- The Right Linux Server Backup Strategy
- Hope for the best and prepare for the worst
- The 3-2-1 Backup Rule
- Three Copies of Data
- Two Different Media Types
- Keep at least one backup copy offsite
- Our Backup Strategy
- What is an Amazon Machine Image?
- Test your backups
- Conclusion
- How To Back Up A Linux Server
- #Backing Up The Server With The Tar Method
- #Tar Command for Creating Backup
- #Tar Command for Extraction
- #Backing up the Server with Bera Backup
- #Features of Bera Backup
- #Bera Backup Properties
- #The Command for Creating Backup
- #The command for Restoring Backup
- #Conclusion
- Marius Rimkus
- Join Cherry Servers Community
The Right Linux Server Backup Strategy
If you run a website or an online business, you need to have a backup strategy to restore data in case of an emergency. Running a critical website without a backup could mean a full data loss, resulting in shutting down your company.
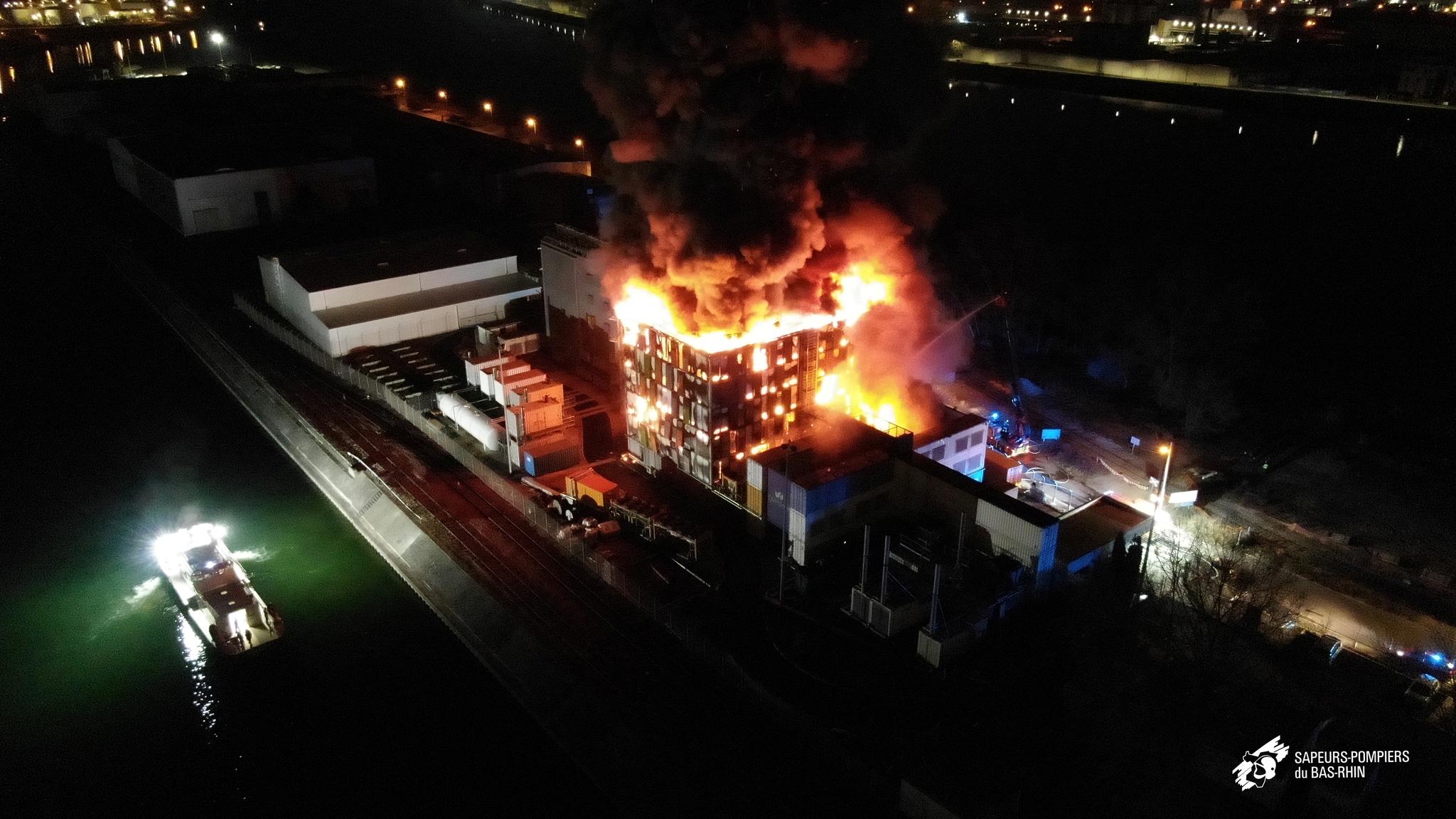
This month an OVH Data Center in Europe burned down and took million of sites and thousands of businesses down.
We at MGT-COMMERCE offer managed hosting for Magento by using Amazon Web Service for more than ten years. With the experience of managing data-critical businesses, we have developed CloudPanel and integrated Automatic Backups as Cloud Features for Amazon Web Service, Digital Ocean, and the Google Cloud.
Hope for the best and prepare for the worst
When we develop a new product, application, or service, we hope for the best, but we also think about the worst-case scenario. To prevent the worst-case scenario, you need a backup, restore, and verification strategy. One of my first mentors always said to me: «If you don’t test your backups, you don’t have backups.»
Having full backups means that you are protected from several risks, including hardware failures, human errors, cyber attacks, data corruption, or natural disasters.
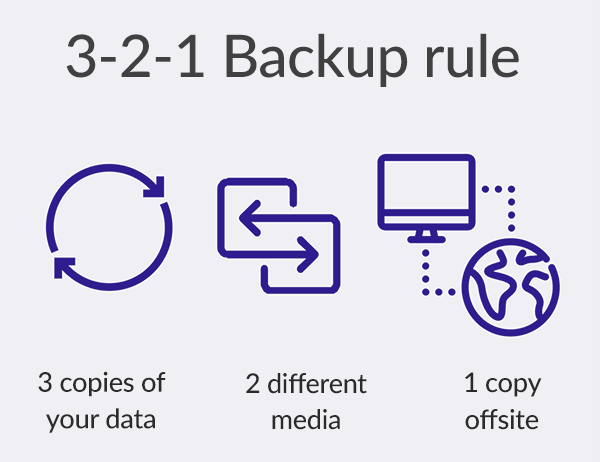
The 3-2-1 Backup Rule
The 3-2-1 Backup Rule is an easy-to-remember acronym for a common approach to keeping your data safe in almost any failure scenario. The rule is: keep at least three (3) copies of your data and store two (2) backup copies on different storage media, with one (1) of them located offsite.
- Have at least three copies of your data.
- Store the copies on two different media.
- Keep IT safe with one backup copy offsite.
Three Copies of Data
In addition to your primary data, keeping at least two additional backups is recommended. The more backup copies you have, the less chance you have to lose all of them at once. Thus, the 3-2-1 backup rule states that you need at least three copies of your data, meaning the primary data and two backups of this data.
Two Different Media Types
It should go without saying that storing several backups of your data in the same server/instance is hardly logical. Murphy’s Law or wear and tear, or the drives were bought together and have the same mean time between failures (MTBF) rates. It is quite common after a drive failure to experience failure from another drive in the same storage around the same time.
Keeping two copies of data on different storage media types, such as internal hard disk drives plus removable storage media (tape, external hard drive, USB drive, etc.) is strongly recommended.
Keep at least one backup copy offsite
As it is evident that a local disaster can damage all copies of data stored in one place, the 3-2-1 backup rule says: keep at least one copy of your data in a remote location, such as offsite storage or the cloud.
While storing one backup copy offsite strengthens your data security, having another backup copy onsite provides for faster and simpler recovery in case of failure.
Our Backup Strategy
We at MGT-COMMERCE manage small and enterprise auto-scaling customers. The average customer is using 150 GB disk space, and the MySQL database is between 5-10 GB big.
In the company’s early days, we used open-source backup software like rsnapshot for incremental data backups and a bash script for backing up the MySQL database via mysqldump every 4 hours.
This approach worked very well with small data amounts and small databases but not with projects with many data changes and big databases because the calculation of the incremental changes needs time and slows down the disk performance. Running mysqldump every couple of hours is locking and blocking the performance and can cause downtime.
For many years now, we are doing hourly backups for all of our customers by using Amazon Machine Images (AMI).
What is an Amazon Machine Image?
An Amazon Machine Image (AMI) is basically a full backup of the entire instance, including all associated disks.
- Easy to create and manage via AWS SDK
- Restore within minutes
- No deterioration in performance
- Stored in different data centers
- You pay for the data changes, not for the created AMIs
- Easy to copy to other AWS Regions
- Can take advantage of Amazon EBS encryption
- Market Leader — used by million of companies
Disadvantages:
- Cost estimation is difficult
- An instance (source) needs to be launched for restoring files, directories or databases
Today we are performing > 25.000 backups per day with a retention period of 7 days.
The retention period can be configured individually on the instance level of each customer.
Test your backups
You can have hourly backups or offsite backups, but they are worthless if they are not working when you need them.
CloudPanel is creating a dump of each database every night at 4:15 AM and stores them in the directory /home/cloudpanel/backups/$databaseName .
This dump is useful for updating dev, test, or staging environments where the database doesn’t need to be up to date.
For many customers, we have bash scripts in place (cron jobs) that update the test/stage environment every night. We rsync the differences between test/stage and import the database from the night.
A very good approach is to have a cheap test/stage server separate from your production environment, e.g., by using another cloud provider.
On a daily basis, you rsync all files and import the latest database dump from the night.
In case of an emergency, you have multiple backups in different data centers and one offsite backup available.
Conclusion
As you have learned, having a good backup and recovery strategy is a must-have if you don’t want to risk a data or business loss. Suppose you are a developer, agency, or a managed service provider. In that case, it should be one of your highest priorities because even experts with > 20 years of experience are human and make mistakes.
If you are using a managed hosting service that takes care of your application, you should ask how they perform backups and how often.
Quite often, backups are not included and need to be done by yourself.
Nevertheless, it’s highly recommended to have your offsite backup because you only know how good a company is if it already happened and you always want to be prepared for the worst case.
He has over 20 years of experience as a PHP Developer and Linux System Administration. He likes to develop solutions to make complicated things easy to use.
How To Back Up A Linux Server
With the growth of public cloud infrastructures, Linux has risen in importance as the most compatible open-sourced operating system that takes full advantage of what the cloud has to offer by stretching its capabilities.
Linux servers are known for providing high-end security, and that’s why many developers use these to keep backups of their sites. Just like conventional open-sourced Linux systems, these servers are chosen for their stability, security, and flexibility advantages.
Backups are important because they help prevent permanent loss of valuable data, making it imperative for system admins to know all their Linux server backup options. This is even more critical for people who work with enterprise-level data.
However, with security and flexibility as its attributes, backing up a Linux server is not easy. Several utilities and software can be used, and we’ll show you how to make backups using two of the easiest methods: the ‘Tar’ approach and the ‘Bera’ backup method.
#Backing Up The Server With The Tar Method
For this tutorial, we opt for an Ubuntu operating system, one of the more popular Linux-based servers used.
#Tar Command for Creating Backup
sudo tar –cvpzf backup.tar.gz –exclude=/home/server/backup.tar.gz –one-file-system This is a simple tar command that initiates backup. It will archive all the files you have on your server into a g-zipped compressed format. We’ve chosen backup.tar as the name for your backup and wrote -exclude to not ‘include’ this backup into a backup created earlier.
This command will also create a new directory for you to back up your Linux server as file permissions are preserved. This makes it easier to not only restore your server but save time configuring files and folders the way you opted initially.
After you’ve typed the code mentioned above, hit Enter .
You’ll see the system beginning to archive all the files on your server system. By backing up the root directory, it tends to recourse itself back into other previous directories.
Make sure your server is not performing maintenance procedures. Otherwise, the backup will take hours.
#Tar Command for Extraction
sudo tar –xvpzf /home/server/backup.tar.gz –C / --numeric-owner The system will start un-archiving as it overwrites all the files you backed up before and rewrite the files that were installed before if you had a functioning system.
In case of a complete system re-installation, all the files will be restored to how they were.
The -f option is for the name of the drive you used to store your backup. In this case, since it was Home-Back-Server chosen as the location and it was a root backup, try restoring it to the same folder to avoid confusions and simultaneously uncompressing the files too.
Once the extraction is finished, just reboot and your system will be restored to the way it was when you backed it up.
Note: You can also make backups and store them onto a USB drive, but it is not recommended if it is a massive backup, and the speed of the transfer will be slower as compared to a system-root/server location.
#Backing up the Server with Bera Backup
Bera Backup is a tool that can help make comprehensive Linux server backups and allows more file extensions than the normal Tar method.
This way, you can save a lot of time in case of server migration. The process is also more straightforward compared to the Tar method.
#Features of Bera Backup
You can migrate an entire server in less than ten minutes. The simplicity of the Bera backup tool makes it a much easier to understand method for backing up your server.
You can include tabs, folders, and receive periodic notifications during backups. Since Bera is based on RSync, the process is more secure than the conventional ‘Tar’ method.
#Bera Backup Properties
File Backups – For the important files and folders to include them in the backup
System Configurations – For Files like iptables, crontabs, users and all installed packages
#The Command for Creating Backup
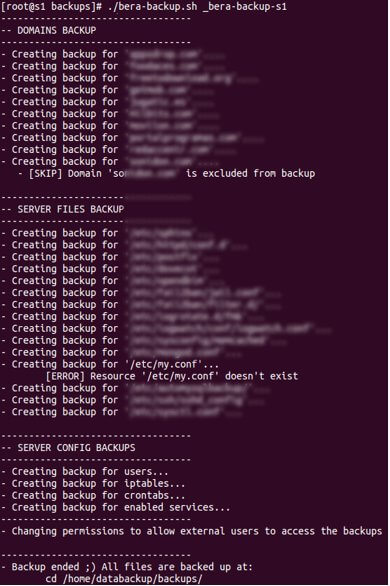
./bera-backup.sh _path_config_backup Hit Enter and Bera will start with the backup process. You’ll see the program execute the following:
Note: It is highly recommended to have root permissions enabled before starting with the backup, to remove any permission problems that may occur during and after restoring the backup of your Linux server.
#The command for Restoring Backup
Type the following command:
./bera-restore.sh _path_config_restore Don’t forget the path you chose before you made the backup; this will replace ‘_path’ to extract the backup from the location.
While defining the backup, you can take your pick from several configurable parameters for server commands for Bera Restoration Procedure, these are highlighted below:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| backupOrigin | Indicates ‘local’ if the backup is on the server itself, or ‘ssh’ for download from another location |
| backupLocalDir | Local directory where the backup is (or where it will be downloaded via SSH). |
| backupRemoteUser | User for the SSH connection to the server where the backup is |
| backupremoteserver | Remote SSH server where the backup is |
| backupRemotePort | SSH server port |
| backupRemoteDir | Remote directory where the backup is |
#Conclusion
You should have website backups just for the peace of mind that your content is safe at all times.
Backups also help ensure that your website remains available to your visitors at all times, even if something terrible has happened.
Creating backups for your Linux server might seem complicated, but you can get the job done in a variety of ways. In addition to the methods mentioned above, also try Linux server backup tools such as Rsync Commands or Bacula and NAKIVO Hyper-V Backup for users using Hyper-V virtualized environments
While making backups is not difficult, choosing the right path and the right configurations is what gets challenging. It is also important to ensure that you don’t choose a cheap hosting service for your website.
If you’d like more information about using Linux Servers to their full potential or backing them up properly, get in touch with us today. Our Linux Server specialists are here to help you 24/7.
Marius Rimkus
I’m a keen technology enthusiast with strong interest in GPU computing and DevOps culture. I believe Agile development helps companies reach utmost customer satisfaction and makes their services stand out in the market.
Join Cherry Servers Community
Get monthly practical guides about building more secure, efficient and easier to scale systems on an open cloud ecosystem.