- How to send broadcast message to console in Linux from C program
- 4 Answers 4
- How to Send a Message to Logged Users in Linux Terminal
- How to Send Broadcast Message to Logged-in Users on Linux Terminals
- Send Messages to Logged-in Users Using the Wall Command
- Send Messages to a Specific Logged-in User
- Отправить сообщение другому пользователю на сервере в Unix/Linux
- Отправить сообщение другому пользователю на сервере в Unix/Linux
- -=== СПОСОБ 1 — Используем echo команду ==-
- -=== СПОСОБ 2 — Используем write команду ==-
- -=== СПОСОБ 3 — Используем wall команду ==-
How to send broadcast message to console in Linux from C program
I have written a deamon in C working on Linux, and now I need to be able to send short messages to Linux console like the commad «wall» does, or how init does when it reboots the system. How to do that from inside my program ? best regards Marek
Yes, one of option I heard of just now, would like to avoid this because of 4 different syslog daemons like syslog-ng, rsyslog.
Leave the configuration of syslog daemons to sysadmins. But document exactly how your software is using syslog(3) ; also, some systems don’t have consoles watched by humans.
4 Answers 4
The current console linux device is /dev/console , but you need to be root to write to this file. See the man page for console for more info, but here is an extract:
Common ways to start a process on a console are:
- (a) tell init(8) (in inittab(5)) to start a mingetty(8) (or agetty(8)) on the console;
- (b) ask openvt(1) to start a process on the console;
- (c) start X — it will find the first unused console, and display its output there.(There is also the ancient doshell(8).)
To send messages to multiple terminals/consoles use the ttymsg() on various tty nodes.
For a good example on how to use this is your C program, checkout the source of the walk command. We can see precisely how it prepares a message buffer and sends it as a broadcast to various terminals of all the currently logged-in users.
How to Send a Message to Logged Users in Linux Terminal
How can I send a messages to logged on users in a Linux server? If you are asking this question, then this guide will help you learn how to do that. We will demonstrate how to send a message to all or a specific logged on user, on the terminal in Linux.
Linux offers a variety of means for sending messages to users logged on to a server as explained in the two methods below.
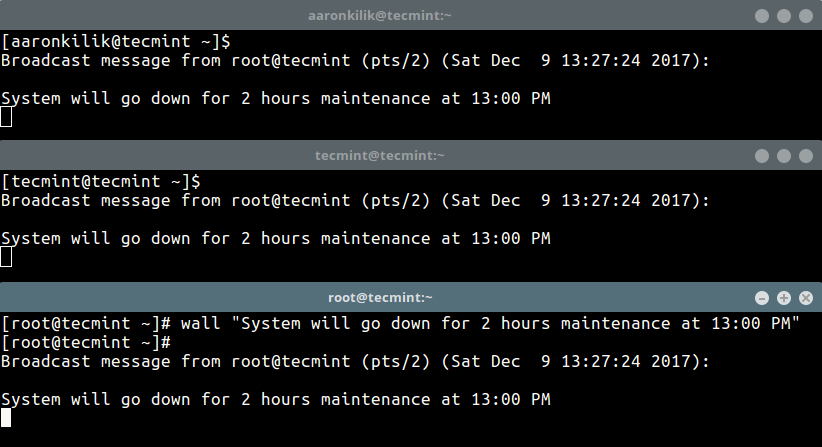
In the first method, we will use wall command – write a message to all currently logged in users on the terminal as shown.
# wall "System will go down for 2 hours maintenance at 13:00 PM"
To disable the normal banner printed by wall, for example:
Broadcast message from [email protected] (pts/2) (Sat Dec 9 13:27:24 2017):
Add the -n (Suppress the banner) flag, this however, can only be used by the root user.
# wall -n "System will go down for 2 hours maintenance at 13:00 PM"
In the second method, we will use write command, which comes pre-installed on all if not most Linux distributions. It allows you to send a message to another user in the terminal using tty.
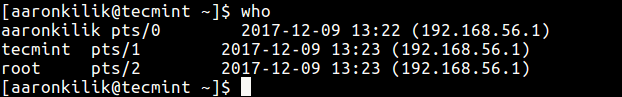
First check the all logged on users with the who command as shown.
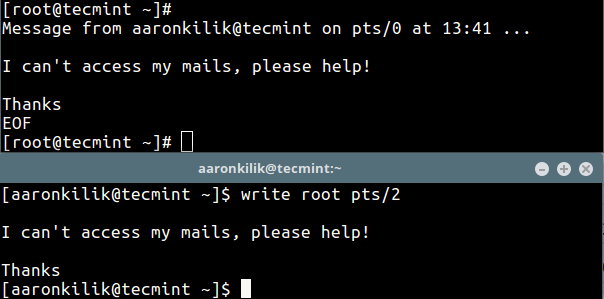
There are currently two users are active on the system (tecmint and root), now the user aaronkilik is sending a message to the root user.
$ write root pts/2 #press Ctrl+D after typing the message.
That’s all! Do share with us other methods or commands for sending messages to all logged on users through the terminal in Linux. If you have any queries, please use the feedback form below.
How to Send Broadcast Message to Logged-in Users on Linux Terminals
Linux is a multi-user operating system that allows multiple users to log in and use the system. This implies that at any given time, you might have several users logged in.
Sometimes, you might need to send a message or notification to all the users without necessarily placing a phone call or sending them emails. This is mostly when you want to announce a maintenance task or instruct them to log out.
In this guide, we will demonstrate how you can send messages to all logged-in users in the system. This only applies to users who are logged in via a terminal window using an SSH client such as PuTTY.
Send Messages to Logged-in Users Using the Wall Command
The wall command is a command-line utility that displays messages to all logged-in users on the terminal.
The wall command takes the following basic syntax:
If no file is specified, then the wall command reads the message from standard input and broadcasts it to all logged-in users.
For example, the following command reads the message enclosed in quotation marks as the argument and sends it to all logged-in users
# wall "The system will be shutting down at 1500HRS for maintenance. Apologies for any inconvenience caused".
When viewed from a logged-in user (in this case bob), the message appears as shown on the terminal window.
To display a message from a file, invoke the wall command followed by the file name as shown.
This is how the user receives the message on the terminal.
Send Messages to a Specific Logged-in User
Alternatively, you can use the write command to send a message to a specific user. To list all the currently logged-in users, invoke the who command:
For example, to send a message to a user called winnie and notify her about a system restarting in the next 3 hours, run the following write command with the echo command.
$ echo "This system will be restarted in 3 hours" | write winnie
On the user’s terminal, the message will appear as shown.
Conclusion
We have covered various ways of sending a message or notification to logged-in users using the wall and write commands. We hope that you can now send messages to logged-in users without a problem.
Отправить сообщение другому пользователю на сервере в Unix/Linux
Отправить сообщение другому пользователю на сервере в Unix/Linux
Так бывает, что на сервере работают и другие пользователи одновременно с вами. Допустим вам, необходимо выполнить перезагрузку ОС так,чтобы другие юзеры не пострадали и успели сохранить свои данные до ребута. Сейчас я расскажу как можно это сделать несколькими способами.
Для начала, посмотрим кто находится в системе:
18:07:26 up 38 days, 6:22, 2 users, load average: 1.22, 1.24, 1.25 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT captain pts/0 159.224.217.24 17:46 1.00s 0.45s 0.00s w captain pts/1 159.224.217.24 17:58 7:05 0.11s 0.11s bash -l
Так же, можно использовать:
captain pts/0 2017-11-18 17:46 00:05 143820 (159.224.217.24) captain pts/1 2017-11-18 17:58 . 145964 (159.224.217.24)
Для примера, я залогинился на сервер дважды от одного и того же юзера.
-=== СПОСОБ 1 — Используем echo команду ==-
Можно отправить сообщение другому пользователю следующим образом:
# echo -e "\033[0;31m Can I reboot this server. OK? \033[0m" > /dev/pts/1
- echo -e «\033[0;31m Can I reboot this server… OK? \033[0m» — Команда.
- /dev/pts/1 — Это открытая сессия пользователя.
PS: Я использую в данном примере подсветку, чтобы можно было сразу ее увидеть и другому пользователю все было понятно.
-=== СПОСОБ 2 — Используем write команду ==-
Так же, можно использовать следующий пример:
Напишите сообщение и отправьте его через нажатие ‘Enter’, и оно будет отправлено в терминал юзера. Используйте Ctrl+D чтобы прервать утилиту write.
Можно написать сообщение в файл (предположим — send_to_user.txt):
И потом, чтобы отправить данное послание, используйте:
$ cat send_to_user.txt | write captain pts/1
Очень простая и полезная тулза.
-=== СПОСОБ 3 — Используем wall команду ==-
Для отправки широковещательного сообщения всем подключенным пользователям, используется команда wall (wall = write to all):
$ wall I will reboot this server at 02:00!
Но данное сообщение будет отправлено только после того, как вы нажмете — Ctrl+D
Можно написать сообщение в файл (предположим — send_to_user.txt):
И потом, чтобы отправить данное послание, используйте:
$ cat send_to_user.txt | wall
Вот и все, статья «Отправить сообщение другому пользователю в Unix/Linux» завершена.