- Use Port Knocking To Secure SSH Service (Debian/Ubuntu)
- What is Port Knocking in SSH
- Step 1: Install and Configure Knockd on Debian/Ubuntu Server
- Step 2: Close SSH Port 22
- Step 3: Use Knock Client to Send Knock Sequence
- Auto Restart Knockd
- SSH Passwordless Login
- Wrapping Up
- How to Use Port Knocking To Secure SSH Service in Linux
- Step 1: Install and Configure knockd
- Step 2: Close SSH Port 22 On Firewall
- Step 3: Configure a knock client to Connect to SSH Server
Use Port Knocking To Secure SSH Service (Debian/Ubuntu)
In this tutorial, I’m going to show you how to use port knocking to secure SSH service on Debian and Ubuntu servers.
What is Port Knocking in SSH
Port knocking is a way to allow only legitimate users to access services on a server and the service in this tutorial is the SSH service. SSH service is running on the server but the SSH port is closed from the outside world by firewall rules, so no one can connect directly to SSH port 22.
The server also runs a knockd daemon, which has the ability to change firewall rule and temporarily open SSH port 22 to a user if that user hit (or knock) some specific ports in a sequence. So the knock sequence is kind of like a password for the SSH port. Only legitimate users with the right knock sequence can trigger knocked to open SSH port. When the legitimate user wants to log out, another knock sequence is used to close the SSH port.
Now we will discuss how to install and configure knockd and set up firewall rule. This tutorial assumes you are using Linux on the client computer.
Step 1: Install and Configure Knockd on Debian/Ubuntu Server
Run the following command to install knocked from the default software repository.
sudo apt-get install knockd
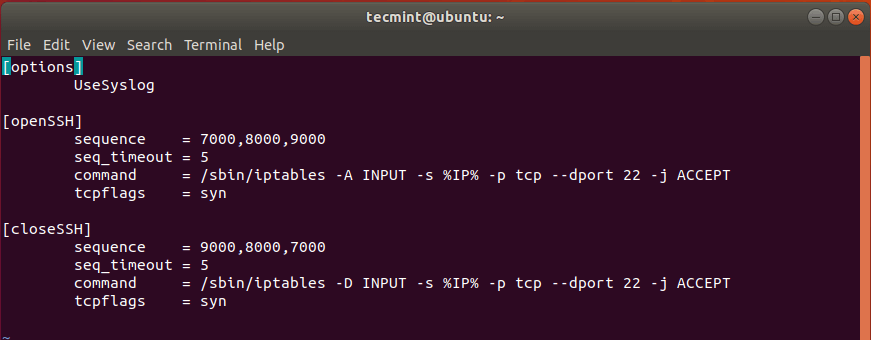
Edit main configuration file with a command-line text editor like Nano.
You need to change three items in this file. In the [openSSH] section, the default opening knock sequence is 7000,8000,9000 . You can change this to your own liking, such as 10001,10002,10003 . You can also define 4 or more ports for the sequence. You don’t need to open these ports in firewall.
Then in the iptables command, change -A to -I , so this iptables rule will be the first in the rule chain. Order in iptables rule chain matters. When you send the right knock sequence, knockd will execute this iptables command to open SSH port for your IP address only. All other IP addresses are still not allowed to connect to the SSH port.
Next, in the [closeSSH] section, change the default closing knock sequence to your liking, such as 10003,10002,10001 .
Next, run the following command to find out the name of main network interface on the server.
As you can see, mine is ens18 . Now edit /etc/default/knockd config file.
sudo nano /etc/default/knockd
Change 0 to 1 to enable autostart at system boot.
knockd by default listens on eth0 interface. You server’s network interface might not be eth0 , so in this case you need to change it. Find the following line.
Remove # and change eth1 to the name of the main network interface on your server.
KNOCKD_OPTS color: #ff00ff;">ens18"
Save and close the file. Then start knockd daemon
sudo systemctl start knockd
sudo systemctl enable knockd
Check its status to see if it’s running.
Step 2: Close SSH Port 22
To close SSH port 22 in UFW firewall, first you need to list the current firewall rules.
As you can see, the first rule and the third rule open the SSH port. To close TCP port 22, delete these two rules.
sudo ufw delete 3 sudo ufw delete 1
Hint: You should delete the rule with a bigger index number first.
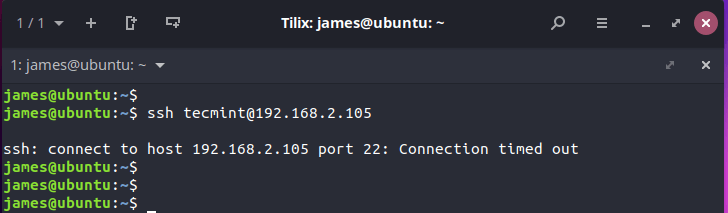
Now if you try to SSH into your server, the SSH service won’t respond to your request.
Step 3: Use Knock Client to Send Knock Sequence
The knockd daemon is bundled with a knock client called knock , so on your Debian or Ubuntu client computer, you can install it by running:
sudo apt-get install knockd
In order to trigger the server firewall to TCP port 22, you need to send the correct knock sequence from the client computer.
knock -v 10.0.0.104 10001 10002 10003
hitting tcp 10.0.0.104:10001 hitting tcp 10.0.0.104:10002 hitting tcp 10.0.0.104:10003
Knock attempt can fail if there’s a high latency between your client and your server. You may need to send the knock sequence multiple times if the SSH port is still closed.
Once the knock attempt is successful, you can SSH into your server. After you’ve done all your work, you can use port knocking to close SSH port for your IP.
knock -v 10.0.0.104 10003 10002 10001
Note that knockd will only respond to knock sequence sent to the main network interface (aka the main IP address). If the server has multiple IP address, and you try to send the knock sequence on another IP address, knockd won’t be able to open SSH port.
Auto Restart Knockd
If the knockd daemon stops running on the server, then you can’t SSH into your server. To prevent this from happening, you can create a cron job to automatically restart the knockd once an hour.
Edit root user’s crontab file.
Add the following line in the file.
@hourly systemctl restart knockd
Note: Even if knockd stops running, you can still access your server by using your hosting provider’s web-based console, then you can manually start knockd , so you will have SSH access again.
SSH Passwordless Login
You can further strength the security of your SSH service by enabling public key authentication (passwordless login).
Wrapping Up
I hope this tutorial helped you set up port knocking on Debian/Ubuntu server. You may also want to check out other security tutorials.
As always, if you found this post useful, then subscribe to our free newsletter to get new tutorials.
How to Use Port Knocking To Secure SSH Service in Linux
Port Knocking is a nifty technique of controlling access to a port by only allowing legitimate users access to the service running on a server. It works in such a way that when the right sequence of connection attempts is made, the firewall gladly opens the port that was closed.
The logic behind port knocking is to safeguard your Linux system from automated port scanners which prowl for open ports. In this guide, we examine how you can install port knocking and how you can configure it to secure SSH service. For demonstration purposes, we will use Ubuntu 18.04.
Step 1: Install and Configure knockd
To get started, log in to your Linux system and install the knockd daemon as shown.
Once installed, open the knockd.conf configuration with your preferred text editor. Here, we are using the vim command-line text editor.
The default configuration file appears as follows.
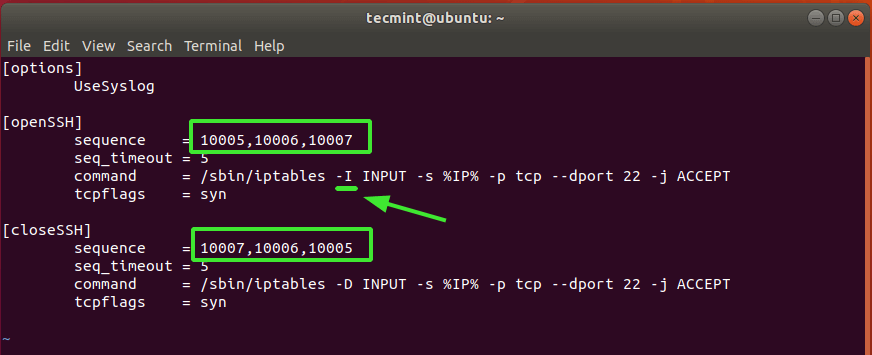
Under the [openSSH] section, we need to change the default knocking sequence – 7000,8000,9000 – to something else. This is because these values are already known and can compromise the security of your system.
For testing purposes, we have set the values to 10005, 10006, 10007. This is the sequence that will be used to open the SSH port from a client system.
In the third line – beginning with command, change -A to -I just after the /sbin/iptables command and before INPUT .
And lastly, under the [closeSSH] section, again, change the default sequence to your preferred choice. This is the sequence that will be used to close the SSH connection once the user is done and logs out of the server.
Here’s our complete configuration.
Once you are done, save the changes and exit.
Another configuration we need to modify is the /etc/default/knockd. Once again, open it using your text editor.
$ sudo vim /etc/default/knockd
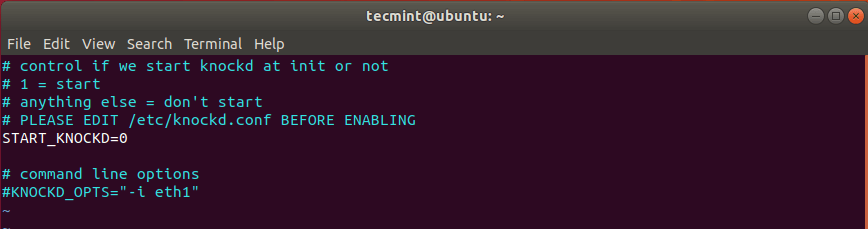
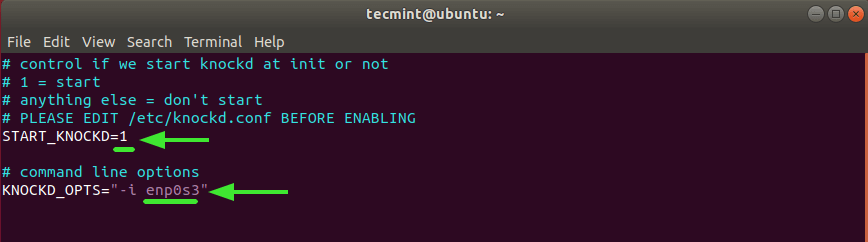
Locate the line START_KNOCKD=0 . Uncomment it and set the value to 1 .
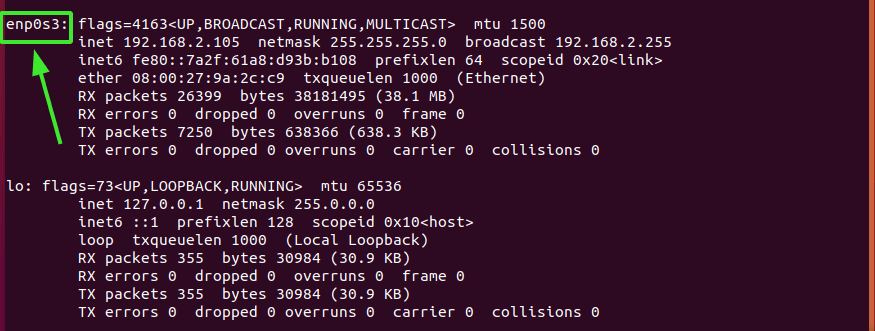
Next, head over to the line KNOCKD_OPTS=”-i eth1” Uncomment it and replace the default eth1 value with the active network interface of your system. To check your network interface simply run the ip addr or the ifconfig command.
For our system, enp0s3 is the active network card.
The complete configuration is as shown.
Save the changes and exit.
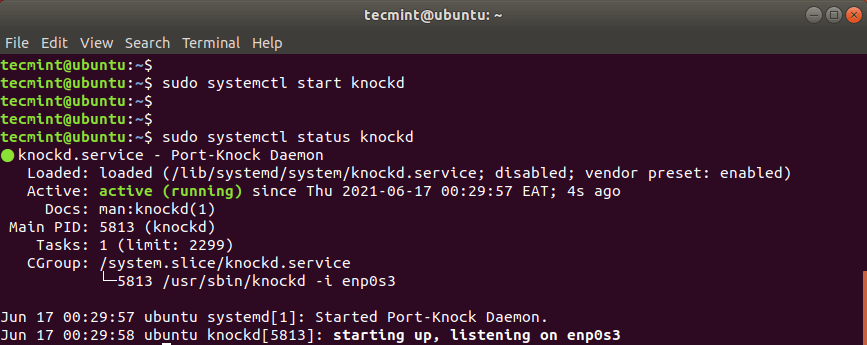
Then start and enable knockd daemon as shown.
$ sudo systemctl start knockd $ sudo systemctl enable knockd
To check the status of knockd daemon, run the command:
$ sudo systemctl status knockd
Step 2: Close SSH Port 22 On Firewall
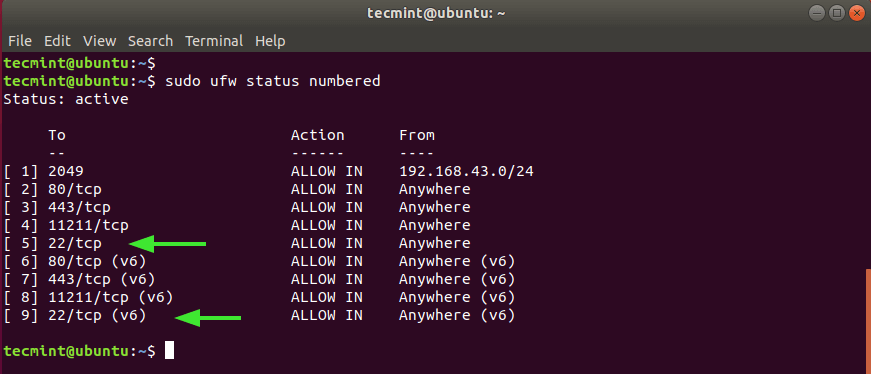
Since the objective of the knockd service is to either grant or deny access to ssh service, we are going to close the ssh port on the firewall. But first, let’s check the status of the UFW firewall.
From the output, we can clearly see that SSH port 22 is open on both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols numbered 5 and 9 respectively.
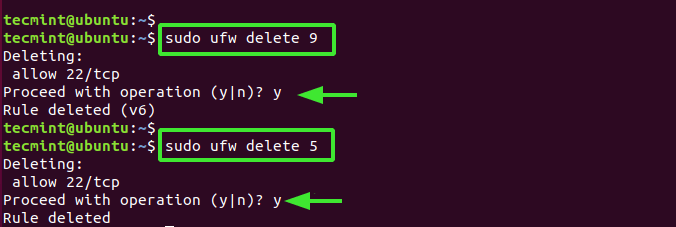
We need to delete these two rules as shown, starting with the highest value – which is 9.
$ sudo ufw delete 9 $ sudo ufw delete 5
Now, if you attempt to log in remotely to the server, you will get a connection timeout error as shown.
Step 3: Configure a knock client to Connect to SSH Server
In the final step, we will configure a client and attempt to log in by first sending the knock sequence that we configured on the server.
But first, install knockd daemon just as you did on the server.
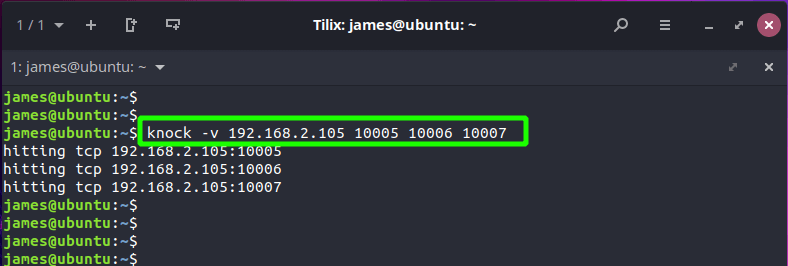
Once the installation is complete, send the knock sequence using the syntax shown
$ knock -v server_ip knock_sequence
In our case, this translates to:
$ knock -v 192.168.2.105 10005 10006 10007
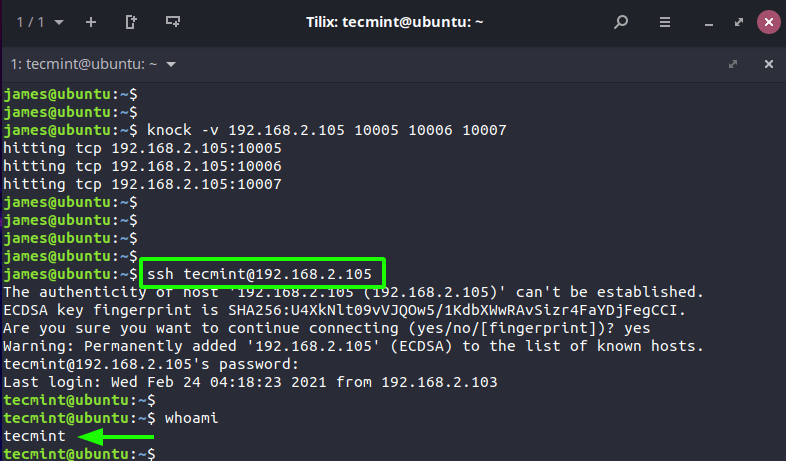
You should get output similar to what we have, depending on your sequence. This shows that the knock attempts were successful.
At this point, you should be in a position to successfully log in to the server using SSH.
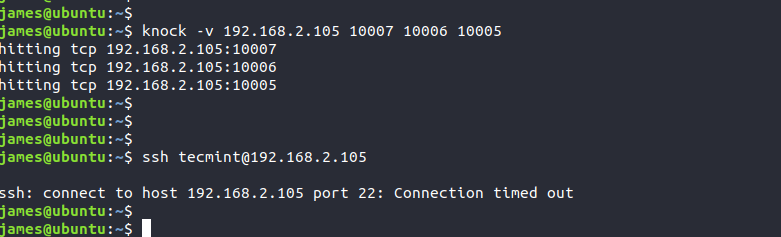
Once you are done doing your job on the remote server, close the SSH port by sending the closing knock sequence.
$ knock -v 192.168.2.105 10007 10006 10005
Any attempts to log in to the server will fail as demonstrated.
Closing Thoughts
This wraps up this guide on how to leverage port knocking to secure the SSH service on your server. A better and easier approach would be to configure password SSH authentication using SSH key pairs. This ensures that only the user with the private key can authenticate with the server on which the public key is stored.

![knockd[13204] could not open eth0 eth0 No such device exists](https://www.linuxbabe.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/knockd13204-could-not-open-eth0-eth0-No-such-device-exists.png)