- How to Use Sed to Find and Replace a String in a File
- sed Find and Replace Syntax
- sed Replace Examples
- Replace First Matched String
- Global Replace
- Match and Replace All Cases
- Ignore Substrings
- Find and Replace Strings With Slashes
- Find and Replace with Regular Expressions
- Reference Found String
- Create a Backup
- Recursive Find and Replace
- How to Replace a String in a File in Bash
- Sample Data for Bash String Replacement
- General Syntax for Sed: Replace String in a File
- Example 1: Replace File with the ‘sed’ Command
- Example 2: Replace File with the ‘sed’ Command with ‘g’ and ‘i’ Flag
- Example 3: Replace File with `sed` Command and Matching Digit Pattern
- Replace String in a File with `awk` Command
- Example 4: Replace File with `awk` Command
- Example 5: Replace string in file with Pure Bash Scripting
- Example 6: Replace string in file with Perl one liner
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
How to Use Sed to Find and Replace a String in a File
The sed (stream editor) utility is a line-oriented text parsing and transformation tool. The sed command uses a simple programming language and regular expressions to process text streams and files. The most used feature of the sed command is string substitution.
This guide shows how to use sed to find and replace strings through examples.
- Access to the command line/terminal.
- A text file (this guide provides an example.txt file).
- Basic terminal commands (grab our free cheat sheet).
sed Find and Replace Syntax
The syntax to find and replace text using the sed command is:
The command consists of the following:
- -i tells the sed command to write the results to a file instead of standard output.
- s indicates the substitute command.
- / is the most common delimiter character. The command also accepts other characters as delimiters, which is useful when the string contains forward slashes.
- is the string or regular expression search parameter.
- is the replacement text.
- g is the global replacement flag, which replaces all occurrences of a string instead of just the first.
- is the file where the search and replace happens.
The single quotes help avoid meta-character expansion in the shell.
The BDS version of sed (which includes macOS) does not support case-insensitive matching or file replacement. The command for file replacement looks like this:
Alternatively, install the GNU version of sed on macOS with homebrew:
Run the GNU sed command as follows:
Replace the sed command with gsed to follow the examples below.
sed Replace Examples
The examples from this guide use a sample file to replace strings.
1. Create a sample text file:
2. Add the following contents:
foobarbazfoobarbaz foo bar baz foo bar baz Foo Bar Baz Foo Bar Baz FOO BAR BAZ FOO BAR BAZ /foo/bar/baz /foo/bar/bazUse the file as input to test the examples below.
Note: For a full sed command tutorial for Linux, check out our sed command Linux guide.
Replace First Matched String
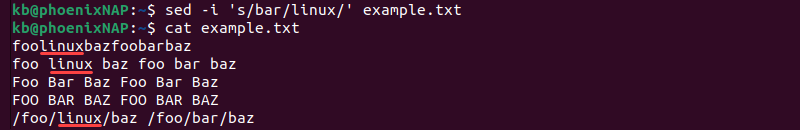
1. To replace the first found instance of the word bar with linux in every line of a file, run:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/' example.txt2. The -i tag inserts the changes to the example.txt file. Check the file contents with the cat command:
The command replaces the first instance of bar with linux in every line, including substrings. The match is exact, ignoring capitalization variations.
Global Replace
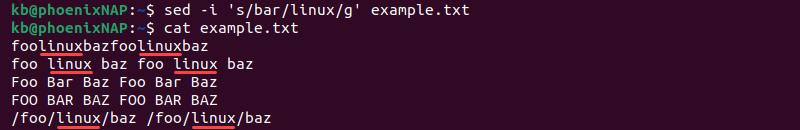
To replace every string match in a file, add the g flag to the script. For example:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/g' example.txtThe command globally replaces every instance of bar with linux in the file.
Match and Replace All Cases
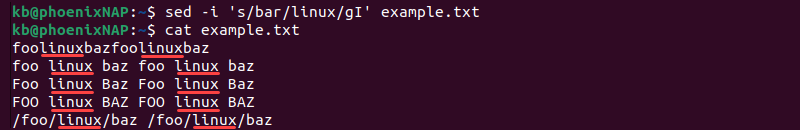
To find and replace all instances of a word and ignore capitalization, use the I parameter:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/gI' example.txtThe command replaces all instances of the word bar in the text, ignoring capitalization.
Ignore Substrings
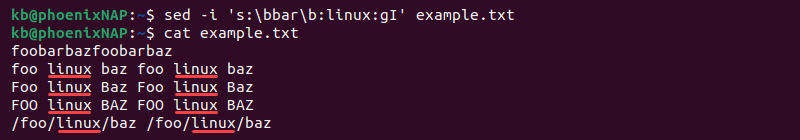
Add word boundaries ( \b ) to the sed command to ignore substrings when replacing strings in a file. For example:
sed -i 's/\bbar\b/linux/gI' example.txtAlternatively, change the delimiter to make the command easier to read:
sed -i 's:\bbar\b:linux:gI' example.txtThe command ignores substrings, matching only the whole word.
Find and Replace Strings With Slashes
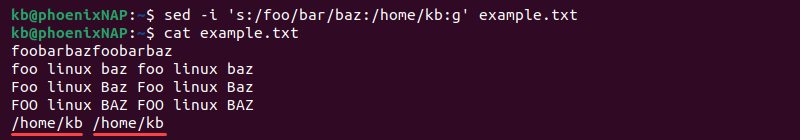
Escape the forward slash character to find and replace a string with slashes. For example, to replace /foo/bar/baz with /home/kb, use the following syntax:
sed -i 's/\/foo\/bar\/baz/\/home\/kb/g' example.txtAlternatively, change the delimiter to avoid escaping characters:
sed -i 's:/foo/bar/baz:/home/kb:g' example.txtUse this syntax to replace paths and other strings with slashes.
Find and Replace with Regular Expressions
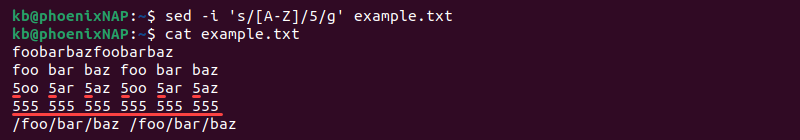
The search pattern for the sed command accepts regular expressions, similar to grep regex. For example, to match all capital letters and replace them with 5, use:
The regex pattern helps find all capital letters and replaces them with the number in the file.
Reference Found String
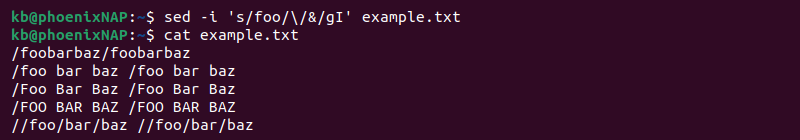
Use the ampersand character ( & ) to reference the found string. For example, to add a forward slash (/) before every instance of foo in a file, use:
Instead of retyping the search parameter, the & sign references the found string.
Create a Backup
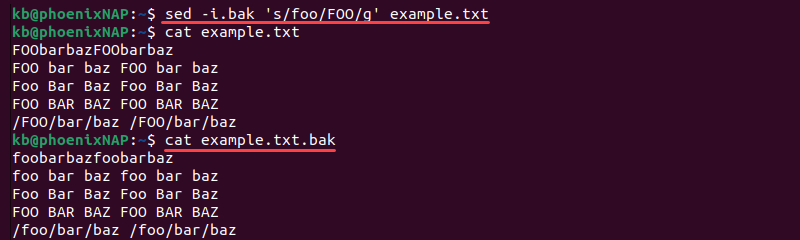
To create a backup file before overwriting the existing one, add the .bak parameter to the -i tag.
sed -i.bak 's/foo/FOO/g' example.txtThe command creates a backup ( example.txt.bak ) before overwriting the original. Use this method to keep a copy in the original format and avoid overwriting.
Recursive Find and Replace
Use the find command to search for files and combine it with sed to replace strings in files recursively. For example:
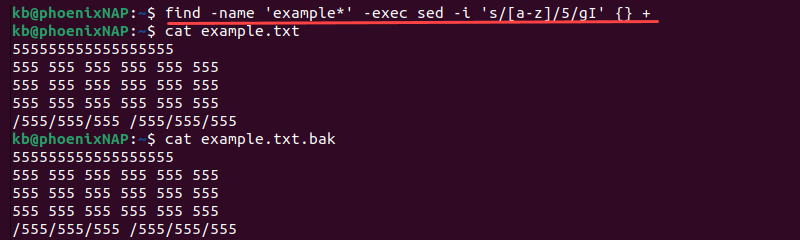
find -name 'example*' -exec sed -i 's/[a-z]/5/gI' <> +The command finds all files starting with example and executes the sed command on the files. The executed command replaces all letters with 5, ignoring capitalization.
After going through the examples in this guide, you know how to use sed to replace strings in files. The sed command is a powerful text manipulation utility with many advanced features.
Next, check out the awk or gawk command to learn about other text manipulation tools.
How to Replace a String in a File in Bash
As a programmer, you might need to work with different types of files to store data temporarily or permanently. Sometimes, you may need to replace part of the file or modify the particular content of the file. To replace content in a file, you must search for the particular file string. The ‘sed’ command is used to replace any string in a file using a bash script. This command can be used in various ways to replace the content of a file in bash. The ‘awk’ command can also be used to replace the string in a file. This tutorial will show you how to replace any string value from a file using a bash script.
Sample Data for Bash String Replacement
A text file named Sales.txt with the following content is created to show the replacement operations.
Sales.txt
01/01/2020 60000 Dhaka
10/02/2020 76000 Rajshahi
21/03/2020 54000 Khulna
15/04/2020 78000 Chandpur
17/05/2020 45000 Bogra
02/06/2020 67000 Comilla
General Syntax for Sed: Replace String in a File
The basic syntax of the `sed` command for replacing the particular string in a file is given below.
Every part of the above syntax is explained below.
‘-i’ option is used to modify the content of the original file with the replacement string if the search string exists in the file.
‘s’ indicates the substitute command.
‘search_string’ contains the string value that will be searched in the file for replacement.
‘replace_string’ contains the string value that will be used to replace the content of the file that matches the ‘search_string’ value.
‘filename’ contains the filename where the search and replace will be applied.
Example 1: Replace File with the ‘sed’ Command
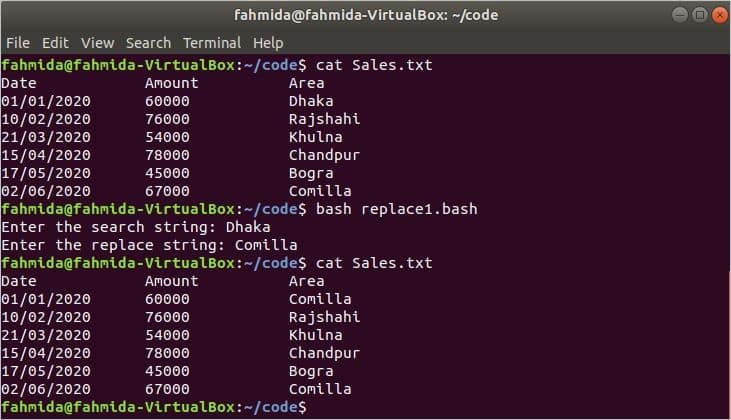
In the following script, the search-and-replace text will be taken from the user. If the search string exists in ‘Sales.txt’, then it will be replaced by the replacement string. Here, a case-sensitive search will be performed.
# Assign the filename
filename = «Sales.txt»
# Take the search string
read -p «Enter the search string: » search
# Take the replace string
read -p «Enter the replace string: » replace
if [ [ $search ! = «» && $replace ! = «» ] ] ; then
sed -i «s/ $search / $replace /» $filename
fi
Example 2: Replace File with the ‘sed’ Command with ‘g’ and ‘i’ Flag
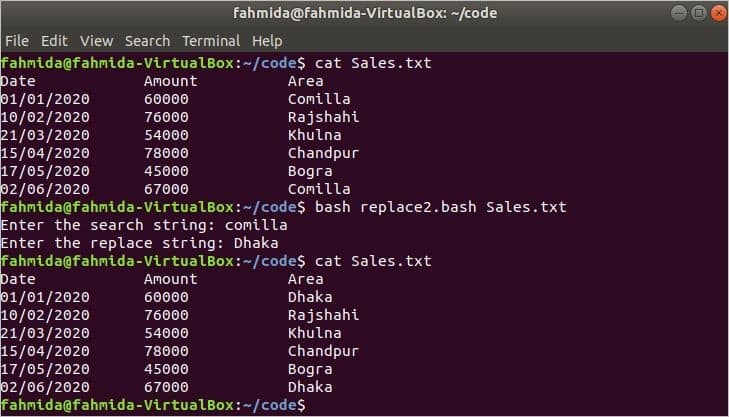
The following script will work like the previous example, but the search string will be searched globally for the ‘g’ flag, and the case-insensitive search will be done for the ‘i’ flag.
# Take the search string
read -p «Enter the search string: » search
# Take the replace string
read -p «Enter the replace string: » replace
if [ [ $search ! = «» && $replace ! = «» ] ] ; then
sed -i «s/ $search / $replace /gi» $1
fi
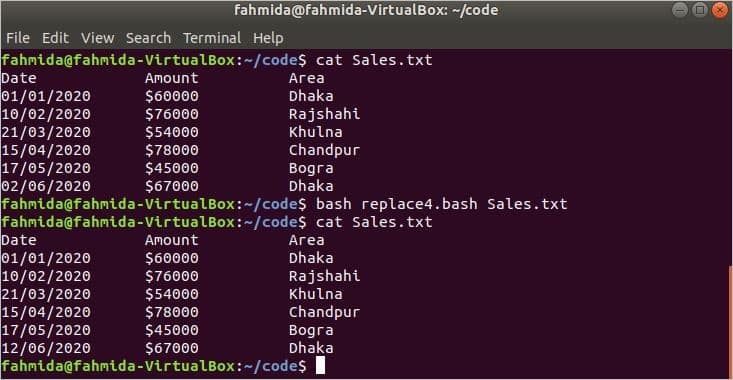
Example 3: Replace File with `sed` Command and Matching Digit Pattern
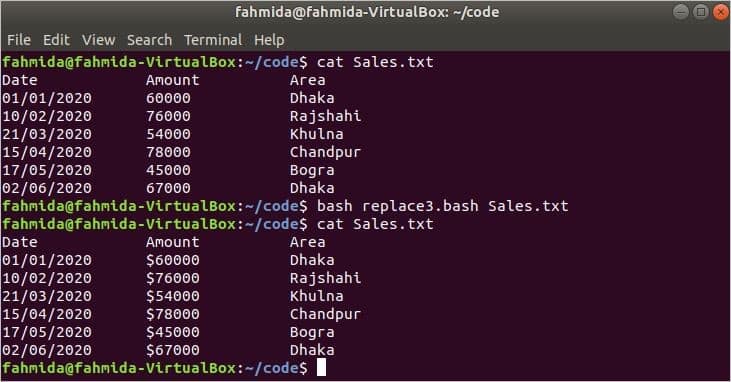
The following script will search for all numerical content in a file and will replace the content by adding the ‘$’ symbol at the beginning of the numbers.
# Check the command line argument value exists or not
if [ $1 ! = «» ] ; then
# Search all string containing digits and add $
sed -i ‘s/\b6\\b/$&/g’ $1
fi
Replace String in a File with `awk` Command
The ‘awk’ command is another way to replace the string in a file, but this command cannot update the original file directly like the ‘sed’ command.
Example 4: Replace File with `awk` Command
The following script will store the updated content in the temp.txt file that will be renamed by the original file.
# Check the command line argument value exists or not
if [ $1 ! = «» ] ; then
# Search all string based on date
awk ‘
fi
In the above example `awk` command is used to search for a string “02/06/2020”, which is the last date in our sample file. The matched string will be replaced by a new string “12/06/2020”. The string resulting whether substituted or not is printed on each line.
Example 5: Replace string in file with Pure Bash Scripting
In this example we will do the same job with a Bash while loop and a bash string replacement command. We will write the output to a tmp file and replace the original at the end of the script. See the code below:
# Replace all instances on line of Khulna with Dhaka
echo $
mv / tmp / Sales.o.txt Sales.txt
You can see the echo command will do a replacement in the line variable, as the script reads each line in the text file, and replace all instances of Khulna with the new string Dhaka. The while loop reads from the input file Sales.txt and writes to the output file /tmp/Sales.o.txt. Finally the temporary output file replaces the original file with the mv command.
Example 6: Replace string in file with Perl one liner
This task is actually super simple with Perl. Perl is an old, less popular language but extremely powerful. This can be done with a line command in the bash command line:
-pi.bak tells perl to process the file in place and also create a backup file with the .bak extension. The replacement will be all instances of Dhaka for Bogra as the new text. Here you can see the easy output of this command:
Conclusion
This article showed you how to use bash scripts to replace strings in a file with search and replace on the command line in bash. There are many ways to do this including with commands sed, awk, perl; you can use native bash scripting with loops and regex and there are more ways even not discussed here. Bash and linux have many ways to do the same job.
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.