- How do I determine the total size of a directory (folder) from the command line?
- How to Get the Size of a Directory in Linux
- Option 1: Display the Size of a Directory Using the du Command
- Option 2: Get Size of Directory in Linux Using tree Command
- Option 3: Find the Size of a Linux Directory Using ncdu Command
- Rukovodstvo
- статьи и идеи для разработчиков программного обеспечения и веб-разработчиков.
- Получить общий размер каталога в Linux
- Введение В Linux команда ls -l выводит список файлов и каталогов по определенному пути с их именами, датами и размерами (использование диска). Первое, что вы заметите при использовании этой команды, это то, что размер каталогов всегда отображается как 4096 байт (или 4,0 КБ, если вы используете ls -lh), даже если они содержат файлы размером более 4 КБ. Причина в том, что ls возвращает метаданные для каталогов, а не фактический размер. Итак, какой самый короткий и простой способ получить размер каталога i
- Вступление
- Получение размера каталога в Linux с помощью du
- Получить размер текущего рабочего каталога
- Получить размер подкаталогов первого уровня
- Получить размер всех подкаталогов
- Получить размер каталога в Linux с помощью tree —du -h
- Заключение
How do I determine the total size of a directory (folder) from the command line?
The -h flag on sort will consider «Human Readable» size values.
If want to avoid recursively listing all files and directories, you can supply the —max-depth parameter to limit how many items are displayed. Most commonly, —max-depth=1
du -h --max-depth=1 /path/to/directory I use du -sh or DOOSH as a way to remember it (NOTE: the command is the same, just the organization of commandline flags for memory purposes)
There is a useful option to du called the —apparent-size. It can be used to find the actual size of a file or directory (as opposed to its footprint on the disk) eg, a text file with just 4 characters will occupy about 6 bytes, but will still show up as taking up ~4K in a regular du -sh output. However, if you pass the —apparent-size option, the output will be 6. man du says: —apparent-size print apparent sizes, rather than disk usage; although the apparent size is usually smaller, it may be larger due to holes in (‘sparse’) files, internal fragmentation, indirect blocks
This works for OS X too! Thanks, I was really looking for a way to clear up files, both on my local machine, and my server, but automated methods seemed not to work. So, I ran du -hs * and went into the largest directory and found out which files were so large. This is such a good method, and the best part is you don’t have to install anything! Definitely deserved my upvote
@BandaMuhammadAlHelal I think there are two reasons: rounding ( du has somewhat peculiar rounding, showing no decimals if the value has more than one digit in the chosen unit), and the classical 1024 vs. 1000 prefix issue. du has an option -B (or —block-size ) to change the units in which it displays values, or you could use -b instead of -h to get the «raw» value in bytes.
How to Get the Size of a Directory in Linux
Many users run Linux from the command line. However, the command line — sometimes known as the terminal — doesn’t have an intuitive interface for checking disk space in Linux.
This guide shows you how to find the size of a specific directory in Linux from the command line.
- A system running Linux
- A command line / terminal window (available by clicking Search, then typing terminal)
- A user account with sudo or root privileges
Note: In Linux, a directory is the equivalent of a folder in Windows. A directory may have directories inside (called subdirectories), or it may only contain files.
Option 1: Display the Size of a Directory Using the du Command
The du command stands for disk usage. This command is included by default in most Linux distributions.
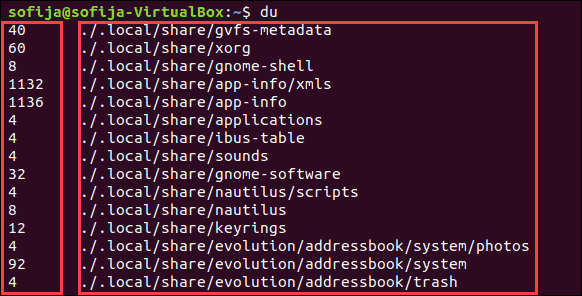
You can display the size of your current directory by typing du in the command line:
The system should display a list of the contents of your home directory, with a number to the left. That number is the size of the object in kilobytes.
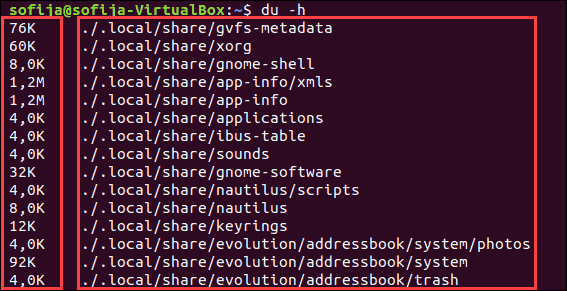
You can add the -h option to make the output more readable:
Each entry will start with a number and a letter. The number is the amount of space used, and the letter (usually K, M, or G) indicates Kilobytes, Megabytes, or Gigabytes. For example:
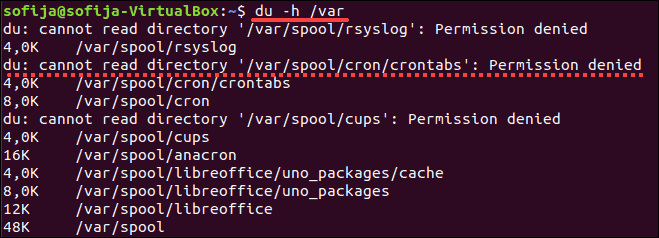
400K – 400 kilobytes 7.3M – 7.3 megabytes 2.2G – 2.2 gigabytesTo find the size of a specific directory different from your current working directory. The du command allows you to specify a directory to examine:
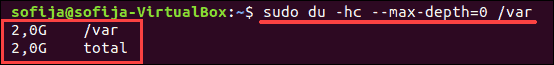
This displays the size of the contents of the /var directory. You may see some entries with an error, as in the image below.
This happens when your user account does not have permission to access a particular directory. Use the sudo or su command to get access privileges:
Note: Some versions of Linux don’t enable sudo by default. You can use the su command to switch to the root user account instead.
To display total disk usage of a particular directory, use the -c command:
Options can be combined. If you wanted to repeat the previous command in human-readable format, enter the following:
You can limit the scan to a certain level of subdirectory by using the max-depth option. For example, to scan only the size of the top directory, use —max-depth=0 :
If you wanted to list only the top directory and the first layer of subdirectories, change —max-depth=1 :
If you run into trouble or want to explore more options for the du command, enter the following command to display the help file:
Option 2: Get Size of Directory in Linux Using tree Command
By default, the tree command is not included in some versions of Linux. To install it, enter the following:
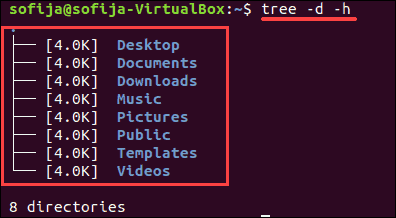
The tree command displays a visual representation of your directories. It uses lines to indicate which subdirectories belong where, and it uses colors to indicate directories and files.
tree can also be used with options. To display a human-readable size of the current directory’s subdirectories, enter the following:
Like the du command, tree can target a specific directory:
This command takes a few moments since the /var directory has many entries.
The tree command also has a help file, which you can access by entering:
Option 3: Find the Size of a Linux Directory Using ncdu Command
The ncdu tool stands for NCurses Disk Usage. Like the tree command, it is not installed by default on some versions of Linux. To install it, enter the following:
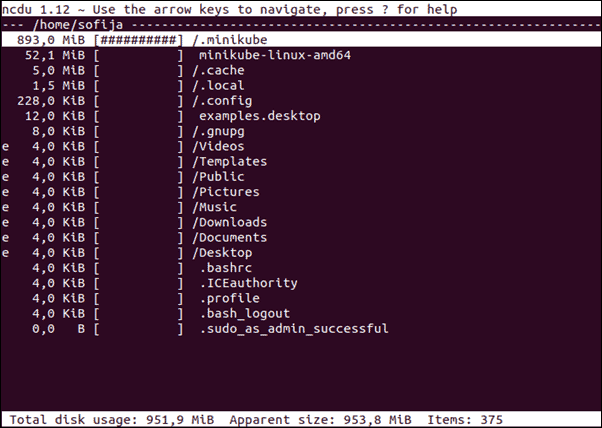
The ncdu utility is an interactive display of your disk usage. For example, enter the following:
In the upper left corner, it displays the current directory being scanned. A column on the left displays the numerical size, a graph of #- signs to indicate the relative size, and the file or directory.
Use the up and down arrows to select different lines. The right arrow will browse into a directory, and the left arrow will take you back.
ncdu can be used to target a specific directory, for example:
For help, press the ? key inside the ncdu interface. To quit, press the letter q .
Note: Learn how to move directories in Linux using the GUI or system commands.
You now have three different options to find the size of a directory in Linux operating systems.
If you want to learn more about directories in Linux, read our article how to rename directories in Linux.
Rukovodstvo
статьи и идеи для разработчиков программного обеспечения и веб-разработчиков.
Получить общий размер каталога в Linux
Введение В Linux команда ls -l выводит список файлов и каталогов по определенному пути с их именами, датами и размерами (использование диска). Первое, что вы заметите при использовании этой команды, это то, что размер каталогов всегда отображается как 4096 байт (или 4,0 КБ, если вы используете ls -lh), даже если они содержат файлы размером более 4 КБ. Причина в том, что ls возвращает метаданные для каталогов, а не фактический размер. Итак, какой самый короткий и простой способ получить размер каталога i
Вступление
В Linux ls -l список файлов и каталогов по определенному пути с их именами, датами и размерами (использование диска). Первое, что вы заметите при использовании этой команды, это то, что размер каталогов всегда отображается как 4096 байт (или 4,0 КБ, если вы используете ls -lh ), даже если они содержат файлы размером более 4 КБ. Причина в том, что ls возвращает метаданные для каталогов, а не фактический размер.
Вы спросите, какой самый короткий и простой способ получить размер каталога в Linux? Чтобы получить общий размер каталога в Linux, вы можете использовать команду du (disk-usage).
В этой статье мы рассмотрим некоторые из наиболее распространенных обычаев du команд, в том числе , но не ограничиваясь du -sh , du -ch и du —max-depth .
Получение размера каталога в Linux с помощью du
Чтобы увидеть полное описание и список аргументов команды du , обратитесь к man du .
Если мы введем du без каких-либо аргументов, он будет рекурсивно перечислить все имена и размеры каталогов для текущего рабочего каталога и всех подкаталогов:
rus:~/nltk_data$ du 2156 ./corpora/state_union 64 ./corpora/names 7624 ./corpora/conll2002 432 ./corpora/toolbox/rotokas ### . 246984 ./corpora 16792 ./tokenizers/punkt/PY3 36028 ./tokenizers/punkt 49420 ./tokenizers 296408 . Получить размер текущего рабочего каталога
Чтобы получить размер только текущего рабочего каталога, а не подкаталогов, мы можем использовать du -s или du —summarize :
Мы можем добавить -h чтобы получить размер в более удобочитаемом формате:
Мы также можем использовать du с $PATH чтобы получить размер каталога, который находится где-то кроме текущего рабочего каталога:
rus:~/nltk_data$ sudo du /var -sh # or "du -sh /var" if you prefer 11G /var Обратите внимание, что вам нужно будет использовать его с sudo для некоторых каталогов, иначе вы получите ошибку Permission denied
Получить размер подкаталогов первого уровня
Чтобы получить размер подкаталогов первого уровня, а также общий размер каталога пути:
rus:~$ sudo du /var/* -shc 6,1M /var/backups 144M /var/cache 4,0K /var/crash 7,2G /var/lib 4,0K /var/local 0 /var/lock 3,0G /var/log 4,0K /var/mail 4,0K /var/metrics 4,0K /var/opt 0 /var/run 3,8M /var/snap 52K /var/spool 72K /var/tmp 28K /var/www 11G total -c или —total возвращает общий размер пути ( 11G total ). * перечисляет все подкаталоги первого уровня в каталоге /var/ . Мы также можем добавить —exclude чтобы исключить любой каталог:
rus:~$ sudo du /var/* -shc --exclude=lib 6,1M /var/backups 144M /var/cache 4,0K /var/crash 4,0K /var/local 0 /var/lock 3,0G /var/log 4,0K /var/mail 4,0K /var/metrics 4,0K /var/opt 0 /var/run 3,8M /var/snap 52K /var/spool 72K /var/tmp 28K /var/www 3,2G total Обратите внимание, что исключение lib также влияет на общий размер ( 3,2G total ). Это также эквивалент sudo du /var/ -h —exclude=lib —max-depth=1
rus:~$ sudo du /var/ -h --exclude=lib --max-depth=1 4,0K /var/mail 52K /var/spool 3,8M /var/snap 4,0K /var/metrics 144M /var/cache 6,1M /var/backups 72K /var/tmp 4,0K /var/crash 3,0G /var/log 4,0K /var/opt 28K /var/www 4,0K /var/local 3,2G /var/ —max-depth=N вернет все уровни подкаталогов, которые равны или меньше числа N Установка —max-depth на 1 возвращает первый уровень, 2
Получить размер всех подкаталогов
Чтобы рекурсивно получить все подкаталоги /var/ , вы можете использовать sudo du /var/ -h . Или вы можете передать значение —max-depth которое, как вы уверены, больше или равно максимальному уровню глубины подкаталога: sudo du /var/ -h —max-depth=999 .
Второй вариант — скорее обходной путь, чем самый эффективный способ.
Получить размер каталога в Linux с помощью tree —du -h
tree — это рекурсивная программа для вывода списка каталогов, которая выводит список каталогов и файлов в древовидном формате. Обратите внимание, что tree не устанавливается по умолчанию. Для Debian / Ubuntu мы можем установить tree , запустив sudo apt install tree .
После завершения установки мы используем команду tree для отображения имен и размеров всех каталогов и файлов по определенному пути в древовидном формате:
rus:~$ tree /var/www/ --du -h /var/www/ ├── [4.2K] demosite │ └── [ 189] index.html └── [ 15K] html └── [ 11K] index.html 23K used in 2 directories, 2 files Заключение
В этой статье мы узнали, как получить размеры каталогов в Linux. Вы можете использовать эти команды на удаленных машинах Linux, серверах и / или машинах Linux с графическим интерфейсом пользователя или без него.
В большинстве случаев достаточно du command. Он также имеет то преимущество, что устанавливается по умолчанию. С другой стороны, команда tree обеспечила бы более наглядный и подробный пользовательский интерфейс для отображения почти тех же результатов, что сделало бы ее мощной альтернативой для du .
Licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0