- How to run a script with root authority in Linux
- 3 Answers 3
- Linux sudo Command – Run Commands with Root Privileges
- Install sudo (sudo command not found error solution)
- sudo Command Syntax
- sudo Parameters
- Display sudo Command Help Information
- Run Command with Root Privilege
- Add User To Sudoers File
- Add User sudo/wheel Group
- List Sudoer User Privileges and Rights
- Run Command As Different User
- Sudo Environment Variables
- Sudo Command Examples
- Run Multiple Commands with sudo
- Compare su vs sudo Command
- Messed Up with Sudoers File
How to run a script with root authority in Linux
I have to develop a Web site written in CGI. I would like to know how to run a script with root authority from CGI. Let’s say the script name is hello , I run it from CGI like system(«pathToTheFile/hello»). Now I would like to run this hello file as root; can anybody help me with this?
Normally the web-server you run to access your CGI script should be run on a system user ad not under root (e.g. a user calles apache who execute the apache httpd); after you just give that user the read and execute access to the script.
3 Answers 3
Generally the safest way to do this kind of thing is to use the setuid feature of UNIX-like OSs. If you set the owner of the hello program to be root , and then set the setuid bit:
Then no matter who executes the program, it will execute as root. This works for native executables, but not for interpreted scripts. If «hello» has to be a script, then this won’t work for you.
Now, I have to say that in general, setuid root programs aren’t a great idea. Often you can create a special user to own the script, and give that user some limited privileges needed, and then make the script setuid to that user.
No, that does not work for scripts. Only binaries. Also, you can’t set that, that would be a big security hole. The existing root account would have to set that. That might be you, however.
@Keith, you could have a script which runs a specially modified setuid shell (a «real» executable) passing another script as the parameter. This would get around that problem. Convoluted, yes, but there are ways around most problems.
@pax, true but you still have to setuid some binary somewhere. And this post didn’t mention that extra step, so I thought I would. Also, I disagree that it’s the safest way, since «no matter who executes» it it gets the elevated privileges. sudo is safer since you can define more fine-grained control over who can execute it (e.g. the UID of the web server only).
@Keith appears to be right: Linux doesn’t allow setuid scripts at all. I had this belief that it was at least configurable, but that doesn’t seem to to be the case; perhaps it once was. *BSD Unices, including OS X, allow them, and that’s where I spend more of my time these days. I edited my answer to reflect this.
Yes some older *nix do allow it, but Linux doesn’t. A good discussion about the history of it is here.
A much safer method of doing things as root from a web page is to disconnect the program execution from the web page. Instead, use Unix local sockets, named pipes, or a directory of queued jobs.
The directory is probably the easiest to handle. Set up a directory that your web page can write files into. When your page needs something done, write a file describing the job. Then you have a program running as root waiting for new jobs. It can run continuously if it needs fast response or it can run every minute or every few minutes using a crontab entry.
The normal method would be to have the executable file owned by the user you want to run it as, then set the SUID bit.
The method of using sudo usually requires user input for the password (there are ways around this but they’re hideously complex).
I suppose I don’t need to mention that setting the SUID bit is a very dangerous thing to do, yes? If there’s any other way to do what you want, you should use it.
One thing you may want to consider is to pose the question not in terms of the solution you need but in terms of the problem you want solved. Running as root is a solution and not necessarily a good one. Post what you’re trying to achieve rather than how, and we can help you out in a far less dangerous way.
Linux sudo Command – Run Commands with Root Privileges
sudo command is a special command which is used to execute normal user commands with root privileges without logging as the root user. The sudo term is the short form of the “SuperUser Do” or “substitute user do“. This is not a security problem because in order to execute commands as root the user should have already provided the required privileges in the /etc/sudoers file. If not the user can not execute commands with root privileges. The sudo command also used to run commands with different user privileges. The sudo command provides the root or superuser privileges for only the current command or application. So this means sudo provides temporary administrative rights to the current normal user.
The sudo is create in 1980 but gained popularity in 1994 with the unofficial for called “CU sudo“. Then with extra development by fixing issues, problems and integration with more Linux distributions the name changed into “sudo“.
Install sudo (sudo command not found error solution)
The sudo command is preinstalled in most of the Linux distributions and its core of the daily system adminsitration. But for different reasons it may not be installed or removed in some cases. You will get an error like “sudo command not found error”. The sudo command can be install with the package name “sudo” for the most of the Linux distributions.
Install sudo For Ubuntu, Debian, Mint, Kali:
Install sudo For Fedora, CentOS, RHEL, SUSE:
sudo Command Syntax
sudo command is used at the start of the command which means the root privielges are elevated before the execution of the command.
- PARAMETER is the sudo command parameters.
- COMMAND is the command which will be executed with root or different user privilege.
sudo Parameters
Even sudo command a lot of options or parameters the most popular options are like below.
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| -b | Run command background |
| -E | Preserve the environment |
| -h | Display help information |
| -l | List allowed commands |
| -n | Run non-interactive |
| -s | Run specified shell environment |
| -u | Run with specified user privileges other than root |
| -V | Print verbose or debug output |
Display sudo Command Help Information
The sudo command provides the -h option in order to list help information with available options. Alternatively the long format of the -h option which is –help can be also used to print help.
Run Command with Root Privilege
According to its syntax, the sudo command can be used to run different commands with the root privileges like below. In the following example, we will print the /etc/passwd content using the cat command. Normally the passwd file can be only read by the root user. The current user password will be asked for authentication. After successful authentication, the password will be cached and will not be asked for a short period.
The output is like below. Where every user in the system is listed with the information like loginshell, userid, home directory etc.
[sudo] password for ismail: root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin/nologin bin:x:2:2:bin:/bin:/usr/sbin/nologin sys:x:3:3:sys:/dev:/usr/sbin/nologin sync:x:4:65534:sync:/bin:/bin/sync games:x:5:60:games:/usr/games:/usr/sbin/nologin man:x:6:12:man:/var/cache/man:/usr/sbin/nologin lp:x:7:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/usr/sbin/nologin mail:x:8:8:mail:/var/mail:/usr/sbin/nologin news:x:9:9:news:/var/spool/news:/usr/sbin/nologin uucp:x:10:10:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/usr/sbin/nologin proxy:x:13:13:proxy:/bin:/usr/sbin/nologin www-data:x:33:33:www-data:/var/www:/usr/sbin/nologin backup:x:34:34:backup:/var/backups:/usr/sbin/nologin list:x:38:38:Mailing List Manager:/var/list:/usr/sbin/nologin irc:x:39:39:ircd:/var/run/ircd:/usr/sbin/nologin Add User To Sudoers File
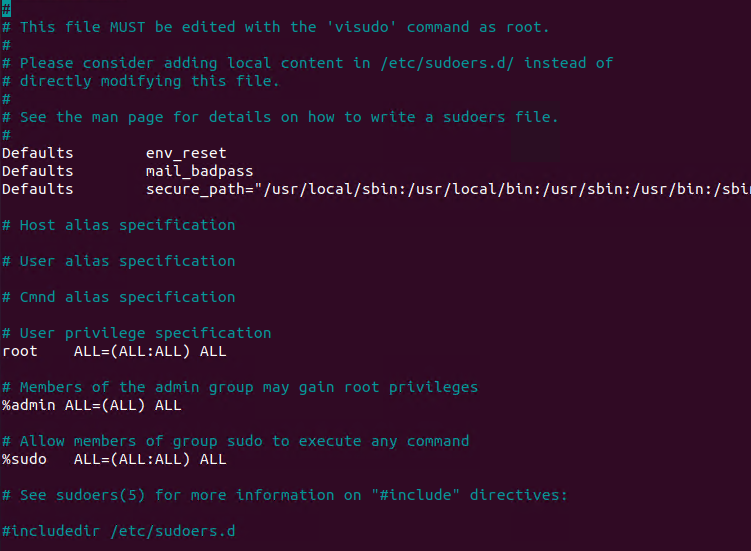
In order to use the sudo command the current user should be added to the sudo configuration file named /etc/sudoers . This file stores configuration about the sudo command like which user can run the sudo command and what privileges can be provided. The sudoers file can be edited in different ways like using a regular text file editor but the visudo command is provided to edit sudoers file in a more fashionable way.
For example, we can skip asking a password for every sudo command execution for the user ismail with the following line. In the following line, the user ismail can run every command as root and other users without asking a password.
ismail ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALLIn the following configuration, we will enable the passwordless execution but restrict the commands the user can run. The user can only run the /bin/mkdir and /bin/rmdir commands. The commands should be provided with their full or absolute paths.
ismail ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:/bin/mkdir,/bin/rmdirWe can configure the sudo permissions for a specific Linux group. In the following example we will give the admin group the sudo privileges for all commands without password.
Add User sudo/wheel Group
Running sudo command requires some privileges. In order to run sudo command the current user should have the user of the sudo or wheel groups. The sudo group is used in Debian, Ubuntu, Mint, Kali. The wheel group is used in Fedora, CentOS, RHEL and SUSE.
Add User To sudo Group:
Add User To wheel Group:
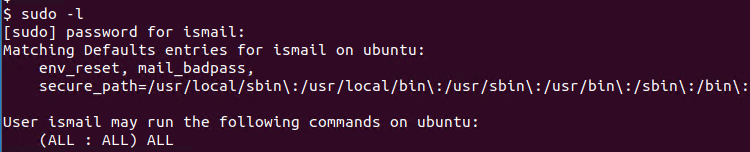
List Sudoer User Privileges and Rights
The sudo command provides the -l option in order to list current user sudoer file configuration and privileges. This will list secure paths for the current user where these paths executables can be executed securely. Also available commands for the current user listed like below.
Run Command As Different User
Even the sudo command is mainly used and popular for executing commands with root privileges it can be also used for to execute commands with different user privileges. The -u option is used to set the username as a parameter. In the following example we will execute the mkdir command with the user ali .
$ sudo -u ali mkdir /home/ali/backupSudo Environment Variables
As a command line or bash tool, the sudo command comes with useful environment variables. These environment variables are used to set current users and new user environments.
SUDO_ASKPASS is used to enable or disable asking password for the user.
SUDO_COMMAND is set the command executed by the sudo.
SUDO_EDITOR is the editor used to edit sudoers file which is nano in most of the cases.
SUDO_PROMPT used as the default password prompt.
SUDO_UID stores the user id of the user who invoked sudo command.
Sudo Command Examples
In this part, we will make some examples of popular use cases about the sudo command. In the following example, we will edit the index.html file with the www user privileges.
$ sudo -u www vim /var/www/html/index.html $ sudo -u www vim /var/www/html/index.php $ sudo -u www vim /var/www/html/index.cgiIn the following example, the log files about the system will be displayed. Normally these log files are only viewed by the root and admin users.
$ sudo -u adm cat /var/log/syslogWe can edit another user’s home directory content like a file. In the following example, we will change the file which is owned and stored by the ahmet home user directory.
$ sudo -u ahmet vim /home/ahmet/names.txtThe system can be shutdown using the sudo command with a normal user like below.
If you want to change a different user password and do not want to log in to this user or root you can use the sudo to change another user password like below. In the following example, the user named elif password will be changed.
Run Multiple Commands with sudo
Single sudo may run multiple commands at a single execution. This is mainly related to the bash features where a single line may contain multiple commands which are separated with the ; .
$ sudo sh -c "cd /home/ismail; mkdir backup; cd backup; touch text.txt"Multiple commands can be also executed with different user privileges like below.
$ sudo -u ismail sh -c "cd /home/ismail; mkdir backup; cd backup; touch text.txt"Compare su vs sudo Command
su is another command which is used to change the current user into the root or another user. It may seem the su and sudo commands are the same but they are not. sudo the command executes given commands without changing the current user sessions by just changing the command execution privileges. Where the su command directly changes the current user session into other users and you can not make operations with the previous user unless not change back to this user.
Messed Up with Sudoers File
You can edit the sudoers file in different ways. But the best way is using the visudo command which will open the sudo command with a default text editor. But if you create a regular text file and copy ass a sudoers file and if you have a typing error the sudoers file format will be corrupt and the sudoers file will not work. Please take the following suggestion into consideration when editing the sudoers file to prevent errors and malfunction.
- Do not edit sudoers file directly and use the visudo command which will check the edited sudoers file when exiting.
- If there is an error in the sudoers file and can not use the sudo command use the su command which will log in as the root user.
- If you made an error in sudoers file and can not run the sudo command and using this system as VM just shut down the system and mount the disk file and change the sudoers file.