- How to list all physically installed Network Cards (Debian)?
- 8 Answers 8
- Как узнать сетевую карту в Linux
- Информация о сетевой карте с помощью Ethtool
- Информация о сетевой карте в lshw
- Список сетевых карт в lspci
- Информация о сетевой карте с помощью ip
- Выводы
- How to find Ethernet network interface card information in Linux
- Method One: ethtool
- Method Two: lshw
- Method Three: lspci
- Support Xmodulo
- How can I list installed network cards using Terminal?
- You must log in to answer this question.
- Linked
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
How to list all physically installed Network Cards (Debian)?
Do you have physical access to the host? Can you confirm that any expansion cards are properly seated? Are all NIC’s from the same manufacturer?
Hello Tok. Thanks for your answer.No the NIC’s are not from the same manufacturer (one should be from intel and the other from realtek). =>Your question sounds interesting. What could be the effect/result if the cards are from different manufacturers? And I do not have physical access to the server and do not know if they are correctly installed. thanks. jens.
8 Answers 8
You can use lshw to see all devices on a machine. To view just the network devices enter:
This is definitely not a widely available program, and especially not so on machines where I’m trying to figure out basic things like how many physical network devices there are. On my local workstation, where I can install software like lshw, I already know things like what network cards are installed.
@pyasi, I think this reply does not answer the question, because the network class will contain all virtual networks too, e.g. VLANs, bonding, .
find /sys/class/net -type l -not -lname '*virtual*' -printf '%f\n' Shows just interfaces that relate to a physical NIC.
Tried to find a type option to ip link show that would display non-logical, but alas:
ip link help 2>&1 | grep -A10 'TYPE :=' TYPE :=
It seems to be the one thing that ip link show cannot do. At least not without resorting to a script that first lists each of the above and then does grep -v against a final run without type specified.
This definitely seems like something ip link should be able to handle. If using a lot of virtual interfaces (say for bridging or vlan) and especially if these virtual interfaces have been renamed.
ip link show will list everything that looks like a network interface.
. which makes it not suitable for the question asked. The asker said he or she wanted a list that didn’t include everything, but rather just a subset.
ls -d /sys/class/net/eth* | wc -l This does not work in general because ethernet device names do not have to start with eth. Many (all?) major linux distros are now using «predictable ethernet interface names» with systemd, resulting in wired interface names like en0 or enp0s25, so looking for eth* will miss those.
Give this a try: $ ls -l /sys/class/net/ | grep -v virtual . It filters all virtual network interfaces out. Work on ubuntu running in a Virtual Box.
/proc/net/dev file has details on all interfaces. e.g.
$ cat /proc/net/dev Inter-| Receive | Transmit face |bytes packets errs drop fifo frame compressed multicast|bytes packets errs drop fifo colls carrier compressed lo: 3562 60 0 0 0 0 0 0 3562 60 0 0 0 0 0 0 wlan0: 2491781197 2034240 0 0 0 0 0 0 261797069 1502752 0 0 0 0 0 0 eth0: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 As you can see, many columns and details are not very easy to read when you cat the file so I would suggest to use ifconfig command which reads that file and formats output nicely.
To list all interfaces use
that will show you the unconfigured/down network interfaces as well as configured and active ones, as read from /proc/net/dev
Как узнать сетевую карту в Linux
Иногда нужно посмотреть сетевые карты в Linux, подключенные к компьютеру, узнать имя продукта или технические характеристики карты, а также скорость передачи данных. Например, когда вы хотите проверить совместимость сетевого драйвера или модуля ядра с Ethernet адаптером необходимо знать его аппаратные спецификации, такие как: номер модели и производитель, (например: Broadcom NetXtreme, Intel I350), скорость (например: (1 Гбит/сек, 10 Гбит/сек), режим соединения (full/half duplex) и т д.
Также эта информация вам понадобится, если вы хотите подобрать драйвер для своего wifi адаптера. В этой инструкции я расскажу как узнать сетевую карту Linux и посмотреть все доступные ее характеристики.
Информация о сетевой карте с помощью Ethtool
Если вас интересует информация о проводной сетевой карте Ehternet, то вы можете воспользоваться утилитой Ethtool. Это инструмент командной строки для проверки и изменения настроек PCI Ethernet карт. Для установки Ethtool в Ubuntu или Debian используйте команду:
В других дистрибутивах установка производится аналогичным образом, только нужно использовать подходящий пакетный менеджер.
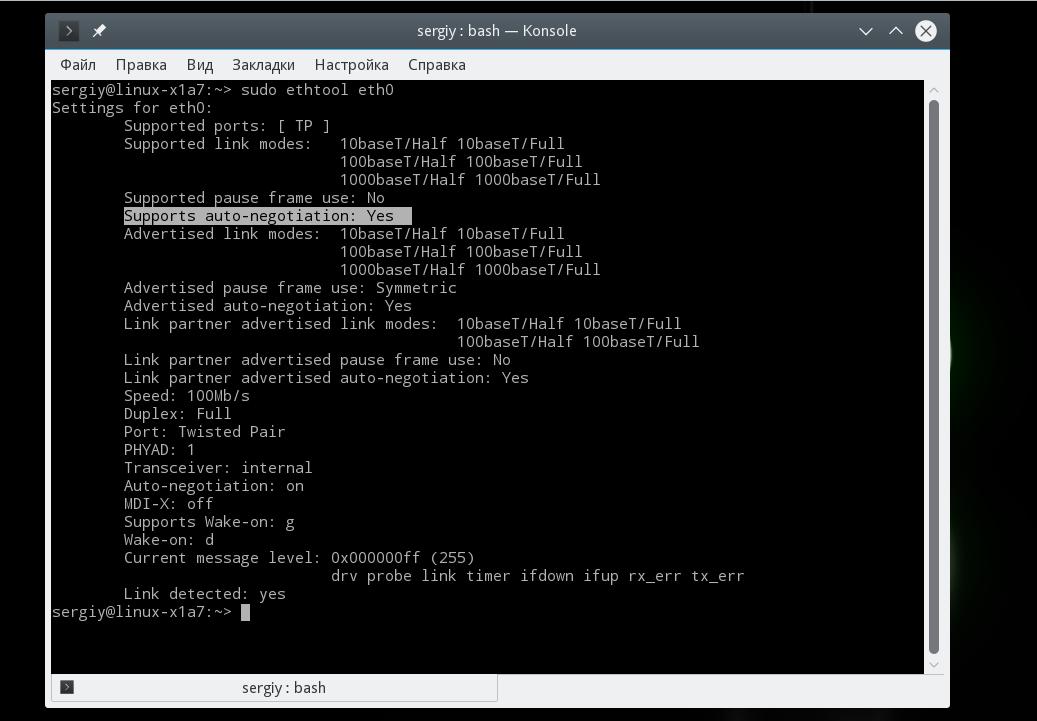
Для отображения настроек сетевой карты в ethtool запустите утилиту передав в параметрах имя сетевого адаптера. Права суперпользователя здесь нужны для того, чтобы утилита могла получить информацию о настройках локальной сети и статусе соединения.
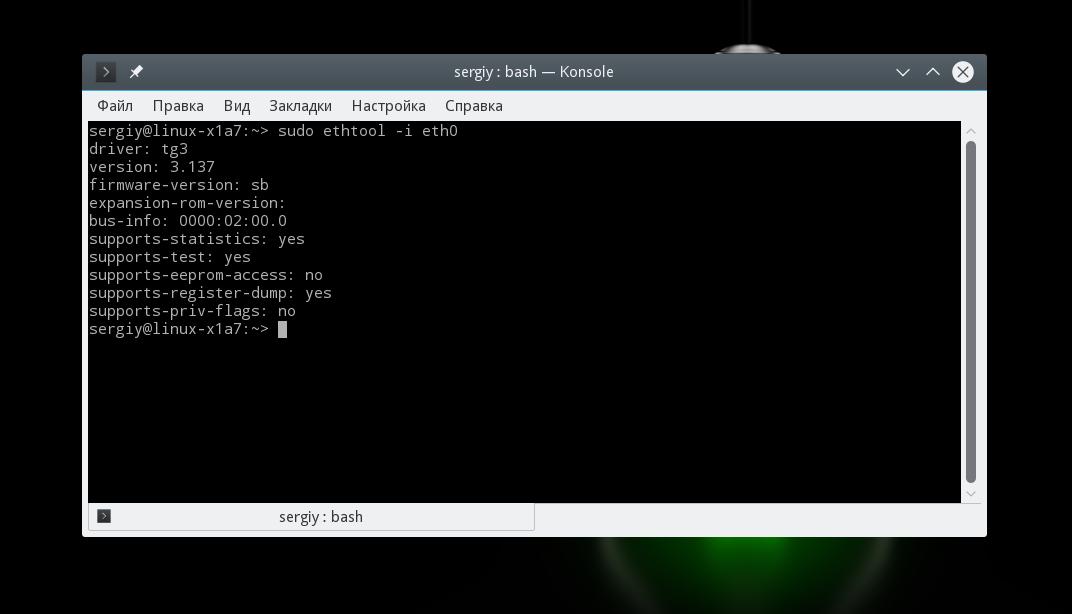
Здесь вы можете посмотреть поддерживаемые режимы работы Supported link modes, скорость Speed и тип коннектора Port, а также состояние подключения. Для просмотра информации о сетевом драйвере и прошивке используйте опцию i:
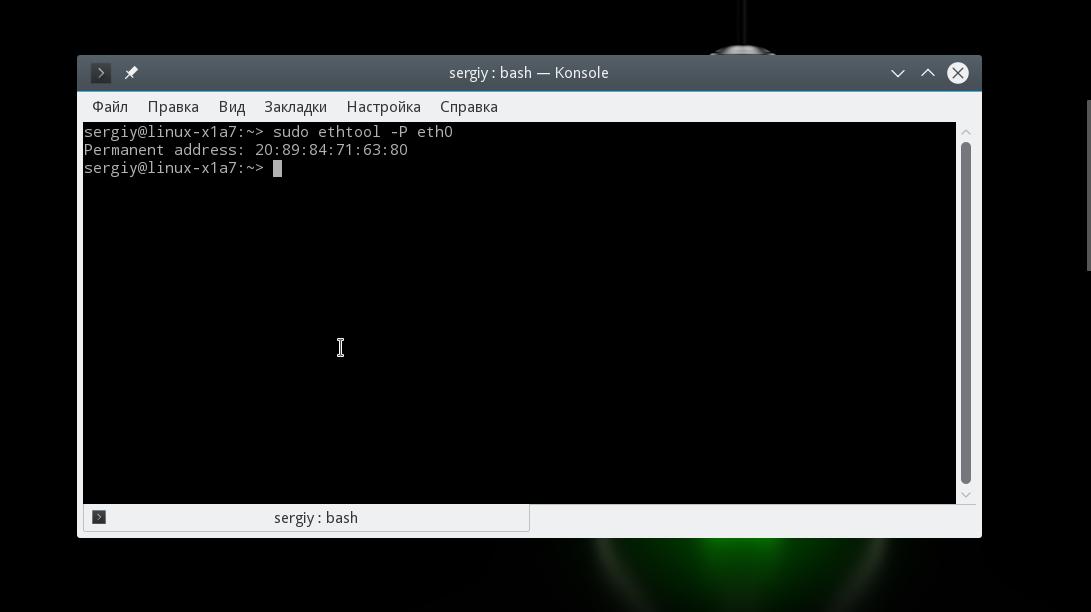
Здесь вы можете видеть какие режимы поддерживает прошивка, а также ее версию. Если вас интересует MAC адрес выполните:
Информация о сетевой карте в lshw
Во втором способе мы воспользуемся утилитой для отображения подробной информации об аппаратуре Linux — lshw. С помощью нее вы можете посмотреть информацию не только о карте Ethernet, но и о Wifi адаптере, а также посмотреть список сетевых карт.
Для установки lshw на Ubuntu или Debian наберите:
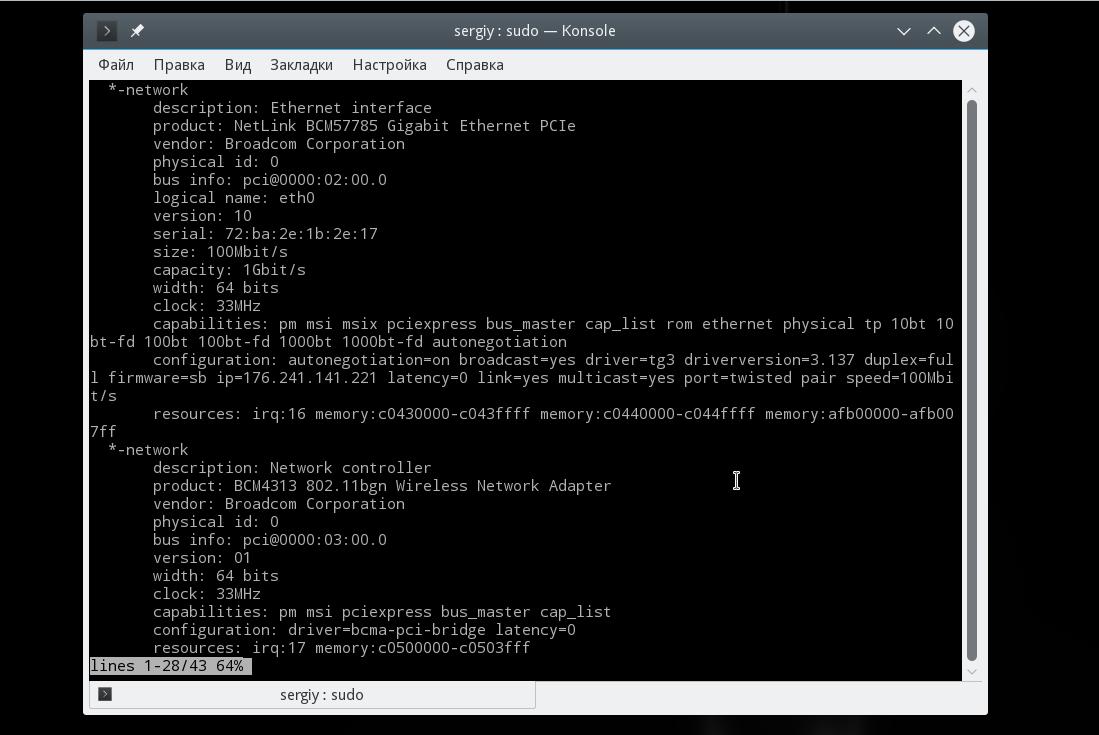
Чтобы посмотреть узнать сетевую карту linux и просмотреть подробные сведения о ней, запустите утилиту со следующими параметрами:
В выводе команды вы увидите все подключенные к системе сетевые интерфейсы, кроме того, тут показывается более подробная информация, чем в выводе предыдущей утилиты. В самом начале вы видите производителя — vendor и имя продукта — product, скорость передачи данных size, а также в разделе configuration можно найти поле driver, где указан используемый драйвер.
Список сетевых карт в lspci
Если вам нужно узнать только продукт и имя производителя вашей сетевой карты можно использовать lspci. Обычно lscpi уже предустановлена в системе, но если нет ее можно установить командой:
sudo apt install pciutils
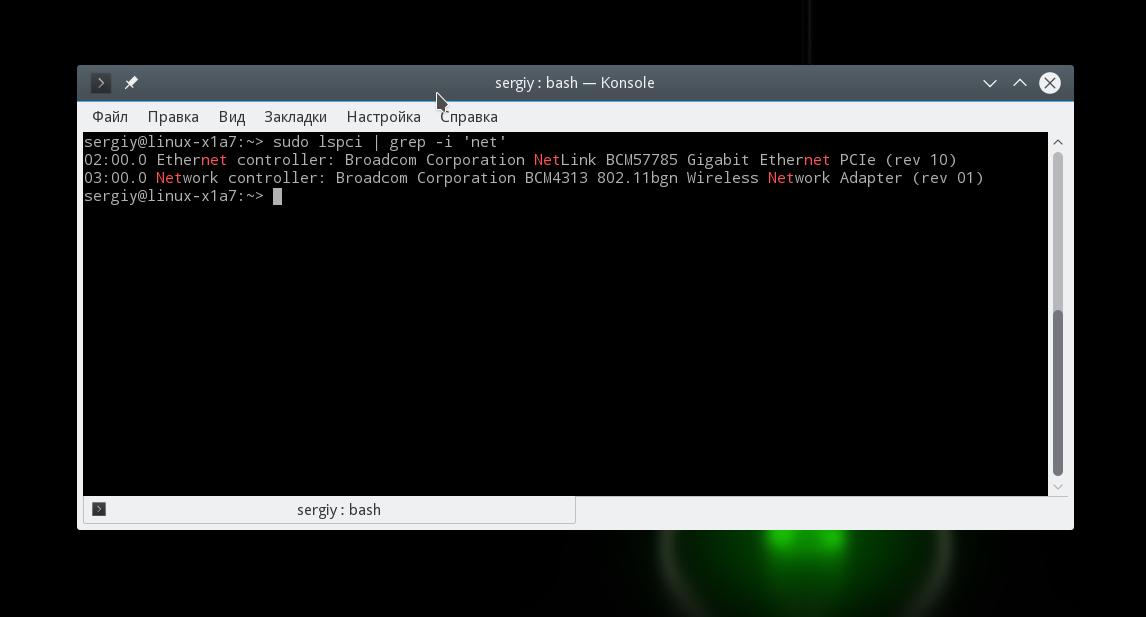
Теперь для просмотра доступных сетевых карт используйте:
Тут вы можете видеть, что к системе подключены две сетевые карты linux, для проводного интернета и беспроводная, обе от Broadcom.
Информация о сетевой карте с помощью ip
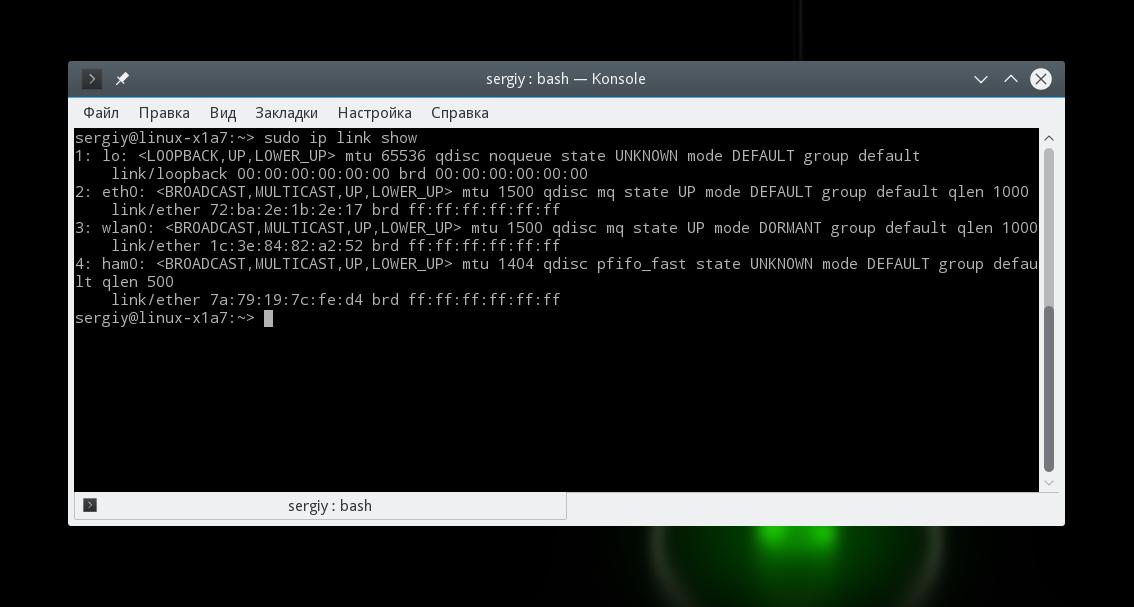
Утилита ip позволяет посмотреть более подробную информацию о сетевом протоколе для вашей карты. Для просмотра информации выполните:
На снимке экрана вы видите две физические сетевые карты linux — wlan0 и eth0, а также два виртуальных устройства. Для каждой из карт можно узнать состояние и MAC адрес.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели несколько способов узнать сетевую карту Linux. Вы можете посмотреть не только производителя и название устройства, но и его характеристики, такие как скорость сетевой карты linux, используемый драйвер и MAC адрес. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to find Ethernet network interface card information in Linux
Sometimes you may want to know the product name or hardware settings of the network interface cards (NICs) attached to your Linux system. For example when you check whether a particular network device driver or a kernel module is compatible with your Ethernet adapter, you need to know its hardware specification such as NIC model/vendor (e.g., Broadcom NetXtreme, Intel I350), speed (e.g., 1GB/s, 10GB/s), link mode (e.g., full/half duplex), etc.
In this tutorial, I will describe how to find Ethernet NIC information from the command line in Linux.
Method One: ethtool
The first method is to use ethtool , a command-line tool for checking or modifying PCI-based Ethernet card settings.
To install ethtool on Ubuntu or Debian:
$ sudo apt-get install ethtool
To install ethtool on Fedora, CentOS or RedHat:
To display hardware settings of a network interface card with ethtool , run the following command. It is assumed that the NIC card is assigned the name eth0 . The reason for sudo access in this case is to allow ethtool to obtain wake-on-LAN settings and link status.
Settings for eth0: Supported ports: [ TP ] Supported link modes: 10baseT/Half 10baseT/Full 100baseT/Half 100baseT/Full 1000baseT/Full Supports auto-negotiation: Yes Advertised link modes: 10baseT/Half 10baseT/Full 100baseT/Half 100baseT/Full 1000baseT/Full Advertised pause frame use: No Advertised auto-negotiation: Yes Speed: 1000Mb/s Duplex: Full Port: Twisted Pair PHYAD: 1 Transceiver: internal Auto-negotiation: on MDI-X: Unknown Supports Wake-on: g Wake-on: g Link detected: yes
To find Ethernet device driver and firmware information:
driver: bnx2 version: 2.1.6 firmware-version: bc 5.2.3 NCSI 2.0.6 bus-info: 0000:03:00.0 supports-statistics: yes supports-test: yes supports-eeprom-access: yes supports-register-dump: yes
To find factory-default MAC address information:
Permanent address: 9c:8e:99:12:2d:8a
Method Two: lshw
The second method is via lshw , a command-line utility for showing detailed hardware specification of a Linux machine.
To install lshw on Ubuntu or Debian:
To install lshw on CentOS or RedHat, first set up Repoforge repository on your system, and then run:
To install lshw on Fedora, simply run:
To show detailed vendor information of your NIC, run the following.
*-network description: Ethernet interface product: NetXtreme II BCM5709 Gigabit Ethernet vendor: Broadcom Corporation physical id: 0 bus info: [email protected]:03:00.0 logical name: eth0 version: 20 serial: d4:85:64:77:f3:54 size: 1GB/s capacity: 1GB/s width: 64 bits clock: 33MHz capabilities: pm vpd msi msix pciexpress bus_master cap_list rom ethernet physical tp 10bt 10bt-fd 100bt 100bt-fd 1000bt-fd autonegotiation configuration: autonegotiation=on broadcast=yes driver=bnx2 driverversion=1.7.5 duplex=full firmware=5.2.3 NCSI 2.0.6 ip=192.168.10.78 latency=0 link=yes multicast=yes port=twisted pair speed=1GB/s resources: irq:16 memory:f4000000-f5ffffff memory:e6100000-e610ffff(prefetchable)
Method Three: lspci
If all you need to know is the product/vendor name of your Ethernet card, you can use lspci command which displays information about PCI buses and connected PCI devices.
To install lspci on Ubuntu or Debian:
$ sudo apt-get install pciutils
To install lspci on CentOS, Fedora or RedHat:
$ sudo yum install pciutils
To find the name of Ethernet card(s) available on your system, run the following.
03:00.0 Ethernet controller: Broadcom Corporation NetXtreme II BCM5709 Gigabit Ethernet (rev 20)
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.
How can I list installed network cards using Terminal?
while the above works, there are other options with less typing.
you can also use ifconfig and iwconfig for additional information or information about a specific device
ifconfig eth0 iwconfig wlp1s0 sort of depends on the sort of information you wish to display.
lspci : will list all PCI devices
lspci | egrep -i --color 'network|ethernet' The command will list network cards available and installed and highlight Ethernet if found .
If the cards are installed physically but not configured you can see them like this:
The following command provides detailed information about the hardware:
This command will show you the current NetworkManager configuration:
You must log in to answer this question.
Linked
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.14.43533
Ubuntu and the circle of friends logo are trade marks of Canonical Limited and are used under licence.
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.