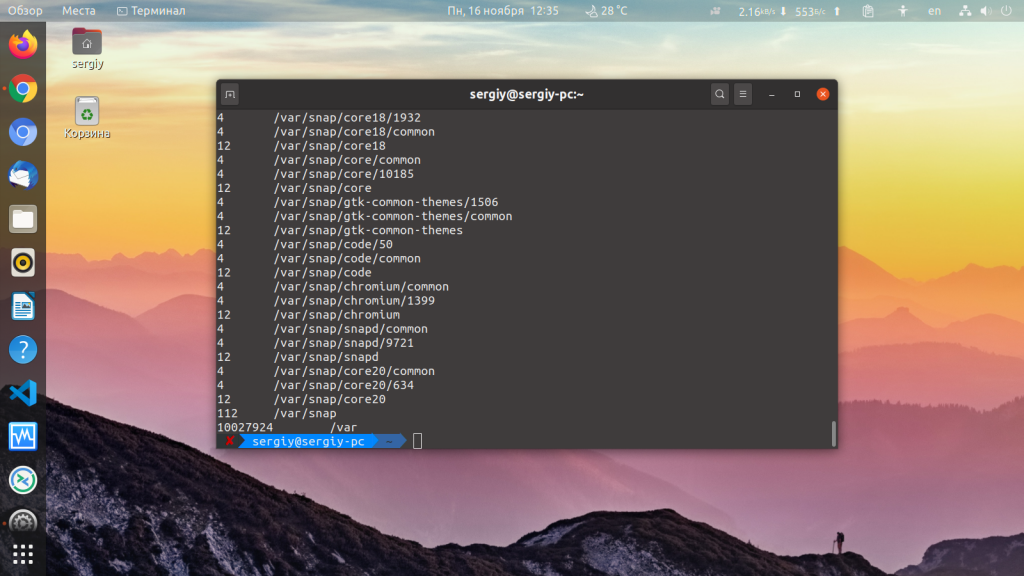
You can display the size of your current directory by typing du in the command line:
The system should display a list of the contents of your home directory, with a number to the left. That number is the size of the object in kilobytes.
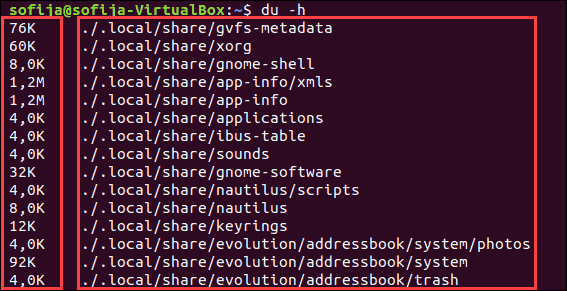
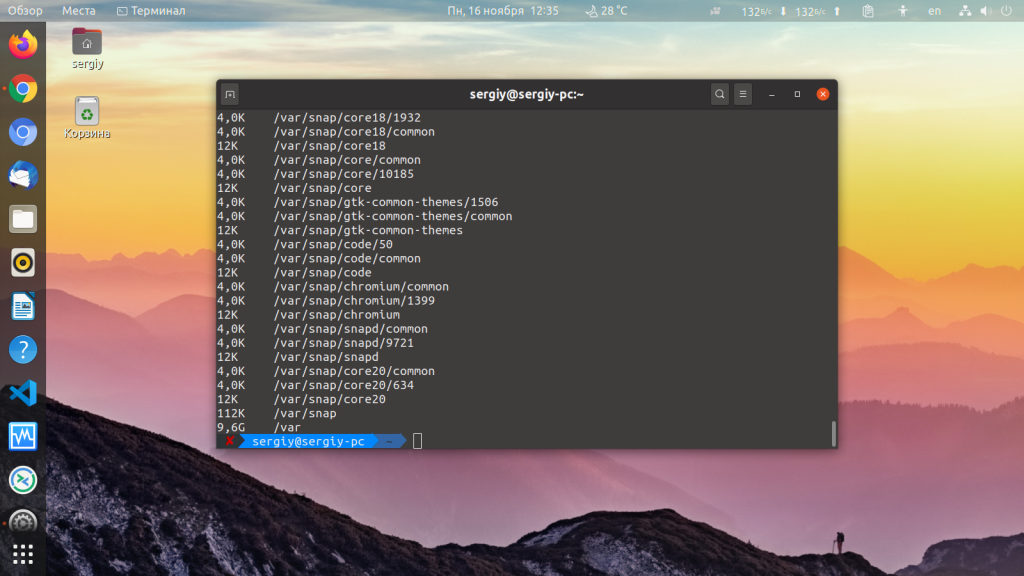
You can add the -h option to make the output more readable:
Each entry will start with a number and a letter. The number is the amount of space used, and the letter (usually K, M, or G) indicates Kilobytes, Megabytes, or Gigabytes. For example:
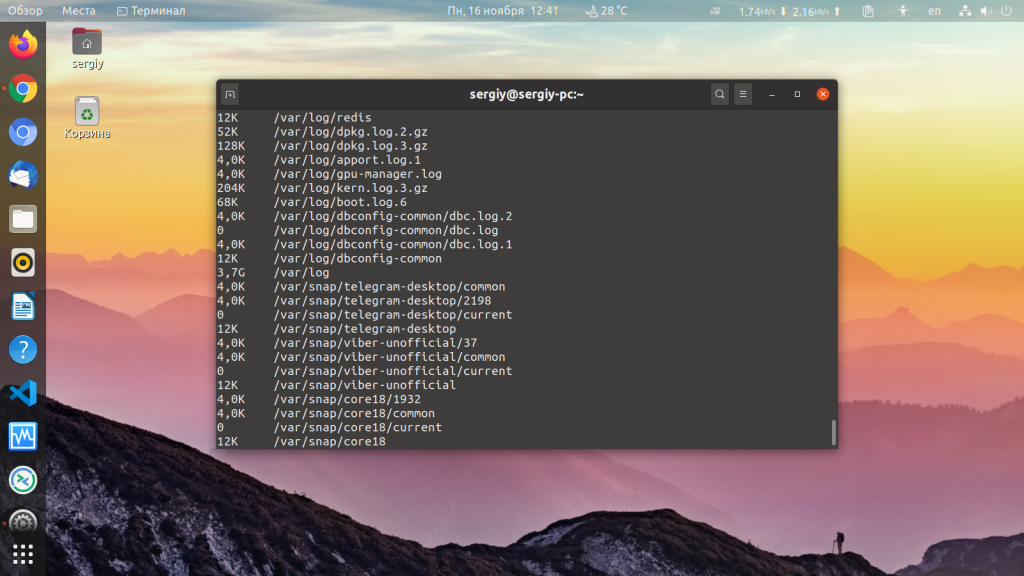
400K – 400 kilobytes 7.3M – 7.3 megabytes 2.2G – 2.2 gigabytesTo find the size of a specific directory different from your current working directory. The du command allows you to specify a directory to examine:
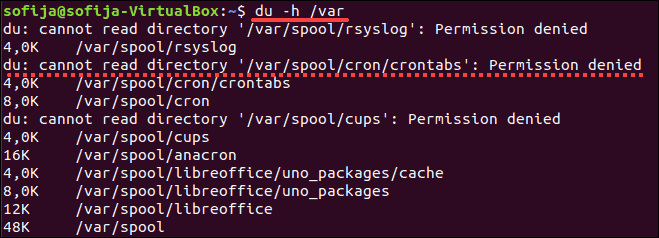
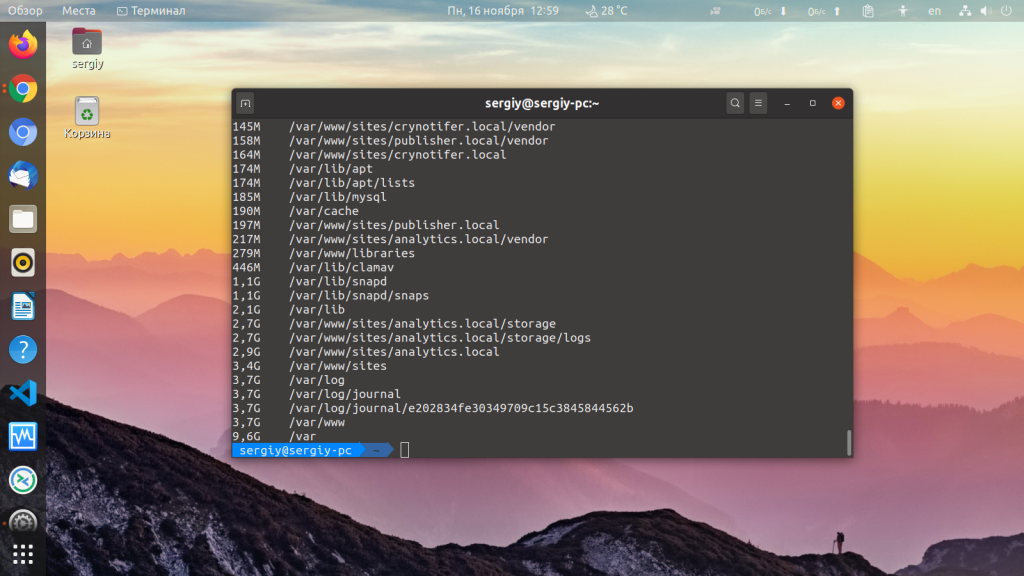
This displays the size of the contents of the /var directory. You may see some entries with an error, as in the image below.
This happens when your user account does not have permission to access a particular directory. Use the sudo or su command to get access privileges:
Note: Some versions of Linux don’t enable sudo by default. You can use the su command to switch to the root user account instead.
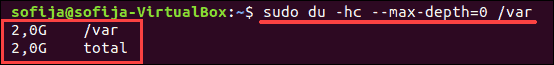
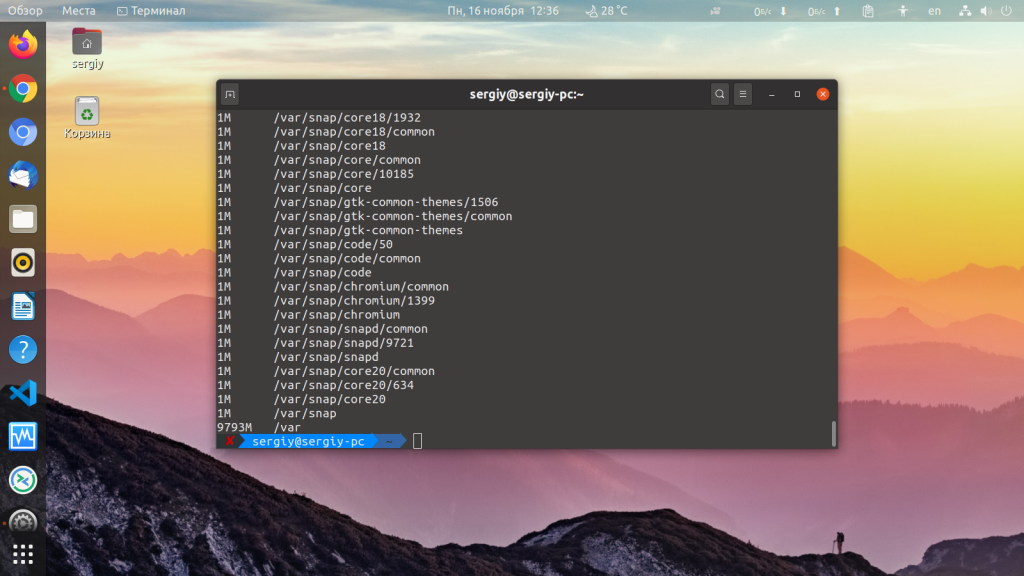
To display total disk usage of a particular directory, use the -c command:
Options can be combined. If you wanted to repeat the previous command in human-readable format, enter the following:
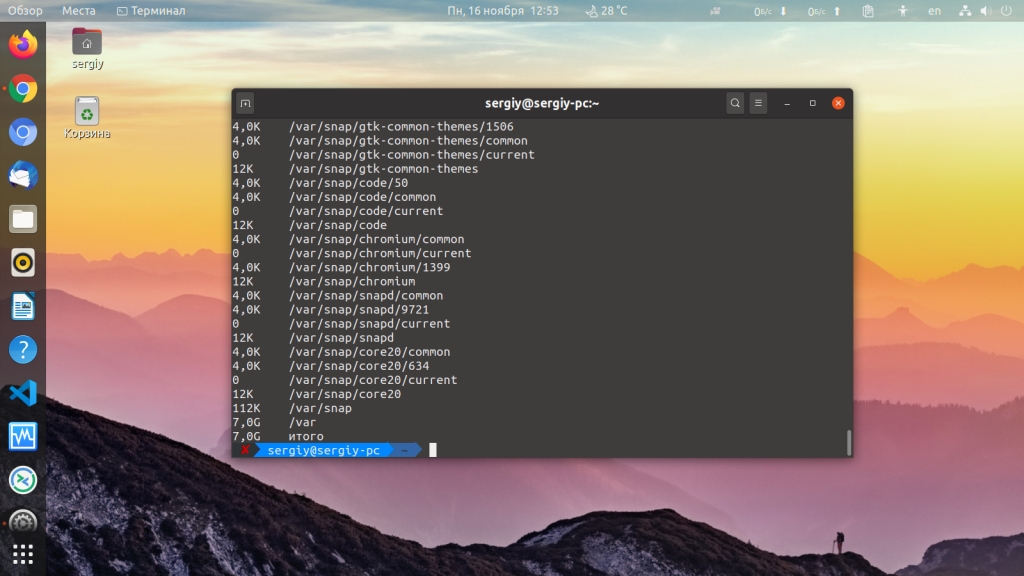
You can limit the scan to a certain level of subdirectory by using the max-depth option. For example, to scan only the size of the top directory, use —max-depth=0 :
If you wanted to list only the top directory and the first layer of subdirectories, change —max-depth=1 :
If you run into trouble or want to explore more options for the du command, enter the following command to display the help file:
Option 2: Get Size of Directory in Linux Using tree Command
By default, the tree command is not included in some versions of Linux. To install it, enter the following:
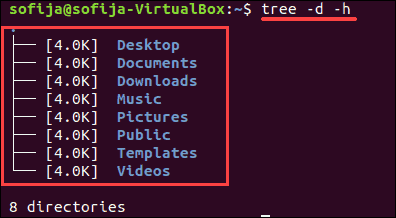
The tree command displays a visual representation of your directories. It uses lines to indicate which subdirectories belong where, and it uses colors to indicate directories and files.
tree can also be used with options. To display a human-readable size of the current directory’s subdirectories, enter the following:
Like the du command, tree can target a specific directory:
This command takes a few moments since the /var directory has many entries.
The tree command also has a help file, which you can access by entering:
Option 3: Find the Size of a Linux Directory Using ncdu Command
The ncdu tool stands for NCurses Disk Usage. Like the tree command, it is not installed by default on some versions of Linux. To install it, enter the following:
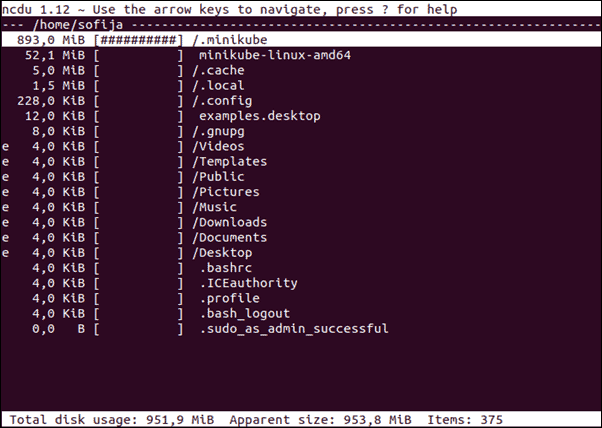
The ncdu utility is an interactive display of your disk usage. For example, enter the following:
In the upper left corner, it displays the current directory being scanned. A column on the left displays the numerical size, a graph of #- signs to indicate the relative size, and the file or directory.
Use the up and down arrows to select different lines. The right arrow will browse into a directory, and the left arrow will take you back.
ncdu can be used to target a specific directory, for example:
For help, press the ? key inside the ncdu interface. To quit, press the letter q .
Note: Learn how to move directories in Linux using the GUI or system commands.
You now have three different options to find the size of a directory in Linux operating systems.
If you want to learn more about directories in Linux, read our article how to rename directories in Linux.
Команда du в Linux
Иногда возникает необходимость посмотреть сколько места занимают файлы в определённой папке и найти самые большие файлы для того чтобы их удалить. Конечно, для решения этих задач существует множество инструментов, но самый простой из них, это утилита du. Она позволяет вывести размер всех файлов в определённой папке в байтах или в более удобном формате.
В сегодняшней статье мы разберемся что из себя представляет команда du Linux, а также как ею пользоваться для решения ваших рабочих задач.
Синтаксис и опции команды du
Синтаксис команды очень простой. Вам достаточно передать ей опции и путь к папке с которой следует работать:
$ du опции /путь/к/папке
- -a, —all — выводить размер для всех файлов, а не только для директорий, по умолчанию размер выводится только для папок;
- -B, —block-size — указать единицы вывода размера, доступно: K,M,G,T,P,E,Z,Y для 1024 и KB, MB и так далее для 1000;
- -c, —total — выводить в конце общий размер всех папок;
- -d, —max-depth — максимальная глубина вложенности директорий;
- -h, —human-readable — выводить размер в единицах измерения удобных для человека;
- —inodes — выводить информацию об использованию inode;
- -L, —dereference — следовать по всем символическим ссылкам;
- -l, —count-links — учитывать размер файла несколько раз для жестких ссылок;
- -P, —no-dereference — не следовать по символическим ссылкам, это поведение используется по умолчанию;
- -S, —separate-dirs — не включать размер подпапок в размер папки;
- —si — выводить размер файлов и папок в системе си, используется 1000 вместо 1024;
- -s, —summarize — выводить только общий размер;
- -t, —threshold — не учитывать файлы и папки с размером меньше указанного;
- —time — отображать время последней модификации для файла или папки, вместо времени модификации можно выводить такие метки: atime, access, use, ctime;
- -X, —exclude — исключить файлы из подсчёта;
- -x, —one-file-system — пропускать примонтированные файловые системы;
- —version — вывести версию утилиты.
Здесь перечислены не все опции. Если вам надо больше, смотрите в:
Примеры использования du
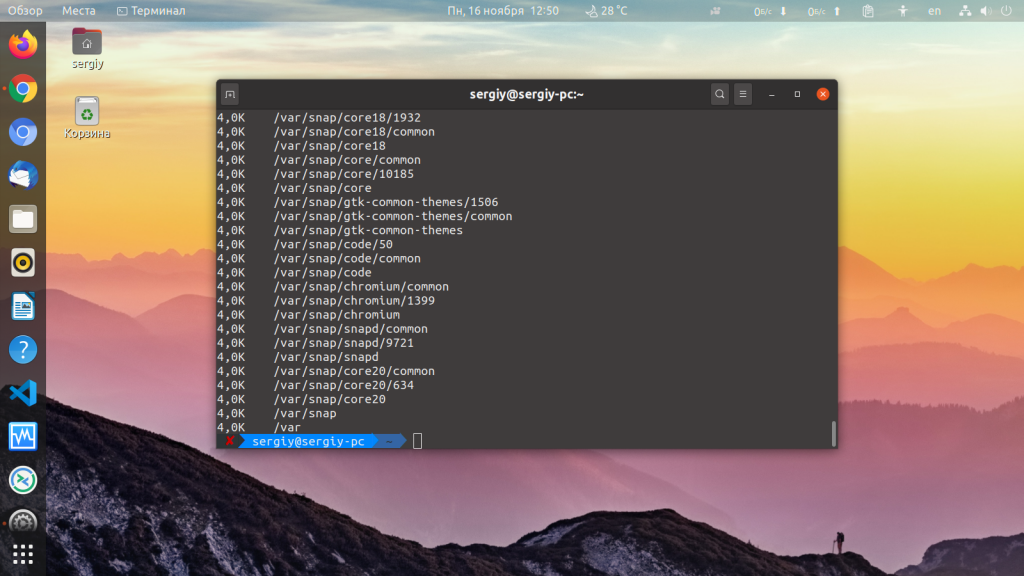
Чтобы просто вывести список папок в определённом каталоге и занимаемое ими место, например, в /var выполните:
По умолчанию размер выводится в байтах. Для того чтобы размер выводился в более читабельном виде используйте опцию -h:
Или вы можете указать размер блока. Тогда точность будет немного ниже, потому что минимальная единица измерения — один блок. Например, для вывода размера папок в мегабайтах с размером блока в 1024 килобайт используйте опцию -B с параметром M:
Если надо выводить размер не только папок, но и файлов, которые там находятся используйте опцию -a:
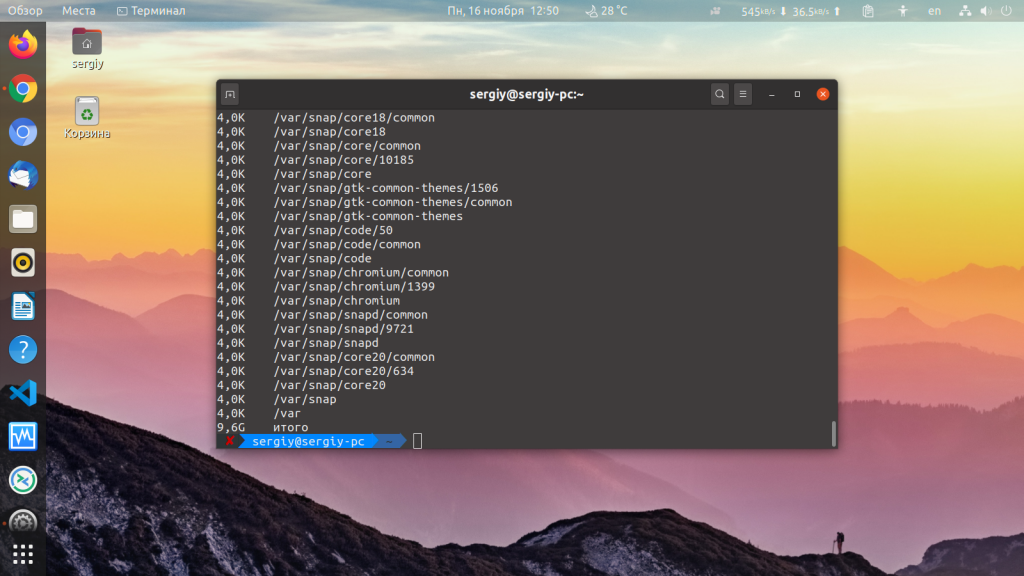
Для того чтобы вывести только общий размер всех файлов и папок нужно применить опцию -s:
Если вы хотите вывести размер папок без вложенных в них подпапок используйте опцию -m:
Ещё можно вывести строчку с общим размером всей папки. Правда использовать эту возможность есть смысл только с опцией -S, потому что общий размер папки во всех других случаях и так отображается:
Если вам надо исключить какие-либо файлы из подсчёта, следует использовать опцию -exclude. Например, давайте исключим все лог файлы:
Чтобы данные были более наглядными их желательно отсортировать. Встроенной поддержки сортировки в du linux нет, зато можно воспользоваться утилитой sort с опцией -h. Эта опция нужна чтобы сортировались единицы измерения в понятном для чтения формате:
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрели основные возможности команды du в Linux. Как видите, несмотря на то, что утилита очень простая, она позволяет посмотреть всё что необходимо. А какими программами вы пользуетесь для просмотра размера файлов и папок? Напишите в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.