- How to Disable SSH Root Login in Linux
- Включение и Отключение входа по SSH. Ограничение доступа по SSH в Linux
- Отключить вход по SSH
- Включить корневой вход по SSH
- Ограничить вход пользователей SSH
- How To Disable Root Login on Ubuntu 20.04
- Prerequisites
- Step 1 — Logging In and Checking auth.log
- Step 2 — Disabling Root Login
- Step 3 — Testing Root Login
- Conclusion
How to Disable SSH Root Login in Linux
The root account is often the most targeted account by crackers via SSH under Linux. An enabled SSH root account on a Linux server exposed to a network or, worse, exposed in Internet can pose a high degree of security concern by system administrators.
The SSH root account should be disabled in all cases in Linux in order to harden your server security. You should login via SSH on a remote server only with a normal user account and, then, change privileges to root account via sudo or su command.
In order to disable SSH root account, first log in to your server console with a normal account with root privileges by issuing the below commands.
$ su tecmint $ sudo su - # Drop privileges to root account
After you’ve logged in to console, open the main SSH configuration file for editing with your favorite text editor by issuing the below command. The SSH main configuration file is usually located in /etc/ssh/ directory in most of Linux distributions.
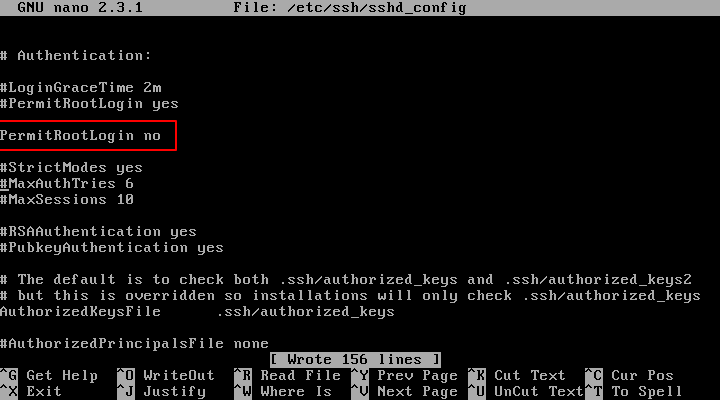
In this file, search for the line “PermitRootLogin” and update the line to look like in the below file excerpt. On some Linux distributions, the “PermitRootLogin” line is preceded by the hashtag sign (#) meaning that the line is commented. In this case uncomment the line by removing the hashtag sign and set the line to no.
After you’ve made the above changes, save and close the file and restart the SSH daemon to apply changes by issuing one of the below commands, specific to your Linux distribution.
# systemctl restart sshd # service sshd restart # /etc/init.d/ssh restart
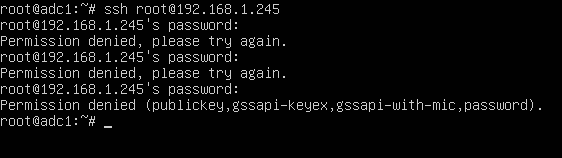
In order to test if the new configuration has been successfully applied, try to login with root account to the server via SSH from a remote system by issuing the below command.
The remote SSH login process for root account should be automatically denied by our SSH server, as illustrated in the below screenshot.
That’s all! You shouldn’t be able remotely login to SSH server with root account via password or via public key authentication mechanisms.
Включение и Отключение входа по SSH. Ограничение доступа по SSH в Linux
Всем известно, что системы Linux имеет доступ пользователя root, и по умолчанию SSH доступ включен для внешнего мира.
По соображениям безопасности не рекомендуется включать доступ ssh для неавторизованных пользователей. Потому что любой хакер может попытаться взломать ваш пароль и получить доступ к вашей системе.
Поэтому лучше завести другую учетную запись, которой вы регулярно пользуетесь, а затем переключиться на пользователя root, используя команду «su–«, когда это необходимо. Прежде чем начать, убедитесь, что у вас есть обычная учетная запись пользователя, и с ее помощью вы можете получить root-доступ.
В Linux очень легко создать отдельную учетную запись, войти в систему как пользователь root и просто запустить команду adduser, чтобы создать отдельного пользователя. Как только пользователь будет создан, просто выполните следующие действия, чтобы отключить вход в систему root через SSH.
Вам может быть интересно:
Мы используем главный файл конфигурации sshd, чтобы отключить вход в систему root, и это может помешать хакеру получить доступ к вашей системе Linux. Здесь же мы можем и включить доступ, а также как ограничить доступ по ssh на основе списка пользователей.
Отключить вход по SSH
Чтобы отключить вход в систему с root, откройте основной файл конфигурации ssh /etc/ssh/sshd_config с выбранным вами редактором. В моем случае я использую редактор Vi или Vim
Найдите в файле следующую строку.
Удалите «#» из начала строки. Сделайте строку похожей на эту.
Далее нам нужно перезапустить службу SSH.
# systemctl restart sshd
или
# /etc/init.d/sshd restart
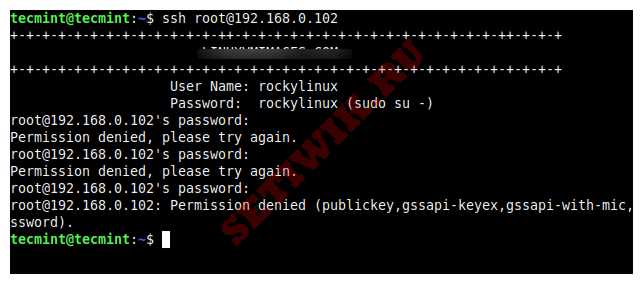
Теперь попробуйте войти в систему пользователем root, вы получите сообщение об ошибке “Permission denied”.
$ ssh root@192.168.0.102
root@192.168.0.102’s password:
Permission denied, please try again.
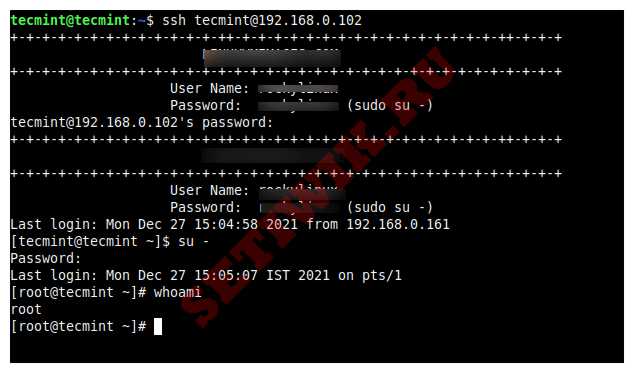
Итак, с этого момента войдите в систему как обычный пользователь, а затем используйте команду «su», чтобы переключиться на пользователя root.
$ ssh root@192.168.0.102
tecmint@192.168.0.102’s password:
Last login: Mon Dec 27 15:04:58 2021 from 192.168.0.161$ su —
Password:
Last login: Mon Dec 27 15:05:07 IST 2021 on pts/1
Включить корневой вход по SSH
Чтобы включить ведение журнала ssh, откройте файл /etc/ssh/sshd_config.
Найдите следующую строку удалите «#» в начале и сохраните файл. (это называется раскоментирование)
Теперь перезапустите службу sshd.
# systemctl restart sshd
или
# /etc/init.d/sshd restart
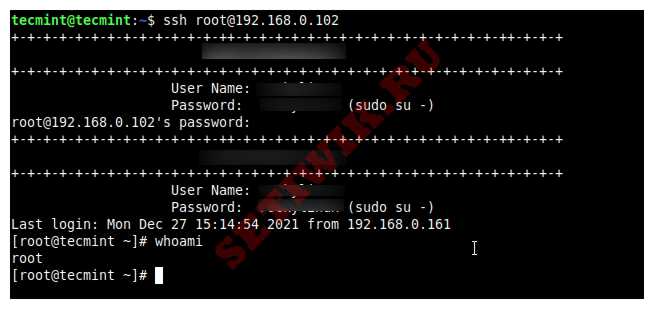
Теперь попробуйте войти в систему с помощью корневого пользователя.
$ ssh root@192.168.0.102
root@192.168.0.102’s password:
Last login: Mon Dec 27 15:14:54 2021 from 192.168.0.161
Ограничить вход пользователей SSH
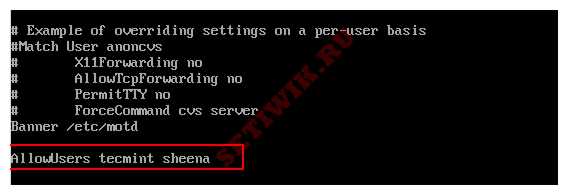
Если у вас в системе большое количество учетных записей пользователей, то имеет смысл ограничить пользователям удаленный доступ по SSH. А тем которым он действительно нужен предоставить доступ по SSH. Откройте файл /etc/ssh/sshd_config.
Добавьте строку разрешенных пользователей в нижней части файла, разделяя пользователей пробелом. Например, пользователи tecmint и sheena имеют доступ к удаленному ssh.
Теперь перезапустите службу ssh
Возможно вам будет интересно: Как исправить ошибку “W: Some index files failed to download” Ошибка в Ubuntu
Вот в принципе и все. Мы рассказали как ограничить доступ SSH, а так же как включить и отключить вход по SSH в системе Linux.
Спасибо за то что дочитали до конца. Оставьте свои отзывы и замечания в разделе комментариев, а так же подписывайтесь на наш Дзен канал.
How To Disable Root Login on Ubuntu 20.04
All Linux-based machines come with a default root user that has all privileges on the machine; by default, you always act as a root user (a superuser). Good security practices recommend that you disable the root login over SSH to prevent unauthorized access to your Linux-based machine by any other user. Disabling root login prevents root access over SSH to your Linux-based machine, which means that no one will have unlimited privileges. Following the recommended security practices, you should create an additional user with almost all superuser privileges to access the account.
In this tutorial, you will disable the root login on Ubuntu, preventing unauthorized root access over SSH and improving your Linux-based system’s security.
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, you will need:
- One Ubuntu 20.04 server with a non-root user with sudo privileges, a firewall, and at least 1GB of RAM, which you can set up by following the Ubuntu 20.04 initial server setup guide.
Step 1 — Logging In and Checking auth.log
In this step, you will access your server via your sudo -enabled, non-root user to check the authentication attempts to your server. By reviewing the authentication log, you may see both authorized and unauthorized login attempts.
During the prerequisites, you created a new user and added that user to the sudo group to grant administrative privileges. You will use this sudo user to access your machine because you won’t be able to SSH as a root user after disabling the root login.
Based on your chosen login method, log into your server using SSH. If you logged into your root account using the SSH keys during the initial server setup, you must use a key-based mechanism as password authentication is disabled when using a key-based login for your server. Otherwise, use the password-based login with the sudo-enabled user password.
Log into your server as your sudo -enabled user (in this tutorial, it will be sammy) using the following command for password-based login:
If using a key-based login method, log into your server as your sudo -enabled user with the following command:
The -i flag represents the identity file from which your_private_key is read for authentication.
Next, inspect the auth.log file by moving to the /var/log directory:
Use cat auth.log to display the contents of the file:
Enter your password if prompted.
You will receive an output similar to this:
OutputMay 29 18:46:32 ubuntu sshd[3886]: Disconnected from invalid user cally 43.155.90.144 port 47454 [preauth] May 29 18:51:56 ubuntu sshd[3890]: Received disconnect from 195.38.129.16 port 10017:11: Bye Bye [preauth] May 29 18:51:56 ubuntu sshd[3890]: Disconnected from authenticating user root 195.38.129.16 port 10017 [preauth] May 29 18:52:24 ubuntu sshd[3892]: Received disconnect from 178.128.234.248 port 58660:11: Bye Bye [preauth] May 29 18:52:24 ubuntu sshd[3892]: Disconnected from authenticating user root 178.128.234.248 port 58660 [preauth] May 29 18:52:34 ubuntu sshd[3894]: Received disconnect from 43.134.106.128 port 33854:11: Bye Bye [preauth] May 29 18:52:34 ubuntu sshd[3894]: Disconnected from authenticating user root 43.134.106.128 port 33854 [preauth] May 29 18:53:07 ubuntu sshd[3896]: Invalid user projects from 176.183.60.72 port 42070 May 29 18:53:07 ubuntu sshd[3896]: Received disconnect from 176.183.60.72 port 42070:11: Bye Bye [preauth] May 29 18:53:07 ubuntu sshd[3896]: Disconnected from invalid user projects 176.183.60.72 port 42070 [preauth] May 29 18:57:27 ubuntu sshd[3900]: Received disconnect from 92.255.85.135 port 20436:11: Bye Bye [preauth] May 29 18:57:27 ubuntu sshd[3900]: Disconnected from authenticating user root 92.255.85.135 port 20436 [preauth] May 29 19:06:40 ubuntu sshd[3903]: Invalid user default from 27.71.207.190 port 57513 May 29 19:06:41 ubuntu sshd[3903]: Connection closed by invalid user default 27.71.207.190 port 57513 [preauth] . The auth.log file logs all authentication attempts made to a server. You might see a lot of unknown and unauthorized requests being received by your server. For this reason, you might want to disable root login on your system and rotate your keys and passwords regularly.
You have now reviewed the authentication logs that indicate your server has received more than just your authentication requests. Next, you will update your server’s SSH configuration so that the root access is completely disabled on your server.
Step 2 — Disabling Root Login
In this step, you will edit the sshd_config file to disable the root login and then restart the sshd daemon to read the configuration after the modifications.
The sshd_config file stores the SSH daemon configuration containing the parameters used by sshd . The daemon is responsible for handling SSH connections. You need to restart the sshd daemon to apply the configuration changes. This configuration change will instruct the sshd not to permit root login over SSH.
Open the file sshd_config located in the /etc/ssh directory using nano or your favorite text editor:
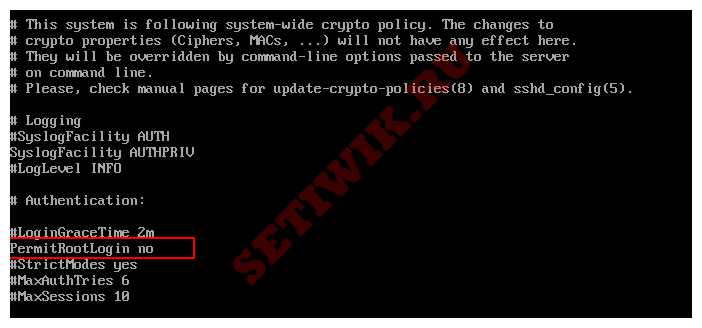
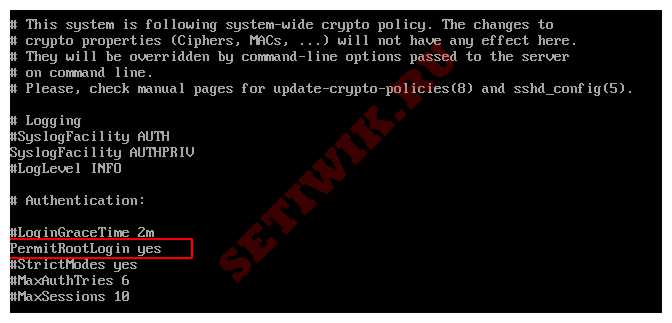
Review the file, looking for the PermitRootLogin line:
Output. #LoginGraceTime 2m PermitRootLogin yes #StrictModes yes #MaxAuthTries 6 #MaxSessions 10 . Change the value of the key PermitRootLogin from yes to no :
Output. #LoginGraceTime 2m PermitRootLogin no #StrictModes yes #MaxAuthTries 6 #MaxSessions 10 . Next, you will restart the sshd daemon to read the configuration after the modifications you just made.
Use the following command to restart the daemon:
This command will restart the sshd service using systemctl .
In this step, you changed the configuration file to deny root login requests and restarted the sshd to read the latest configuration. Next, you will test whether root login is disabled or not by making a root login attempt to your server.
Step 3 — Testing Root Login
After disabling the root login, try logging into a new terminal session with SSH as root. Use the following commands based on your preferred login mechanism.
If using password-based login:
The attempt to SSH as root will fail with an error message like this:
Outputroot@your_server_ip: Permission denied (publickey). To access to server again, log into your server with the sudo -enabled non-root user credentials to confirm that you can still access the server.
If using password-based login:
You can now continue using the server as needed.
Conclusion
In this article, you configured the sshd configuration to disable the root login on Ubuntu. Now you know how to prevent root login to your Linux-based machines, thus adding an extra layer of security to your machines.
To continue setting up your machine, read more on How to Keep Ubuntu 20.04 Servers Updated.
Thanks for learning with the DigitalOcean Community. Check out our offerings for compute, storage, networking, and managed databases.