- How to Reset or Change the Root Password in Linux
- Changing Your Root Password in Ubuntu
- Step 1: Open a Terminal Window
- Step 2: Change Your Root Password
- Resetting a Root Password in Ubuntu
- Step 1: Boot to Recovery Mode
- Step 2: Drop Out to Root Shell
- Step 3: Remount the File System with Write-Permissions
- Step 4: Change the Password
- Changing the Root Password in CentOS
- Step 1: Access the Command Line (Terminal)
- Step 2: Change the Password
- Reset Root Password in CentOS
- Step 1: Access Boot Menu
- Step 2: Edit Boot Options
- Step 3: Remount the Drive
- Step 4: Changing the Password
- Step 5: Restart
- Reset lost root password
- Using sudo
- Using the debug shell
- Using bash as init
- Using a LiveCD
- Change root
- See also
- Recover – Reset Forgotten Linux Root Password
- Recover forgotten root password
- Closing Thoughts
- Related Linux Tutorials:
How to Reset or Change the Root Password in Linux
In Linux, root privileges (or root access) refers to a user account that has full access to all files, applications, and system functions.
Most basic Linux user accounts run with limited privileges. This keeps users from making mistakes or accidentally exposing the system to vulnerabilities.
To use protected operating system features, a Linux user has to temporarily elevate their privileges using a command like sudo . The sudo command tells the system to run a command as a superuser, or root user. When you run a function using sudo , you’ll usually have to enter your password.
Some versions of Linux will elevate your user privileges for a set amount of time around (15 minutes) before reverting. Other versions only perform a single task with elevated privileges.
It’s a good idea to change your passwords regularly and consider using enterprise password management software.
This guide will help you change your Linux root password in Ubuntu or CentOS, or reset the password.
Changing Your Root Password in Ubuntu
Step 1: Open a Terminal Window
Right-click the desktop, then left-click Open in terminal.
Alternately, you can click Menu > Applications > Accessories > Terminal.
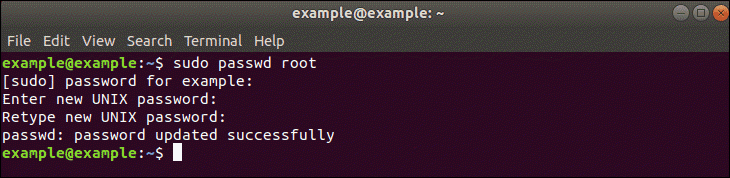
Step 2: Change Your Root Password
In the terminal window, type the following:
The system will prompt you to enter your password – this is the same password you use to log in to the system.
Next, the system will prompt you to enter a new password. Do so, and then re-enter it exactly the same when the system prompts you to retype the password. This double-entry confirms that you have typed the password correctly.
Resetting a Root Password in Ubuntu
In some situations, you may need to access an account for which you’ve lost or forgotten a password.
Step 1: Boot to Recovery Mode
Restart your system. Once you see the splash screen for the computer manufacturer, hold down the shift key. The system should come up with a black and white GRUB, or boot menu, with different Linux kernel versions displayed.
Select the second one from the top – the highest revision, followed by (recovery mode). Press Enter.
Step 2: Drop Out to Root Shell
The system should display a menu with different boot options. Use the arrow keys to navigate to the option labeled root and press Enter.
The system should respond by giving you a command-line interface with a prompt.
Step 3: Remount the File System with Write-Permissions
Right now, your system only has read-only access to your system. That means it can look at the data, but cannot make any changes. But we need write-access to change the password, so we’ll need to remount the drive with the appropriate permissions.
Press Enter. This should allow you to make changes to the data on the hard drive.
Step 4: Change the Password
Substitute the name of the user for username, then press Enter. The system asks you to type a new UNIX password and then to retype it.
Once you’ve entered and confirmed the new password, reboot the system by entering the following:
Hit Enter, and your system should restart. Don’t press any keys, let the system come up to the login screen, and test to make sure the new password works.
Note: Learn how to use the chpasswd command. Chpasswd is helpful for managing multiple passwords and making multiple changes.
Changing the Root Password in CentOS
Changing a password in CentOS is almost identical to changing it in Ubuntu.
Step 1: Access the Command Line (Terminal)
Right-click the desktop, then left-click Open in Terminal. Or, click Menu > Applications > Utilities > Terminal.
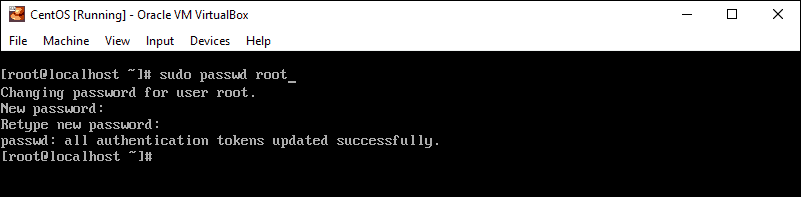
Step 2: Change the Password
At the prompt, type the following, then press Enter:
The system should prompt you to enter your existing password. Do so, then follow the prompts to enter and confirm a new root password.
Reset Root Password in CentOS
This is a similar process as in Ubuntu, with a couple of variations.
Step 1: Access Boot Menu
Restart the system, then tap the Esc key about once per second to launch the GRUB menu.
Step 2: Edit Boot Options
Use the arrows to highlight the version of Linux you boot into, then press e.
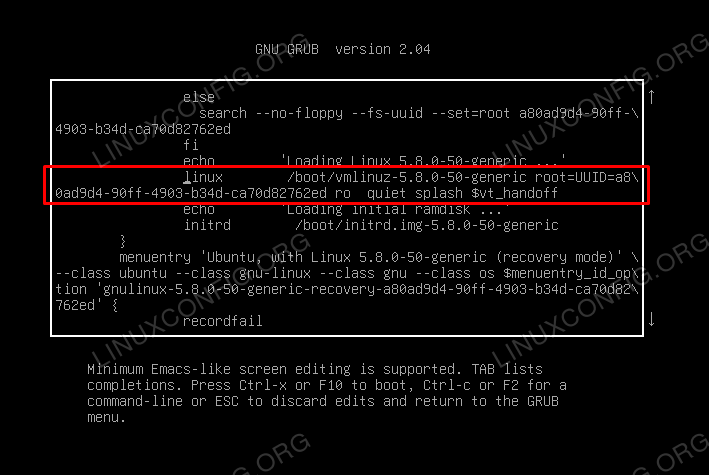
Use the arrows to highlight the line that starts with kernel or Linux.
At the end of the line, add a space then type single. Press Enter, then boot into single-user mode by pressing Ctrl-X or B. (The system will display the command to use.)
Step 3: Remount the Drive
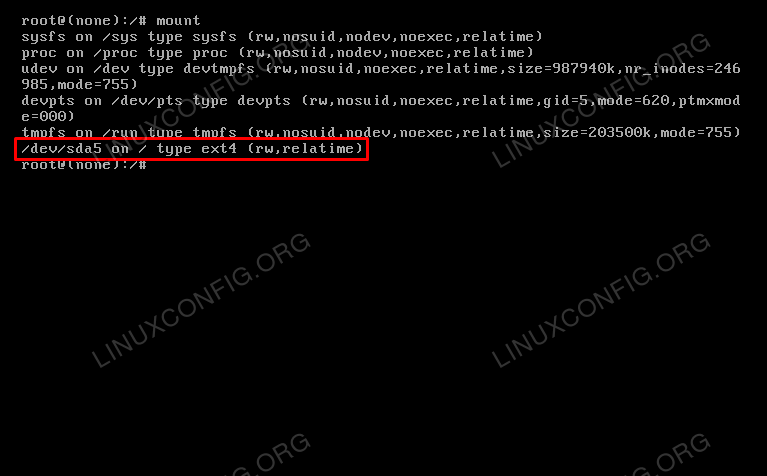
You should have a command line, and you’ll have root privileges. To enable read/write access on your hard drive, type the following:
Step 4: Changing the Password
Press Enter, and the system should prompt you to enter and confirm a new password.
Step 5: Restart
Type the following, pressing enter after each line:
Your system should restart. Confirm that your new password works by logging in.
Note: If you ever come across a Linux boot failure, be sure to save our guide on using GRUB rescue to troubleshoot it.
If you already have access to your user account, resetting or changing your password in Linux is simple.
It can be more challenging if you’ve lost or forgotten a password, but with a little creative restarting and editing, you shouldn’t find it too hard.
Sofija Simic is an experienced Technical Writer. Alongside her educational background in teaching and writing, she has had a lifelong passion for information technology. She is committed to unscrambling confusing IT concepts and streamlining intricate software installations.
In Linux, special tools were developed for managing applications. Application software for Linux typically.
The find command is a useful command-line tool in Linux. It allows you to use the terminal to search for a .
There’s a reason that tech support asks you if you’ve rebooted your Linux server. It’s cliched but true.
This guide is for users who have already configured a CentOS server and installed the Apache HTTP services.
Reset lost root password
This guide will show you how to reset a forgotten root password. Several methods are listed to help you accomplish this.
Warning: An attacker could use some of the methods mentioned below to break into your system. No matter how secure the operating system is or how good passwords are, having physical access amounts to loading an alternate OS and exposing your data, unless you use data-at-rest encryption.
Using sudo
If you have installed sudo and have configured permissions for either the wheel group or a user whose password you recall, you can change the root password by running sudo passwd root .
Using the debug shell
- Append systemd.debug_shell to the kernel parameters.
- This will do a normal boot but start debug-shell.service which runs a root shell ( /bin/sh ) on tty9 . Press Ctrl+Alt+F9 to access it.
- Use the passwd command to create a new password for the root user.
- When done, stop debug-shell.service .
Using bash as init
- Append the init=/bin/bash kernel parameter to your boot loader’s boot entry.
- Your root file system is mounted as read-only now, so remount it as read/write: mount -n -o remount,rw / .
- Use the passwd command to create a new password for the root user.
- Reboot by typing reboot -f and do not lose your password again!
Note: Some keyboards may not be loaded properly by the init system with this method and you will not be able to type anything at the bash prompt. If this is the case, you will have to use another method.
Using a LiveCD
With a LiveCD a couple methods are available: change root and use the passwd command, or erase the password field entry directly editing the password file. Any Linux capable LiveCD can be used, albeit to change root it must match your installed architecture type. Here we only describe how to reset your password with chroot, since manual editing the password file is significantly more risky.
Change root
- Boot the LiveCD and mount the root partition of your main system.
- Use the passwd —root MOUNT_POINTUSER_NAME command to set the new password (you will not be prompted for an old one).
- Unmount the root partition.
- Reboot, and enter your new password.
See also
Recover – Reset Forgotten Linux Root Password
The root account, sometimes called super user, is the admin account on a Linux system, and is essential for performing all kinds of administrative tasks. You’ll need access to it in order to install or remove packages, manage other user accounts, and a lot more things. Anytime you access the root account, either through the su or sudo commands, you’ll be prompted for the root password.
If you have forgotten the password to your system’s root account, you don’t necessarily have to go back to square one and reinstall the whole operating system. It’s possible to recover and reset the root password, even without the old password. In this guide, we’ll take you through the step by step instructions of recovering a forgotten root password on Linux. This will work regardless of the Linux distribution you’re running, as long as its using the GRUB bootloader. Other bootloaders will have similar instructions.
In this tutorial you will learn:
| Category | Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used |
|---|---|
| System | Any Linux distro |
| Software | GRUB bootloader |
| Other | Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo command. |
| Conventions | # – requires given linux commands to be executed with root privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command $ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non-privileged user |
Recover forgotten root password
Follow along with the steps below to reset your root password by entering GRUB recovery mode. In the screenshots below, we are using Ubuntu Linux for an example, but the instructions will apply to any distro. In some cases, you may have to adapt them a little.
- First thing you’ll need to do is reboot the machine and access the GRUB menu. This can be done by holding down the Shift key as the computer is first booting up. Once the menu appears, use your arrow keys to highlight the “Advanced options” selection. On some distros, it may just say the usual name of the operating system, such as “Fedora Workstation”.
The mount command shows that our root partition has been mounted and with read and write permissions
That’s all there is to it. Your computer should boot up like normal, and you will be able to login to the root account (or use commands with sudo) while specifying the password you just set.
Closing Thoughts
In this guide, we saw how to reset the root password on a Linux system, even if the original has been forgotten. Although it sounds complicated, this is a relatively simple task that GRUB can facilitate by allowing us to mount the root partition without loading into the operating system.
Related Linux Tutorials:
Comments and Discussions