- Виртуальное окружение Python (venv)
- Настройка виртуального окружения
- Создание
- Активация
- Автоматическая активация
- Деактивация
- Альтернативы venv
- 101 Python venv Guide: Create, Delete, Activate and Deactivate
- What is Python venv and how it works
- Reason why people use Python virtual environments
- Virtual Environment compared with Kubernetes, Docker or VMWare solution
- Create Python venv Environments with 3 simple commands
- Activate Python venv environment
- Activating Venv in Linux and Apple macOS
- Deleting environment with Pipenv
- Complete Deactivate Python venv
- Deleting a venv environment
- Conclusion
Виртуальное окружение Python (venv)
Все сторонние пакеты устанавливаются менеджером PIP глобально. Проверить это можно просто командой pip show .
root@purplegate:~# pip3 show pytest Name: pytest Version: 5.3.2 Summary: pytest: simple powerful testing with Python Home-page: https://docs.pytest.org/en/latest/ Author: Holger Krekel, Bruno Oliveira, Ronny Pfannschmidt, . License: MIT license Location: /usr/local/lib/python3.8/site-packages Requires: more-itertools, pluggy, py, wcwidth, attrs, packaging Required-by:
Location — путь до ваших глобальных пакетов.
В большинстве случаев, устанавливать пакеты глобально — плохая идея 🙅♂️ Почему? Рассмотрим простой пример:
Допустим у нас есть два проекта: » Project A» и » Project B» . Оба проекта зависят от библиотеки Simplejson . Проблема возникает, когда для «Project A» нужна версия Simplejson 3.0.0, а для проекта «Project B» — 3.17.0. Python не может различить версии в глобальном каталоге site-packages — в нем останется только та версия пакета, которая была установлена последней.
Решение данной проблемы — создание виртуального окружения (virtual environment).
Основная цель виртуального окружения Python — создание изолированной среды для python-проектов
Это означает, что каждый проект может иметь свои собственные зависимости, независимо от других проектов.
Настройка виртуального окружения
Один из самых популярных инструментов для создания виртуального окружения — virtualenv . Однако в данной статье мы будем рассматривать более свежий инструмент venv .
Устанавливать venv не нужно — он входит в стандартную библиотеку Python
Создание
Для создания виртуального окружения, перейдите в директорию своего проекта и выполните:
Флаг -m указывает Python-у запустить venv как исполняемый модуль. venv/ — название виртуального окружения (где будут храниться ваши библиотеки).
В результате будет создан каталог venv/ содержащий копию интерпретатора Python, стандартную библиотеку и другие вспомогательные файлы.
Новые пакеты будут устанавливаться в venv/lib/python3.x/site-packages/
Активация
Чтобы начать пользоваться виртуальным окружением, необходимо его активировать:
source выполняет bash-скрипт без запуска дополнительного bash-процесса.
Проверить успешность активации можно по приглашению оболочки. Она будет выглядеть так:
Также новый путь до библиотек можно увидеть выполнив команду:
python -c «import site; print(site.getsitepackages())»
Интересный факт: в виртуальном окружении вместо команды python3 и pip3, можно использовать python и pip
Автоматическая активация
В некоторых случаях, процесс активации виртуального окружения может показаться неудобным (про него можно банально забыть 🤷♀️).
На практике, для автоматической активации перед запуском скрипта, создают скрипт-обертку на bash :
#!/usr/bin/env bash source $BASEDIR/venv/bin/activate python $BASEDIR/my_app.py
Теперь можно установить права на исполнение и запустить нашу обертку:
chmod +x myapp/run.sh ./myapp/run.sh
Деактивация
Закончив работу в виртуальной среде, вы можете отключить ее, выполнив консольную команду:
Альтернативы venv
На данный момент существует несколько альтернатив для venv:
- pipenv — это pipfile, pip и virtualenv в одном флаконе;
- pyenv — простой контроль версий Питона;
- poetry — новый менеджер для управления зависимостями;
- autoenv — среды на основе каталогов;
- pew — инструмент для управления несколькими виртуальными средами, написанными на чистом Python;
- rez — интегрированная система конфигурирования, сборки и развертывания пакетов для программного обеспечения.
Стоит ли использовать виртуальное окружение в своей работе — однозначно да. Это мощный и удобный инструмент изоляции проектов друг от друга и от системы. С помощью виртуального окружения можно использовать даже разные версии Python!
Однако рекомендуем присмотреться к более продвинутым вариантам, например к pipenv или poetry .
101 Python venv Guide: Create, Delete, Activate and Deactivate
Learn the basics of venv create, delete and activate commands to optimize your work!
You are quite efficient if you install third-party applications system-wide. After all, you get it once and then use the package from different python projects, this saves in a lot of time and space on the disk. However, some problems might arise with junk and overlapping libraries or environments.
You can avoid all of this by following our tutorial on how to activate, deactivate, delete and create Python venv environments with command examples that work on Linux, Windows and Mac.
What is Python venv and how it works
The PATH variable gets changes once you activate your environment. On Linux and macOS you can see by printing the path with echo $path. On Windows, you need to use %PATH%(in cmd.exe) or $Env:Path ( in PowerShell).
Now when you enter a command which can’t be found in the current working directory then your operating system begins to look at all paths there in the PATH variable. The same is for Python. Whenever you import any library it started to look in your PATH for library locations.
This is where the new magic of venv occurs; if it is in front of other paths, the operating system shall look first there before peeking into the system-wide directories such as /usr/bin. Therefore, anything which gets installed in venv is found first and that’s how you can override system-wide packages and tools.
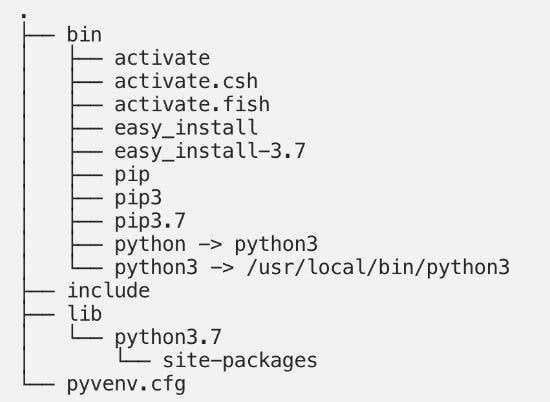
On Linux and MacOS, you shall see the follow tree structure:
- On Linux and macOS Python command is made available as both Python and Python, the version to is pinned to the one with which you have created venv by creating a symlink to it.
- Python binary on windows is copied over to the scripts directory.
- Packages that are installed end up in the site-packages directory.
- There are activation scripts for different types of shells such as bash, csh, fish and PowerShell.
- You shall find pip under different names like pip and pip3, specifically under the name pip3.7 as we had version 3.7 installed.
Reason why people use Python virtual environments
As you can imagine that project Paul is written down against a specific version of Library Ninja. You may need to upgrade the library Ninja in the near future. For example, you require the latest version for another project known as IDE. You upgrade library Ninja to the latest and project IDE begins to work fine. But during this what you see is that your previous project A broke badly. After, APIs can change on major version upgrades.
Now, this is a very virtual environment that comes in handy, it is designed to fix such a problem by isolating the project from other and system-wide packages. You install packages within this environment, particularly for the project on which you are working.
The best thing is that it is easy to define and install packages specific to your project. When you use the “requirements.txt” file you can define an exact number of versions tested with code. Now, it also helps other users of the same software as the environment helps others to reproduce the same for which your software was built in the first place.
If you are working on a university or web hosting provider which is a shared host then you shall not able to install system-wide packages as you do not have administrator rights to do so. In such time, venv allows you to get anything you in your project locally.
Virtual Environment compared with Kubernetes, Docker or VMWare solution
You have other options as well to isolate your project:
- In some scenarios, you can get a second system and on it run your code. Though this would not be easy on the pocket your problem shall be solved.
- It is cheap but still needs you to install a complete OS. This is deemed to be a waste in many cases. You may need VMWare or Oracle VirtualBox and then install and fully configure an operating system.
- Then comes containerization with the likes of Kubernetes and Docker. These are quite powerful and a good alternate.
Create Python venv Environments with 3 simple commands
There are many ways to do this but it depends on the version of Python you are running.
Keep two tools in your mind; python poetry and pipenv. Both these combine functions of tools which you are about to learn: virtualenv and pip. Besides this they can add extras such as their ability to perform proper dependency resolution.
Use the following venv module:
[email protected]:~# python –m venv [directory path] Using this command shall help you create a virtual environment in the specific directory plus copies pip into it too. If you are not very sure on what to call the director then it is a commonly seen option and does not leave on guessing.
Other Versions of Python which are older:
Alternate which works for any version of python is using virtualenv package, but first what you need to do is install pip, for this use the following command:
Once this has been installed, create a virtual environment using:
Activate Python venv environment
To activate this on Microsoft Window all you need to do is run a script that gets installed by venv, if you have created this in a directory known myenv, the command shall be as follows:
[email protected]:~#C:\Users\Paul> venv\Scripts\activate.bat Open PowerShell as administrator and run the below:
[email protected]:~#C:\Users\Paul> venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 Activating Venv in Linux and Apple macOS
With the help of the source code command, we activate the virtual environment on Linux and macOS. If this has been created in myvenv directory then the command shall be as followed:
Now you are ready to rock and all, install packages with pip but we suggest that you keep reading to understand more.
Deleting environment with Pipenv
This is much easier, simply use the following command:
Just keep in mind to be within the project directory.
If this does not work, don’t worry remove it manually. For this simply first you need to ask pipenv where the original virtualenv is located and then use the following command:
[email protected]:~# $ pipenv --env/home/paul/.local/share/virtualenvs/ninja-ide This shall output path to the virtual environment along with its files and look similar to the examples mentioned above. After this, all you need to do is remove the entire directory and that’s it you are done.
If you have created with poetry then list the ones which are available by using the following command:
Now, if you want to remove the environment use the poetry env remove command. For this, you need to specify the exact name from the above-mentioned output, such as: poetry env remove test-paul-ninja-env.py. You can also use an IDE such as Ninja to alter and create a script to run these at a scheduled time or in a sequence to save time.
Complete Deactivate Python venv
Once you’re done with your work the best thing is to deactivate it. By doing this you basically leave the virtual environment. If you don’t do this, python code shall execute even if it is outside the project directory it shall run within venv.
The best thing is that it works on Windows, Linux and Mac setups.
Deleting a venv environment
This can be done easily but it depends on what you used to create it. We have listed some common options for you which one you would have created with Virtualenv or Python –m venv.
You first need to deactivate it, and remove the directory and its content. On systems like UNIX and PowerShell, first deactivate it as showed up then:
If you see “venv” as the directory, run the below command to delete it permanently. Be warned that there is no coming back once removed.
Other Python tutorials you will enjoy:
Conclusion
Python venv saves a lot of time and helps organize projects which need isolation from others. This is where you can use our venv guide to create, activate, delete and deactivate environments. Hopefully, our command examples will clarify it all to you as they are compatible with Windows 10, 11, Linux and macOS.