Справочное руководство Nmap (Man Page)
Этот документ описывает версию Nmap 4.22SOC8. Последняя документация доступна на английском языке по ссылке https://nmap.org/book/man.html .
Nmap ( « Network Mapper » ) — это утилита с открытым исходным кодом для исследования сети и проверки безопасности. Она была разработана для быстрого сканирования больших сетей, хотя прекрасно справляется и с единичными целями. Nmap использует «сырые» IP пакеты оригинальным способом, чтобы определить какие хосты доступны в сети, какие службы (название приложения и версию) они предлагают, какие операционные системы (и версии ОС) они используют, какие типы пакетных фильтров/брандмауэров используются и еще множество других характеристик. В то время, как Nmap обычно используется для проверки безопасности, многие системные администраторы находят ее полезной для обычных задач, таких как контролирование структуры сети, управление расписаниями запуска служб и учет времени работы хоста или службы.
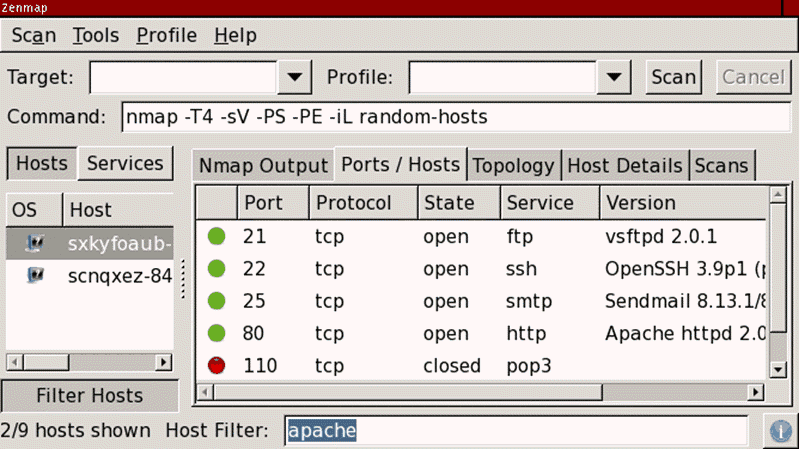
Выходные данные Nmap это список просканированных целей с дополнительной информацией по каждой из них в зависимости от заданных опций. Ключевой информацией является « таблица важных портов » . Эта таблица содержит номер порта, протокол, имя службы и состояние. Состояние может иметь значение open (открыт), filtered (фильтруется), closed (закрыт) или unfiltered (не фильтруется). Открыт означает, что приложение на целевой машине готово для установки соединения/принятия пакетов на этот порт. Фильтруется означает, что брандмауэр, сетевой фильтр, или какая-то другая помеха в сети блокирует порт, и Nmap не может установить открыт этот порт или закрыт . Закрытые порты не связаны ни с каким приложением, но могут быть открыты в любой момент. Порты расцениваются как не фильтрованные , когда они отвечают на запросы Nmap, но Nmap не может определить открыты они или закрыты. Nmap выдает комбинации открыт|фильтруется и закрыт|фильтруется , когда не может определить, какое из этих двух состояний описывает порт. Эта таблица также может предоставлять детали о версии программного обеспечения, если это было запрошено. Когда осуществляется сканирование по IP протоколу ( -sO ), Nmap предоставляет информацию о поддерживаемых протоколах, а не об открытых портах.
В дополнение к таблице важных портов Nmap может предоставлять дальнейшую информацию о целях: преобразованные DNS имена, предположение об используемой операционной системе, типы устройств и MAC адреса.
Типичное сканирование с использованием Nmap показано в Пример 1. Единственные аргументы, использованные в этом примере — это -A , для определения версии ОС, сканирования с использованием скриптов и трассировки; -T4 для более быстрого выполнения; затем два целевых хоста.
# nmap -A -T4 scanme.nmap.org playground Starting Nmap ( https://nmap.org ) Interesting ports on scanme.nmap.org (64.13.134.52): (The 1663 ports scanned but not shown below are in state: filtered) PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 3.9p1 (protocol 1.99) 53/tcp open domain 70/tcp closed gopher 80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.0.52 ((Fedora)) 113/tcp closed auth Device type: general purpose Running: Linux 2.4.X|2.5.X|2.6.X OS details: Linux 2.4.7 - 2.6.11, Linux 2.6.0 - 2.6.11 Interesting ports on playground.nmap.org (192.168.0.40): (The 1659 ports scanned but not shown below are in state: closed) PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 139/tcp open netbios-ssn 389/tcp open ldap? 445/tcp open microsoft-ds Microsoft Windows XP microsoft-ds 1002/tcp open windows-icfw? 1025/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 1720/tcp open H.323/Q.931 CompTek AquaGateKeeper 5800/tcp open vnc-http RealVNC 4.0 (Resolution 400x250; VNC port: 5900) 5900/tcp open vnc VNC (protocol 3.8) MAC Address: 00:A0:CC:63:85:4B (Lite-on Communications) Device type: general purpose Running: Microsoft Windows NT/2K/XP OS details: Microsoft Windows XP Pro RC1+ through final release Service Info: OSs: Windows, Windows XP Nmap finished: 2 IP addresses (2 hosts up) scanned in 88.392 seconds
How to Scan & Find All Open Ports with Nmap
Nmap is the world’s leading port security network scanner. The Nmap hosted security tool can help you determine how well your firewall and security configuration is working.
This guide will show you how to use Nmap to scan all open ports on Linux systems.
- Linux operating system
- Access to a user account with sudo or root privileges
- Access to a command line/terminal window
- The apt package manager, included by default (Debian / Ubuntu)
- The yum package manager, included by default (Red Hat, CentOS)
What Are Ports?
On modern operating systems, ports are numbered addresses for network traffic. Different kinds of services use different ports by default.
For example, regular web traffic uses port 80, while the POP3 email uses port 110. One of the ways that a firewall works is by allowing or restricting traffic over a particular port.
Because the port configuration can cause a security risk, it’s critical to know which ports are open and which are blocked.
If you need assistance with installing Nmap, refer to our tutorial on How to Install Nmap on Linux systems.
How to Scan Nmap Ports
To scan Nmap ports on a remote system, enter the following in the terminal:
Replace the IP address with the IP address of the system you’re testing. This is the basic format for Nmap, and it will return information about the ports on that system.
In addition to scanning by IP address, you can also use the following commands to specify a target:
To scan a range of IP addresses (.1 – .10):
To run Nmap on a subnet:
To scan targets from a text file:
Note: The developers at nmap.org provide a test server that you can experiment on, located at scanme.nmap.org. You can use this to test your Nmap utility.
Scan a Single Port, All Ports, or Series
Nmap commands can be used to scan a single port or a series of ports:
Scan port 80 on the target system:
Scan ports 1 through 200 on the target system:
Scan (Fast) the most common ports:
To scan all ports (1 – 65535):
Other Types of Nmap Port Scans
Different types of scans can be performed:
To scan using TCP connect (it takes longer, but is more likely to connect):
To perform the default SYN scan (it tests by performing only half of the TCP handshake):
To instruct Nmap to scan UDP ports instead of TCP ports (the –p switch specifies ports 80, 130, and 255 in this example):
nmap –sU –p 80,130,255 192.168.0.1Run a fast scan on the target system, but bypass host discovery. (Host discovery uses ping, but many server firewalls do not respond to ping requests. This option forces the test without waiting for a reply that may not be coming):
The nmap utility can be used to detect the operating system of a particular target:
It can also be used to probe for the services that might be using different ports:
Note: The –sV option can be tuned to be more or less aggressive in its scan. Use the ––version-intensity 2 option to specify the level of testing. Replace the number 2 with a number from 0 (light testing) to 9 (run all probes). The more intense the testing, the longer the scan will take.
Common Ports
Here is a brief list of standard ports and their designations:
- 21 – FTP
- 22 – SSH
- 25 – SMTP (sending email)
- 53 – DNS (domain name service)
- 80 – HTTP (web server)
- 110 – POP3 (email inbox)
- 123 – NTP (Network Time Protocol)
- 143 – IMAP (email inbox)
- 443 – HTTPS (secure web server)
- 465 – SMTPS (send secure email)
- 631 – CUPS (print server)
- 993 – IMAPS (secure email inbox)
- 995 – POP3 (secure email inbox)
A Linux firewall can be configured to block all traffic on a particular port.
For example, a firewall can be set to block Port 80, but users won’t be able to load any website in that case. You can use firewall rules to allow some ports, but block others. Use a firewall in conjunction with other network security tools and software to scan traffic on a particular port, and to watch for suspicious traffic.
Nmap Scanning Best Practices
You should only use Nmap port scanning on servers that you own, or that you have permission to scan. Often, port-scanning is seen as an aggressive method, or a prelude to a cyber attack. It is also considered a bad practice to tie up a server’s resources by using Nmap to run repeated scans on the same target.
It is possible that during your scan, you may find unusual activity. For example, you may see a service running on an unusual port number. This means there is something strange going on, and should be investigated.
The OS and Service scanning options are helpful for scanning a particular port or service to get more information. If a service is running on a non-default port, it might be by design – or it might suggest there is a security breach.
Ports often have a default usage. Most ports under 1000 are dedicated and assigned to a specific service.
This guide provided an overview of Nmap scanning and how you can use it for testing ports in Linux. You should now understand how ports work, and why it is important to know how they are used.
Nmap adds a versatile tool to any system administrator’s arsenal for debugging and locating security flaws.