- Scan for Network attached devices
- 3 Answers 3
- Find Devices Connected to Your Network with nmap on Ubuntu 22.04
- Scan your network with Nmap on Ubuntu
- Step 1: Open the Ubuntu command line
- Step 2: Install the network scanning tool Nmap
- Step 3: Determine the IP range/subnet mask of your network
- Alternative Installation via Ubuntu GUI
- Step 4: Scan the network for the connected device(s) with Nmap
- Step 5: Exit the terminal
- Search
- About This Site
- Latest Tutorials
- The 6 Best Network Scanners for Linux
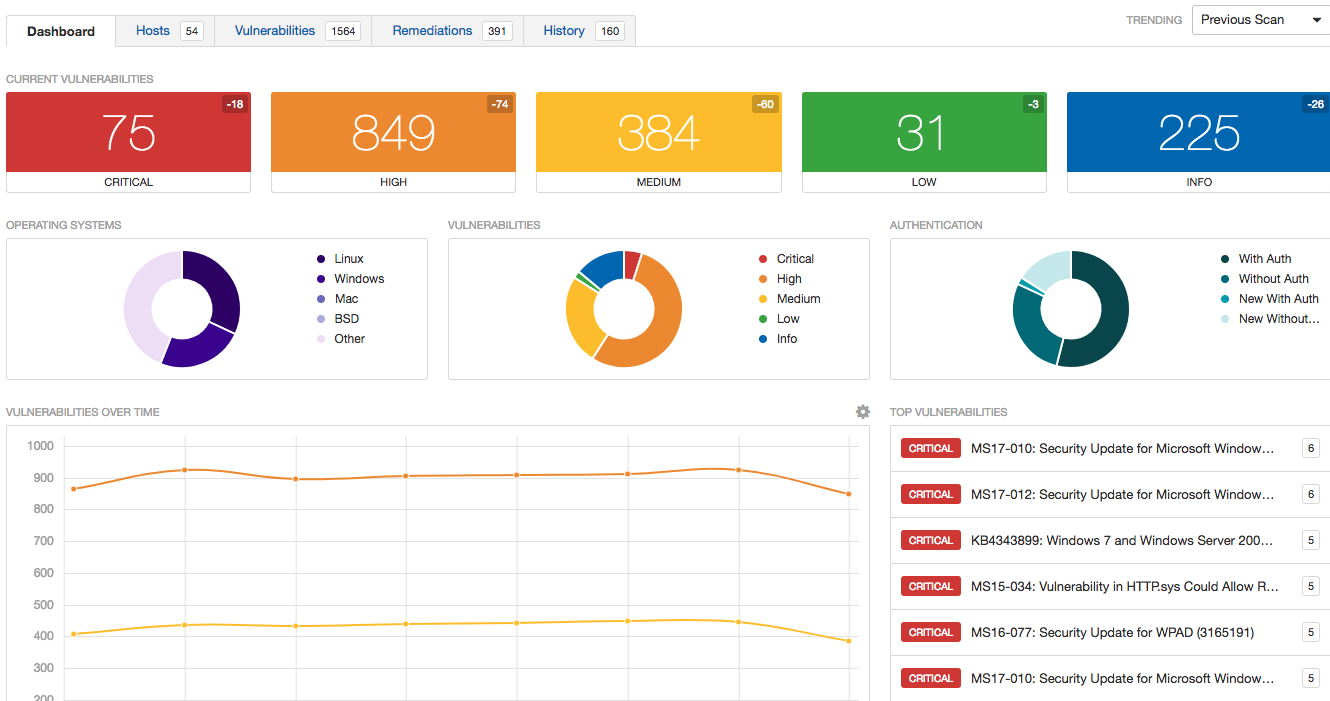
- 1. Nessus
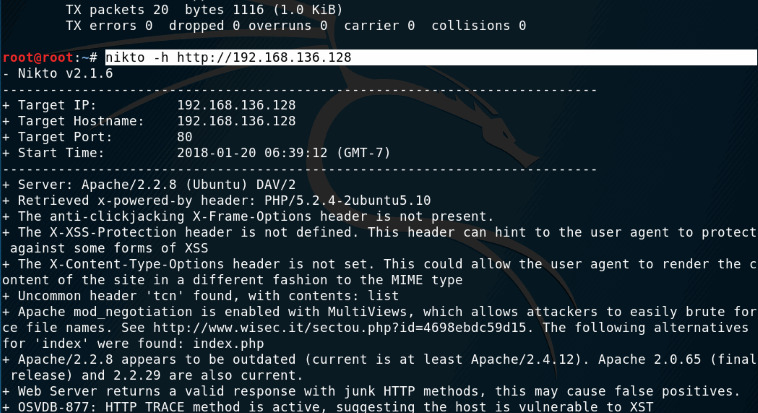
- 2. Nikto
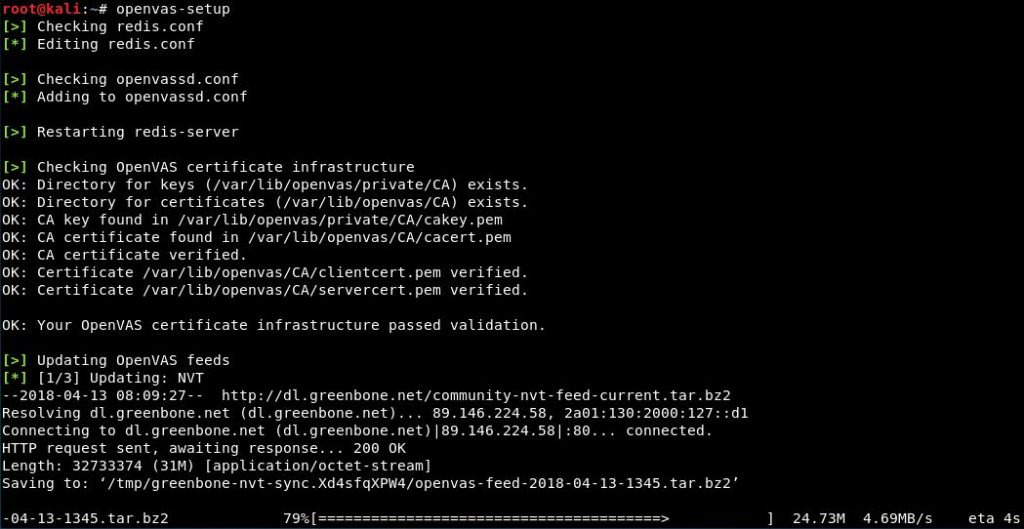
- 3. OpenVAS
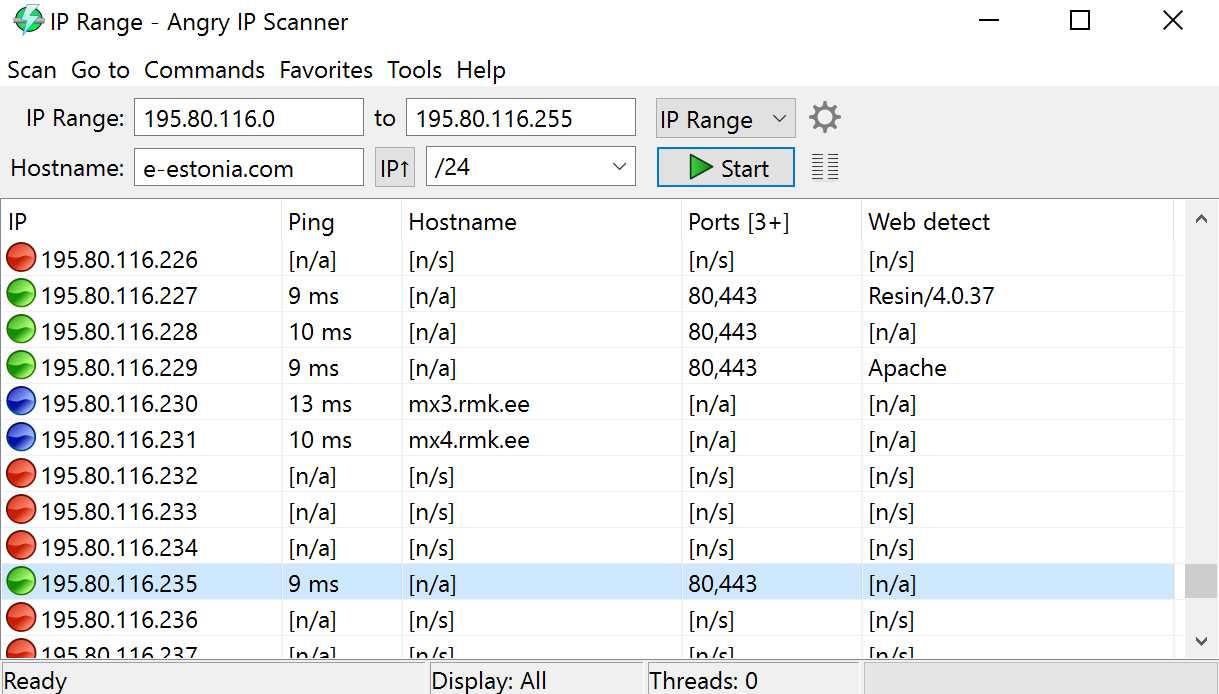
- 4. Angry IP scanner
- 5. Nmap
- 6. Qualys FreeScan
- Conclusion
Scan for Network attached devices
Is there a way to scan for computers on the network through the command line and get their IP, MAC and DNS names without knowing anything about them?
3 Answers 3
nmap -v -sn 192.168.1.0/24 | grep -v down ps. of course you can change subnet settings as you need.
pps. depending on nmap version mac address is displayed or not. 5.21+ (debian testing+) displays. 5.0 (currently in debian stable) not.
arp -a will dump all that information without needing to install nmap . However, nmap does an active scan, so it will be more up to date.
If you really don’t have a clue at all, you should first passively listen to the network. Local networks are quite chatty and mostly a packet is sent to all network devices. By decomposing the layers of the packets, you can learn a lot about the topology. Beware, sometimes this is not possible at all, it depends on the network.
Ethernet frames give you ethernet addresses.
ARP (Address resolution protocol) couples ethernet address to the network address and gives implicit hints about the relations between the network devices.
IP (Internet protocol) gives you a relation between two hosts with ip-addresses.
TCP (Transmission control protocol) gives you an idea about which services (ports) are active and which computers chat with each other.
UDP (User datagram protocol) gives the same information as TCP. You can actually learn more than just do a active scan.
You can use tcpdump or use the pcap library if you want to find specific information. I made a small example in perl. It dumps all hardware addresses, network addresses, tcp and udp ports.
Find Devices Connected to Your Network with nmap on Ubuntu 22.04
As Ubuntu users, we may want to know if we are the only ones using our network, especially the WLAN, or if there are other unwanted users exploiting our network bandwidth. This capability and knowledge are also helpful when we want to be sure that no hacker is accessing our system by connecting to our network.
Scan your network with Nmap on Ubuntu
This article describes step by step how to use the Nmap tool, which provides you with a list of all devices connected to your network. We have run the commands and procedures described in this article on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS.
Step 1: Open the Ubuntu command line
We will be using the Ubuntu command line, the Terminal, in order to view the devices connected to our network. Open the Terminal either through the system Dash or the Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut.
Step 2: Install the network scanning tool Nmap
When it comes to reliable network scanning, Nmap is a tool that you can totally depend on.
Enter the following command as sudo in the Terminal application in order to install the tool.
The system will ask you for the password for sudo since only an authorized user can install/uninstall and configure software on Ubuntu.
The system will also ask you to confirm the installation with y/n. Please type y and press enter to start the installation process.
Step 3: Determine the IP range/subnet mask of your network
To know which devices are connected to your network, you first need to determine the IP range or subnet mask of your network. We will use the ifconfig command to determine this IP. To run the ifconfig command, we need to install the net-tools package on our Ubuntu server or desktop. Use the following command to install net-tools if you do not already have it installed on your system:
$ sudo apt install net-tools
The system will prompt you with a y/n option to confirm the installation. Please enter Y and hit enter to begin the installation process.
Once you have the net-tools utility available, run the following command to get information about the network(s) your system is connected to:
The highlighted IP in the output shows that our system uses the subnet mask 192.168.100.0, and the range is 255. So our network IP range is from 192.168.100.0 to 192.168.100.255.
Alternative Installation via Ubuntu GUI
Instead of using the ifconfig tool, you can also get the subnet mask from the Ubuntu user interface.
Access the settings utility in System Dash and check the details of your network by clicking on the settings icon next to the WLAN or Ethernet network you are connected to.
In this example, we have checked the settings of a wi-fi network we are currently connected to.
The highlighted ipv4 address or the Default Route address indicates that we are connected to a subnet IP 192.168.100.0
Step 4: Scan the network for the connected device(s) with Nmap
Through the Nmap tool, you can scan the report of all devices connected to a network by providing the subnet mask IP as follows:
The output shows that three devices are connected to the network: the router itself, the Linux system I use on my laptop, and my phone.
Step 5: Exit the terminal
Use the following command to exit the terminal application after extracting the information you need:
In this article, you learned how an Ubuntu user could install and use the Nmap command. We showed you how to see which devices are connected to your network. This way, you can verify that no unauthorized device is connected to your network.
Search
About This Site
Vitux.com aims to become a Linux compendium with lots of unique and up to date tutorials.
Latest Tutorials
The 6 Best Network Scanners for Linux
Computer networks facilitate the sharing of information and resources between several interconnected nodes (network points). It is considered the backbone of telecommunications in the field of technology.
The other crucial term in networking is computer network security. It refers to the set of rules and configurations adopted to prevent and monitor the improper use of the network, data modification (integrity) and denial of access and resources to the network.
Having understood these two terms, we can now examine network scanning. Network scanning is mainly about security on computer networks. It is a procedure used to identify nodes in a network, services offered by different devices, identify network security systems in place, operating systems, protect networks from attacks and check the overall health of the network.
In this post, we handpicked the six best network scanners for Linux systems. When choosing a network scanning tool, a network administrator must understand the scanning features of a specific utility and the functional areas it covers.
1. Nessus
At the top of our list is Nessus. It is a popular tool used by network administrators to check for problems on a network. Initially, Nessus was distributed as a freeware utility. This changed quickly over time; it is currently available as a commercial utility. However, there is still a free Nessus package that comes with limited resources and capabilities.
Nessus comes in 3 packages, each with different features. They include Nessus Home, Nessus Professional and Nessus Manager or Nessus Cloud. Nessus was designed to make the entire network and scanning process simple and straightforward.
- Support for a wide range of systems, including cloud, OT (Operating Technology) devices and traditional IT assets
- It is available with 70,000 plug-ins that offer various vulnerability scanning services on a network.
- It supports network inventory with the advanced features available, for example, automated scans, multiple network scans and asset discovery.
- Provides accurate visibility over a network
- Support for IPv4 and Ipv6 network scans.
- It supports automated scheduling of scans and analyzes.
- Generate customized reports and notifications
2. Nikto
Nikto is an open source web server scanner distributed under the General Public License (GPL). Nikto analyzes and performs rapid tests on web servers for up to 7000 potentially malicious applications and files. It also checks for outdated server versions and checks for server configuration objects, such as HTTP options, index files, etc.
- It provides HTTP proxy support.
- Nikto supports the generation of reports in several file formats, including XML, HTML, NBE or CSV.
- Supports scanning multiple servers and ports via input file, which can include Nmap output.
- Increases security by authenticating hosts with Basic and NTLM.
- Allows users to adjust scans and include/exclude various vulnerability checks.
- Nikto provides a platform for customizing reports.
3. OpenVAS
OpenVAS is a free and open source network security scanning utility distributed under the General Public License (GPL). Considered a vulnerability assessment tool, OpenVAS scans a network for connected servers, firewalls, while listening for any configuration errors in services running on those devices.
It has an exclusive feature that allows the evaluation of solutions and reveals false negatives and false positives. For any false positives, OpenVAS provides a report on why a specific vulnerability has been flagged.
The tool supports three types of scans. They include Full Scan, Web Server Scan and WordPress Scan.
A full scan tests the network and all connected devices, such as servers and web applications, for vulnerabilities. A web server scan is used to test networks for any web servers and web application vulnerabilities. The WordPress scan, as the name suggests, scans a system for vulnerabilities in WordPress and the web server.
- OpenVAS is an excellent solution management vulnerability scanning utility.
- Provision of reports for risk assessment and mitigation.
- Support for smart custom scans.
4. Angry IP scanner
Angry IP scanner is a free, open source network scanning tool used to scan IP addresses and ports. Each scan provides information about nodes on the network, such as host names, MAC addresses, NetBIOS information, frequently used IP ranges, presence of web servers, etc.
To speed up the network scanning process, Angry IP Scanner implements a multithreaded approach with each thread scanning a different range of IP addresses. You can save the results in several file formats, such as CSV, TXT and XML.
- It supports scanning of ports and fast IP addresses.
- Implements multithreaded scanning.
- Support for various file formats — CSV, TXT and XML.
5. Nmap

Nmap (Network Mapper) is a security scanner, originally written by Gordon Lyon (also known by his pseudonym Fyodor Vaskovich), used to discover hosts and services on a computer network , thus building a “map” of the network.
We have detailed content about nmap that can be consulted in this link: Scanning Networks with NMAP
6. Qualys FreeScan
Qualys Freescan is a free, open source network scanning utility that helps companies optimize their security and compliance solutions. It scans the network for URLs, IP addresses and local servers for vulnerabilities.
It performs three main checks on a network;
- Vulnerability checks: tests a network for malware attacks and SSL issues.
- OWASP: Checks web application for security issues.
- SCAP checks: (Security Content Automation Protocol) checks the computer’s settings in relation to security content, ie SCAP.
- Qualys performs detailed network vulnerability checks.
- Support for auditing web applications.
- Qualys responds to threats in real time.
- Supports up to 10 free scans.
Conclusion
Each network has its weaknesses in terms of bugs, loopholes and even incorrect settings. All of this can lead an attacker to exploit the vulnerabilities. Network monitoring is therefore a critical activity that every network administrator must perform from time to time to avoid intrusion. Network scanning tools make this task much more comfortable and straightforward.
As an administrator, you will need to make a difficult decision about which tool is best for your network. I suggest you go for a utility that provides advanced exploit detections, comprehensive port scanning and web vulnerability assessments.
In this article, we saw some of the best Linux network scanning tools and, fortunately, most of them are freeware. Go through each one and choose the most suitable for your network.
This article was originally created by Arun Kumar for FOSSLINUX and modified by Marcos Oliveira.