- How can I display all users and groups with a command?
- 2 Answers 2
- You must log in to answer this question.
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- How do I List All Groups in Linux
- Types of Groups in Linux
- Listing Users on Linux
- Listing Users Using the /etc/passwd File
- Listing Usernames Using awk
- Listing Usernames Using getent
- Listing the Connected Users on Your Linux Host
- Listing Groups Using /etc/group File
- Listing Groups Using getent
- Listing Groups for the Current User
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Simran Kaur
- 7 methods to list user groups in Linux? [SOLVED]
- Method-1: Using groups command
- Method-2: Using id command
- Method-3: Using getent command
- Method-4: Using /etc/group file
- Method-5: Using compgen command
- Method-6: Using lid command
- Method-7: Using dscl command (On MacOS)
- Bonus Tip
- What is NEXT?
- Summary
- References
How can I display all users and groups with a command?
users and groups commands display users currently logged in, and groups a user belongs to respectively.
How to display a list of all users and all groups by command-line?
2 Answers 2
You can display with the help of compgen builtin command as follows:
- To display all users run following command:
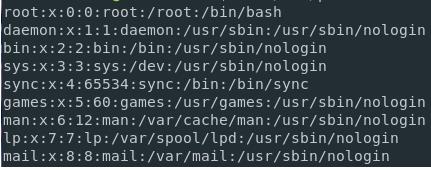
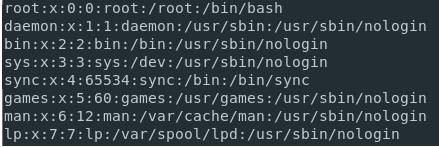
However you can also display all users by cut -d «:» -f 1 /etc/passwd .
Nice! it might be preferable to use getent passwd / getent group instead of cat’ing the local files ( getent should work for non-local accounts as well)
Well, on my ubuntu, I have some files created by docker mount with 999:999 as user:group , but unfortunately none of the above commands prints them.
Here we are going to use getent for the detailed the info
We can list the user with the following command:
We can list the group as follows:
To fetch detail a specific user
Replace the lalit with your user name. Lalit will not be in every system 🙂
You can read the more into about getent here
You must log in to answer this question.
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.13.43531
Ubuntu and the circle of friends logo are trade marks of Canonical Limited and are used under licence.
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
How do I List All Groups in Linux
Linux systems may have several users that are divided into many groups. These groups are the collection of users with the same set of privileges like reading, writing, or executing permission for a particular file or resources shared among the users of that group. Linux allows you to add a new user or the existing user to the existing group for utilizing the privileges of that particular group that it will grant. We will learn about the various Linux groups and how to list all the members of the group.
Types of Groups in Linux
Linux has two types of groups that contain several users:
- Primary or Login Group: it is the group associated with the files created by a specific user. The name for that primary group has the same name as the user’s name that will create that specific file. Each user must belong to exactly a single group.
- Secondary or Supplementary Group: you can use this type of group to grant privileges to a set of users that belong to that group. A user can be assigned to no or more secondary groups.
Listing Users on Linux
For listing all the users present on the Linux system, you can run the cat command on the ‘/etc/passwd” file. This command will help in returning the number of users that are present on the Linux system.
Also, use the “less” or “more” command for navigating within the user’s list.
Listing Users Using the /etc/passwd File
For listing the usernames on the Linux system, you can use the “cat” command and then pipe the output to the “cut” command to isolate the usernames available in the first column in the list. Run the below-mentioned command as shown below.
Listing Usernames Using awk
For listing the usernames on the Linux system, use the “cat” command and then pipe the output to the “awk” command that works similar to the “cat” command.
Here we are using the “awk” interpreter, as shown below.
Listing Usernames Using getent
Use the getent command along with the “passwd” argument for listing the usernames available on Linux. Also, you can mention the optional user that you want to be displayed on the screen.
The getent command retrieves the entries from the Name Service Switch databases. It is a Unix utility for retrieving entries from various data sources. Check the list of the data sources available from the nsswitch.conf, which is stored at /etc.
If you want to list all the users with the help of the getent function, you can run the following command.
Listing the Connected Users on Your Linux Host
To get the list of the users connected to the Linux system, you can use the following command.
Using this command, you will provide the connected users’ list and the shell they are using.
Also, you can use the “users” command to get the same result as the “who” command, as shown below.
Listing Groups Using /etc/group File
Use the most commonly used “cat” command to get the list of the groups available in the “/etc/group” file. When you run the command, you will get the list of the groups.
But if you are looking for the group names that are present in the “/etc/group” file, use the cat command and then pipe the output to the “cut” command as shown below.
Also, if you want to isolate one group to check what users belong to that group, use the below command.
Listing Groups Using getent
You can use the “getent” command for listing the users on the Linux system.
If you do not provide the key, you will get the entire group file.
Listing Groups for the Current User
Using the “group” command will display a list of groups a specific user is in.
If you do not provide any argument, you will get the list of the groups for the user that runs the command.
Conclusion
The Linux system contains users and groups in different files. Sometimes it becomes important to get the user details and to which group they belong. Thus Linux offers some commands that will help you to achieve that. You can run some commands to get the user details and the group to which they belong. You can also get the complete list of users on the Linux system, active users, and groups names.
You can go through this article to get various commands for getting the list of all the groups in Linux and understand how they work.
About the author
Simran Kaur
Simran works as a technical writer. The graduate in MS Computer Science from the well known CS hub, aka Silicon Valley, is also an editor of the website. She enjoys writing about any tech topic, including programming, algorithms, cloud, data science, and AI. Travelling, sketching, and gardening are the hobbies that interest her.
7 methods to list user groups in Linux? [SOLVED]
In operating systems, applications add their own users and groups to the system. From an administrative point of view, this makes it easier for users. Adding users to the application group is the easiest way to edit privileges. As a matter of fact, systems such as LDAP and Active Directory are also built on this method.
There are many methods of listing groups in Linux. In some methods, group information is accessed from the user, while in some methods, users are accessed from group information. We will tell you some of the most used methods with examples.
Method-1: Using groups command
When you run the groups command without any parameters, it lists the group information of the user who opened the terminal:
foc@fedora:~$ groups foc wheel If you type a username after the group command, the groups belonging to that user are listed:
foc@fedora:~$ groups golinux golinux : golinux In this method, groups are listed with user information.
Method-2: Using id command
Like the group command, the id command, when executed without parameters, lists the active user’s groups. But this time group id are also displayed:
foc@fedora:~$ id uid=1000(foc) gid=1000(foc) groups=1000(foc),10(wheel) By typing the username after the id command, the groups belonging to that user are listed with their ids:
foc@fedora:~$ id golinux uid=1001(golinux) gid=1001(golinux) groups=1001(golinux) As the user’s group information increases, the information displayed on the screen may not be understood. With the parameters of the ID command, the output can be made more understandable. For example, to list all group ids and names:
foc@fedora:~$ id -Gn golinux golinux You can get help from the —help page for all its parameters:
foc@fedora:~$ id --help Usage: id [OPTION]. [USER]. Print user and group information for each specified USER, or (when USER omitted) for the current user. -a ignore, for compatibility with other versions -Z, --context print only the security context of the process -g, --group print only the effective group ID -G, --groups print all group IDs -n, --name print a name instead of a number, for -ugG -r, --real print the real ID instead of the effective ID, with -ugG -u, --user print only the effective user ID
Again in this method, groups are listed with their user information.
Method-3: Using getent command
The getent command pulls information from the group database. If there is no central system such as LDAP, Active Directory, it will pull from the local database.
You can pull groups by typing group after getent command:
foc@fedora:~$ getent group root:x:0: bin:x:1: . disk:x:6: lp:x:7: mem:x:8: kmem:x:9: wheel:x:10:foc cdrom:x:11: mail:x:12:
To list users in a group, you must type the group name:
foc@fedora:~$ getent group wheel wheel:x:10:foc To list all groups in the system without details:
foc@fedora:~$ getent group | cut -d: -f1 root bin disk lp mem kmem wheel cdrom mail This method lists both groups and users in that group.
Method-4: Using /etc/group file
On Linux the group information is in the /etc/group file. If a user is added or removed from the group, this file changes.
When you view this file with file view commands like cat , it gives a complex output. To list group information, you can write it like this:
foc@fedora:~$ cut -d: -f1 /etc/group root bin . lp mem kmem wheel . tape video ftp For the total number of groups:
foc@fedora:~$ cat /etc/group | grep -c "" 82 Using awk command we can extract the group names from the /etc/group file using the colon ( : ) delimiter.
Method-5: Using compgen command
Another command you can use to list groups in Linux is compgen . You can list the groups in the system with the -g parameter:
[foc@rocky9 ~]$ compgen -g root bin wheel ftp lock audio users nobody foc Method-6: Using lid command
This command displays information about the specified group, including the GID, group password (if any), and members.
# lid -g nagios nagios(uid=1001) apache(uid=48) snmptt(uid=974) Method-7: Using dscl command (On MacOS)
Using the dscl command on macOS. This command displays information about the specified group on macOS.
dscl . -read /Groups/groupnameBonus Tip
If you want to list the groups of users logged into the system, you can use the following for loop:
[foc@rocky9 ~]$ for user in $(cat /etc/passwd | grep bash | awk -F: '');do groups $user; done root : root foc : foc wheel Note: Bash was chosen as the default shell. If a different shell(zsh,sh etc) is used, it can be written after the grep command.
What is NEXT?
Summary
There is always an alternative on Linux. We have explained different ways to list groups in Linux for you. The commands and methods used may vary according to habits. You can use whichever method is faster and easier for you. Of course the choice is yours.
You can get help with the -h/—help parameter for each command. For more detailed information, you can also access the man page of the commands as in the example:
foc@fedora:~$ man id NAME id - print real and effective user and group IDs SYNOPSIS id [OPTION]. [USER]. .
References
Didn’t find what you were looking for? Perform a quick search across GoLinuxCloud
If my articles on GoLinuxCloud has helped you, kindly consider buying me a coffee as a token of appreciation.

For any other feedbacks or questions you can either use the comments section or contact me form.
Thank You for your support!!