- Список служб Linux с помощью Systemctl
- Список служб Linux
- Отображение статуса службы
- Выводы
- Listing Linux Services With Systemctl
- List Services Using Systemctl in Linux
- List All Services
- List Loaded Services
- Running Services
- Enabled Services
- Disabled Services
- Check Service Status
- Where are systemctl service files
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Syeda Wardah Batool
Список служб Linux с помощью Systemctl
В Linux служба — это программа, работающая в фоновом режиме . Службы можно запускать по запросу или во время загрузки.
Если вы используете Linux в качестве основной операционной системы или платформы разработки, вы будете иметь дело с различными службами, такими как веб-сервер, ssh или cron . Знание того, как перечислить запущенные службы или проверить статус службы, важно при отладке системных проблем.
Большинство последних дистрибутивов Linux используют systemd в качестве системы инициализации и диспетчера служб по умолчанию.
Systemd — это набор инструментов для управления системами Linux. Он используется для загрузки машины, управления службами, автоматического монтирования файловых систем, регистрации событий, настройки имени хоста и других системных задач.
В этой статье объясняется, как составить список служб в Linux.
Список служб Linux
Systemd использует концепцию модулей, которыми могут быть службы, сокеты, точки монтирования, устройства и т. Д. Модули определяются с помощью текстовых файлов в формате ini . Эти файлы содержат информацию об устройстве, его настройках и командах для выполнения. Расширения файлов определяют тип файла модуля. Например, файлы системных сервисных модулей имеют расширение .service .
systemctl — это утилита командной строки, которая используется для управления systemd и службами. Он является частью экосистемы systemd и по умолчанию доступен во всех системах.
Чтобы получить список всех загруженных служебных единиц, введите:
sudo systemctl list-units --type serviceUNIT LOAD ACTIVE SUB DESCRIPTION cron.service loaded active running Regular background program processing daemon . Каждая строка вывода содержит следующие столбцы слева направо:
- UNIT — Название сервисной единицы.
- LOAD — Информация о том, загружен ли файл объекта в память.
- ACTIVE — состояние активации файла модуля высокого уровня, которое может быть активным, перезагружающимся, неактивным, неудачным, активируемым, деактивируемым. Это обобщение столбца SUB .
- SUB — состояние активации файла юнита низкого уровня. Значение этого поля зависит от типа объекта. Например, модуль типа service может находиться в одном из следующих состояний: неработающий, завершенный, сбойный, неактивный или работающий.
- DESCRIPTION — Краткое описание файла объекта.
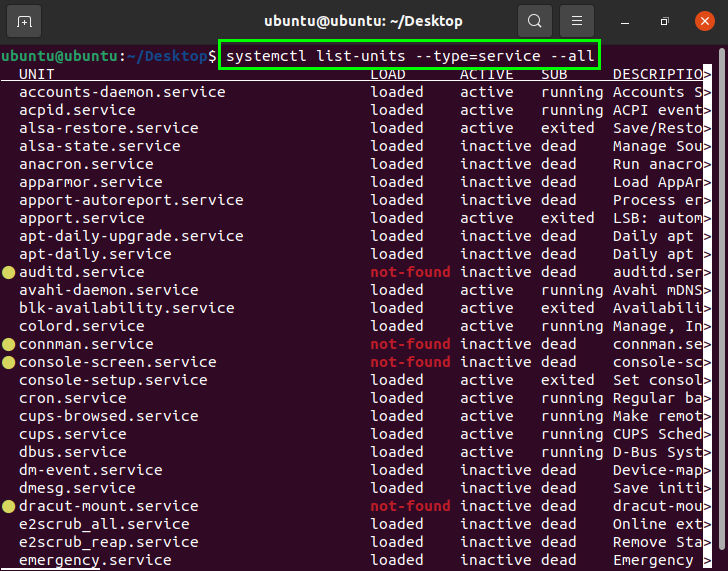
По умолчанию команда перечисляет только загруженные активные юниты. Чтобы увидеть загруженные, но неактивные модули, передайте параметр —all :
sudo systemctl list-units --type service --allЕсли вы хотите увидеть все установленные файлы модулей, а не только загруженные, используйте:
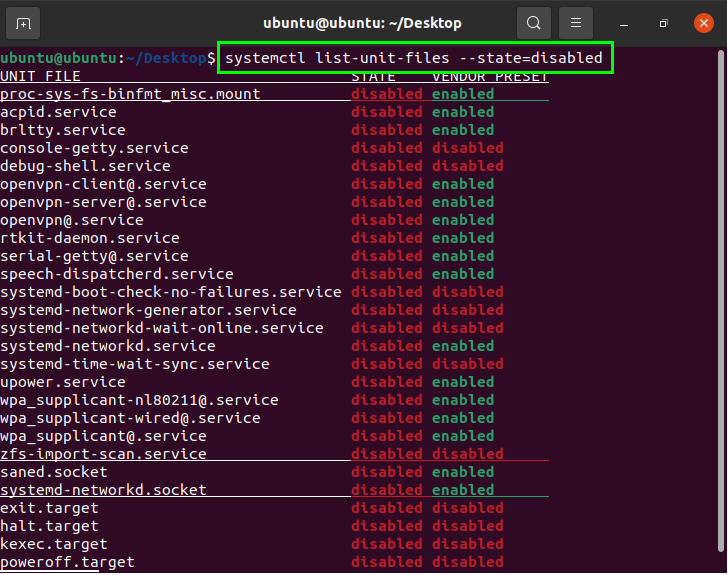
sudo systemctl list-unit-filesОтображение статуса службы
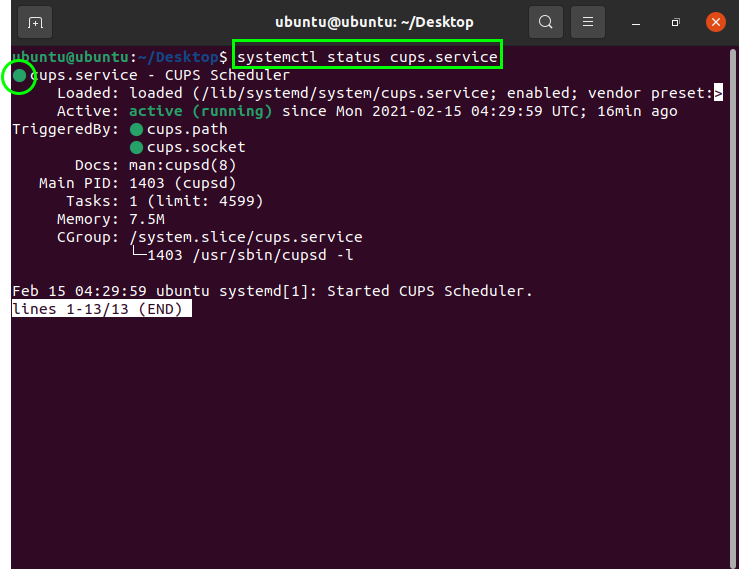
Чтобы проверить статус службы, используйте команду systemctl status :
sudo systemctl status .serviceГде — это имя сервисной единицы, которую вы хотите проверить. Например, чтобы определить текущий статус службы nginx, вы должны запустить:
sudo systemctl status nginx.serviceВы можете опустить суффикс «.service». systemctl status nginx такое же, как systemctl status nginx.service .
● nginx.service - A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2020-12-23 19:13:50 UTC; 5s ago Docs: man:nginx(8) Process: 3061052 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 3061063 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 3061064 (nginx) Tasks: 2 (limit: 470) Memory: 6.0M CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service ├─3061064 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on; └─3061065 nginx: worker process Dec 23 19:13:50 linuxize.dev systemd[1]: Starting A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server. Команда напечатает следующую информацию:
- Loaded — Loaded ли служебный модуль и полный путь к файлу модуля. Он также показывает, разрешен ли запуск устройства во время загрузки.
- Active — активна и работает ли служба. Если ваш терминал поддерживает цвета, а служба активна и работает, точка ( ● ) и часть «активен (работает)» будут напечатаны зеленым цветом. Строка также показывает, как долго работает служба.
- Docs — служебная документация.
- Process — информация о процессах обслуживания.
- Main PID — сервисный PID.
- Tasks — количество задач, учитываемых для объекта, и лимит задач.
- Memory — информация об используемой памяти.
- CGroup — информация о связанных контрольных группах.
Если вы хотите только проверить статус службы, используйте команду systemctl is-active . Например, чтобы убедиться, что служба nginx запущена, вы должны запустить:
systemctl is-active nginx.serviceКоманда покажет вам статус службы. Если служба активна, команда возвращает статус выхода 0, что может быть полезно при использовании команды внутри сценариев оболочки.
Выводы
Мы показали вам, как использовать команду systemctl для systemctl списка служб Linux и проверки их статуса.
Если у вас есть какие-либо вопросы или отзывы, не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии ниже.
Listing Linux Services With Systemctl
A variety of services run continuously on a Linux background, such as network and system services. Services running on Linux are also known as daemons, which refers to a group of processes working on the back-end.
Services can be managed and listed through different methods and tools. The Systemd is a software suite of tools with the ability to manage Linux systems adopted by Linux distribution as a drop-in replacement of the init process.
All system tasks can be controlled through Systemd. The process can be started or ended using this tool, and all enabled and disabled services information can also be listed with Systemd.
List Services Using Systemctl in Linux
Systemctl is a utility with the responsibility to manage and control the systemd system. The systemctl command can be used to list all services in Linux.
We will now show you how systemctl works.
List All Services
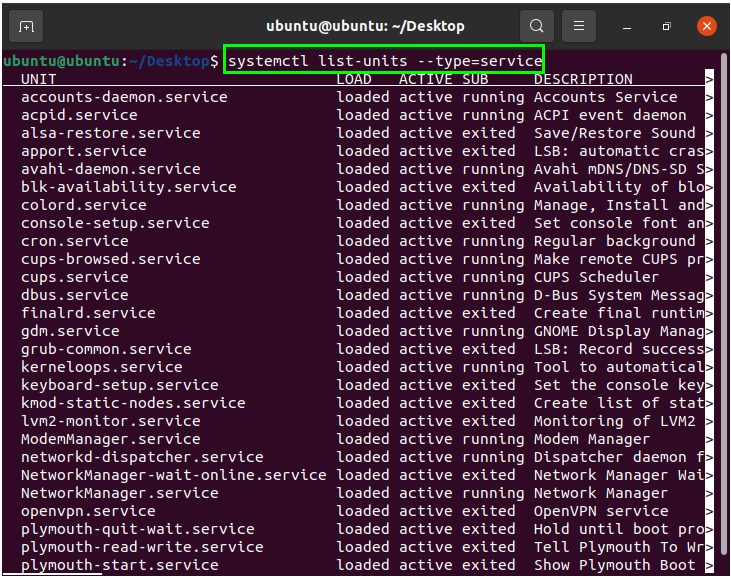
To get a list of all the services on the system, whether they are loaded or inactive, issue the following systemctl command in the terminal:
All services in your system will appear on the screen, as you can see in the output shown in the image above.
List Loaded Services
The following command will list every loaded service that is running, active, or failed:
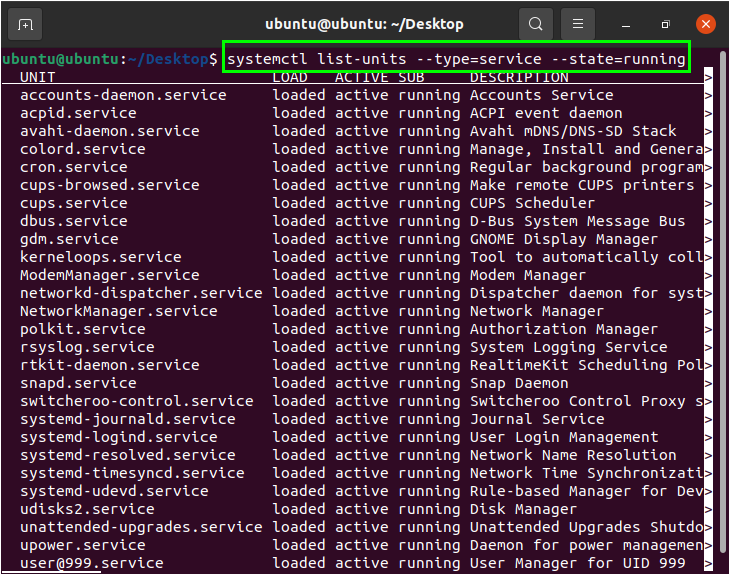
Running Services
In many cases, it can be difficult to distinguish the running services from all the other services. Run the following command to obtain a quick response that shows the loaded and running services in the system:
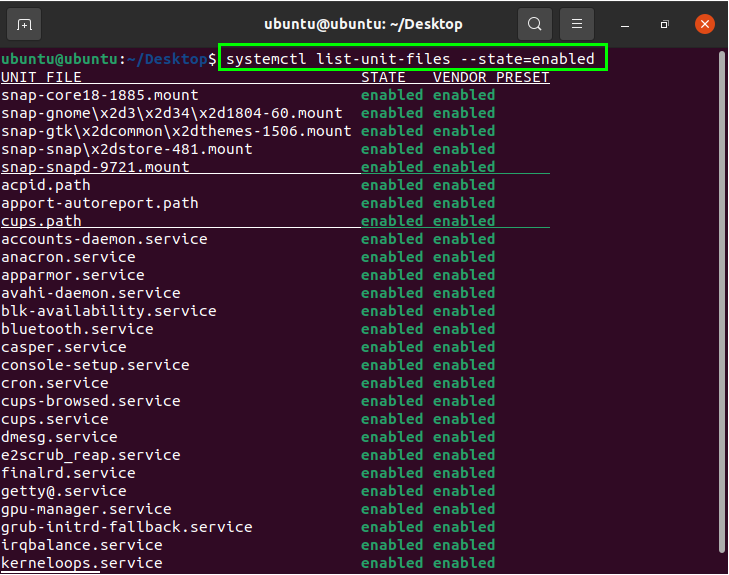
Enabled Services
Enter the following command to check the enabled services in the system:
Disabled Services
Disabled services will not start up or activate automatically. To enable a desired/required service, select the service from the disabled category. The following command is used to obtain a list of the disabled services in the system:
Check Service Status
The “cup” command is used to obtain more information about the status of a service. Cup is a modular printing system through which the computer acts as a print server and displays information. Use the cups command to obtain more information about the enabled/disabled services in the system:
Where are systemctl service files
Systemd configuration files are stored in specific directories. There are System unit directories and User unit directories.
You can find the location of the System Unit and User Unit directories using the pkg-config systemd command.
Run the following commands to find the directories on your system:
$ pkg-config systemd —variable =systemdsystemunitdir
$ pkg-config systemd —variable =systemduserunitdir
You can browse to these directories and see the systemd unit files.
Conclusion
This article showed you how to use systemctl commands to list services in Linux, including multiple options for viewing the services. With the correct knowledge, it is easy to pick the required command.
About the author
Syeda Wardah Batool
I am a Software Engineer Graduate and Self Motivated Linux writer. I also love to read latest Linux books. Moreover, in my free time, i love to read books on Personal development.