- bash script: to check if Apache server is up and running
- 8 Answers 8
- 3 Ways to Check Apache Server Status and Uptime in Linux
- 1. Systemctl Utility
- 2. Apachectl Utilities
- On Debian/Ubuntu
- On RHEL/CentOS
- 3. ps Utility
- Useful Commands to Manage Apache Web Server in Linux
- Install Apache Server
- Check Apache Version
- Check Apache Configuration Syntax Errors
- Start Apache Service
- Enable Apache Service
- Restart Apache Service
- View Apache Service Status
- Reload Apache Service
- Stop Apache Service
- Show Apache Command Help
bash script: to check if Apache server is up and running
I am new to bash scripting and trying to figure out why the below script is outputting that Apache server is not running whereas it is running properly.
ps cax | grep httpd if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then echo "Process is running." else echo "Process is not running." fi I’m running it on Ubuntu 14.04.2 LTS Also, how do I make changes to the script that this can test apache server installed on another machine. Kindly help
Try with sudo . I can’t remember when Ubuntu started using systemd, but you could probably use service apache2 status .
8 Answers 8
This is a working sample of bash script which check the apache status, restart it automatically if down, and alert by telegram bot within unicode emoji.
#!/bin/bash telegram=(xxxxx, yyyyyy) if ! pidof apache2 > /dev/null then # web server down, restart the server echo "Server down" /etc/init.d/apache2 restart > /dev/null sleep 10 #checking if apache restarted or not if pidof apache2 > /dev/null then for i in "$" do curl -s -X POST https://api.telegram.org/botxxxxxx:yyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy/sendMessage -d chat_id="$i" -d text="`echo -e '\U0001F525'` Apache stoped on Molib Stage. Automatically restarted succesfully." done else for i in "$" do curl -s -X POST https://api.telegram.org/botxxxxxx:yyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy/sendMessage -d chat_id="$i" -d text="`echo -e '\U0001F525'` Apache stoped on Molib Stage. Automatically restart failed. Please check manually." done fi fi 3 Ways to Check Apache Server Status and Uptime in Linux
Apache is a world’s most popular, cross platform HTTP web server that is commonly used in Linux and Unix platforms to deploy and run web applications or websites. Importantly, it’s easy to install and has a simple configuration as well.
In this article, we will show how to check Apache web server uptime on a Linux system using different methods/commands explained below.
1. Systemctl Utility
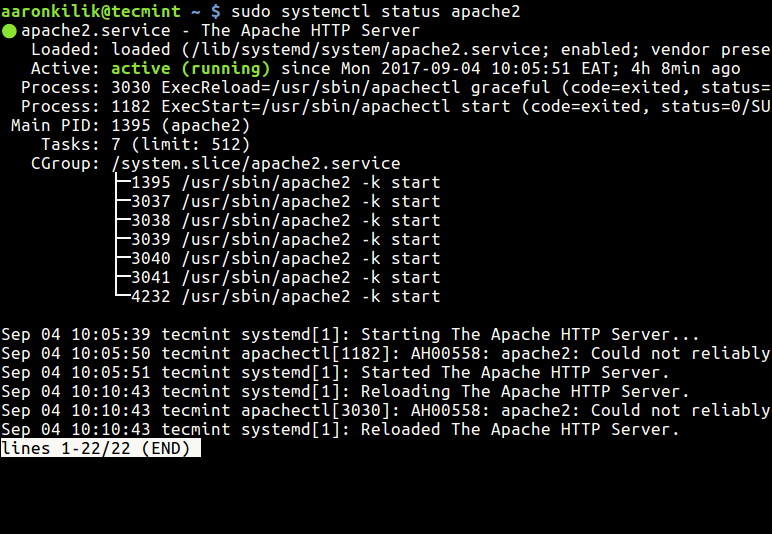
Systemctl is a utility for controlling the systemd system and service manager; it is used it to start, restart, stop services and beyond. The systemctl status sub-command, as the name states is used to view the status of a service, you can use it for the above purpose like so:
$ sudo systemctl status apache2 #Debian/Ubuntu # systemctl status httpd #RHEL/CentOS/Fedora
2. Apachectl Utilities
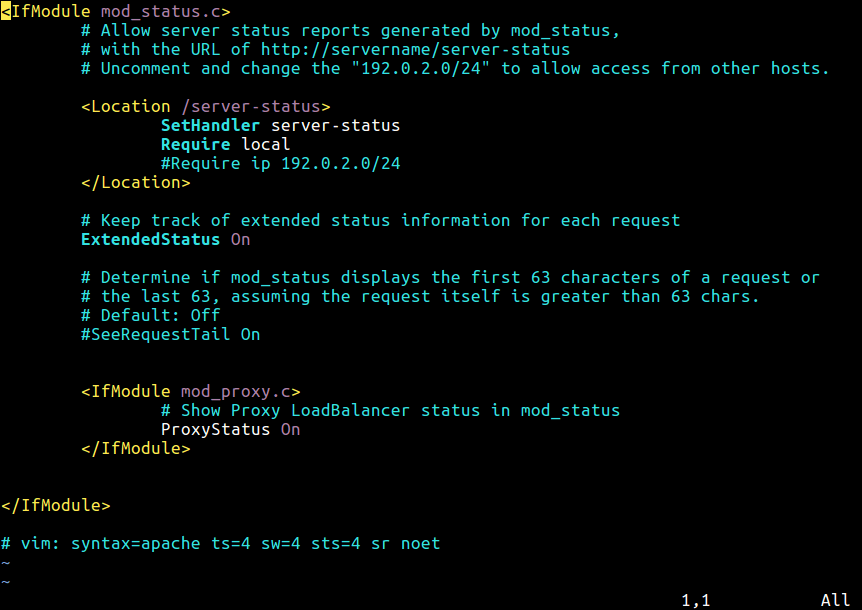
Apachectl is a control interface for Apache HTTP server. This method requires the mod_status (which displays info about the server is performing including its uptime) module installed and enabled (which is the default setting).
On Debian/Ubuntu
The server-status component is enabled by default using the file /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/status.conf.
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/status.conf
On RHEL/CentOS
To enable server-status component, create a file below.
# vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/server-status.conf
and add the following configuration.
SetHandler server-status #Require host localhost #uncomment to only allow requests from localhost
Save the file and close it. Then restart the web server.
If you are primarily using a terminal, then you also need a command line web browser such as lynx or links.
$ sudo apt install lynx #Debian/Ubuntu # yum install links #RHEL/CentOS
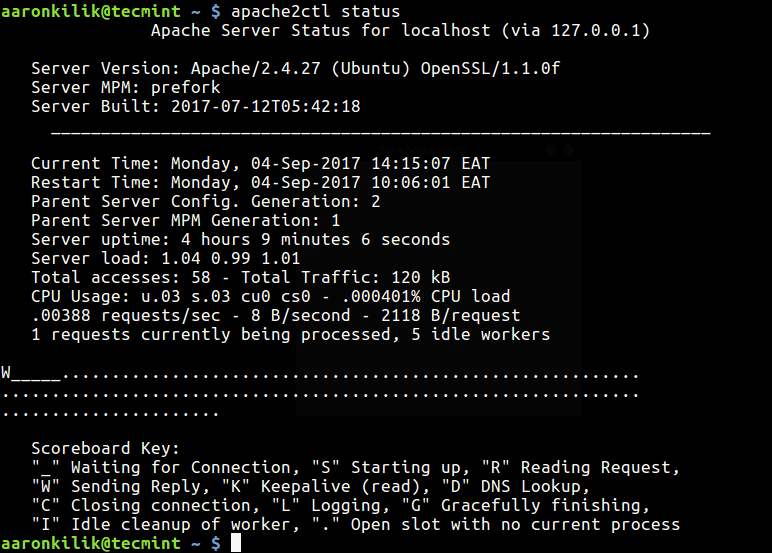
Then run the command below to check the Apache service uptime:
Alternatively, use the URL below to view the Apache web server status information from a graphical web browser:
http://localhost/server-status OR http:SERVER_IP/server-status
3. ps Utility
ps is a utility which shows information concerning a selection of the active processes running on a Linux system, you can use it with grep command to check Apache service uptime as follows.
- -e – enables selection of every processes on the system.
- -o – is used to specify output (comm – command, etime – process execution time and user – process owner).
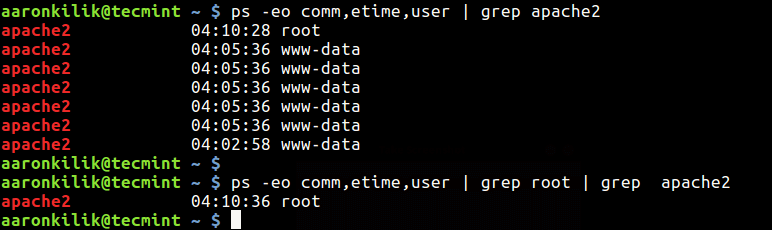
# ps -eo comm,etime,user | grep apache2 # ps -eo comm,etime,user | grep root | grep apache2 OR # ps -eo comm,etime,user | grep httpd # ps -eo comm,etime,user | grep root | grep httpd
The sample output below shows that apache2 service has been running for 4 hours, 10 minutes and 28 seconds (only consider the one started by root).
Lastly, check out more useful Apache web server guides:
In this article, we showed you three different ways to check Apache/HTTPD service uptime on a Linux system. If you have any questions or thoughts to share, do that via the comment section below.
Useful Commands to Manage Apache Web Server in Linux
In this tutorial, we will describe some of the most commonly used Apache (HTTPD) service management commands that you should know as a developer or system administrator and you should keep these commands at your fingertips. We will show commands for both Systemd and SysVinit.
Make sure that, following commands are must be executed as a root or sudo user and should work on any Linux distribution such as CentOS, RHEL, Fedora Debian, and Ubuntu.
Install Apache Server
To install Apache web server, use your default distribution package manager as shown.
$ sudo apt install apache2 [On Debian/Ubuntu] $ sudo yum install httpd [On RHEL/CentOS] $ sudo dnf install httpd [On Fedora 22+] $ sudo zypper install apache2 [On openSUSE]
Check Apache Version
To check the installed version of your Apache web server on your Linux system, run the following command.
$ sudo httpd -v OR $ sudo apache2 -v
Sample Output
Server version: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS) Server built: Nov 5 2018 01:47:09
If you want to display the Apache version number and compile settings, use the -V flag as shown.
$ sudo httpd -V OR $ sudo apache2 -V
Sample Output
Server version: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS) Server built: Nov 5 2018 01:47:09 Server's Module Magic Number: 20120211:24 Server loaded: APR 1.4.8, APR-UTIL 1.5.2 Compiled using: APR 1.4.8, APR-UTIL 1.5.2 Architecture: 64-bit Server MPM: prefork threaded: no forked: yes (variable process count) Server compiled with. -D APR_HAS_SENDFILE -D APR_HAS_MMAP -D APR_HAVE_IPV6 (IPv4-mapped addresses enabled) -D APR_USE_SYSVSEM_SERIALIZE -D APR_USE_PTHREAD_SERIALIZE -D SINGLE_LISTEN_UNSERIALIZED_ACCEPT -D APR_HAS_OTHER_CHILD -D AP_HAVE_RELIABLE_PIPED_LOGS -D DYNAMIC_MODULE_LIMIT=256 -D HTTPD_ROOT="/etc/httpd" -D SUEXEC_BIN="/usr/sbin/suexec" -D DEFAULT_PIDLOG="/run/httpd/httpd.pid" -D DEFAULT_SCOREBOARD="logs/apache_runtime_status" -D DEFAULT_ERRORLOG="logs/error_log" -D AP_TYPES_CONFIG_FILE="conf/mime.types" -D SERVER_CONFIG_FILE="conf/httpd.conf"
Check Apache Configuration Syntax Errors
To check your Apache configuration files for any syntax errors run the following command, which will check the validity of the config files, prior to restart the service.
$ sudo httpd -t OR $ sudo apache2ctl -t
Sample Output
AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using tecmint.com. Set the 'ServerName' directive globally to suppress this message Syntax OK
Start Apache Service
To start the Apache service, run the following command.
------------ On CentOS/RHEL ------------ $ sudo systemctl start httpd [On Systemd] $ sudo service httpd start [On SysVInit] ------------ On Ubunt/Debian ------------ $ sudo systemctl start apache2 [On Systemd] $ sudo service apache2 start [On SysVInit]
Enable Apache Service
The previous command only starts the Apache service for the meantime, to enable it auto-start at system boot, run the following command.
------------ On CentOS/RHEL ------------ $ sudo systemctl enable httpd [On Systemd] $ sudo chkconfig httpd on [On SysVInit] ------------ On Ubunt/Debian ------------ $ sudo systemctl enable apache2 [On Systemd] $ sudo chkconfig apache2 on [On SysVInit]
Restart Apache Service
To restart Apache (stop and then start the service), run the following command.
------------ On CentOS/RHEL ------------ $ sudo systemctl restart httpd [On Systemd] $ sudo service httpd restart [On SysVInit] ------------ On Ubunt/Debian ------------ $ sudo systemctl restart apache2 [On Systemd] $ sudo service apache2 restart [On SysVInit]
View Apache Service Status
To check the Apache service run time status information, run the following command.
------------ On CentOS/RHEL ------------ $ sudo systemctl status httpd [On Systemd] $ sudo service httpd status [On SysVInit] ------------ On Ubunt/Debian ------------ $ sudo systemctl status apache2 [On Systemd] $ sudo service apache2 status [On SysVInit]
Reload Apache Service
If you have made any changes to the Apache server configuration, you can instruct the service to reload its configuration by running the following command.
------------ On CentOS/RHEL ------------ $ sudo systemctl reload httpd [On Systemd] $ sudo service httpd reload [On SysVInit] ------------ On Ubunt/Debian ------------ $ sudo systemctl reload apache2 [On Systemd] $ sudo service apache2 reload [On SysVInit]
Stop Apache Service
To stop the Apache service, use the following command.
------------ On CentOS/RHEL ------------ $ sudo systemctl stop httpd [On Systemd] $ sudo service httpd stop [On SysVInit] ------------ On Ubunt/Debian ------------ $ sudo systemctl stop apache2 [On Systemd] $ sudo service apache2 stop [On SysVInit]
Show Apache Command Help
Last but not least, you can get help about the Apache service commands under systemd by running the following command.
$ sudo httpd -h OR $ sudo apache2 -h OR $ systemctl -h apache2
Sample Output
Usage: httpd [-D name] [-d directory] [-f file] [-C "directive"] [-c "directive"] [-k start|restart|graceful|graceful-stop|stop] [-v] [-V] [-h] [-l] [-L] [-t] [-T] [-S] [-X] Options: -D name : define a name for use in directives -d directory : specify an alternate initial ServerRoot -f file : specify an alternate ServerConfigFile -C "directive" : process directive before reading config files -c "directive" : process directive after reading config files -e level : show startup errors of level (see LogLevel) -E file : log startup errors to file -v : show version number -V : show compile settings -h : list available command line options (this page) -l : list compiled in modules -L : list available configuration directives -t -D DUMP_VHOSTS : show parsed vhost settings -t -D DUMP_RUN_CFG : show parsed run settings -S : a synonym for -t -D DUMP_VHOSTS -D DUMP_RUN_CFG -t -D DUMP_MODULES : show all loaded modules -M : a synonym for -t -D DUMP_MODULES -t : run syntax check for config files -T : start without DocumentRoot(s) check -X : debug mode (only one worker, do not detach)
You can find more information about systemctl by consulting: How to Manage ‘Systemd’ Services and Units Using ‘Systemctl’ in Linux.
You might also like to read these following Apache related articles.
That’s all for now! In this article, we’ve explained the most commonly used Apache/HTTPD service management commands that you should know, including starting, enabling, restarting and stopping Apache. You can always reach us via the feedback form below for any questions or comments.