- Linux и Android
- How to Use Sed to Find and Replace a String in a File
- sed Find and Replace Syntax
- sed Replace Examples
- Replace First Matched String
- Global Replace
- Match and Replace All Cases
- Ignore Substrings
- Find and Replace Strings With Slashes
- Find and Replace with Regular Expressions
- Reference Found String
- Create a Backup
- Recursive Find and Replace
Linux и Android
Довольно часто при работе с текстовыми файлами вам нужно находить и заменять строки текста в одном или нескольких файлах.
sed — это потоковый редактор. Он может выполнять основные операции с текстом над файлами и входными потоками, такими как конвейеры. С помощью sed вы можете искать, находить и заменять, вставлять и удалять слова и строки. Он поддерживает базовые и расширенные регулярные выражения, которые позволяют сопоставлять сложные шаблоны.
В этой статье мы поговорим о том, как находить и заменять строки с помощью sed. Мы также покажем вам, как выполнять рекурсивный поиск и замену.
Существует несколько версий sed, с некоторыми функциональными отличиями между ними. macOS использует версию BSD, а большинство дистрибутивов Linux поставляются с предварительно установленной GNU sed по умолчанию. Мы будем использовать версию GNU.
- -i — По умолчанию sed записывает свой вывод в стандартный вывод. Эта опция указывает sed редактировать файлы на месте. Если указано расширение (например, -i.bak), будет создана резервная копия исходного файла.
- s — Команда замены, вероятно, наиболее часто используемая команда в sed.
- / / / — Разделитель символов. Это может быть любой символ, но обычно используется символ косой черты (/).
- SEARCH_REGEX — Обычная строка или регулярное выражение для поиска.
- REPLACEMENT — Строка замены.
- g — Флаг глобальной замены. По умолчанию sed читает файл построчно и изменяет только первое вхождение SEARCH_REGEX в строке. Если указан флаг замены, будут заменены все вхождения.
- INPUTFILE — Имя файла, для которого вы хотите выполнить команду.
Давайте рассмотрим примеры использования команды sed для поиска и замены текста в файлах с некоторыми из его наиболее часто используемых опций и флагов.
123 Foo foo foo foo /bin/bash Ubuntu foobar 456Как вы могли заметить, в предыдущем примере подстрока foo внутри строки foobar также заменяется. Если такое поведение вас не устраивает, используйте выражение «boundery» (\b) на обоих концах строки поиска. Это гарантирует, что отдельные слова не совпадут.
Чтобы сделать сопоставление с шаблоном нечувствительным к регистру, используйте флаг I. В приведенном ниже примере мы используем флаги g и I:
Если вы хотите найти и заменить строку, содержащую символ разделителя (/), вам нужно использовать обратную косую черту (\), чтобы экранировать ее. Например, чтобы заменить /bin/bash на /usr/bin/zsh, вы бы использовали следующую команду:
Более простой и читаемый вариант — использовать другой символ-разделитель. Большинство людей используют вертикальную черту (|) или двоеточие (:), но вы можете использовать любой другой символ:
Вы также можете использовать регулярные выражения. Например, чтобы найти все трехзначные числа и заменить их строкой number:
Еще одна полезная особенность sed — вы можете использовать символ амперсанда &, который соответствует подходящему шаблону. Символ может быть использован несколько раз.
И последнее, но не менее важное: всегда полезно сделать резервную копию при редактировании файла с помощью sed. Для этого просто добавтьте расширение к опции -i. Например, чтобы отредактировать файл file.txt и сохранить исходный файл как file.txt.bak, вы должны ввести:
Иногда вам нужно рекурсивно искать в каталогах файлы, содержащие заданную строку, и заменять эту строку во всех файлах. Это можно сделать с помощью таких команд, как find или grep, для рекурсивного поиска файлов в каталоге и передачи имен файлов в sed.
Следующая команда будет рекурсивно искать файлы в текущем рабочем каталоге и передавать имена файлов в sed.
Чтобы избежать проблем с файлами, содержащими пробел в их именах, используйте опцию -print0, которая указывает find печатать имя файла, с символом null после него, и направлять вывод в sed с помощью xargs -0:
Чтобы исключить каталог, используйте опцию -not -path. Например, если вы заменяете строку в локальном репозитории git, чтобы исключить все файлы, начинающиеся с точки (.), выполните:
Другой вариант — использовать команду grep для рекурсивного поиска всех файлов, содержащих заданный шаблон, а затем передать имена файлов в sed:
Хотя сначала это может показаться сложным, поиск и замена текста в файлах с помощью sed очень просты. Чтобы узнать больше о командах, опциях и флагах sed, почитайте руководство GNU sed и учебник Grymoire sed.
How to Use Sed to Find and Replace a String in a File
The sed (stream editor) utility is a line-oriented text parsing and transformation tool. The sed command uses a simple programming language and regular expressions to process text streams and files. The most used feature of the sed command is string substitution.
This guide shows how to use sed to find and replace strings through examples.
- Access to the command line/terminal.
- A text file (this guide provides an example.txt file).
- Basic terminal commands (grab our free cheat sheet).
sed Find and Replace Syntax
The syntax to find and replace text using the sed command is:
The command consists of the following:
- -i tells the sed command to write the results to a file instead of standard output.
- s indicates the substitute command.
- / is the most common delimiter character. The command also accepts other characters as delimiters, which is useful when the string contains forward slashes.
- is the string or regular expression search parameter.
- is the replacement text.
- g is the global replacement flag, which replaces all occurrences of a string instead of just the first.
- is the file where the search and replace happens.
The single quotes help avoid meta-character expansion in the shell.
The BDS version of sed (which includes macOS) does not support case-insensitive matching or file replacement. The command for file replacement looks like this:
Alternatively, install the GNU version of sed on macOS with homebrew:
Run the GNU sed command as follows:
Replace the sed command with gsed to follow the examples below.
sed Replace Examples
The examples from this guide use a sample file to replace strings.
1. Create a sample text file:
2. Add the following contents:
foobarbazfoobarbaz foo bar baz foo bar baz Foo Bar Baz Foo Bar Baz FOO BAR BAZ FOO BAR BAZ /foo/bar/baz /foo/bar/bazUse the file as input to test the examples below.
Note: For a full sed command tutorial for Linux, check out our sed command Linux guide.
Replace First Matched String
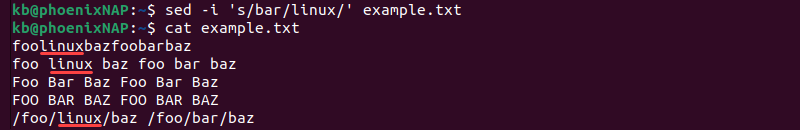
1. To replace the first found instance of the word bar with linux in every line of a file, run:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/' example.txt2. The -i tag inserts the changes to the example.txt file. Check the file contents with the cat command:
The command replaces the first instance of bar with linux in every line, including substrings. The match is exact, ignoring capitalization variations.
Global Replace
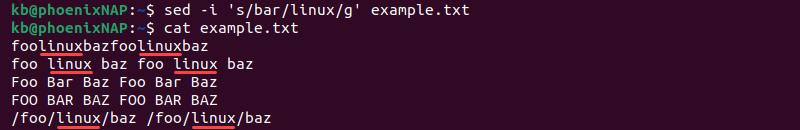
To replace every string match in a file, add the g flag to the script. For example:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/g' example.txtThe command globally replaces every instance of bar with linux in the file.
Match and Replace All Cases
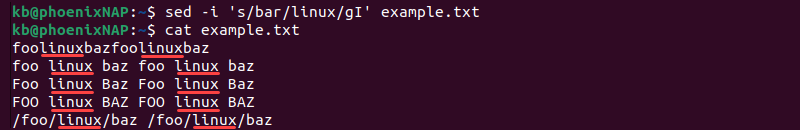
To find and replace all instances of a word and ignore capitalization, use the I parameter:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/gI' example.txtThe command replaces all instances of the word bar in the text, ignoring capitalization.
Ignore Substrings
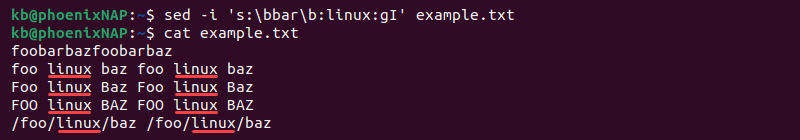
Add word boundaries ( \b ) to the sed command to ignore substrings when replacing strings in a file. For example:
sed -i 's/\bbar\b/linux/gI' example.txtAlternatively, change the delimiter to make the command easier to read:
sed -i 's:\bbar\b:linux:gI' example.txtThe command ignores substrings, matching only the whole word.
Find and Replace Strings With Slashes
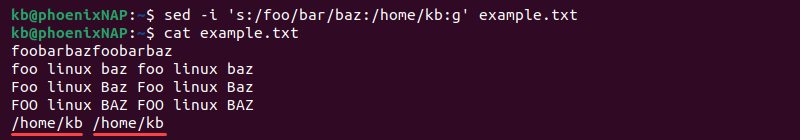
Escape the forward slash character to find and replace a string with slashes. For example, to replace /foo/bar/baz with /home/kb, use the following syntax:
sed -i 's/\/foo\/bar\/baz/\/home\/kb/g' example.txtAlternatively, change the delimiter to avoid escaping characters:
sed -i 's:/foo/bar/baz:/home/kb:g' example.txtUse this syntax to replace paths and other strings with slashes.
Find and Replace with Regular Expressions
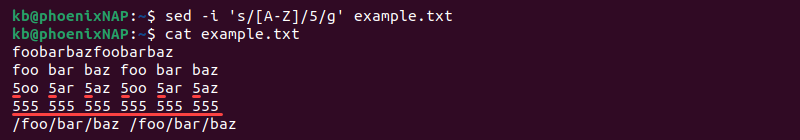
The search pattern for the sed command accepts regular expressions, similar to grep regex. For example, to match all capital letters and replace them with 5, use:
The regex pattern helps find all capital letters and replaces them with the number in the file.
Reference Found String
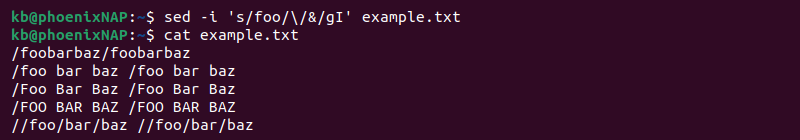
Use the ampersand character ( & ) to reference the found string. For example, to add a forward slash (/) before every instance of foo in a file, use:
Instead of retyping the search parameter, the & sign references the found string.
Create a Backup
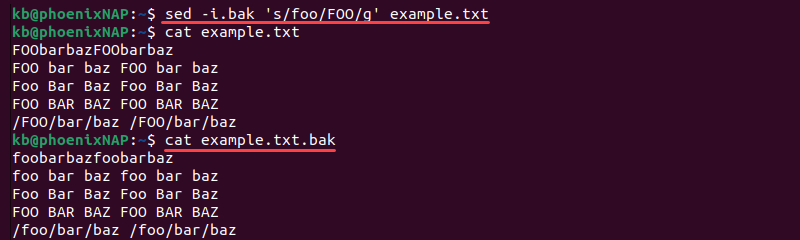
To create a backup file before overwriting the existing one, add the .bak parameter to the -i tag.
sed -i.bak 's/foo/FOO/g' example.txtThe command creates a backup ( example.txt.bak ) before overwriting the original. Use this method to keep a copy in the original format and avoid overwriting.
Recursive Find and Replace
Use the find command to search for files and combine it with sed to replace strings in files recursively. For example:
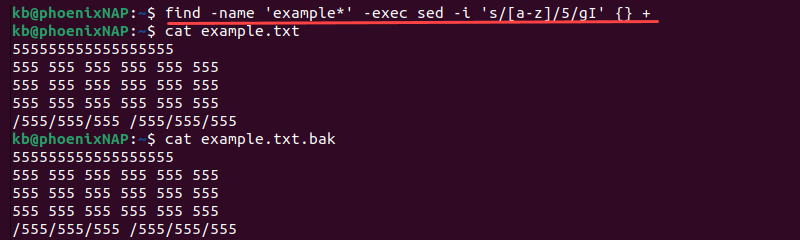
find -name 'example*' -exec sed -i 's/[a-z]/5/gI' <> +The command finds all files starting with example and executes the sed command on the files. The executed command replaces all letters with 5, ignoring capitalization.
After going through the examples in this guide, you know how to use sed to replace strings in files. The sed command is a powerful text manipulation utility with many advanced features.
Next, check out the awk or gawk command to learn about other text manipulation tools.