- how to show or display hidden files in linux
- ls command
- dir command
- KDE File Manager (dolphin)
- Gnome File Manager (files or nautilus)
- Xfce File Manager (thunar)
- Midnight Commander
- How to see hidden files and folders in the Debian
- View hidden files using the command-line
- View hidden files by using the GNOME Filemanager
- Using the Keyboard shortcut
- How to show Hidden Files and Folders in Ubuntu
- How to Show Hidden Files in Ubuntu
- 1. Keyboard shortcut
- 2. In the file manager
- 3. In other graphics applications
- 4. Via a terminal
- Hidden and Displaying Files via Command
- file .hidden
- Automatic script
- All Ubuntu ls Show Hidden Files Command
- ls command in Linux/Unix
- ls syntax
- ls command options
- ls command examples
- ls command examples
This post and this website contains affiliate links. See my disclosure about affiliate links.
how to show or display hidden files in linux
In Linux, as you should already know, there is the concept of hidden files and hidden folders. It is not exactly hidden in the literal sense, but all that means is that the file managers and file system utilities will not display these types of files (or folders) by default.
- These files are usually a mechanism to store user preference or system files that are not modified by user regularly.
- They are also used by different utilities to store configuration and state of the programs. As these files are not actively used by user on a normal day-to-day basis, it makes sense to hide them in most cases.
- It also allows the file manager utilities to prevent cluttering up the user interface and provide a soft division between user files and user specific configuration files.
Any file or folder whose name start with a dot (.) is a hidden file, also known as dot file. These files will not be displayed by default when listing the contents of a folder. These files can be referenced just as any file, by using the name of the file (including the dot).
We will see how you can view these files using the most popular directory listing commands and file managers.
ls command
The ls command is probably the most used command line utility and it lists the contents of the specified directory. In order to display all files, including the hidden files in the folder, use the -a or –all option with ls.
This will display all the files, including the two implied folders: . (current directory) and .. (parent folder). If you want to omit the display of these two folders, then use the -A or –almost-all option.
This is quite useful, if you are using the output of the command as input to some other script. You probably do not the script to loop in the current folder (depending on the script).
If you want to display only the hidden files, then you will need to specify a regular expression with the ls command., the following will display just the hidden file and folders.
The -d option is to ensure that the directory contents are not printed out for each directory in the list.
dir command
Another popular command used to display directory contents is dir. Almost all options for dir is the same as ls, which means everything that was shown for ls in the previous section will work for dir as well.
will display all files, hidden files and the implied folders (. and ..).
will display all files, folders including the hidden folders but excluding both . and ..
will display just the hidden files and hidden folders.
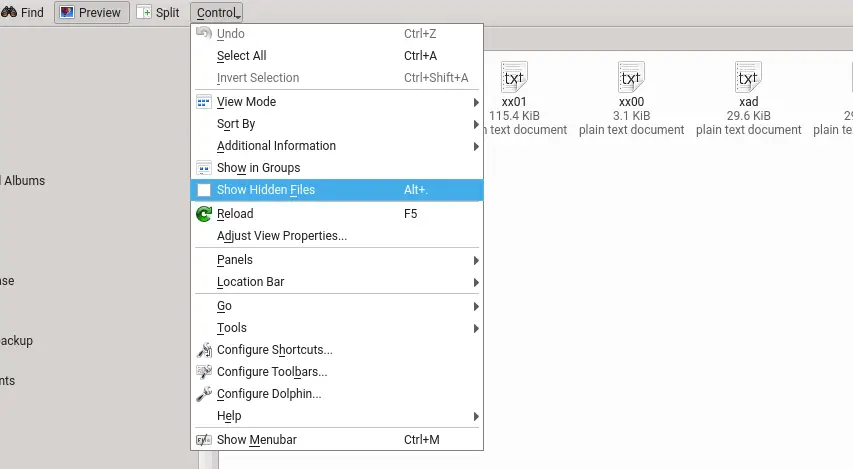
KDE File Manager (dolphin)
The default file manager in KDE is Dolphin. The default setting in Dolphin is not to display hidden or dot files. There are couple of different ways you can enable the option here.
The easiest is probably the keyboard shortcut Alt+. (Alt and dot). You can easily enable the display and disable it again using the same shortcut.
The other option is using the menu option. Click on the Hamburger icon on the menu bar (for Settings/Configuration). In the drop down menu, you will see the option named Show Hidden Files. Click and select it on it to enable the display of hidden files.
You can leave that option selected, if you want to always display the hidden files. The other commonly used file manager is Konqueror, which uses embedded dolphin to display the file system, as well.
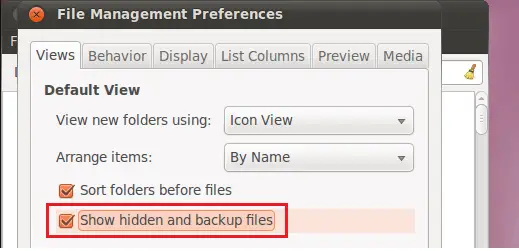
Gnome File Manager (files or nautilus)
The default file manager in Gnome on most distros is Gnome Files. It was formerly known as Nautilus. The keyboard shortcut to display hidden files in Nautilus is Ctrl+H. This shortcut can be used to toggle the display of dot files.
The other option is to change it in the configuration. Open Edit -> Preferences and navigate to the Views tab. Select the option Shown hidden and backup files. In modern or latest versions, this option is in Files -> Preferences menu.
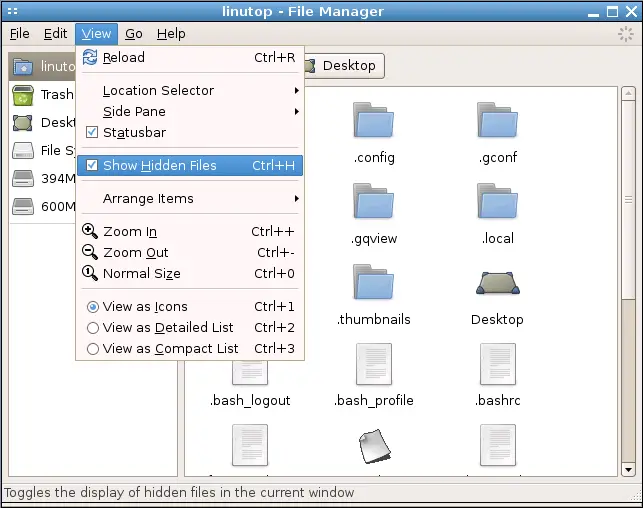
Xfce File Manager (thunar)
Xfce is a popular light weight desktop environment, and the default file manager is thunar. The keyboard shortcut is display hidden files is again Ctrl+H just as with Gnome File Manager.
You can find the option with in the menu as well, as with other file managers. Click on View in the menu bar, and select Show Hidden Files option.
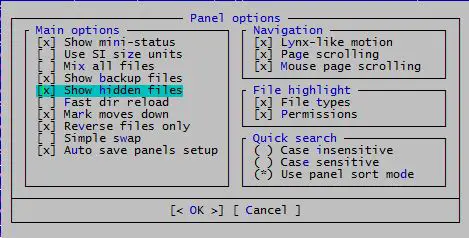
Midnight Commander
Midnight Commander is a command line based file manager which has a loyal following. The keyboard shortcut to display dot files here is Alt + . (Alt-Period).
There is also a configuration setting with in Panel Options. Open Options from the menu and then Panel Options. Select the option Show Hidden Files.
No matter which file manager you are using, there should be an option to display hidden files. Most times, it is disabled by default and as it should be. You can try first by right clicking and checking the context menu. The next place to check is either the Settings or Preferences dialog which is often in the Edit or View menu.
As the last resort, read the manual.
How to see hidden files and folders in the Debian
Sometimes, we have to keep some files hidden it can be done for different reasons like when we have important files and don’t want others to see it, or to prevent it from accidental deletion especially when we are sharing our system with other users. Some OS files are also kept hidden by default by the OS as they are critical for the functionality of the system. Any changes or accidental deletion of these files can lead to major errors or even cause applications to stop functioning. However, sometimes we need to access these hidden files for troubleshooting or some other reasons. In this article, we will explain how to see hidden files and folders in the Debian File browser using the following ways.
We have run the commands and procedures mentioned in this article on a Debian 10 OS.
View hidden files using the command-line
Normally ls command is used for displaying files in a specific directory. But once the ls command is combined the –a option, you can use it for displaying the hidden files too.
Open the Terminal application by going into the activities tab on the top left corner of your desktop. Then in the search bar, type terminal. When the Terminal icon appears, click on it to launch it. Now in the Terminal, execute the following command:
In the following output, the files starting with dot (.) character are hidden files.
View hidden files by using the GNOME Filemanager
Hidden files can also be viewed within a file manager. Open the file manager from the Activities menu on the top left corner of your desktop. Once the file manager is open, go to the view menu in the top right corner of its window. From the menu that appears, check the box next to the option Show Hidden Files.
Now you will be able to see the hidden files and folders in your File manager. In the following screenshot, the files starting with dot (.) character are hidden files.
Using the Keyboard shortcut
There is also a default shortcut available for viewing the hidden files in the Linux file manager. Open the file manager and simply press Ctrl+H and you will be able to see hidden files starting with (.) character along with the regular files. In the following screenshot, the files starting with dot (.) character are hidden files.
That is all there is to it! I hope it will be helpful whenever you need to access the hidden files and folders in a Debian OS.
How to show Hidden Files and Folders in Ubuntu
The hidden elements are elements that are not visible by default when the user views the contents of a folder. This ability to hide items to protect files from accidental manipulations and reduce the display of folders in which they are stored.
The hidden elements are identified in the previous point name. A file named ” .test ” will be recognized by the system as a hidden file so that a file named “test ” will not be.
How to Show Hidden Files in Ubuntu
There are many situations where it may be useful to display them. However, note that if these files are hidden, it’s for good reason … so be careful with handling.
1. Keyboard shortcut
These shortcuts are valid in most applications.
2. In the file manager
Most file managers have a box-to-box located in the “View” menu. This check is often called “Show hidden files”.
For example, in Thunar , pull down the View menu and check “Show hidden files”.
3. In other graphics applications
In the “Open …” menu or “Save As …” from certain applications, the two previous methods do not work, it may nevertheless be useful to save a file in a hidden folder. He usually just make a right click in the file explorer and select “Show hidden files”.
4. Via a terminal
To display all items, including hidden elements, simply add the argument -a ( “all” in English):
ls , for more information on using the command ls .
Hidden and Displaying Files via Command
file .hidden
If you want to make an invisible element in Nautilus , in each relevant file, create a text file named .hidden and place are the names of items you want to hide.There should only be one item per line.
(This trick makes them invisible files in Nautilus , they remain visible mode console .)
For example, to apply this tip to a set of files with the extension * .pyc, you can use the following commands:
Automatic script
For a right click of the menu features hide files or folders you can use a script to Nautilus .
For this you must:
Create a blank file in the folder scripts for Nautilus : /home/
Feature for Precise 12.04 LTS : The folder containing the scripts for Nautilus is /home//.gnome2/nautilus-scripts .
#! / bin / bash printf % s " $ NAUTILUS_SCRIPT_SELECTED_FILE_PATHS " | while read -r line do if grep -q " $ " ".hidden" Then sed -i '/ ^ $ / d " " .hidden " else echo " $ " >> " .hidden " fi done
To make it work, it must make the script executable. Right-click on this newly created file and “properties” tab → “permissions”, check “Allow executing file as a program” .
A new entry appears when making a right click in Nautilus in the “Scripts” with the name given to the file containing the code. This entry allows you to add or delete the names of the selected files and folders in the file .hidden .
All Ubuntu ls Show Hidden Files Command
ls command in Linux/Unix
ls is a Linux shell command that lists directory contents of files and directories.
ls syntax
$ ls [options] [file|dir]
ls command options
| option | description |
|---|---|
| ls -a | list all files including hidden file starting with ‘.’ |
| ls –color | colored list [=always/never/auto] |
| ls -d | list directories – with ‘ */’ |
| ls -F | add one char of */=>@| to enteries |
| ls -i | list file’s inode index number |
| ls -l | list with long format – show permissions |
| ls -la | list long format including hidden files |
| ls -lh | list long format with readable file size |
| ls -ls | list with long format with file size |
| ls -r | list in reverse order |
| ls -R | list recursively directory tree |
| ls -s | list file size |
| ls -S | sort by file size |
| ls -t | sort by time & date |
| ls -X | sort by extension name |
ls command examples
You can press the tab button to auto complete the file or folder names.
List directory Documents/Books with relative path:
List directory /home/user/Documents/Books with absolute path.
List user’s home directory (e.g: /home/user):
List with long format and show hidden files:
Recursive directory tree list:
List only text files with wildcard:
ls redirection to output file:
List files and directories with full path:
ls command examples
You can press the tab button to auto complete the file or folder names.
List directory Documents/Books with relative path:
List directory /home/user/Documents/Books with absolute path.
$ ls /home/user/Documents/Books
List user’s home directory (e.g: /home/user):
List with long format and show hidden files:
Recursive directory tree list:
List only text files with wildcard:
ls redirection to output file:
List files and directories with full path: