- How to get Linux distribution name and version?
- 9 Answers 9
- Как узнать версию Linux
- Команда lsb_release
- Команда hostnamectl
- Команда uname — версия ядра
- Файл /etc/os-release
- Файл /etc/issue
- Файлы /etc/***release и /etc/***version
- Файл /proc/version
- Через графические утилиты
- Заключение
- How to Check Linux OS Version
- Differences between OS and Kernel Version?
- Commands to Check Linux Version
- How to Check Linux OS Version
- The /etc/os-release File
- The lsb_release Command
- The Inxi Tool
- The hostnamectl Command
- uname command
- The /etc/issue file
- Conclusion
How to get Linux distribution name and version?
You might want to edit the title to make it clear the question is about doing it from C source, not as a script writer or user at the command line.
@Kolob Those were most emphatically not «more sensible» for this question; I have rolled back your change.
9 Answers 9
+1 this finally was «standardized» among the distro’s. Go back far enough though and this file doesn’t exist, instead each distro put their own file like /etc/redhat-release.
This will only work on LSB compliant Linux distributions, but is not guaranteed to work on non-compliant distributions. OTOH, it will also work on other LSB compliant non-Linux Unices. E.g. I’m pretty sure it won’t work on Adroid.
Note that on e.g. Gentoo Linux lsb_release is not always present by default. I just checked, and it’s provided by an optional package sys-apps/lsb-release, currently not installed on my system.
Will lsb-release works on all the follow Distrubtions?: Debian / Ubuntu | Red Hat Enterprise / Fedora Linux / Suse Linux / Cent OS ?
on my system yields the following from the bash (terminal) prompt:
Ubuntu 10.04.4 LTS 2.6.32-41-generic x86_64 I believe uname -mr returns the version of the Linux Kernel, so ‘lsb_release -ds’ should be all you need for the release name and version, assuming the description format is consistent across releases. Thanks, I was wondering how you were supposed to use the short parameter, I was trying it ‘lsb_release -s’ and was wondering why it was failing. Cheers!
trying this way is an interesting one and less restrictive than lsb-release.
This is the best answer, to only retrieve the name of the distro one can do: cat /etc/*-release | grep ID | head -n1 | cut -d ‘=’ -f2
What’s the purpose of getting that information?
If you’re trying to detect some features or properties of the system (e.g. does it support some syscall or does it have some library), instead of relying on output of lsb_release you should either:
- try to use given features and fail gracefully (e.g. dlopen for libraries, syscall(2) for syscalls and so on)
- make it a part of your ./configure check if applicable (standard FOSS way of automatically recognizing system features/properties)
Note that the first way above applies even if your software is binary-only.
dl = dlopen(module_path, RTLD_LAZY); if (!dl) < fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open module: %s\n", module_path); return; >funcptr = dlsym(dl, module_function); if (!funcptr) < fprintf(stderr, "Failed to find symbol: %s\n", module_function); return; >funcptr(); dlclose(dl); Как узнать версию Linux
Когда мы говорим о Linux, то обычно подразумеваем какой-либо дистрибутив Linux. Также под Linux мы можем иметь ввиду ядро Linux.
Иногда требуется определить версию Linux, в которой вы работаете. Пользователь может не знать или забыть, какая версия дистрибутива или какая версия ядра Linux используется. Если это чужая система, то может потребоваться узнать название используемого дистрибутива.
В данной статье рассматриваются различные способы, которые помогут нам определить используемую версию Linux. Рассматривается несколько команд для определения версии Linux. Приведенные команды универсальны и не зависят от дистрибутива. Возможно, некоторые из них могут не работать в каких-то дистрибутивах, в таком случае переходите к следующей команде и пробуйте ее.
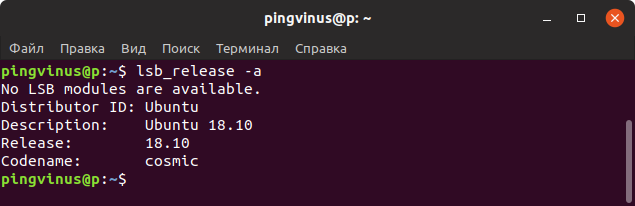
Команда lsb_release
Команда lsb_release выводит информацию о дистрибутиве.
Префикс lsb в названии команды относится к проекту Linux Standard Base, который был создан с целью создания ряда стандартов для выпуска дистрибутивов Linux, чтобы уменьшить различия между отдельными дистрибутивами. Предполагается, что использование LSB снижает затраты, связанные с переносом приложений на разные дистрибутивы, а также снижает усилия, связанные с поддержкой этих приложений.
Чтобы отобразить информацию о дистрибутиве выполните команду:
lsb_release -a No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID: Ubuntu Description: Ubuntu 18.10 Release: 18.10 Codename: cosmicВыводится название дистрибутива, номер версии и кодовое имя.
Можно использовать опцию -d , чтобы показать только строку Description, которая обычно содержит и название и версию дистрибутива.
lsb_release -d Description: Ubuntu 18.10Команда hostnamectl
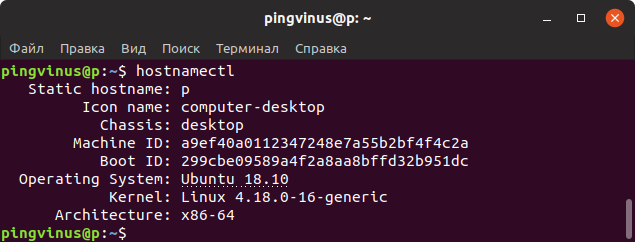
Команда hostnamectl , выполненная без параметров или с ключом status , выводит текущую информацию о системе.
hostnamectl Static hostname: p Icon name: computer-desktop Chassis: desktop Machine ID: abc231434aabcb. a Boot ID: 51dcaa2321bbbb. a Operating System: Ubuntu 18.10 Kernel: Linux 4.18.0-16-generic Architecture: x86-64Помимо данных дистрибутива, выводится версия ядра и архитектура.
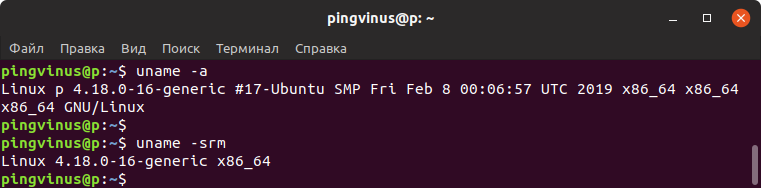
Команда uname — версия ядра
Команда uname выводит информацию о текущем ядре системы Linux, а также некоторые дополнительные данные.
Чтобы вывести всю информацию, используется ключ -a
uname -a Linux p 4.18.0-16-generic #17-Ubuntu SMP Fri Feb 8 00:06:57 UTC 2019 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/LinuxДля удобства можно выводить только название ядра ( -s ) , версию ядра ( -r ) и архитектуру ( -m )
uname -srm Linux 4.18.0-16-generic x86_64Файл /etc/os-release
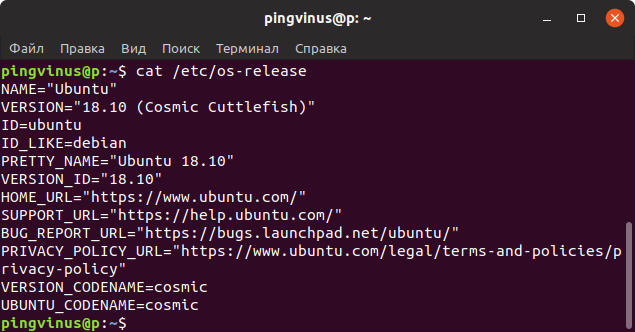
В файле /etc/os-release содержится информация о дистрибутиве, включая URL-адреса сайт системы и некоторые дополнительные данные. Данный файл присутствует в дистрибутивах, использующих systemd.
Чтобы вывести содержимое файла /etc/os-release можно воспользоваться командой cat:
cat /etc/os-release NAME="Ubuntu" VERSION="18.10 (Cosmic Cuttlefish)" ID=ubuntu ID_LIKE=debian PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 18.10" VERSION_ID="18.10" HOME_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/" SUPPORT_URL="https://help.ubuntu.com/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/" PRIVACY_POLICY_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/legal/terms-and-policies/privacy-policy" VERSION_CODENAME=cosmic UBUNTU_CODENAME=cosmicФайл /etc/issue
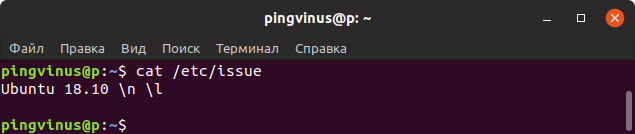
Файл /etc/issue содержит текст, который выводится в качестве приглашения ко входу в систему. Обычно текст представляет собой название дистрибутива и версию.
Выведем содержимое файла /etc/issue командой cat:
cat /etc/issue Ubuntu 18.10 \n \lФайлы /etc/***release и /etc/***version
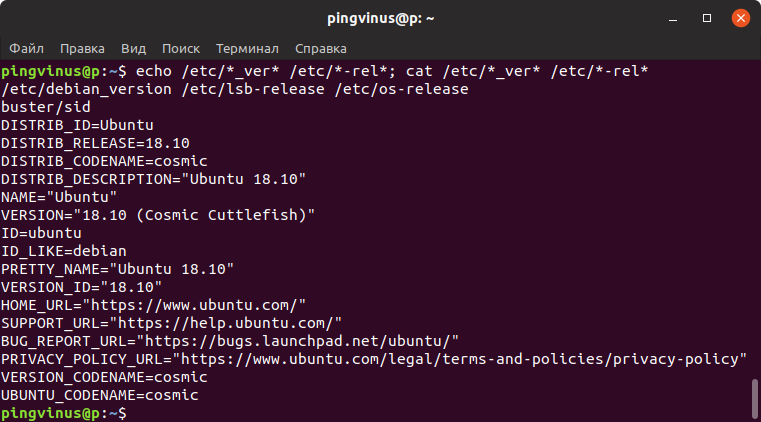
Если вы используете старый или какой-то специфический дистрибутив Linux, то информация о системе может хранится в файле /etc/abc-release или /etc/abc-version .
Вместо abc обычно указывается краткий идентификатор дистрибутива или lsb, если система совместима со стандартами LSB. Вместо символа — может быть символ _ . Например, для дистрибутива Fedora используется файл /etc/fedora-release
Необязательно знать названия этих файлов. Можно воспользоваться следующей командой, чтобы автоматически определить названия и вывести содержимое этих файлов:
echo /etc/*_ver* /etc/*-rel*; cat /etc/*_ver* /etc/*-rel* /etc/debian_version /etc/lsb-release /etc/os-release buster/sid DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu DISTRIB_RELEASE=18.10 DISTRIB_CODENAME=cosmic DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 18.10" NAME="Ubuntu" VERSION="18.10 (Cosmic Cuttlefish)" ID=ubuntu ID_LIKE=debian PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 18.10" VERSION_ID="18.10" HOME_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/" SUPPORT_URL="https://help.ubuntu.com/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/" PRIVACY_POLICY_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/legal/terms-and-policies/privacy-policy" VERSION_CODENAME=cosmic UBUNTU_CODENAME=cosmicФайл /proc/version
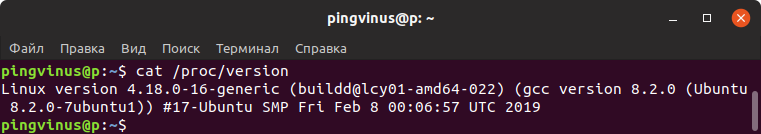
Информацию о ядре Linux также можно получить из файла /proc/version
cat /proc/version Linux version 4.18.0-16-generic (buildd@lcy01-amd64-022) (gcc version 8.2.0 (Ubuntu 8.2.0-7ubuntu1)) #17-Ubuntu SMP Fri Feb 8 00:06:57 UTC 2019Через графические утилиты
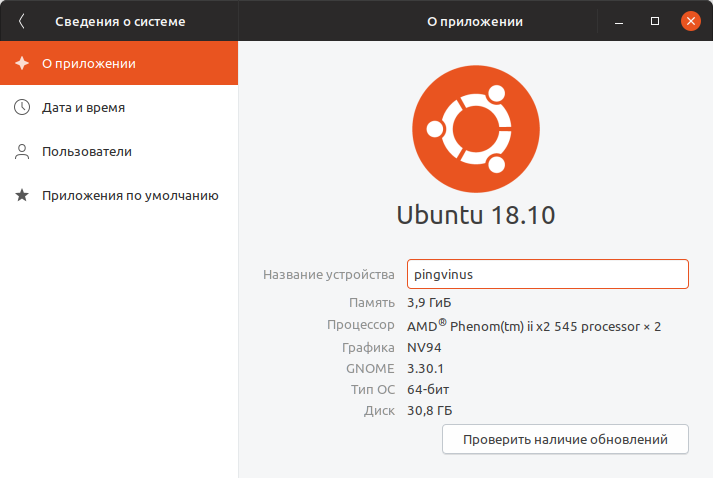
Многие дистрибутивы позволяют просмотреть некоторую информацию о системе, используя графические утилиты. Например, в Ubuntu это можно сделать из утилиты Параметров системы, на вкладке Сведения о системе .
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели различные способы получения информации о дистрибутиве и ядре системы Linux. Какие-то способы могут не работать в некоторых дистрибутивах Linux.
How to Check Linux OS Version
Linux is a free and open-source operating system and it has various distributions such as Ubuntu, Red Hat, Debian, Fedora, CentOS, OpenSUSE, and Arch. Every Linux operating system has a Linux Kernel, software collections, and GNU tools and libraries. Determining the Linux distribution, Kernel version, and Linux version is very important to figure out which package manager to use for installing new packages.
Linux operating system version is the very first thing we need to know before installing software, applying security updates, applying bug fixes, or deciding which development framework to use. When you install bug fixes or security updates, your OS version changes.
In this tutorial, we learn how to check the Linux OS Version.
Differences between OS and Kernel Version?
Linux OS is a system software that provides an interface between the computer and the user. When your computer boots, the OS is the first software that loads. However, Kernel is the base of the Linux operating system that converts commands to machine language.
The Linux OS version is not always the same as the Kernel version. OS release means the stable version of the Linux distribution, but the Linux Kernel version is the build number of the source Kernel that is used as a base of the operating system. A version of every package is associated with the Kernel version.
Commands to Check Linux Version
The following table lists some of the most common ways to identify Linux OS version:
| Options | Description |
| /etc/os-release | OS release file that contains OS name and version information |
| lsb_release -a | Displays Linux Standard Base (LSB) information about the operating system, including release codename and version number |
| /proc/version | Displays Linux Kernel and GCC version of your Linux distribution |
| hostnamectl | Displays Linux OS distribution name, computer hostname, Kernel release, and system hardware architecture |
| /etc/issue | File content contains Distribution version information |
| uname -r | Displays only the Linux Kernel version |
How to Check Linux OS Version
There are a variety of ways to check the Linux OS versions, based on your Linux distribution. For example, the lsb_release packages are not installed on Red Hat Linux distractions by default, and the hostnamectl command works only on the systemd based distributions.
The following command examples show you how to check the OS version on your Linux system:
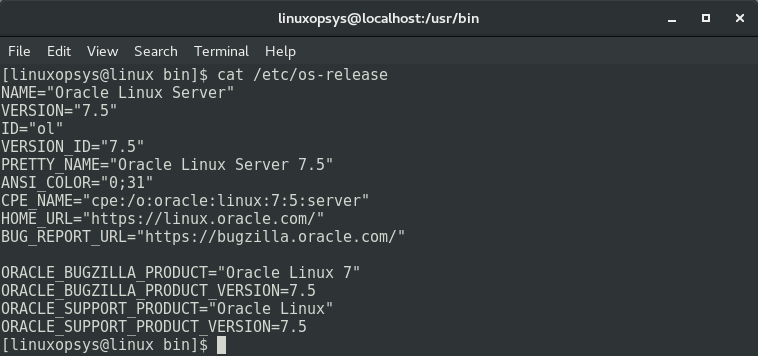
The /etc/os-release File
The /etc/os-release file contains Linux OS identification information, which includes Linux distribution name and distribution version.
Run the following cat command on the /etc/os-release file to check the configuration of your Linux system:
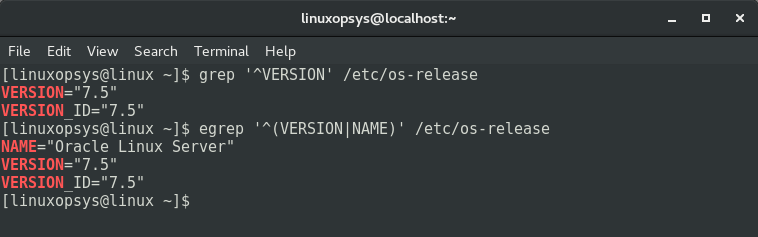
You can also type the following command to filter out OS Version information:
grep ‘^VERSION’ /etc/os-releaseThe lsb_release Command
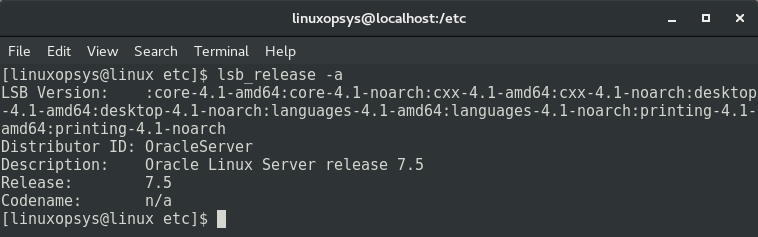
Use the lsb_release command line utility to display Linux Standard Base (LSB) information about the Linux distribution installed on your system. It shows details such as release codename, Linux version number, and distributor ID.
The lsb_release command is part of the software package known as the LSB core, and it is not installed by default on various Linux distributions, such as Red Hat and CentOS.
This command provides different options to display specific information, such as -v for version, -i for operating system identification data, -r for release, -a for all, and -d for description.
For example, the following command displays all release related information about your Linux distribution:
The Inxi Tool
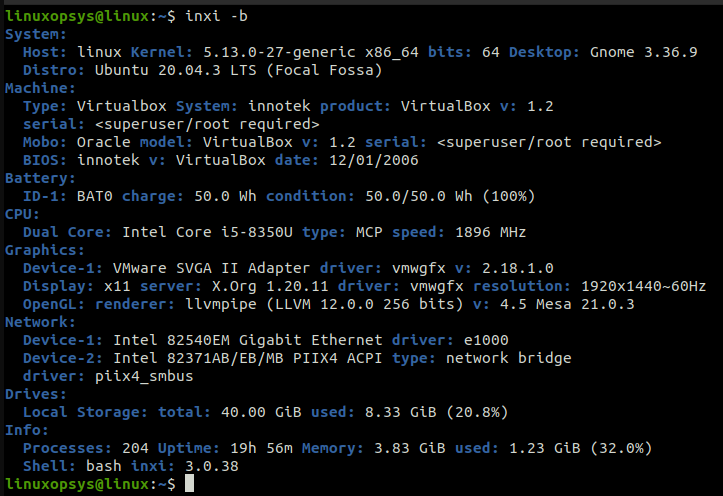
The Inxi is a powerful command line script that provides system information. This command line utility can be used to display hardware configuration, system configuration, GCC version, Linux Kernel version number, and a variety of other useful information.
For example, use the inxi -b command to display all configuration information about your Linux system:
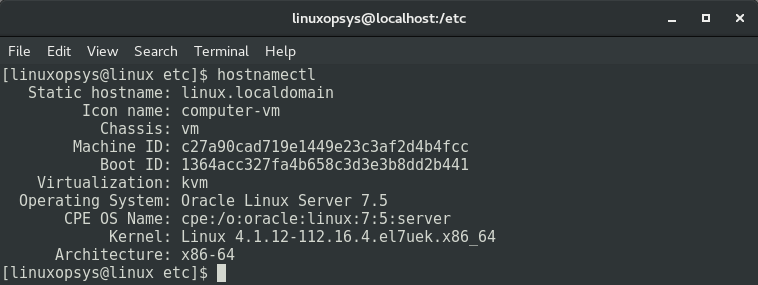
The hostnamectl Command
When used without any options, hostnamectl can be used to display static hostname, machine ID, boot ID, virtualization, OS name and version, and Kernel release. For example:
You may also use the hostnamectl command to update static hostname and transient hostname.
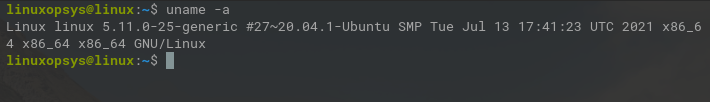
uname command
To check the system information you can use uname command. You can use -a option to print all information that includes OS Version.
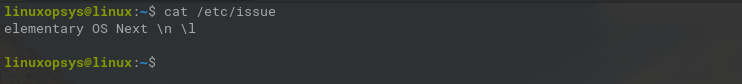
The /etc/issue file
The /etc/issue file contains system identification information that is displayed before the login prompt.
You can use more, less, or cat command to view the content of the file:
You may also find Linux distribution-related information in /etc/*release file. This is mostly found in old release versions.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned about different ways to check the Linux OS version. Some commands have Linux distribution dependence so try which one works for you.
If this resource helped you, let us know your care by a Thanks Tweet. Tweet a thanks