- How to remove all default gateways
- How to Add and Delete Static Route in Linux using IP Command
- Viewing the existing routing table
- Adding a static route using IP command
- Permanently adding static route (RHEL, Fedora, CentOS)
- Permanently adding static route (Ubuntu / Debian)
- Deleting a static route
- 10+ ip route command examples in Linux [Cheat Sheet]
- Types of route
- Syntax for ip route command
- Different examples to use ip route command
- 1. List current routing table using ip route command
- 2. Add a new route using ip route command
- 3. Add a new default gateway route using ip route command
- 4. Add a new route to specific device with ip route command
- 5. Delete a route using ip route command
- 6. Modify an existing route using ip route command
- 7. Clear routes with flush using ip route command
- 8. Clear all the routes using ip route command
- 9. Get a single route to a destination
- 10. Get a single route from the source
- 11. List routes with given scope only
- 12. List routes for specified device only
- Conclusion
- What’s Next
- Further Reading
How to remove all default gateways
I’m running a custom built Linux machine, so not all Linux commands are available.
I execute network related commands, so I need to set a default gateway right before I run my command, then remove that gateway immediately afterward. To do that I run all my commands in one line:
/sbin/route add default gw 10.10.10.10;my command;/sbin/route del default gw 10.10.10.10; The problem is, for some reason I once found 2 default gateways on the same machine which caused all my commands to fail because even if I set my default gateway before running my test, it is still messed up and can’t run my test. So is there a way to remove ALL default gateways in one command ? I have a large amount of machines that are increasing and it won’t be practical to plant a script on every machine. I need a command as simple as the following:
/sbin/route del all default;set my default gw;mycommand;/sbin/route del all default; All I have found so far is a command to remove a default gateway but not all of them /sbin/route del default which won’t work for me. /sbin/route help displays the following
/sbin/route --help Usage: route [] Edit the kernel's routing tables Options: -n Don't resolve names -e Display other/more information -A inet Select address family How to Add and Delete Static Route in Linux using IP Command
Part of the skill set for any Linux user, and particularly a systems administrator, is the ability to perform some network tweaks on a Linux system. This includes adding and deleting routes to enable the system to communicate with other systems o a local network. In this guide, we explore exactly how you can go about adding and deleting routes on a Linux system.
Viewing the existing routing table
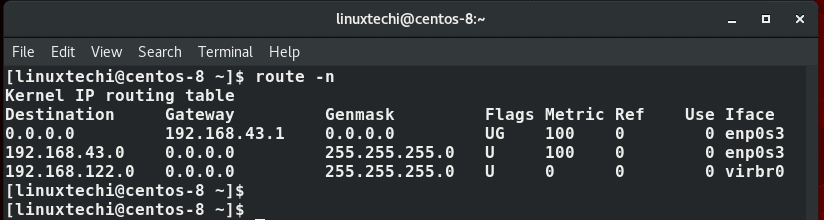
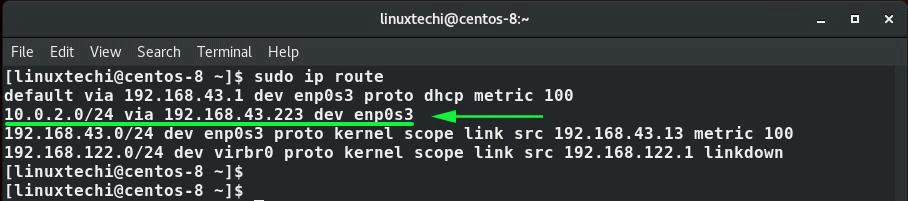
Before we embark on adding or deleting routes, it’s prudent to check the existing default routes on a system. To do so, simply launch your terminal and issue the command:
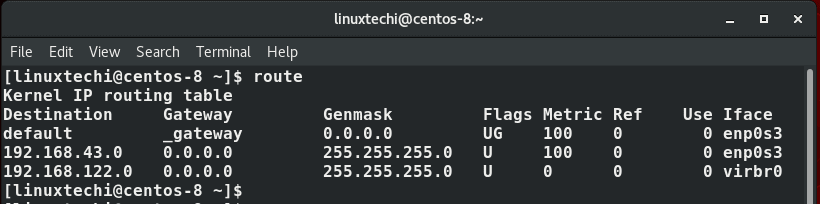
$ ip route show Or $ ip route list
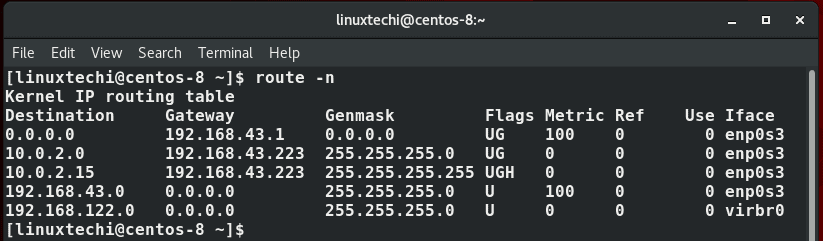
Similar statistics can be displayed using route command,
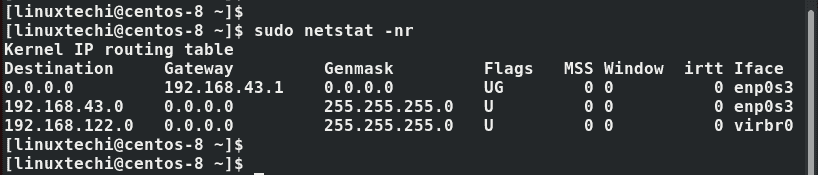
Also, you can use the good old netstat command, which is usually used for printing interface statistics as well as the routing table to achieve the same result.
With the default routing statistics in mind, let’s now move a step further and add some routes to our system.
Adding a static route using IP command
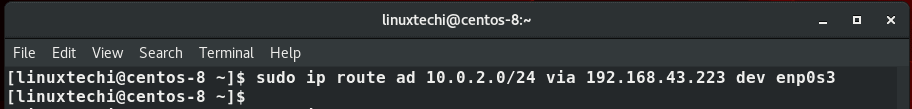
Suppose you want to take a backup of a Linux machine and push the backup file to another backup server in the subnet 10.0.2.0/24 . However, for one reason or the other, you cannot reach the backup server via the default gateway. In this case, you will have to create a new route for backup server subnet via another IP, say 192.168.43.223 via the interface enp0s3 .
The command for this will be
$ sudo ip route add 10.0.2.0/24 via 192.168.43.223 dev enp0s3
- 10.0.2.0 -> is the network you want to connect to
- /24 -> is the subnet mask
- 192.168.43.223 -> is the IP through which we will reach the server
- enp0s3 -> is the network interface
You can confirm whether new static route add been in route table using “ip route show” command.
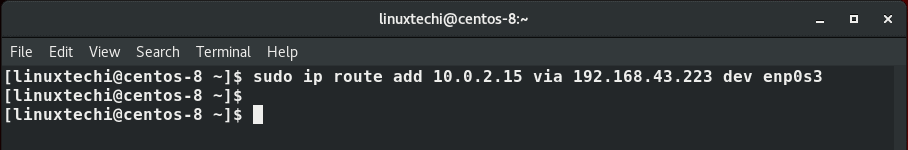
To add the specific IP of the backup server, say 10.0.2.15 run the command:
$ sudo ip route add 10.0.2.15 via 192.168.43.223 dev enp0s3
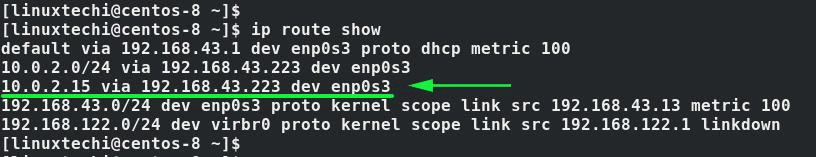
Once again, you can check the routing changes to see if the changes exist using the ip route show command:
Permanently adding static route (RHEL, Fedora, CentOS)
The routes we have just added are temporary and will not survive a reboot. To make the routes persistent, you need to manually add them.
In the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory, create an interface file route-interface where the interface attribute is your network interface name. In our case, this will be route-enp0s3 .
$ vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-enps03
Next, we will add the routes as shown:
10.0.2.0/32 via 192.168.43.1 10.0.2.15 via 192.168.43.1
Save the file and exit. Then restart NetworkManager Service
$ sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager
Permanently adding static route (Ubuntu / Debian)
For Debian distributions, edit the file /etc/network/interfaces
$ sudo vim /etc/network/interfaces
Append the following line:
up route add -net 10.0.2.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.43.1 dev enp0s3
Save and exit the file. Finally, for the changes to come into effect, run below commands
$ sudo ifdown enp0s3 && sudo ifup enp0s3
Deleting a static route
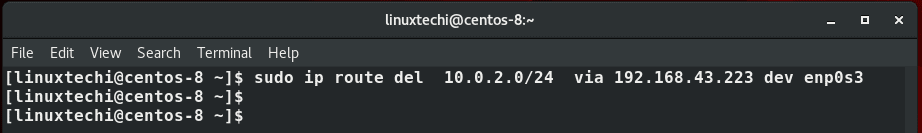
To delete a specific route, use the ip route del command. For example, to remove the route address we just added, run the command:
$ sudo ip route del 10.0.2.0/24 via 192.168.43.223 dev enp0s3
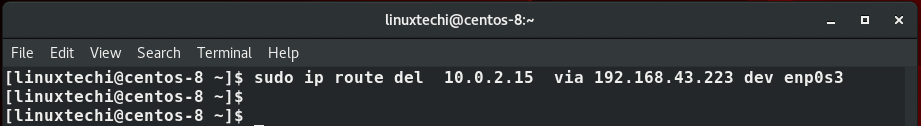
To delete a single IP route in a subnet run the command
$ sudo ip route del 10.0.2.15 via 192.168.43.223 dev enp0s3
To delete default route run:
$ sudo ip route del default
To add a default route run below ‘ip route add’ command,
$ sudo ip route add default via dev interface
$ sudo ip route add default via 192.168.43.1 dev eth0
We hope that this tutorial was informative and provided you with insights into how you can go about adding and deleting static route in Linux.
Also Read : 12 ip Command Examples for Linux Users
10+ ip route command examples in Linux [Cheat Sheet]
In Linux, ip command is used to show or manipulate routing, devices, policy routing and tunnels. ip route is a part of ip command. It helps to manage the route entries in the kernel routing tables that keep information about paths to other networked nodes. The routes can be set for different IP addresses (destination). You can use ip route command to add, delete, change, and list the routes.
Types of route
Following are the different types of routes.
- unicast: It describes real paths to the destinations covered by the route prefix.
- unreachable: Unreachable destinations. The packets are discarded and the ICMP message host unreachable is generated.
- blackhole: Unreachable destinations. The packets are discarded silently.
- prohibi: Unreachable destinations. The packets are discarded and the ICMP message communication administratively prohibited is generated.
- local: The destinations are assigned to this host.
- broadcast: The destinations are broadcast addresses. The packets are sent as link broadcasts.
- throw: The packets are dropped and the ICMP message net unreachable is generated.
- nat: A special nat route. The destinations covered by the prefix are considered dummy (or external) addresses and require translation to real (or internal) ones before forwarding.
- anycast: The destinations are anycast addresses assigned to this host. They are not implemented.
- multicast: A special type for multicast routing. It is not present in normal routing tables.
Syntax for ip route command
The syntax for ip route command is:
Some important commands in ip route are:
Different examples to use ip route command
1. List current routing table using ip route command
You can use ip route list or ip route show command to list current routes or routing table.
Sample Output:
2. Add a new route using ip route command
The ip route add command is used to add a new route for the specified network range. You will need root privileges to execute the command.
Sample Output:
You can also use ip route only to list the routing table.
3. Add a new default gateway route using ip route command
A default gateway is the IP address of the router that connects your host to remote networks. You can use the following command to add a new default gateway route.
$ sudo ip route add default via
Sample Output:
4. Add a new route to specific device with ip route command
The below command adds a new route specifying the network interface or network device as the gateway.
Sample Output:
5. Delete a route using ip route command
You can use the ip route delete command to delete a route from the routing table.
Sample Output:
6. Modify an existing route using ip route command
You can change a route using the ip route change command.
Sample Output:
For example, to change the default gateway route, you can use the below command.
7. Clear routes with flush using ip route command
The ip route flush command clears a route from the routing table for a particular destination.
Sample Output:
8. Clear all the routes using ip route command
You can also use ip route flush command to remove all the routes from the routing table.
$ sudo ip route flush table main Sample Output:
9. Get a single route to a destination
The below command is used to get a single route to a destination address and prints its contents.
$ ip route get to destination Sample Output:
deepak@ubuntu:~$ ip route get to 192.168.0.133 192.168.0.133 dev enp0s3 src 192.168.0.103 uid 1000 cache
10. Get a single route from the source
You can run the following command to get a single route from the source address.
$ ip route get destination from source Sample Output:
deepak@ubuntu:~$ ip route get to 192.168.0.133 from 192.168.0.103 192.168.0.133 from 192.168.0.103 dev enp0s3 uid 1000 cache 11. List routes with given scope only
You can run the below command to list routes with the given scope only.
$ ip route list scope scope_value Sample Output:
12. List routes for specified device only
The following command lists the routes with the specified device only.
Sample Output:
To view the routes with device name enp0s3, you can use:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned how we can manage the routing table using the ip route command in the Linux system. You can add, delete, change, and list the routes in the routing table. If you still have any confusion, feel free to ask us in the comment section.
What’s Next
Further Reading
Didn’t find what you were looking for? Perform a quick search across GoLinuxCloud
If my articles on GoLinuxCloud has helped you, kindly consider buying me a coffee as a token of appreciation.

For any other feedbacks or questions you can either use the comments section or contact me form.
Thank You for your support!!