- Linux sed замена символов
- Основные команды Sed
- Удалить что-то из файла
- Сделать замену
- Экранирование символов в sed
- Два условия одновременно в Sed
- Получить диапазон строк
- Заменить всё между определёнными символами
- Создать функцию
- Отбросить всё, что левее определённого слова
- Отбросить всё, что правее определённого слова
- Удаление переходов на новую строку
- Удалить всё после определённой строки
- How to Use Sed to Find and Replace a String in a File
- sed Find and Replace Syntax
- sed Replace Examples
- Replace First Matched String
- Global Replace
- Match and Replace All Cases
- Ignore Substrings
- Find and Replace Strings With Slashes
- Find and Replace with Regular Expressions
- Reference Found String
- Create a Backup
- Recursive Find and Replace
Linux sed замена символов
Вам могут пригодится также статьи AWK и GREP
Примеры я показываю в Bash под Windows 10 или в Bash в Linux .
Основные команды Sed
Для того чтобы применить SED достаточно ввести в командную строку
echo ice | sed s / ice / fire /
Обратите внимание на то, что использовать / не обязательно.
Вы можете после s поставить какой-то другой символ, например : или , или |
Результат будет тем же, главное, чтобы все три разделителя были одинаковыми и сам символ был без дополнительных смыслов.
echo mice | sed s / m / r /
echo mice | sed s , m , r ,
echo mice | sed s : m : r :
Если вы выбрали |, то команду нужно взять в кавычки — у | есть особая роль в bash — pipeline
Если вы редактируете пути до файлов (а они содержат /) то это как раз тот случай, когда удобно выбрать другой разделитель
Например, нужно заменить /bin/bash на /bin/sh
Намного удобнее использовать @ как разделитель чем экранировать каждый слеш.
Сравните две идентичные команды
sed ‘s @ /bin/bash @ /bin/sh @ ‘ /etc/passwd
sed ‘s / \ /bin \ /bash / \ /bin \ /sh / ‘ /etc/passwd
Удалить что-то из файла
За удаление отвечает опция d про неё вы можете прочитать отдельную статью sed d
Также можно удалять заменой на пустое место
И удалять с помощью других опций, например, q
Сделать замену
За замену отвечает опция s про неё вы можете прочитать отдельную статью sed s — substitute
Экранирование символов в sed
Специальные символы экранируются с помощью \
Что включать в специальные символы зависит от того, какой sed вы используете, но $.*[\^ а также пробелы и кавычки советую экранировать всегда.
Пробел также можно заменять на \s
. в регулярных выражениях обозначает один любой символ кроме начала новой строки \n поэтому, если вы хотите написать url используйте \
Пример экранирования точек и кавычек для смены локали в CentOS можете изучить здесь
Предположим, что есть файл input.txt следующего содержания
Here is a String / it has a Name Here is an Integer / it has a Name Here is a Float it / has a Name
Мы хотим отбросить всё, что находится левее /a, включая /a, и записать в файл.
В результате получим ошибку
-e expression #1, char 15: unknown option to `s’
Чтобы команда заработала нужно добавить \ перед /
Here is a String Here is an Integer Here is a Float
Экранирование пробелов может пригодиться при замене одной фразы на другую
Чтобы в скрипте sites.sh из директории /opt/andrei/scripts/ заменить фразу Bike website topbicycle.ru на Travel website heihei.ru нужно выполнить
sed -i s/Bike \ website \ topbicycle.ru/Travel \ website \ heihei.ru/ /opt/andrei/scripts/sites.sh
Два условия одновременно в Sed
Предположим, что у нас есть файл input.txt следующего содержания
Here is a String /b it has a Name Here is an Integer /b it has a Name Here is a Float /b it has a Name
Мы хотим отбросить всё, что находится левее /b, включая /b, и всё, что правее has.
Таким образом, в каждой строчке должно остаться только слово it.
Нужно учесть необходимость экранирования специального символа / а также мы хотим направить вывод в файл.
sed ‘s/^.*\/b// ; s/has.*//’ input.txt > output.txt
Получить диапазон строк
В случае, когда Вы работаете с большими файлами, например с логами, часто бывает нужно получить только определённые строки, например, в момент появления бага.
Копировать из UI командной строки не всегда удобно, но если Вы примерно представляете диапазон нужных строк — можно скопировать только их и записать в отдельный файл.
Например, Вам нужны строки с 9570 по 9721
sed -n ‘9570,9721p;9722q’ project-2019-10-03.log > bugFound.txt
Заменить всё между определёнными символами
Удалить всё что находится между квадратными скобками включая скобки
sed ‘s/\[.*\]//’ input.txt > output.txt
Создать функцию
Чтобы каждый раз не вспоминать команды sed можно создать функцию
Возьмём команду, которая удаляет комментарии и пустые строки из предыдущего примера и запишем как функцию clean_file.
Первым делом в коносли нужно написать в терминале function clean_file < и нажать Enter
Затем ввести выражение sed -i ‘/^#/d ; /^$/d’ $1
$1 означает, что функция будет принимать один аргумент. Это, конечно, будет название файла.
Затем нужно снова нажать Enter и в новой строке написать > и нажать Enter ещё раз
$ function clean_file < >sed -i ‘/^#/d;/^$/d’ $1 > >
Убедитесь, что файл содержит комментарии и пустые строки. Если нет — создайте для чистоты эксперимента.
clean_file websites
cat websites
Отбросить всё, что левее определённого слова
Предположим, что у нас есть файл input.txt следующего содержания
Here is a String it has a Name Here is an Integer it has a Name Here is a Float it has a Name
Мы хотим отбросить всё, что находится левее слова it, включая слово it, и записать в файл.
sed ‘s/^.*it//’ input.txt > output.txt
^ означает, что мы стартуем с начала строки Результат:
Для доступности объясню синтаксис сравнив две команды. Посмотрите внимательно, когда мы заменяем слово Here на There.
There находится между двумя слэшами. Раскрашу их для наглядности в зелёный и красный.
sed ‘s/Here/There/‘
А когда мы хотим удалить что-то, мы сначала описываем, что мы хотим удалить. Например, всё от начала строки до слова it.
Теперь в правой части условия, где раньше была величина на замену, мы ничего не пишем, т.е. заменяем на пустое место. Надеюсь, логика понятна.
sed ‘s/^.*it//‘ > output.txt
Отбросить всё, что правее определённого слова
Предположим, что у нас есть файл input.txt следующего содержания
Here is a String / it has a Name Here is an Integer / it has a Name Here is a Float / it has a Name
Мы хотим отбросить всё, что находится правее слова is, включая слово is, и записать в файл.
Удаление переходов на новую строку
Удалить всё после определённой строки
Допустим Вы хотите удалить все строки после третьей
sed 3q input.txt > output.txt
How to Use Sed to Find and Replace a String in a File
The sed (stream editor) utility is a line-oriented text parsing and transformation tool. The sed command uses a simple programming language and regular expressions to process text streams and files. The most used feature of the sed command is string substitution.
This guide shows how to use sed to find and replace strings through examples.
- Access to the command line/terminal.
- A text file (this guide provides an example.txt file).
- Basic terminal commands (grab our free cheat sheet).
sed Find and Replace Syntax
The syntax to find and replace text using the sed command is:
The command consists of the following:
- -i tells the sed command to write the results to a file instead of standard output.
- s indicates the substitute command.
- / is the most common delimiter character. The command also accepts other characters as delimiters, which is useful when the string contains forward slashes.
- is the string or regular expression search parameter.
- is the replacement text.
- g is the global replacement flag, which replaces all occurrences of a string instead of just the first.
- is the file where the search and replace happens.
The single quotes help avoid meta-character expansion in the shell.
The BDS version of sed (which includes macOS) does not support case-insensitive matching or file replacement. The command for file replacement looks like this:
Alternatively, install the GNU version of sed on macOS with homebrew:
Run the GNU sed command as follows:
Replace the sed command with gsed to follow the examples below.
sed Replace Examples
The examples from this guide use a sample file to replace strings.
1. Create a sample text file:
2. Add the following contents:
foobarbazfoobarbaz foo bar baz foo bar baz Foo Bar Baz Foo Bar Baz FOO BAR BAZ FOO BAR BAZ /foo/bar/baz /foo/bar/bazUse the file as input to test the examples below.
Note: For a full sed command tutorial for Linux, check out our sed command Linux guide.
Replace First Matched String
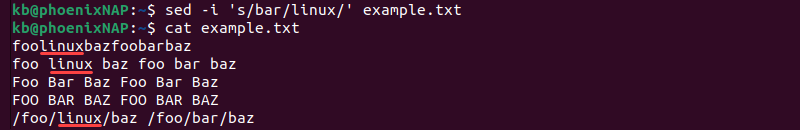
1. To replace the first found instance of the word bar with linux in every line of a file, run:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/' example.txt2. The -i tag inserts the changes to the example.txt file. Check the file contents with the cat command:
The command replaces the first instance of bar with linux in every line, including substrings. The match is exact, ignoring capitalization variations.
Global Replace
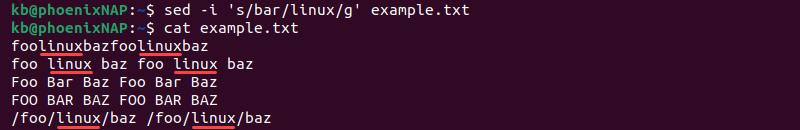
To replace every string match in a file, add the g flag to the script. For example:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/g' example.txtThe command globally replaces every instance of bar with linux in the file.
Match and Replace All Cases
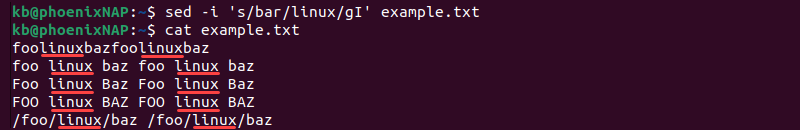
To find and replace all instances of a word and ignore capitalization, use the I parameter:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/gI' example.txtThe command replaces all instances of the word bar in the text, ignoring capitalization.
Ignore Substrings
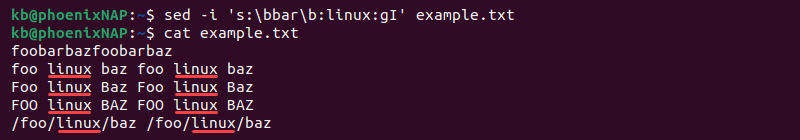
Add word boundaries ( \b ) to the sed command to ignore substrings when replacing strings in a file. For example:
sed -i 's/\bbar\b/linux/gI' example.txtAlternatively, change the delimiter to make the command easier to read:
sed -i 's:\bbar\b:linux:gI' example.txtThe command ignores substrings, matching only the whole word.
Find and Replace Strings With Slashes
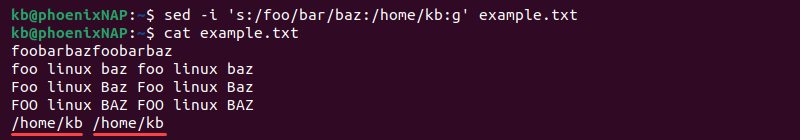
Escape the forward slash character to find and replace a string with slashes. For example, to replace /foo/bar/baz with /home/kb, use the following syntax:
sed -i 's/\/foo\/bar\/baz/\/home\/kb/g' example.txtAlternatively, change the delimiter to avoid escaping characters:
sed -i 's:/foo/bar/baz:/home/kb:g' example.txtUse this syntax to replace paths and other strings with slashes.
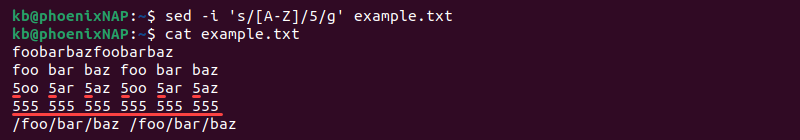
Find and Replace with Regular Expressions
The search pattern for the sed command accepts regular expressions, similar to grep regex. For example, to match all capital letters and replace them with 5, use:
The regex pattern helps find all capital letters and replaces them with the number in the file.
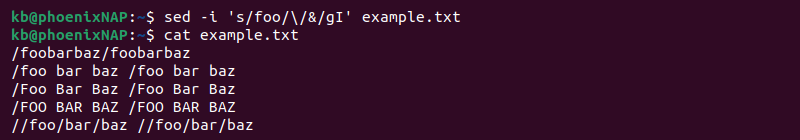
Reference Found String
Use the ampersand character ( & ) to reference the found string. For example, to add a forward slash (/) before every instance of foo in a file, use:
Instead of retyping the search parameter, the & sign references the found string.
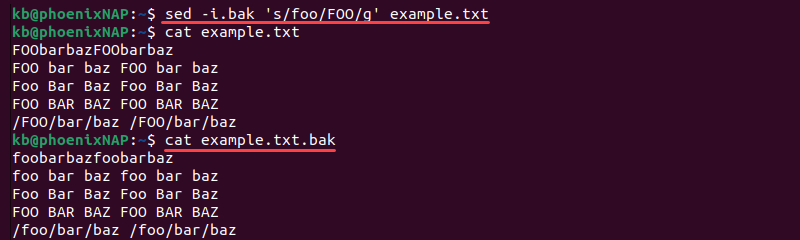
Create a Backup
To create a backup file before overwriting the existing one, add the .bak parameter to the -i tag.
sed -i.bak 's/foo/FOO/g' example.txtThe command creates a backup ( example.txt.bak ) before overwriting the original. Use this method to keep a copy in the original format and avoid overwriting.
Recursive Find and Replace
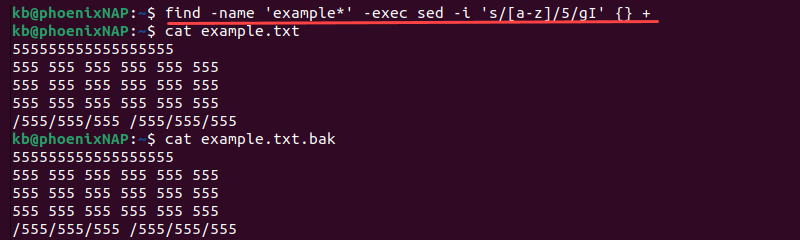
Use the find command to search for files and combine it with sed to replace strings in files recursively. For example:
find -name 'example*' -exec sed -i 's/[a-z]/5/gI' <> +The command finds all files starting with example and executes the sed command on the files. The executed command replaces all letters with 5, ignoring capitalization.
After going through the examples in this guide, you know how to use sed to replace strings in files. The sed command is a powerful text manipulation utility with many advanced features.
Next, check out the awk or gawk command to learn about other text manipulation tools.