- How to Restart Samba Server?
- Method 1: Using the “systemctl” Command
- Restart Samba Server
- Check Samba Status
- Method 2: Using the “service” Command
- Restart Samba Server
- Conclusion
- Install and Configure Samba
- What you’ll learn
- What you’ll need
- 2. Installing Samba
- 3. Setting up Samba
- What we’ve just added
- 4. Setting up User Accounts and Connecting to Share
- Connecting to Share
- If you’d like to take your configuration further…
- Restart Samba Server In 2 easy Commands
- What is samba?
- Installing Samba on Linux
- Installing Samba on Debian-based Linux
- Installing Samba on Arch-based Linux
- Start Samba Server
- Restart samba services
- Restart Samba Ubuntu
- Restart Samba Server on Raspberry pi
- Restart samba without disconnecting users
- Samba restart vs reload
How to Restart Samba Server?
On Linux, Samba Server allows the file-sharing mechanism across the different operating systems in a network. It is an open-source software tool, beneficial for accessing desktop files from a Linux system and sharing with macOS, and Windows.
It contains a configuration file in which time-by-time modifications occur. So it is recommended to restart it after editing to make the changes effective.
This post pens down possible ways to restart Samba Server on Linux with the following highlights:
Method 1: Using the “systemctl” Command
The “systemctl” command-line tool manages the “systemd” initialization system and service manager. It allows the user to interact with the services using options such as “start”, “enable”, “stop”, “disable” and view.
Restart Samba Server
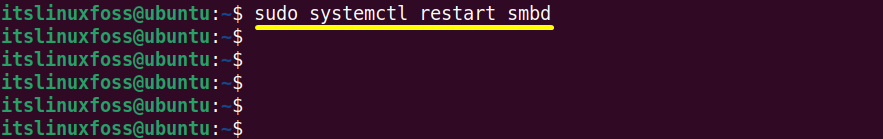
Execute the “systemctl” command followed by the “restart” options and the superuser privileges i.e “sudo” to restart the samba server:
$ sudo systemctl restart smbd
The error-free output confirms that “smbd(Samba)” server is restarted.
Check Samba Status
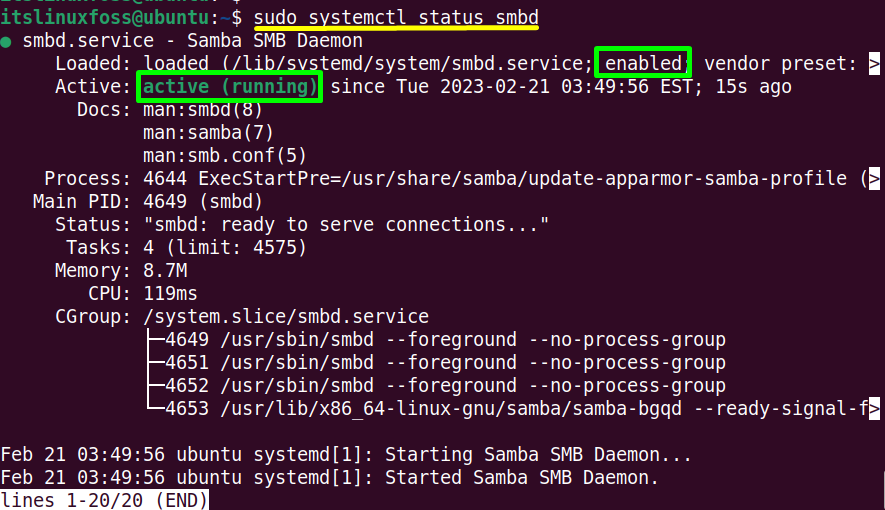
If the user wants to check the current status of the “Samba” server then use the “status” with the “systemctl” command:
$ sudo systemctl status smbd
The Samba server is now in “active (running)” state.
Method 2: Using the “service” Command
The other tool is the “service” command utility utilized to execute a SystemV init script located in the in /etc/init.d directory. It can also start, stop, restart, reload, and enable the services like the systemctl command.
Restart Samba Server
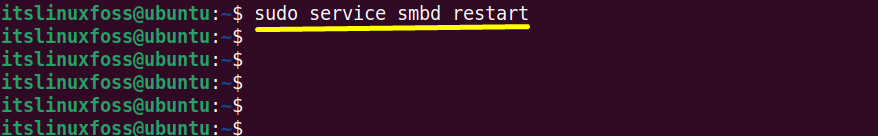
Type the “restart” flag alongside the “sudo” and “service” commands for restarting the “smbd” server in the following way:
$ sudo service smbd restart
It provides the same output as the “systemctl” command.
Conclusion
Linux offers the “systemctl” and “service” command line tools to restart the “Samba” server instantly. Both commands use the “sudo” i.e root user access if the normal user is logged in. All Linux distributions support these built-in command utilities. This post has demonstrated all possible ways to restart the Samba Server.
Install and Configure Samba
A Samba file server enables file sharing across different operating systems over a network. It lets you access your desktop files from a laptop and share files with Windows and macOS users.
This guide covers the installation and configuration of Samba on Ubuntu.
What you’ll learn
What you’ll need
If you have everything ready, let’s dive straight into the installation process on the next step!
Originally authored by Aden Padilla.
2. Installing Samba
sudo apt update sudo apt install samba We can check if the installation was successful by running:
The following should be its output:
samba: /usr/sbin/samba /usr/lib/samba /etc/samba /usr/share/samba /usr/share/man/man7/samba.7.gz /usr/share/man/man8/samba.8.gz 3. Setting up Samba
Now that Samba is installed, we need to create a directory for it to share:
The command above creates a new folder sambashare in our home directory which we will share later.
The configuration file for Samba is located at /etc/samba/smb.conf . To add the new directory as a share, we edit the file by running:
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf At the bottom of the file, add the following lines:
[sambashare] comment = Samba on Ubuntu path = /home/username/sambashare read only = no browsable = yes Then press Ctrl-O to save and Ctrl-X to exit from the nano text editor.
What we’ve just added
Now that we have our new share configured, save it and restart Samba for it to take effect:
sudo service smbd restart Update the firewall rules to allow Samba traffic:
4. Setting up User Accounts and Connecting to Share
Since Samba doesn’t use the system account password, we need to set up a Samba password for our user account:
sudo smbpasswd -a username Note
Username used must belong to a system account, else it won’t save.
Connecting to Share
On Ubuntu: Open up the default file manager and click Connect to Server then enter:
On macOS: In the Finder menu, click Go > Connect to Server then enter:
On Windows, open up File Manager and edit the file path to:
Note: ip-address is the Samba server IP address and sambashare is the name of the share.
You’ll be prompted for your credentials. Enter them to connect!
If you’d like to take your configuration further…
Restart Samba Server In 2 easy Commands
Learning to restart samba is quite essential if you run your samba server. Samba is a suite of Linux programs that could set up a full-blown server on a Linux machine. Despite being a native Linux program, it is fully interoperable and compatible with Microsft client hosts. Samba is a versatile suite of programs. It can be installed on multiple programs like Linux, Unix, FreeBSD, etc. It can interact with Windows clients remotely and send, receive, or store data on its file system using the CIFS (Common Internet File System) protocol. This article provides you with complete detail on installing, starting, or restarting the samba server.
What is samba?
According to its official website, It is a complete software package that allows the network administrator to choose the setup, configuration, and system equipment. It was initially released in the year 1992 and is still widely used. The Samba software suite is used to provide services to clients irrespective of their platform, whether Windows, OSX, Linux , or others, using the SMB/CIFS Protocols. Enthusiasts often use the samba suite of software you run their personal storage server.
Installing Samba on Linux
Samba is a free and open-source project, just like Linux itself. Anyone can download it, use it or modify it as per his needs. It can be downloaded and installed on Linux using multiple ways. It could be installed using the default package manager of your Linux distro, or you could download its source code from its official git repository and then build it locally on your computer. In this section, we show you how to install and start samba using the default package manager on Debian-based Linux distros and Arch-based Linux. After installing Samba run the “samba –version” to verify your download.
Installing Samba on Debian-based Linux
Debian-based distributions are pretty popular among users, such as Ubuntu. Mint, Kali, etc. All Debian-based Linux distributions use dpkg as their default package manager. Follow the given instructions to install and start samba on Debian Linux.
- Open the terminal emulator (CTRL + ALT + T ).
- In the bash shell, type “sudo apt update “.
- Enter your root password to continue.
- Let the repository database update.
- Now when done, type “sudo apt install samba“.
- Let the download comlplete and it would install auotmatically.
Installing Samba on Arch-based Linux
Popular Arch-based Linux distributions are Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Vanilla Arch itself, etc. The default package manager for all Arch-based Linux distributions is Pacman. Follow the given steps to install and start samba on Arch Linux.
- Open the terminal emulator (CTRL + ALT + T ).
- In the bash shell, type “sudo pacman -Syu” to sync repositories.
- Enter your root password to continue.
- Let the repository database update.
- Now when done, type “sudo pacman -S samba“.
- Let the download comlplete and it would install auotmatically.
Start Samba Server
Before you directly start or restart samba server, there are a lot of configurations and file access management stuff that need to be taken care of. We show you how to properly configure and restart the samba server without any security flaw or misconfiguration to work seamlessly with its windows or other clients. Follow the provided steps to restart samba server.
mkdir /home/_username_/sambashare/- Now add the created shared dircttory, to the samba configuration file. The following command open the samba configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf At the bottom of the configuration file, add the following information. After editing the file, press Ctrl + O to save the file and Ctrl + X to exit the nano text editor.
sudo service smbd restart- Now set-up a samba user account to connect to the samba server. The name of the account must match the system account name or it won’t work correctly, set a different password of your choise for the samba account.
sudo smbpasswd -a usernameAfter this configuration, you are ready to access the samba shared folder in your local network using the local IP of your samba installed machine. To know your local IP run the ‘ifconfig’ command in the terminal shell and look for an inet address concerning your network interface. Use this local IP from another system in your network to access the shared samba folder content.
- Access the shared folder from a different system using the windows file explorer with the local IP of your samba server and shared folder. Enter the URL in “smb://192.168.43.12/sambashare” like format. you would be prompted to enter your username and password to gain access to the shared folder.
Restart samba services
If your samba version is not working as intended or you have made some changes in the smb.conf file, but the changes do not seem to appear. In such a scenario, you need to restart samba services to get them working correctly and updated as you intended. Run the following command in the terminal shell to restart samba services.
sudo service smbd restartThis command would stop the samba services and start them over again. If you recently updated or installed your samba package, then chances are this command wouldn’t work. If the above command doesn’t work, run the following command to restart samba services.
sudo /etc/init.d/samba restartRestart Samba Ubuntu
Ubuntu is by far is one of the most popular Linux distributions. Ubuntu server is used widely in the server space to run server services like Samba or apache server. The following commands can be used to restart the samba services on your Ubuntu server.
sudo service smbd restartRestart Samba Server on Raspberry pi
Raspberry pi is a mini-computer that runs the Debian-based Raspberry OS. The following commands can be used to start, restart, stop and check the status of the Samba services on the Raspberry pi computer.
sudo service smbd status. // to check the status of service sudo service smbd start. // to start the service. sudo service smbd stop. // to stop the service completely sudo service smbd restart. // to restart samba services.Restart samba without disconnecting users
If you’ve made changes in the smb.conf file and want to make the change work without disconnecting the current user, run the following command in the terminal emulator to restart only the service configuration without disconnecting the users.
smbcontrol smbd reload-config // This command would load the config changes without alterning current users.Samba restart vs reload
The main difference between samba restart and reload is that the samba restart command stops the service entirely, disconnecting all the current connected users and then starting the service again from scratch. While the samba reload command does not stop the samba service entirely, it just reloads the configuration file again in the working memory with the newly updated configuration with minimum effect on the connected users.