- How To Check Your Ubuntu Version (Using the Command Line and GUI)
- An Overview of Ubuntu (and Why You Might Need to Check Your Version of It)
- Is your WordPress site slow?
- How To Check Your Ubuntu Version in the Command Line (4 Methods)
- 1. Use the lsb_release -a Command
- 2. Use the /etc/lsb-release or /etc/os-release Command
- 3. Check the /etc/issue File
- 4. Use the hostnamectl Command
- How To Check Your Ubuntu Version in the GUI Settings?
- Summary
- How to Check Linux OS Version
- Differences between OS and Kernel Version?
- Commands to Check Linux Version
- How to Check Linux OS Version
- The /etc/os-release File
- The lsb_release Command
- The Inxi Tool
- The hostnamectl Command
- uname command
- The /etc/issue file
- Conclusion
How To Check Your Ubuntu Version (Using the Command Line and GUI)
Ubuntu is an open source Operating System (OS) used by people all over the world. Although it is user-friendly and customizable, it may not always be compatible with additional software. As such, you’ll need to check if your version of Ubuntu will integrate with other programs.
Fortunately, it’s relatively easy to check your Ubuntu version. You can do so using commands in the terminal or by accessing the settings in the Graphical User Interface (GUI).
In this guide, we’ll discuss what Ubuntu is and why you might want to check which version of it you are running. Then, we’ll explain how to perform this check using various easy methods. Let’s get started!
An Overview of Ubuntu (and Why You Might Need to Check Your Version of It)
Ubuntu is a Linux-based OS popular across the world. You can use the desktop, server, or core versions, depending on your needs.
The platform is entirely free. It also has some advantages over other OS such as Windows or macOS.
For example, it uses open source software and provides a secure development environment. As such, Ubuntu can be a helpful tool for web developers.
You can also customize most aspects of your User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX). Therefore, Ubuntu could be an excellent choice if you feel limited by other OS options.
Is your WordPress site slow?
Uncover performance bottlenecks to deliver a better user experience and hit your business’s revenue goals. Free Audit
There are updated releases of Ubuntu approximately every six months. New versions of the software usually include maintenance and hardware updates that help the OS run more smoothly. As such, it’s in your best interest to stay up to date with the latest release. However, you may not know if you’re running the latest version of Ubuntu. Therefore, you might like to check your OS and see if you need to update it. Furthermore, you may need to check your Ubuntu version when installing third-party software. Not all other platforms may be compatible with the OS updates, so it’s worth investigating this before you install them. Finally, you may run into some issues when using Ubuntu. If this happens, you can turn to technical support forums such as the official Ubuntu Forums. You can improve your forum experience by providing your version of Ubuntu. With this information, other members can assist you more precisely. Wondering if your version of Ubuntu will integrate with other programs? 🤔 It’s easy to check. and this guide is here to help! 💪 Click to Tweet
How To Check Your Ubuntu Version in the Command Line (4 Methods)
You can check your Ubuntu version quickly using the command line (also known as the terminal). You can access this tool by using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Alt + T. Once you have the command line open, you can use a few different methods to find out your Ubuntu version. Let’s explore some of them.
1. Use the lsb_release -a Command
The lsb_release command shows you details about your Linux distribution. For example, it displays data concerning LSB modules. It also shows the ID and release number of the distributor. When you add “-a” to the end of this command, it returns all possible information. This method is pretty straightforward, so you might want to utilize it if you need to find out your Ubuntu version quickly. To start, open up your terminal and type in this command:
Then hit your Enter key to return the results. They should look something like this. You can see your Ubuntu version next to the Description heading. You can also see data about your LSB modules and the codename for your distributor.
2. Use the /etc/lsb-release or /etc/os-release Command
The /etc/lsb-release command can show you your Ubuntu version with separate lines for the release number and its description. It is designed for older systems, so you may like to use it if you’re running an outdated version of Ubuntu. You can also obtain the same information using the /etc/os-release command. This is compatible with Ubuntu 16.04 and higher. As before, open your terminal and enter one of the above commands. You’ll need to add “cat” before either of them:
Then, you’ll see a list of information that includes the number of your Ubuntu version and its release name. Additionally, there are a few links to the Ubuntu website and resources that can help you. Using the /etc/lsb-release command will return simpler results that show you the release ID, description, and codename. It doesn’t include the links and the Ubuntu version name.
3. Check the /etc/issue File
The /etc/issue file is a text-based document. It contains system identification data. Using this method is simpler because the command won’t display anything other than your Ubuntu version. As such, you may like to utilize this file if you’re in a hurry and don’t need to gather any additional information about your system. As with the previous commands, you’ll need to enter “cat” before the command. Type this into your terminal:
Hit Enter, and you’ll see a single line of text. Your version of Ubuntu is the series of numbers before LTS. You don’t need to do anything else here.
4. Use the hostnamectl Command
Finally, you can use the hostnamectl command. This is typically used when you want to change the hostname of your system. However, it also returns information such as your Ubuntu version and machine ID. Open up your terminal and type in this command:
Next, press your Enter key and you’ll see a list of information. Here you can see both your Ubuntu version and your Ubuntu Linux kernel version. That’s it! Those are the main methods you can use to find the version of your Ubuntu OS.
How To Check Your Ubuntu Version in the GUI Settings?
If you’d rather not use the command line, you can also find your Ubuntu version in your GUI settings. You might prefer to use this method if you’re still getting used to working with the OS and its layout. However, it is a bit more time-consuming. First, head to Show Applications. It’s the icon in the bottom left of your screen: 


Summary
- Use the lsb_release -a command.
- Use the /etc/lsb-release or /etc/os-release command.
- Check the /etc/issue file.
- Use the hostnamectl command.
- Check the Ubuntu version in your GUI settings.
Did you know that Kinsta offers Ubuntu and other development tools as part of our DevKinsta suite? Sign up today for one of our hosting packages to access this feature and many other website services!
Get all your applications, databases, and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 260 PoPs worldwide
Get started with a free trial of our Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
How to Check Linux OS Version
Linux is a free and open-source operating system and it has various distributions such as Ubuntu, Red Hat, Debian, Fedora, CentOS, OpenSUSE, and Arch. Every Linux operating system has a Linux Kernel, software collections, and GNU tools and libraries. Determining the Linux distribution, Kernel version, and Linux version is very important to figure out which package manager to use for installing new packages.
Linux operating system version is the very first thing we need to know before installing software, applying security updates, applying bug fixes, or deciding which development framework to use. When you install bug fixes or security updates, your OS version changes.
In this tutorial, we learn how to check the Linux OS Version.
Differences between OS and Kernel Version?
Linux OS is a system software that provides an interface between the computer and the user. When your computer boots, the OS is the first software that loads. However, Kernel is the base of the Linux operating system that converts commands to machine language.
The Linux OS version is not always the same as the Kernel version. OS release means the stable version of the Linux distribution, but the Linux Kernel version is the build number of the source Kernel that is used as a base of the operating system. A version of every package is associated with the Kernel version.
Commands to Check Linux Version
The following table lists some of the most common ways to identify Linux OS version:
| Options | Description |
| /etc/os-release | OS release file that contains OS name and version information |
| lsb_release -a | Displays Linux Standard Base (LSB) information about the operating system, including release codename and version number |
| /proc/version | Displays Linux Kernel and GCC version of your Linux distribution |
| hostnamectl | Displays Linux OS distribution name, computer hostname, Kernel release, and system hardware architecture |
| /etc/issue | File content contains Distribution version information |
| uname -r | Displays only the Linux Kernel version |
How to Check Linux OS Version
There are a variety of ways to check the Linux OS versions, based on your Linux distribution. For example, the lsb_release packages are not installed on Red Hat Linux distractions by default, and the hostnamectl command works only on the systemd based distributions.
The following command examples show you how to check the OS version on your Linux system:
The /etc/os-release File
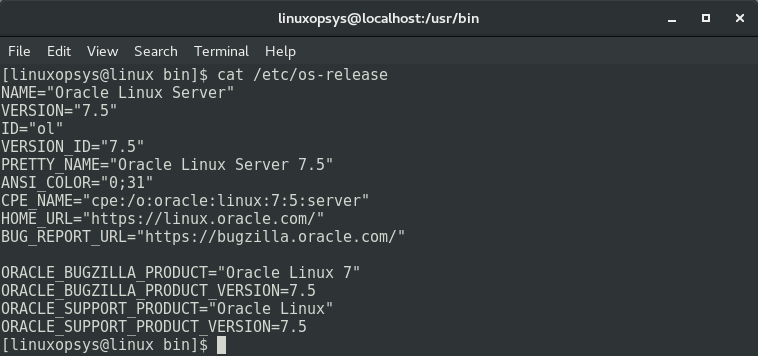
The /etc/os-release file contains Linux OS identification information, which includes Linux distribution name and distribution version.
Run the following cat command on the /etc/os-release file to check the configuration of your Linux system:
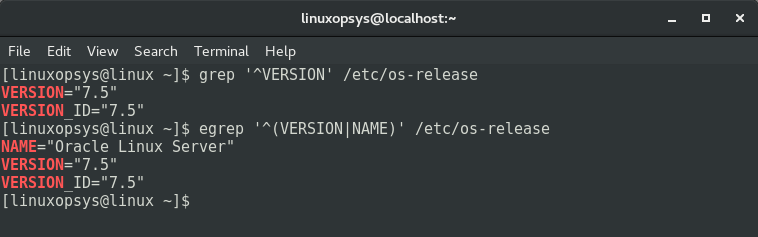
You can also type the following command to filter out OS Version information:
grep ‘^VERSION’ /etc/os-releaseThe lsb_release Command
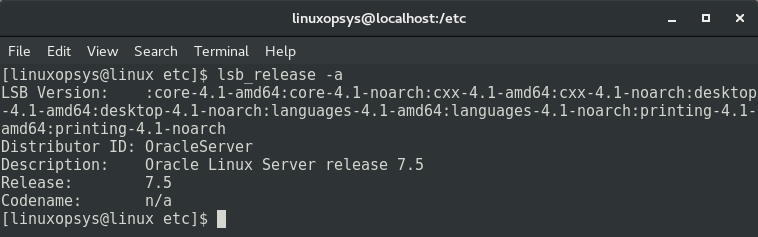
Use the lsb_release command line utility to display Linux Standard Base (LSB) information about the Linux distribution installed on your system. It shows details such as release codename, Linux version number, and distributor ID.
The lsb_release command is part of the software package known as the LSB core, and it is not installed by default on various Linux distributions, such as Red Hat and CentOS.
This command provides different options to display specific information, such as -v for version, -i for operating system identification data, -r for release, -a for all, and -d for description.
For example, the following command displays all release related information about your Linux distribution:
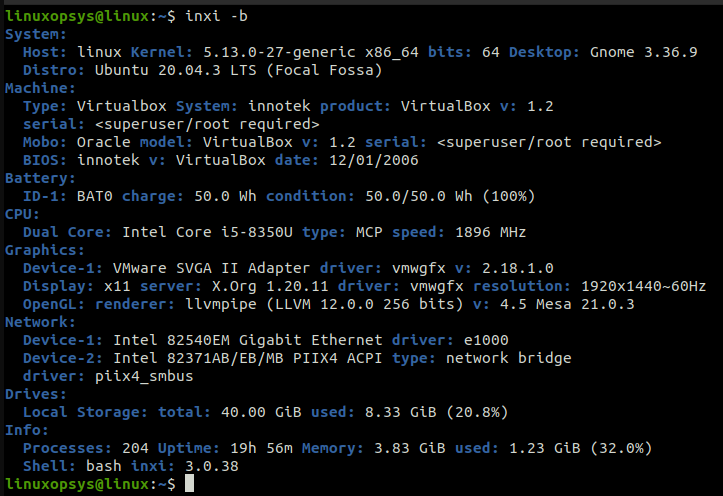
The Inxi Tool
The Inxi is a powerful command line script that provides system information. This command line utility can be used to display hardware configuration, system configuration, GCC version, Linux Kernel version number, and a variety of other useful information.
For example, use the inxi -b command to display all configuration information about your Linux system:
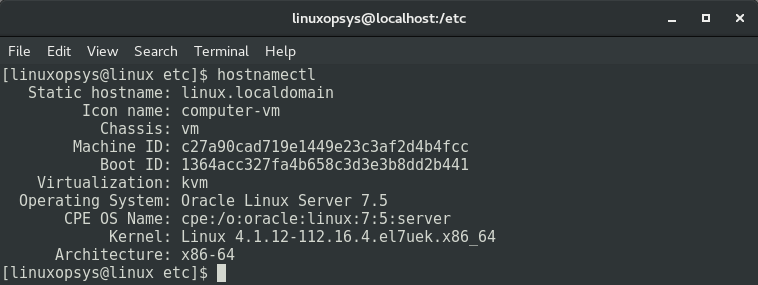
The hostnamectl Command
When used without any options, hostnamectl can be used to display static hostname, machine ID, boot ID, virtualization, OS name and version, and Kernel release. For example:
You may also use the hostnamectl command to update static hostname and transient hostname.
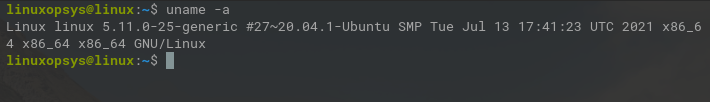
uname command
To check the system information you can use uname command. You can use -a option to print all information that includes OS Version.
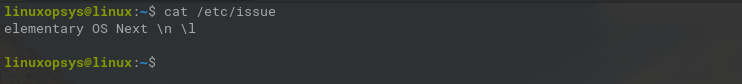
The /etc/issue file
The /etc/issue file contains system identification information that is displayed before the login prompt.
You can use more, less, or cat command to view the content of the file:
You may also find Linux distribution-related information in /etc/*release file. This is mostly found in old release versions.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned about different ways to check the Linux OS version. Some commands have Linux distribution dependence so try which one works for you.
If this resource helped you, let us know your care by a Thanks Tweet. Tweet a thanks