- Поиск больших файлов Linux
- Поиск больших файлов Linux
- 1. GDMap
- 2. Утилита ncdu
- 3. Утилита du
- 4. Утилита find
- Выводы
- How to Find Out Top Directories and Files (Disk Space) in Linux
- How to Find Biggest Files and Directories in Linux
- Find Largest Directories in Linux
- Find Out Top File Sizes Only
- Linux Command , how to find files by size larger than x?
- 4 Answers 4
- What’s a command line way to find large files/directories to remove and free up space?
- 13 Answers 13
Поиск больших файлов Linux
Если на вашем жёстком диске закончилось свободное пространство, самый простой способ его освободить — найти и удалить самые большие и при этом ненужные файлы. Такая задача может возникнуть как на сервере, так и на домашнем компьютере, поэтому существуют удобные решения для обоих ситуаций. Способов поиска больших файлов существует очень много.
Как вы уже поняли, в этой небольшой инструкции мы рассмотрим, как найти большие файлы Linux с помощью графического интерфейса или консольных утилит. Будем двигаться от самого простого к более сложному.
Поиск больших файлов Linux
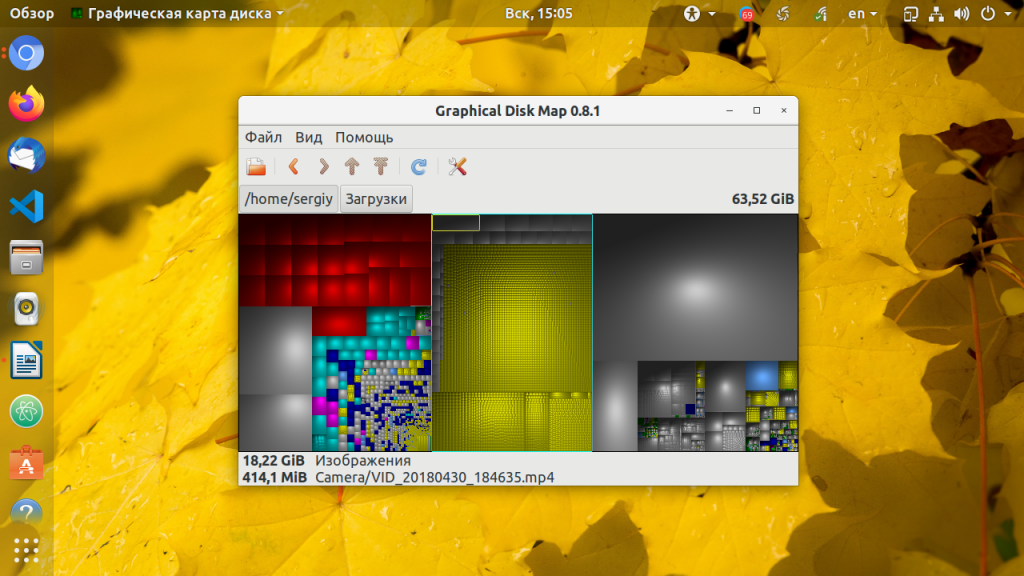
1. GDMap
Несмотря на то, что графических утилит есть около десятка, все они мне не очень нравятся. Например в Gnome можно использовать GDMap, а в KDE — fileslight. Обе утилиты сканируют файловую систему и выводят все файлы в виде диаграммы. Размер блока зависит от размера файла. Чем больше файл или папка, тем больше блок. Для установки GDMap в Ubuntu выполните:
Затем запустите утилиту из главного меню. По умолчанию она отображает домашнюю папку. Здесь можно оценить, какие файлы самые увесистые.
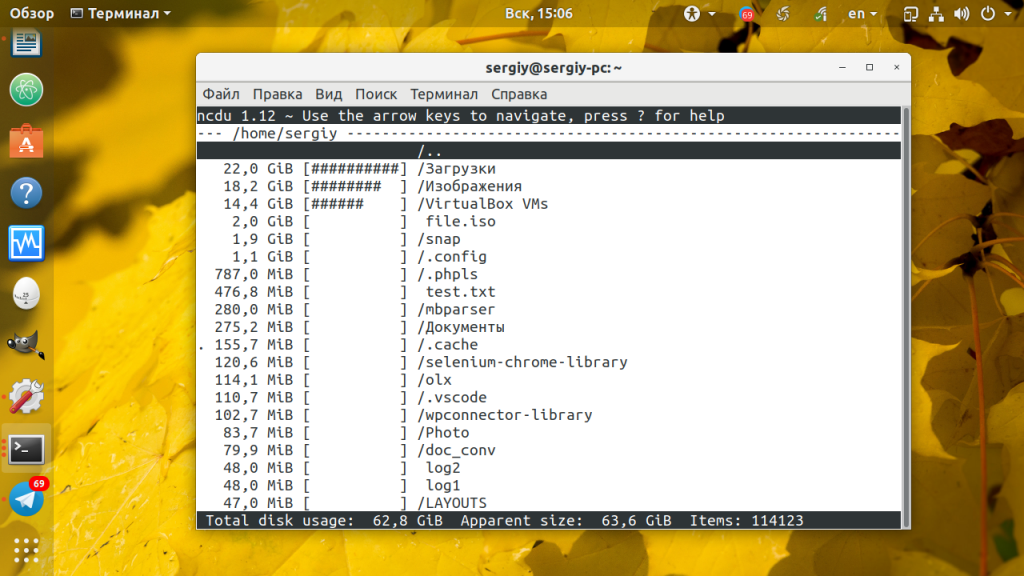
2. Утилита ncdu
Это псевдографическая утилита, которая работает в терминале Linux. Она отображает список файлов и директорий по объёму и, что самое интересное, тут же позволяет удалять ненужные файлы. Для установки утилиты выполните:
Затем запустите утилиту, передав ей в качестве параметра папку, которую надо просканировать. Можно проверить ту же домашнюю папку:
У утилиты очень простое управление. Для перемещения по списку используйте кнопки со стрелками вверх и вниз, для открытия папки — клавишу Enter, а для удаления файла — кнопку d. Также можно использовать для перемещения кнопки в Vim стиле — h, j, k, l.
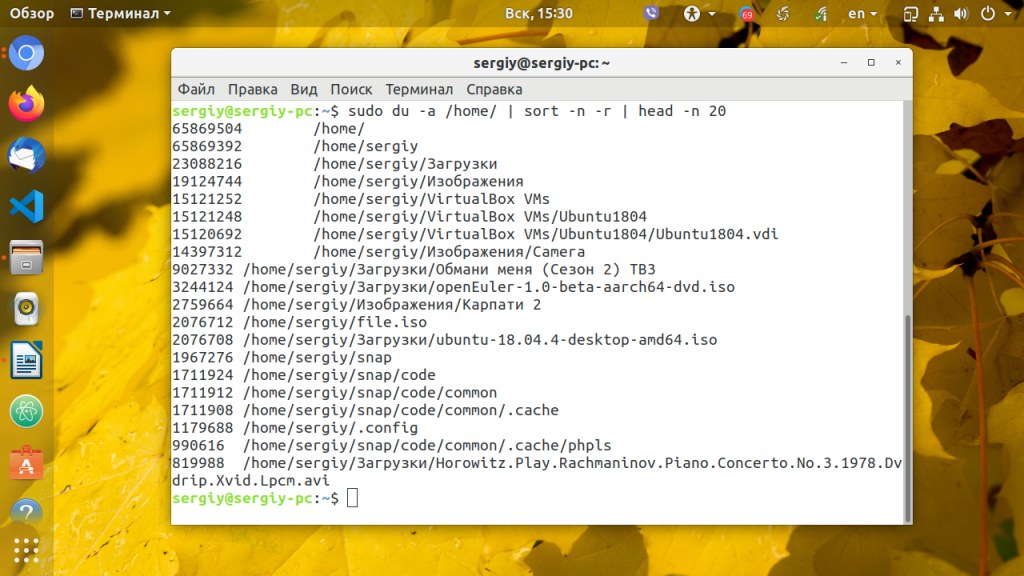
3. Утилита du
Если у вас нет возможности устанавливать новые утилиты, может помочь установленная по умолчанию во всех дистрибутивах утилита du. С помощью следующей команды вы можете вывести 20 самых больших файлов и папок в нужной папке, для примера снова возьмём домашнюю папку:
sudo du -a /home/ | sort -n -r | head -n 20
Мы не можем использовать опцию -h для вывода размера в читабельном формате, потому что тогда не будет работать сортировка.
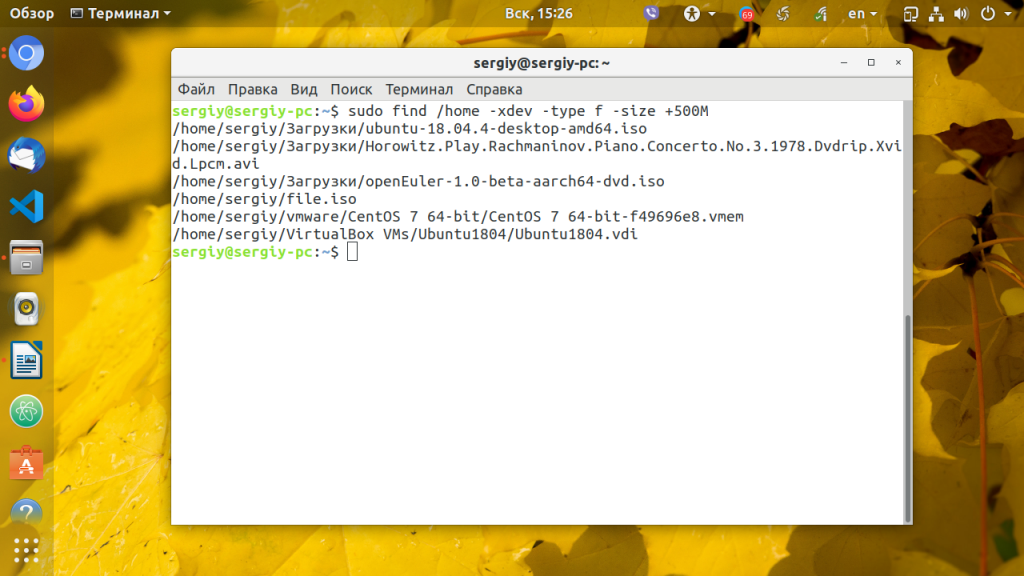
4. Утилита find
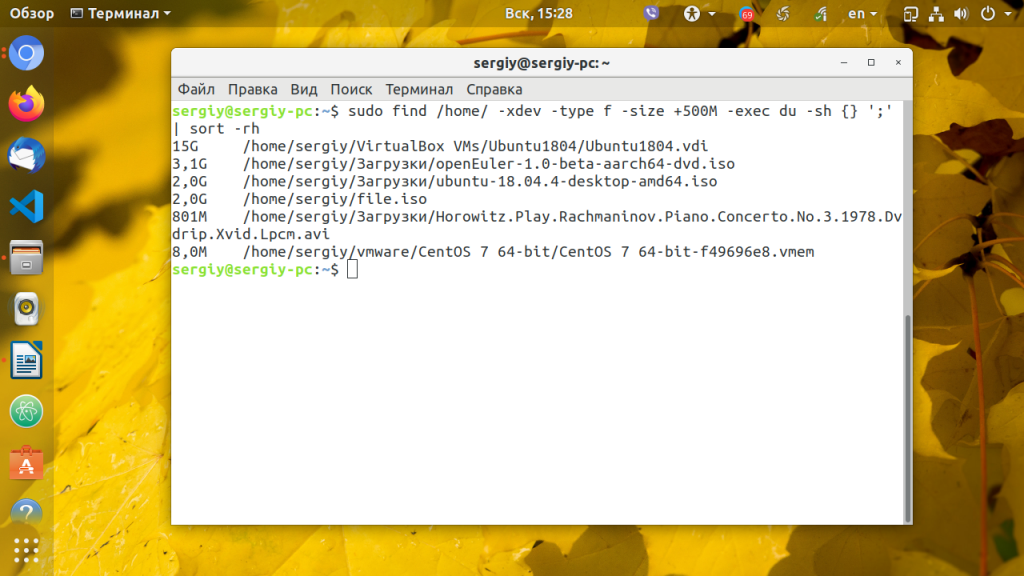
С помощью команды find вы тоже можете искать большие файлы Linux. Для этого используйте опцию -size. Например, давайте найдём файлы, которые больше 500 мегабайтов в той же домашней папке:
sudo find /home -xdev -type f -size +500M
Можно пойти ещё дальше — вывести размер этих файлов и отсортировать их по размеру:
find / -xdev -type f -size +100M -exec du -sh <> ‘;’ | sort -rh
Самые большие файлы Linux будут сверху, а более мелкие — ниже.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы разобрались, как выполняется поиск больших файлов Linux. После того, как вы их нашли, остаётся выбрать ненужные и удалить, если подобное происходит на сервере, то, обычно, это логи различных сервисов или кэш. Обратите внимание, что после удаления файлов место в файловой системе может и не освободится. Для полного освобождения места следует перезагрузить компьютер. Это довольно частая проблема на серверах и VPS.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to Find Out Top Directories and Files (Disk Space) in Linux
As a Linux administrator, you must periodically check which files and folders are consuming more disk space. It is very necessary to find unnecessary junk and free up from your hard disk.
This brief tutorial describes how to find the largest files and folders in the Linux file system using du (disk usage) and find command. If you want to learn more about these two commands, then head over to the following articles.
How to Find Biggest Files and Directories in Linux
Run the following command to find out top biggest directories under /home partition.
# du -a /home | sort -n -r | head -n 5
The above command displays the biggest 5 directories of my /home partition.
Find Largest Directories in Linux
If you want to display the biggest directories in the current working directory, run:
Let us break down the command and see what says each parameter.
- du command: Estimate file space usage.
- a : Displays all files and folders.
- sort command : Sort lines of text files.
- -n : Compare according to string numerical value.
- -r : Reverse the result of comparisons.
- head : Output the first part of files.
- -n : Print the first ‘n’ lines. (In our case, We displayed the first 5 lines).
Some of you would like to display the above result in human-readable format. i.e you might want to display the largest files in KB, MB, or GB.
The above command will show the top directories, which are eating up more disk space. If you feel that some directories are not important, you can simply delete a few sub-directories or delete the entire folder to free up some space.
To display the largest folders/files including the sub-directories, run:
Find out the meaning of each option using in above command:
- du command: Estimate file space usage.
- -h : Print sizes in human-readable format (e.g., 10MB).
- -S : Do not include the size of subdirectories.
- -s : Display only a total for each argument.
- sort command : sort lines of text files.
- -r : Reverse the result of comparisons.
- -h : Compare human readable numbers (e.g., 2K, 1G).
- head : Output the first part of files.
Find Out Top File Sizes Only
If you want to display the biggest file sizes only, then run the following command:
# find -type f -exec du -Sh <> + | sort -rh | head -n 5
To find the largest files in a particular location, just include the path beside the find command:
# find /home/tecmint/Downloads/ -type f -exec du -Sh <> + | sort -rh | head -n 5 OR # find /home/tecmint/Downloads/ -type f -printf "%s %p\n" | sort -rn | head -n 5
The above command will display the largest file from /home/tecmint/Downloads directory.
That’s all for now. Finding the biggest files and folders is no big deal. Even a novice administrator can easily find them. If you find this tutorial useful, please share it on your social networks and support TecMint.
Linux Command , how to find files by size larger than x?
I’m trying to find files with size larger than «x» , ex: 32 bytes But what I found in ls —help was only ls -S , that just sort by size and not satisfied my demand I’m new to Linux , I’ve tried Google but I don’t know what keywords should I use to find answer , could somebody give me advice , thank you !
Your question is not about programing but about linux command that would be better in serverfault.com. If you want to ask something about shell script please read this first. stackoverflow.com/help/mcve
4 Answers 4
Try to use the power of find utility.
Find files greater than 32 bytes:
Of course you could also ask for files smaller than 32 bytes:
And files with exact 32 bytes:
For files with 32 bytes or more:
Or not smaller than 32 bytes (the same as above, but written another way):
And files between 32 and 64 bytes:
And you can also apply other common suffixes:
If you get find: illegal option — i error, specify the folder to search in after find . Add a dot to find files in the current folder: find . -size +32k -size -64M
You can change 32 for the size you want. In this case, I used your example.
Both answers you two provided me are excellent 😀 But I think I will give @rslemos the best answer tag since he’s «1 minute earier» , but still thanks to you !
Explanation: Use unix command find Using -size oprator
The find utility recursively descends the directory tree for each path listed, evaluating an expression (composed of the ‘primaries’ and ‘operands’) in terms of each file in the tree.
Solution: According to the documentation
-size n[ckMGTP] True if the file's size, rounded up, in 512-byte blocks is n. If n is fol- lowed by a c, than the primary is true if the file's size is n bytes (charac- ters). Similarly if n is followed by a scale indicator than the file's size is compared to n scaled as: k kilobytes (1024 bytes) M megabytes (1024 kilobytes) G gigabytes (1024 megabytes) T terabytes (1024 gigabytes) P petabytes (1024 terabytes) Usage: perform find operation with -size flag and threshold measurement arguments: more than(+)/less than(-), number(n) and measurement type (k/M/G/T/P).
Formula: find -size [+/-]
1.Greater Than — Find all files in my current directory (.) that greater than 500 kilobyte
2.Less Than — Find all files in my current directory (.) that less than 100 megabyte.
3.Range — Find specific file (test) in my current directory (.) that greater than 500 kilobyte less than 100 megabyte (500k-1000k)
find . -name "test" -size +500k -size -100M 4.Complex Range with Regex Find all .mkv files in all filesystem (root /) that are greater than 1 gigabyte and created this month, and present info of them.
find / -name "*.mkv" -size +1G -type f -ctime -4w | xargs ls -la What’s a command line way to find large files/directories to remove and free up space?
What’s odd is I have two servers that are running the same thing. One is at 50% disk usage and the other is 99%. I can’t find what’s causing this.
13 Answers 13
If you just need to find large files, you can use find with the -size option. The next command will list all files larger than 10MiB (not to be confused with 10MB):
If you want to find files between a certain size, you can combine it with a «size lower than» search. The next command find files between 10MiB and 12MiB:
find / -size +10M -size -12M -ls apt-cache search ‘disk usage’ lists some programs available for disk usage analysis. One application that looks very promising is gt5 .
From the package description:
Years have passed and disks have become larger and larger, but even on this incredibly huge harddisk era, the space seems to disappear over time. This small and effective programs provides more convenient listing than the default du(1). It displays what has happened since last run and displays dir size and the total percentage. It is possible to navigate and ascend to directories by using cursor-keys with text based browser (links, elinks, lynx etc.)
On the «related packages» section of gt5, I found ncdu . From its package description:
Ncdu is a ncurses-based du viewer. It provides a fast and easy-to-use interface through famous du utility. It allows to browse through the directories and show percentages of disk usage with ncurses library.