- How to change ubuntu’s server date and time via command line?
- 7 Answers 7
- NTP сервер на Linux Ubuntu
- Установка сервера
- Настройка NTP
- Дополнительные настройки
- Тестирование
- Настройка клиента Linux
- NTP
- ntpdate
- Настройка клиента Windows
- Некоторые ошибки
- 1. the NTP socket is in use, exiting
- 2. Connection refused
- 3. no server suitable for synchronization found
- Commands to Sync Time with NTP Server in Linux
- What is NTP
- How to Enable NTP Synchronization on Linux
- How to Enable NTP for Linux Distributions without “systemd”
- How To Setup NTP Server using timedatectl on Linux
- Get current Timezone
- Set timedatectl NTP Server
- Recent Posts
How to change ubuntu’s server date and time via command line?
The Ubuntu server’s current date and time is different from the time zone date and time. I have tried using:
sudo date "30 Sep 2015 4:43:42" to change it but it did not change the date and time, just printed on terminal the date and time I changed, but when I executed:
The date and time is still the old one. What is the correct way to change date and time of Ubuntu Server?
7 Answers 7
You can set the system date with this command:
sudo date --set="2015-09-30 10:05:59.990" Then when using date , it should be showed correctly.
Now you should also the set hardware clock in the BIOS of the system, that the setting persists over a reboot (dureing the startup the system time is set to the value of the hardware clock). Do that with hwclock :
This gets the system clocks (sys) value and sets the hardware clock (hc). Check it with the hwclock command. Both hwclock and date should now show the same date and time.
To set your timezone, you can use this command:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure tzdata BTW: If you use a this machine as a server, I strongly recommend using an NTP-Client to sync the time over network. So you can guarantee that all your servers have the exactly same time set. This will sync the time while the machine runs. If you have applications which are dependent of synced time over server, I recommend the NTP-Daemon. The longer it runs in the background, the more precise is the time.
NTP сервер на Linux Ubuntu
Опубликовано: 12.01.2018
Тематические термины: NTP, Linux, Ubuntu. Следить за актуальностью времени на всех узлах локальной сети удобнее с помощью сервера синхронизации времени NTP. В инструкции рассказано об установке и настройке такого сервера на Linux Ubuntu Server 16.04. Данное руководство можно использовать для настройки ntpd на любом другом Linux (например, Debian или CentOS).
Установка сервера
Настройка NTP
pool ru.pool.ntp.org iburst
server ntp2.vniiftri.ru iburst prefer
pool 0.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
pool 1.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 127.127.1.0
* iburst — отправлять несколько пакетов (повышает точность); ru.pool.ntp.org / 0.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org / 1.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org — адреса серверов, с которыми наш сервер будет сверять время; server — указывает на выполнение синхронизации с сервером, а не пулом серверов; prefer — указывает на предпочитаемый сервер. server 127.127.1.0 — позволит в случае отказа сети Интернет брать время из своих системных часов. Настраиваем безопасность:
restrict default kod notrap nomodify nopeer noquery
restrict 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict ::1
- restrict default — задает значение по умолчанию для всех рестриктов.
- kod — узлам, которые часто отправляют запросы сначала отправить поцелуй смерти (kiss of death), затем отключить от сервера.
- notrap — не принимать управляющие команды.
- nomodify — запрещает команды, которые могут вносить изменения состояния.
- nopeer — не синхронизироваться с хостом.
- noquery — не принимать запросы.
- restrict 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 — разрешить синхронизацию для узлов в сети 192.168.0.0/24.
- IP адреса127.0.0.1 и ::1 позволяют обмен данные серверу с самим собой.
Настройки по умолчанию могут быть разные для IPv4 и IPv6:
restrict -4 default kod notrap nomodify nopeer noquery
restrict -6 default kod notrap nomodify nopeer noquery
systemctl restart ntp || service restart ntp
Если используется брандмауэр, добавляем правило:
iptables -I INPUT 1 -p udp —dport 123 -j ACCEPT
ufw allow in on enp2s0 to any port 123 proto udp
* где enp2s0 — сетевой интерфейс, на котором слушает наш сервер.
Дополнительные настройки
Настройка файла хранения логов:
Тестирование
Проверить состояние получения эталонного времени можно командой:
Мы должны увидеть, примерно, следующее:
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
ru.pool.ntp.org .POOL. 16 p — 64 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
ntp.ubuntu.com .POOL. 16 p — 64 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
*91.189.94.4 17.253.34.253 2 u 58 64 377 55.802 3.790 0.412
-91.189.91.157 132.246.11.231 2 u 56 64 377 113.456 -1.746 0.334
+91.189.89.198 192.53.103.108 2 u 1 64 377 54.595 4.229 0.608
+91.189.89.199 17.253.34.253 2 u 61 64 377 54.061 2.637 0.557
- remote — адрес сервера времени, с которым синхронизируется наш сервер;
- refid — вышестоящий сервер (с которым сервер из графы выше получает время);
- st — уровень сервера (stratum);
- t — пир (unicast или multicast);
- when — когда последний раз сверялось время;
- poll — периодичность синхронизации с этим сервером;
- reach — состояние работоспособности. Если удалось произвести синхронизации восемь раз в подряд становится равным 377;
- delay — время задержки;
- offset — разница между нашим временем и временем на сервере; положительное — наши часы спешат, отрицательное — отстают;
- jitter — смещение времени на удаленном сервере;
- * — с этим сервером синхронизирует время наш ntpd;
- + — сервер можно использовать для сверки часов;
- — — не рекомендован для синхронизации;
- x — не доступен.
Проверить отдачу времени сервером можно введя команду на другом Linux:
Правильный ответ имеет следующий вид:
ntpdate[3576]: adjust time server 192.168.0.15 offset 0.017657 sec
* время было рассинхронизировано на 0.017657 секунд.
Отобразить текущее время можно командой:
Если после синхронизации время некорректно, настраиваем правильный часовой пояс:
cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Moscow /etc/localtime
Настройка клиента Linux
Для клиентов можно выбрать 2 стратегии настройки — с помощью ntp или утилиты ntpdate.
NTP
В настройка /etc/ntp.conf в качестве сервера оставляем только наш локальный сервер, например:
Остальные pool и server удаляем или комментируем.
systemctl restart ntp || service restart ntp
ntpdate
Утилита командной строки выполняет разовую синхронизацию. Чтобы автоматизировать процесс, добавляем задание в cron:
0 0 * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate 192.168.0.15
* в данном примере задание будет выполняться раз в день в 00:00. /usr/sbin/ntpdate — полный путь расположения утилиты, в разных системах может быть разным — проверить стоит командой which ntpdate.
Настройка клиента Windows
В командной строке выполняем:
w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:»192.168.0.15,0×8″ /syncfromflags:manual /update
Некоторые ошибки
1. the NTP socket is in use, exiting
Как правило, данная ошибка возникает при попытке синхронизировать время с помощью ntpdate, когда в системе работает демон ntp.
Причина: NTP сокет в системе уже занят, как правило, ntpd.
Решение: либо не использовать ntpdate, так как ntp умеет сверять время, либо отключить сервис ntpd командой service ntp stop.
2. Connection refused
Возникает при попытке выполнить команду ntpq -p.
Причина: нет разрешения на обращение к серверу.
Решение: проверьте, удастся ли выполнить запрос командой ntpq -pn 127.0.0.1 или ntpq -pn ::1. Также убедитесь, что настройка restrict позволяет серверу подключаться к самому себе по нужному протоколу.
3. no server suitable for synchronization found
Ошибка появляется при попытке синхронизировать время с другим сервером синхронизации.
Причина: сервер синхронизации не доступен по одной из причин: 1) не работает или выключен, 2) установлен restrict, 3) на сервере не запущен ntpd, 4) нет сетевой доступности из-за проблем на сети или брандмауэра.
- Убедиться, что сервер доступен по сети.
- Проверить настройки ntp.conf — наличие соответствующего restrict.
- Проверить состояние сервиса командой service ntp status.
- Проверить настройки брандмауэра — убедиться в наличие правила, которое разрешает UDP порт 123.
Commands to Sync Time with NTP Server in Linux
For many people, computer clocks in your devices, network machines, and servers are generally accurate. But that’s not true! These clocks are manually maintained and backed by batteries which over time drift the clock, especially in the older machines.
So why is accurate time so important? Having exact time on your machine is quite significant because of several reasons. Many aspects of your computer activity are linked with time. Perfectly synched time is crucial for tracking security-related issues; troubleshooting can become quite difficult if the timestamps in log files are incorrect. Even for financial services, keeping accurate time is critical.
Many companies solve time-related issues by connecting their networks with NTP. So what is NTP? Let’s dig into it first:
What is NTP
The full form of NTP is “Network Time Protocol”, which has been one of the most authentic ways to synchronize the clock over a network. If your system uses NTP, you don’t need to check and set your time manually. It automatically updates the clock every time the device reboots. It is an extremely accurate way to update the clock of your device. Since the internet is everywhere, NTP is being used by every modern computer.
How to Enable NTP Synchronization on Linux
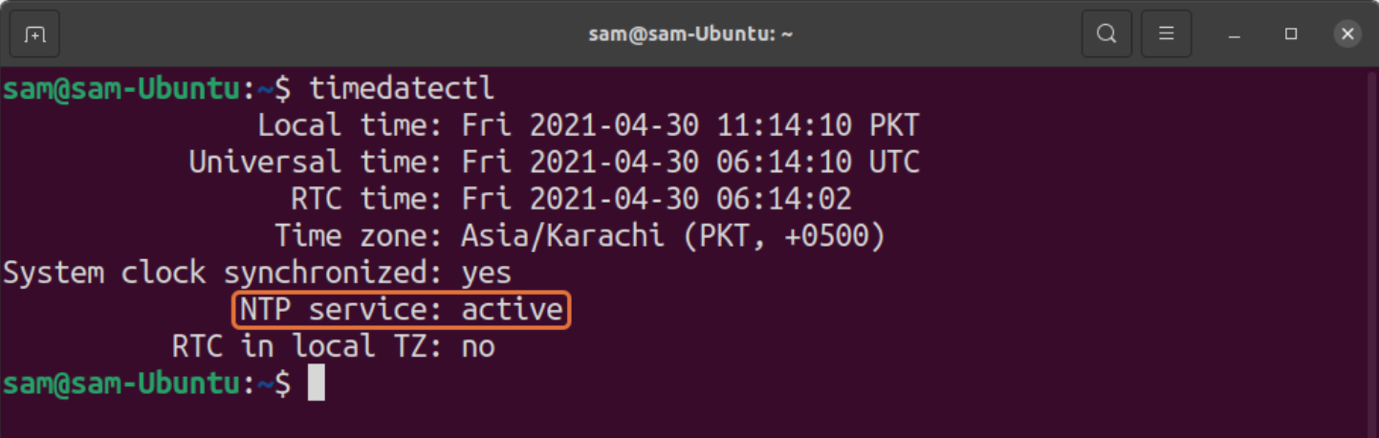
Most of the Linux distributions are using “systemd”, which comes with NTP for clock synchronization. To verify this, use the command given below:
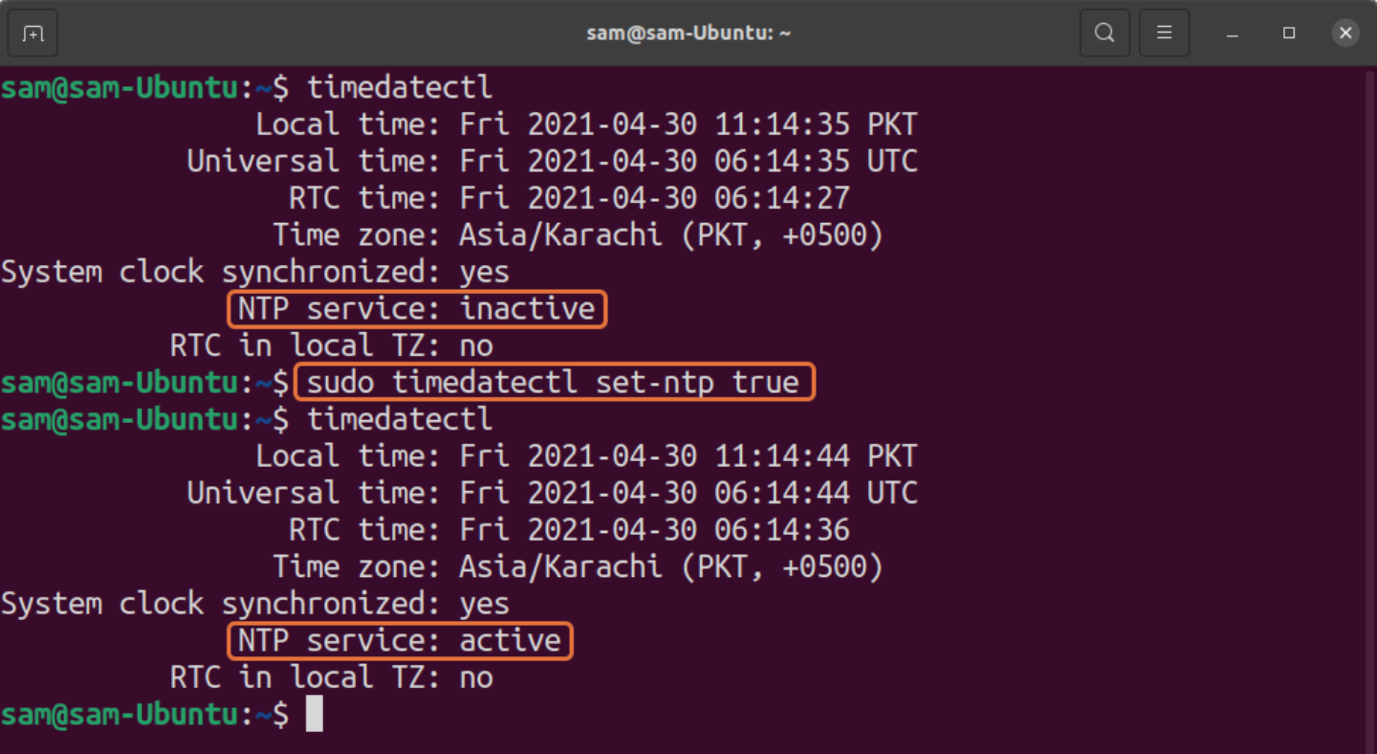
It indicates that NTP is active. If, for some reasons, it is not active, then use the below-mentioned command to enable it:
How to Enable NTP for Linux Distributions without “systemd”
But what if your distribution does not come with “systemd”? Well, in that case, you can install NTP.
How To Setup NTP Server using timedatectl on Linux
Systemd has built-in tools to manage time on Linux, which shipped in most Linux distro which uses systemd such as RHEL/CentOS, Fedora, Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Archlinux. The timedatectl command allows you to change time, date, and timezone on Linux system.
In this tutorial, we’ll manage time in Linux by setting the date, time and timezone using timedatectl command. It’s a best practice to use the correct time on your Linux server to make troubleshooting or checking file log more easiers.
Get current Timezone
Using timedatectl command is straight forward, let’s get our current time and timezone
To get list of known timezone, run following command
timedatectl list-timezones
To set timezone, use sub-command set-timezone, for example
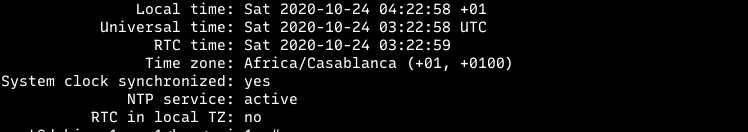
timedatectl set-timezone "Africa/Casablanca" the timezone will changes after that command executed, which can be verify using timedatectl status
Set timedatectl NTP Server
The best way to keep time synced and updated is using NTP (Network Time Protocol). The list of public NTP server can be found on ntppool.org
To enable NTP run following command
If you notice we haven’t set the NTP server, to check the NTP server list used execute timedatectl show-timesync –all
LinkNTPServers= SystemNTPServers= FallbackNTPServers=0.debian.pool.ntp.org 1.debian.pool.ntp.org 2.debian.pool.ntp.org 3.debian.pool.ntp.org ServerName=2.debian.pool.ntp.org ServerAddress=2606:4700:f1::123 RootDistanceMaxUSec=5s PollIntervalMinUSec=32s PollIntervalMaxUSec=34min 8s PollIntervalUSec=34min 8s NTPMessage={ Leap=0, Version=4, Mode=4, Stratum=3, Precision=-26, RootDelay=48.583ms, RootDispersion=671us, Reference=A230E10, OriginateTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:29:02 +01, ReceiveTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:29:02 +01, TransmitTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:29:02 +01, DestinationTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:29:02 +01, Ignored=no PacketCount=79, Jitter=322us } Frequency=607537
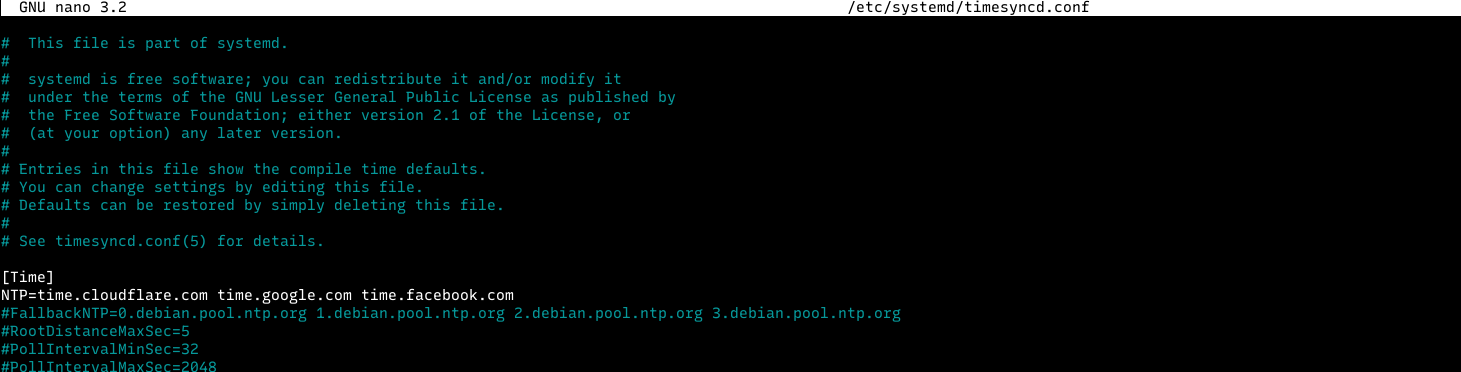
NTP server used by timedatectl stored at /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf file, change the NTP= line to
NTP=time.cloudflare.com time.google.com time.facebook.com
restart the systemd-timesyncd services to applied the changes
systemctl restart systemd-timesyncd.service
Check the NTP server timedatectl show-timesync —all
LinkNTPServers= SystemNTPServers=time.cloudflare.com time.google.com time.facebook.com FallbackNTPServers=0.debian.pool.ntp.org 1.debian.pool.ntp.org 2.debian.pool.ntp.org 3.debian.pool.ntp.org ServerName=time.cloudflare.com ServerAddress=2606:4700:f1::1 RootDistanceMaxUSec=5s PollIntervalMinUSec=32s PollIntervalMaxUSec=34min 8s PollIntervalUSec=1min 4s NTPMessage={ Leap=0, Version=4, Mode=4, Stratum=3, Precision=-25, RootDelay=48.599ms, RootDispersion=534us, Reference=A230E10, OriginateTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:39:41 +01, ReceiveTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:39:41 +01, TransmitTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:39:41 +01, DestinationTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:39:41 +01, Ignored=no PacketCount=1, Jitter=0 } Frequency=664177
The reason I prefer using a well-known company for NTP server because I notice some NTP server randomly disappear from internet, and the uptime under 90% in a month which unacceptable for production server.