- How To Set/Change Time, Date And Timezone In Linux?
- 1) How To Check Current Date, Time And Timezone Information In Linux?
- 2) How To Set/Change Date And Time In SysVinit Systems?
- 3) How To Set/Change Date And Time In systemd Systems?
- 4) How To Change The TimeZone In systemd Systems?
- 5) How To Change The TimeZone In RHEL 6/CentOS 6 Systems?
- 6) How To Automatically Adjust Your Linux System Clock?
- How To Set or Change Time Zone/Date/Time on Ubuntu
- Using timedatectl to Control the System Time and Date
- Display Current Date and Time with timedatectl
- Sync Time to NIST Atomic Clock
- How to Change the Time
- How to Change the Date
- How to Set a Timezone in Ubuntu
- How to Set Universal Time (UTC) in Ubuntu
- How to Sync Hardware Clock
- Set Hardware Clock to Sync to Local Timezone
- Set the Hardware Clock to Sync with UTC
- Set Time, Date Timezone in Ubuntu Older Versions From Command Line
How To Set/Change Time, Date And Timezone In Linux?
If you missed to set the proper timezone, date and time while installing the OS. Don’t worry it can be changed at any point of time.
If we bought the server from some providers and they might have set the timezone based on their location.
Say for example, if you buy a server from USA then they will build a system based on their GEO location.
If so, don’t worry you can simply change the timezone and date formats as per your requirement using the below commands on your Linux Box.
In this article, i have covered all the possible methods with all Major Linux Distribution such as CentOS, Redhat (RHEL), Fedora, Ubuntu, Debian, Mint & openSUSE systems.
Also, we have updated the information based on the system manager such as SysVinit and systemd. Timezone is controlled by /etc/localtime file.
The below files are belongs to timezone on Linux.
- /usr/share/zoneinfo: This directory contains timezone files.
- /etc/localtime: This file is symlink with timezone file.
- /etc/timezone: This file is holding timezone name on debian based systems.
- /etc/sysconfig/clock: This file is holding timezone name on RHEL based systems.
1) How To Check Current Date, Time And Timezone Information In Linux?
Use the following commands to check the current date, time and timezone information in Linux systems.
To check current system date and time.
# date Fri Apr 5 09:32:38 CDT 2019
To display current system date and time with UTC format.
# date -u Fri Apr 5 14:32:54 UTC 2019
Run the following command to display Hardware Clock (RTC).
# hwclock --show Fri 05 Apr 2019 14:33:13 PM UTC -1.027744 seconds
To check the timezone on SysVinit systems.
# date Fri Apr 5 09:32:38 CDT 2019 [For Details] # ls -lh /etc/localtime lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 37 Feb 19 06:08 /etc/localtime -> ../usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Chicago
We can sell all the details together in the single command for systemd systems. See the details below.
# timedatectl Local time: Fri 2019-04-05 09:37:57 CDT Universal time: Fri 2019-04-05 14:37:57 UTC RTC time: Fri 2019-04-05 14:37:56 Time zone: America/Chicago (CDT, -0500) NTP enabled: yes NTP synchronized: yes RTC in local TZ: no DST active: yes Last DST change: DST began at Sun 2019-03-10 01:59:59 CST Sun 2019-03-10 03:00:00 CDT Next DST change: DST ends (the clock jumps one hour backwards) at Sun 2019-11-03 01:59:59 CDT Sun 2019-11-03 01:00:00 CST
2) How To Set/Change Date And Time In SysVinit Systems?
Use the following commands to set or change the time and date as you wish in Linux SysVinit systems. If you requires locale’s then you can set accordingly.
Common Syntax:
To set new date and time in one shot, use the following format.
# date --set="6 Apr 2019 11:30:00" Sat Apr 6 11:30:00 CDT 2019
You can double confirm this by running date command once again.
# date Sat Apr 6 11:30:04 CDT 2019
To set only time, use the following format.
To set only date, use the following format.
# date +%Y%m%d -s "20190409" 20190409 # date Tue Apr 9 00:00:02 CDT 2019
# date +%T%p -s "01:15:00AM" 01:15:00AM
To set the hardware clock to local time.
# hwclock --set --date="2019-04-06 11:30:00" --localtime
To set the hardware clock to UTC time.
# hwclock --set --date="2019-04-06 11:30:00" --utc
3) How To Set/Change Date And Time In systemd Systems?
Use the following commands to set or change the time and date as you wish in Linux systemd systems.
Common Syntax:
# timedatectl set-time YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
To change the new date and time in one shot, use the following format.
# timedatectl set-time '2019-04-07 08:30:10'
To set only time, use the following format.
# timedatectl set-time '09:45:20'
To set only date, use the following format.
# timedatectl set-time '2019-04-10'
Use the following format to set RTC time.
# timedatectl set-local-rtc 0
4) How To Change The TimeZone In systemd Systems?
For systemd system, use the timedatectl command to change the timezone. Navigate to the following url to change the timezone in Linux.
$ sudo timedatectl set-timezone America/Chicago If you would like to restart the timedatectl service, use the following command.
# systemctl restart systemd-timedated
Run the following command to verify the new timezone.
# timedatectl Local time: Tue 2019-02-19 06:08:15 CST Universal time: Tue 2019-02-19 12:08:15 UTC RTC time: Tue 2019-02-19 12:08:15 Time zone: America/Chicago (CST, -0600) NTP enabled: no NTP synchronized: no RTC in local TZ: no DST active: no Last DST change: DST ended at Sun 2018-11-04 01:59:59 CDT Sun 2018-11-04 01:00:00 CST Next DST change: DST begins (the clock jumps one hour forward) at Sun 2019-03-10 01:59:59 CST Sun 2019-03-10 03:00:00 CDT 5) How To Change The TimeZone In RHEL 6/CentOS 6 Systems?
For RHEL/CentOS systems, use the following command to change the timezone.
# unlink /etc/localtime # ln -s /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Los_Angeles /etc/localtime Run the following command to check the new timezone in RHEL/CentOS systems.
# date Tue Feb 19 04:17:00 PST 2019 # ls -lh /etc/localtime lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 39 Feb 17 10:45 /etc/localtime -> /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Los_Angeles
6) How To Automatically Adjust Your Linux System Clock?
If you would like to sync your Linux system clock to remote NTP server then you have configure it.
To do so, navigate the following urls because we had written an detailed articles about these in the past.
How To Set or Change Time Zone/Date/Time on Ubuntu
Modern operating systems detect and synchronize time using NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) time servers. NIST operates an atomic clock that neither gains nor loses a second in 300 million years.
However, you may find that your system needs to be synchronized with NIST time servers properly.
This guide shows you how to check and change Ubuntu’s time, date, and timezone.
- Some operations may require sudo or root privileges
- The command line/terminal window (Ctrl-Alt-T)
Using timedatectl to Control the System Time and Date
Most modern Linux distributions such as Fedora, Debian, Ubuntu, Arch, CentOS v.7.x+, and other Unix-based systems provide the timedatectl utility. This command allows you to control and edit time and date settings using the command line.
Display Current Date and Time with timedatectl
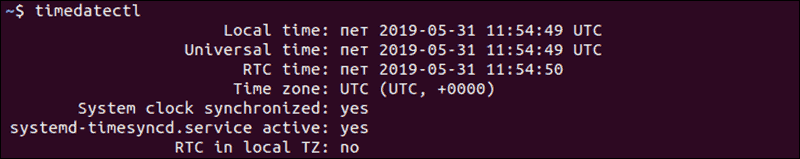
To display the current time and date information, use the command:
The output provides local time, universal time, and the timezone and informs you if the synchronization process is enabled.
Sync Time to NIST Atomic Clock
Set the Ubuntu system to synchronize to the NIST atomic clock with the following command:
To adjust the time and date manually, turn off NTP synchronizing with:
Note: NTP stands for Network Time Protocol.
How to Change the Time
To set the time to your specifications, use the following command:
timedatectl set-time 21:45:53The time format is HH:MM:SS (Hours, Minutes, Seconds). Ensure the automatic time synchronization is off to enable changes.
How to Change the Date
Use the same command to define the date on the system:
timedatectl set-time 2019-04-10The date format is YYYY-MM-DD (Year, Month, and Day).
How to Set a Timezone in Ubuntu
The timedatectl command additionally allows you to synchronize your systems with a time zone of your choosing. To change the time zone, follow the steps below:
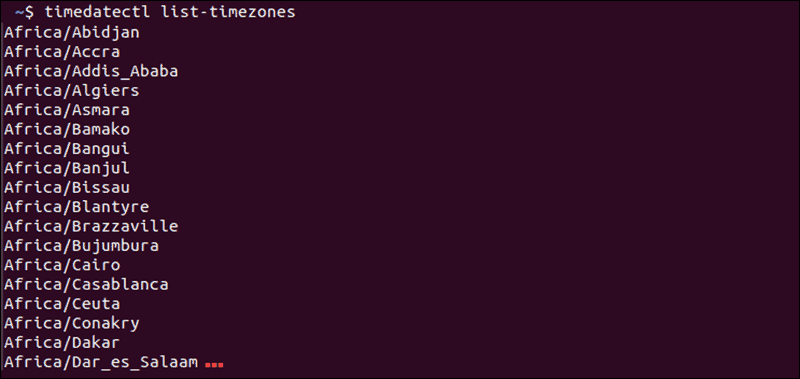
1. To list the names of the time zones, use:
timedatectl list-timezones2. Find the location closest to you, then enter the following:
timedatectl set-timezone Region/Location3. Replace Region/Location with a name from the time zone list.
The time zone list is extensive. Filter the list by keyword by piping the grep command:
timedatectl list-timezones | grep keywordSubstitute keyword for any keyword you wish, such as America , Asia , or New_York . If you get an error, double-check your spelling and make sure that you are using capital letters correctly.
How to Set Universal Time (UTC) in Ubuntu
UTC stands for Coordinated Universal Time and appears in scientific calculations and synchronizing between time zones across the globe. Synchronize your system with the following command:
timedatectl set-timezone UTCThere is no immediate output; however, you can check the applied settings with timedatectl .
Note: GMT and Zulu Time are often used to refer to UTC. They are equivalent terms when fractions of a second are not relevant.
How to Sync Hardware Clock
RTC stands for Real-Time Clock, another name for the hardware clock the computer. The system has a tiny quartz crystal and a battery that keeps time when the system disconnects from a network.
Set Hardware Clock to Sync to Local Timezone
To have the Real-Time Clock synchronize to your local time zone, enter:
timedatectl set-local-rtc 1You may get an error in this mode, since updating the hardware clock to the local time zone is unsupported.
Set the Hardware Clock to Sync with UTC
Set the hardware clock to synchronize with UTC by entering the following command:
timedatectl set-local-rtc 0As with the previous command, there is no confirmation that the change has applied. Verify the change manually with the timedatectl command.
Set Time, Date Timezone in Ubuntu Older Versions From Command Line
Older Ubuntu versions may not support the timedatectl command. Find out how to check the Ubuntu version.
There are alternative commands to display and adjust system time setting from a command line. Use the commands listed below:
sudo date -s "YY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS"Replace YY-MM-DD with Year-Month-Day, and HH:MM:SS with Hour:Minute:Second. You can set just the date or only the time, depending on your needs.
sudo hwclock --show --verboseNote: Some versions may not support the —verbose option, and it may not work on a virtual machine. The hardware clock may not hold the same time as the operating system.
sudo hwclock --set --date "MM/DD/YY HH:MM:SS"This command tells the system to set the HC (hardware clock) to SYS (system):
Use this command to reverse the previous process.
This guide showed you how to set the time, date, and time zone on your Ubuntu system. Setting the system to synchronize with NTP is typically the best course of action.
Vladimir is a resident Tech Writer at phoenixNAP. He has more than 7 years of experience in implementing e-commerce and online payment solutions with various global IT services providers. His articles aim to instill a passion for innovative technologies in others by providing practical advice and using an engaging writing style.
Your server’s MySQL time zone and your own might be out of sync. Read this article to learn 2 ways of editing .
Finding out which Ubuntu version is running on your system can be important when troubleshooting issues or .
In this tutorial, learn the five most commonly used commands to check memory usage in Linux. We also provide .
You have probably noticed your Linux OS slowing down, especially when working harder. Understanding CPU .