How Do I Read Email with Linux?
If you log in as hermie now (pressing alt-F2 to access another virtual console would be convenient), you’ll be greeted with the following cheery little message: You have new mail.
You can receive and read your incoming email by using the mail command again.
Here’s a sample mail session (text in bold is what you would enter):
Mail version 5.6 6/1/95. Type ? for help.
«/var/spool/mail/hermie»: 1 message 1 new
>N 1 root@fritz.com Mon Feb 10 14:58 «Gone Fishing»
>N 2 D.Rhodes@spam.net Mon Feb 10 15:37 «Make Money Fast!»
N 3 Chris@qwerty.com Mon Feb 10 15:37 «Tennis, Anyone?»
& 1
Message 1:
Date: Mon, 10 Feb 1997 14:58:12 -0500
From: root@fritz.com
To: hermie@fritz.com
Subject: Gone Fishing
I’ve decided to kick back this afternoon and go fishing.
So if this crazy Linux system rolls over and dies,
I suggest you do likewise.
& q
Saved 1 message in /home/hermie/mbox
Held 2 messages in /var/mail/spool/hermie
Let’s look at what just happened. After you entered the mail command, the system informed you of the version of the mail program that is running and told you how to get help for it.
The next line tells you that there is one new message in your mailbox, and that your incoming mail is stored in the file /var/spool/mail/hermie. (Each user on the system has a mail file in the /var/spool/mail directory.) When new mail arrives, Linux tacks it onto the end of the recipient’s mail file.
Note: You should never directly edit your mail file—always use mail or another email program to handle your mail. (If you’re editing your mail file when a new message arrives, it will be lost.) But it’s quite all right to scan your mail file with grep or some other utility that doesn’t try to modify it. (You might want to apply grep to your mail to find a particular string, such as the email address of a person who has corresponded with you.)
>N 1 root@fritz.com Mon Feb 10 14:58 «Gone Fishing»
is referred to as a header line, and it tells you a number of things. The > tells you which message is the current one—the one you’re working with.
The N 1 indicates that you’re dealing with message 1 and that it’s flagged as a new message. (Later, the flag could be U for unread or O for an old message.) The rest of the line tells you who the message is from, when it was sent, and the Subject line.
The ampersand (&) on the following line is the mail prompt. In this example, we entered a 1 to display the first message, and the message text is shown on the lines that follow. Unfortunately, we can’t tell from the context whether to roll over and die or just go fishing.
Using the Mail Console Client
The most basic client for creating and reading e-mail is the mail command. Although it doesn’t have many advanced features, it is fast. So some Linux users like to use it for sending simple messages. (It is also sometimes used in scripts.)
To read mail, open a command console, log on using the account whose mail you want to read, and enter the command mail. A list of all messages in your mailbox will be displayed. You can then use any of the commands listed in Table-1 to work with the messages in the mailbox or compose new mail messages.
- Type mail followed by the e-mail address of the recipient.
For example:
mail wally@cleaver.com
Mail responds by prompting you for the subject. - Type the subject line and press Enter.
Mail then waits for you to enter the text of the message. - Type the message text. Use the Enter key to start new lines.
You can enter as many lines as you wish for the message. - Press Ctrl+D to finish the message.
The following prompt will appear:
Cc: - Enter one or more carbon copy addresses if you want others to receive a copy. Otherwise, press Enter.
You’re done! The message is on its way.
Using Evolution
Evolution is a graphical e-mail client that’s similar in many ways to Microsoft Outlook. It includes not only e-mail features, but also a contact list, a calendar, a task manager, and other Outlook-like features.
To start Evolution, click the E-Mail icon that’s located in the panel at the top of the GNOME screen. The first time you run Evolution, a configuration wizard will guide you through the necessary configuration. You need to supply basic information about your e-mail account, such as your e-mail address and the name of your mail server.
In this tutorial:
- Managing Linux Systems
- Planning a Linux Server Installation
- Partitions
- Installing Fedora 7
- Getting Used to Linux
- Understanding the file system
- On Again, Off Again
- Using GNOME
- Managing User Accounts
- Linux Network Configuration
- Restarting Your Network
- Working with Network Configuration Files
- The ifcfg files
- The resolv.conf file
- DHCP and DNS
- Configuring DHCP
- Running a DNS Server
- Running Apache
- Starting and Stopping Apache
- Confirming that Apache Is Running
- Using the HTTP Configuration Tool
- Restricting Access to an Apache Server
- Configuring Virtual Hosts
- Setting the Apache User Account
- Running Sendmail
- Installing Sendmail
- Modifying sendmail.mc
- Using SpamAssassin
- Using the Mail Console Client
- Running FTP
- Starting the vsftpd Service
- Configuring FTP
Read and send mail
The mail program is a very basic command-line email utility that can be used to read mail or send mail to users. This program only supports reading the local email queue, not emails stored on remote servers.
To send emails using the mail command, you must provide options such as the subject, recipient’s address, carbon copy address, etc. To specify a subject, use the -s option. To set a carbon copy address, use the -c option. The recipient’s email address terminates the mail command’s line. After you type the mail command, the program waits for input. After you are done writting the message, you can signal the end of the message by pressing Ctrl+D.

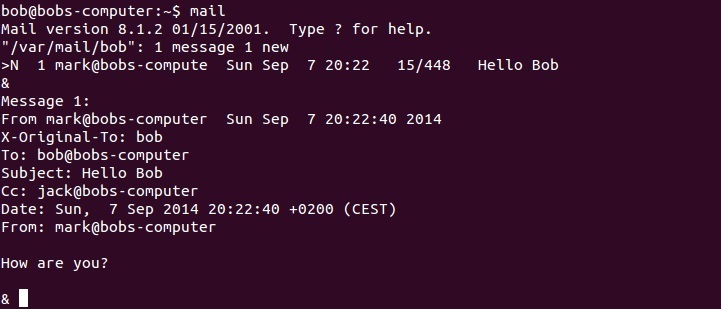
In the picture above you can see that we’ve sent an email with the subject Hello to the user bob. A carbon copy has been sent to the user jack.
To send e-mails to users on the same local mail server, you can specify only the username. However, if you want to send e-mails to users on another server or network, you must specify the full e-mail address.
Using the mail command with no arguments displays all messages in your mailbox, as shown in the picture below:

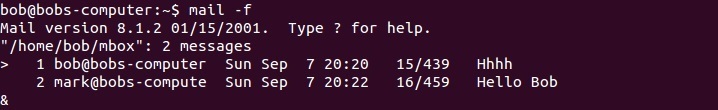
After you view a message in your mailbox, the message is written to the file in your home directory (e.g. /home/bob/mbox). You can these messages by using the mail -f command:
The mail command is in the /usr/bin directory and is linked to the mailx command, a newer version of the program.